semaphore.h
TaskQueue.h
threadgroup.h
ThreadPool.h
ThreadPool
semaphore
基于条件变量和锁实现的信号量post和wait语义
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
namespace toolkit {
class semaphore {
public:
explicit semaphore(size_t initial = 0) {
#if defined(HAVE_SEM)
sem_init(&_sem, 0, initial);
#else
_count = 0;
#endif
}
~semaphore() {
#if defined(HAVE_SEM)
sem_destroy(&_sem);
#endif
}
void post(size_t n = 1) {
#if defined(HAVE_SEM)
while (n--) {
sem_post(&_sem);
}
#else
std::unique_lock<std::recursive_mutex> lock(_mutex);
_count += n;
if (n == 1) {
_condition.notify_one();
} else {
_condition.notify_all();
}
#endif
}
void wait() {
#if defined(HAVE_SEM)
sem_wait(&_sem);
#else
std::unique_lock<std::recursive_mutex> lock(_mutex);
while (_count == 0) {
_condition.wait(lock);
}
--_count;
#endif
}
private:
#if defined(HAVE_SEM)
sem_t _sem;
#else
size_t _count;
std::recursive_mutex _mutex;
std::condition_variable_any _condition;
#endif
};
} /* namespace toolkit */
#endif /* SEMAPHORE_H_ */
!TaskQueue
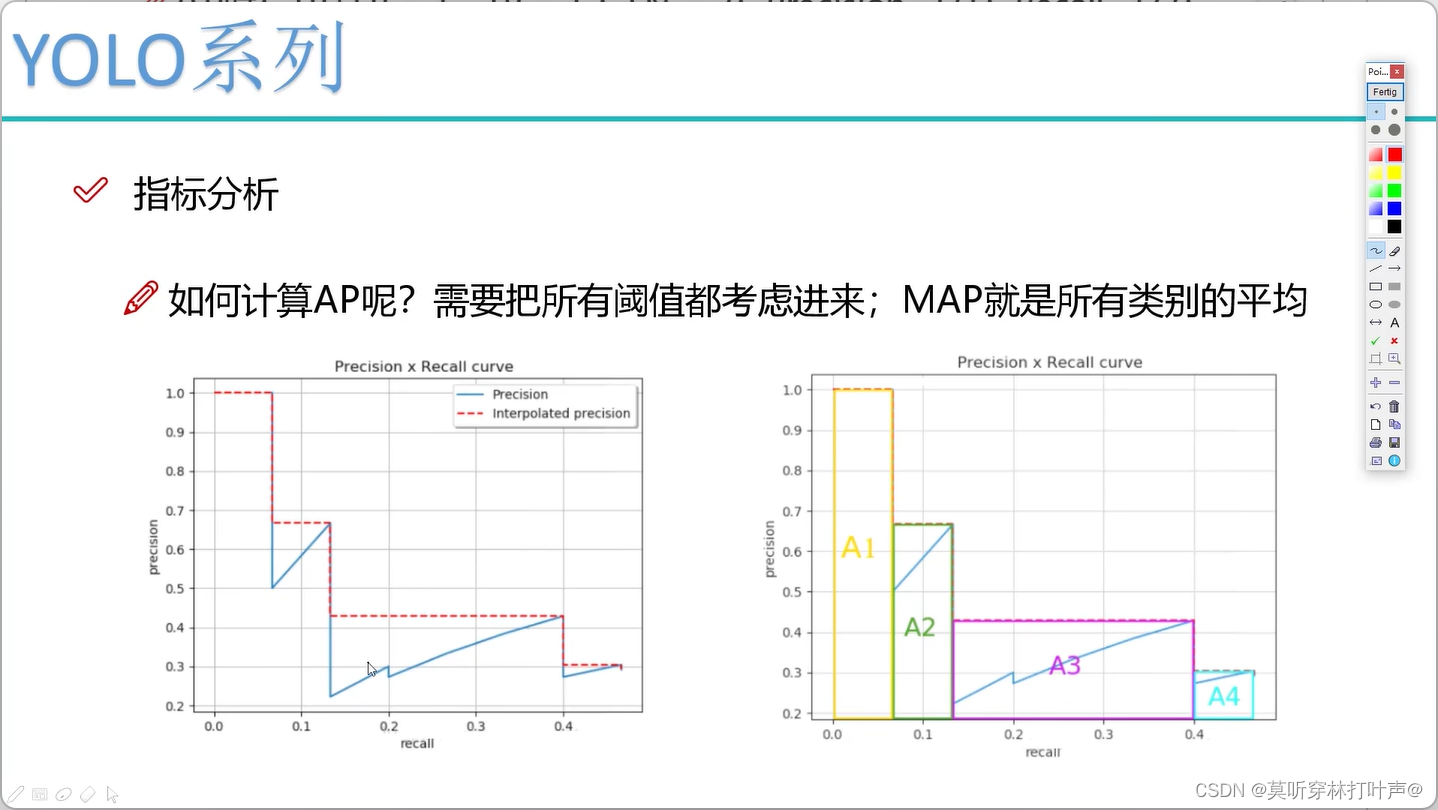
实现了一个基于函数对象的任务列队,该列队是**线程安全(互斥量)的,任务列队任务数由信号量(生产者消费者模型)**控制
#ifndef TASKQUEUE_H_
#define TASKQUEUE_H_
#include <mutex>
#include "Util/List.h"
#include "semaphore.h"
namespace toolkit {
//实现了一个基于函数对象的任务列队,该列队是线程安全的,任务列队任务数由信号量控制
template<typename T>
class TaskQueue {
public:
//打入任务至列队
template<typename C>
void push_task(C &&task_func) {
{
std::lock_guard<decltype(_mutex)> lock(_mutex);
_queue.emplace_back(std::forward<C>(task_func));
}
_sem.post();
}
template<typename C>
void push_task_first(C &&task_func) {
{
std::lock_guard<decltype(_mutex)> lock(_mutex);
_queue.emplace_front(std::forward<C>(task_func));
}
_sem.post();
}
//清空任务列队
void push_exit(size_t n) {
_sem.post(n);
}
//从列队获取一个任务,由执行线程执行
bool get_task(T &tsk) {
_sem.wait();
std::lock_guard<decltype(_mutex)> lock(_mutex);
if (_queue.empty()) {
return false;
}
tsk = std::move(_queue.front());
_queue.pop_front();
return true;
}
size_t size() const {
std::lock_guard<decltype(_mutex)> lock(_mutex);
return _queue.size();
}
private:
List <T> _queue;
mutable std::mutex _mutex;
semaphore _sem;
};
} /* namespace toolkit */
#endif /* TASKQUEUE_H_ */
thread_group
unordered_map<thread::id, shared_ptr<thread>> 指向线程的智能指针
#ifndef THREADGROUP_H_
#define THREADGROUP_H_
#include <thread>
#include <unordered_map>
namespace toolkit {
class thread_group {
private:
thread_group(thread_group const &);
thread_group &operator=(thread_group const &);
public:
thread_group() {}
~thread_group() {
_threads.clear();
}
bool is_this_thread_in() { //当前调用线程在线程组中嘛
auto thread_id = std::this_thread::get_id();
if (_thread_id == thread_id) {
return true;
}
return _threads.find(thread_id) != _threads.end();
}
bool is_thread_in(std::thread *thrd) {//该线程在线程组中嘛
if (!thrd) {
return false;
}
auto it = _threads.find(thrd->get_id());
return it != _threads.end();
}
template<typename F>
std::thread *create_thread(F &&threadfunc) {
auto thread_new = std::make_shared<std::thread>(threadfunc);
_thread_id = thread_new->get_id();
_threads[_thread_id] = thread_new;
return thread_new.get();
}
void remove_thread(std::thread *thrd) {
auto it = _threads.find(thrd->get_id());
if (it != _threads.end()) {
_threads.erase(it);
}
}
void join_all() {
if (is_this_thread_in()) {
throw std::runtime_error("thread_group: trying joining itself");
}
for (auto &it : _threads) {
if (it.second->joinable()) {
it.second->join(); //等待线程主动退出
}
}
_threads.clear();
}
size_t size() {
return _threads.size();
}
private:
std::thread::id _thread_id;
std::unordered_map<std::thread::id, std::shared_ptr<std::thread>> _threads;
};
}
UML
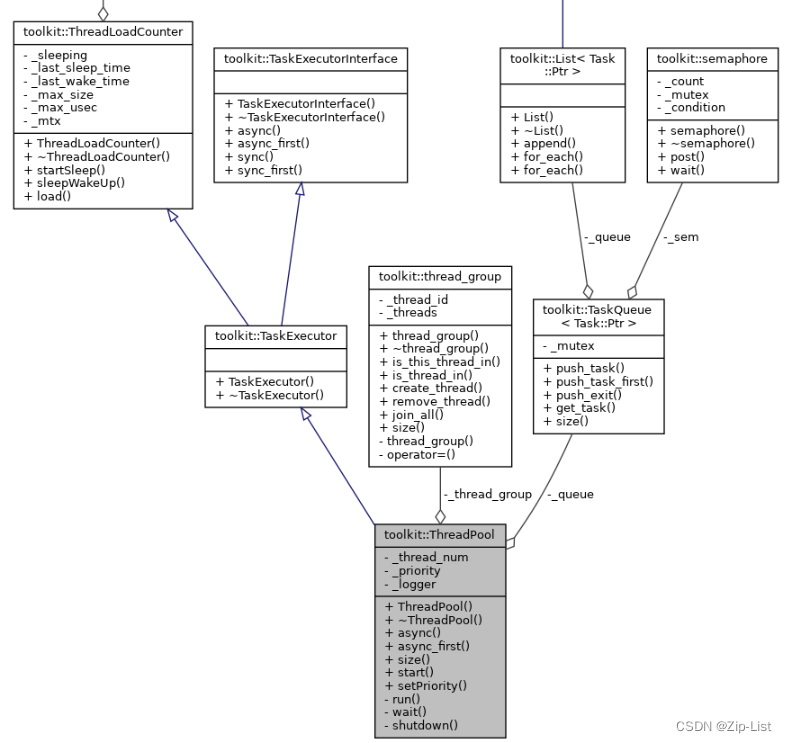
结构
size_t _thread_num;
TaskQueue<Task::Ptr> _queue;
thread_group _thread_group;
Priority _priority;
Logger::Ptr _logger;
async (post)
生产_queue中的任务(post)
//把任务打入线程池并异步执行
Task::Ptr async(TaskIn task, bool may_sync = true) override {
if (may_sync && _thread_group.is_this_thread_in()) {
task();
return nullptr;
}
auto ret = std::make_shared<Task>(std::move(task));
_queue.push_task(ret); //post
return ret;
}
!run (wait)
start开启N个线程,消费_queue中的任务
void start() {
if (_thread_num <= 0) {
return;
}
size_t total = _thread_num - _thread_group.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < total; ++i) {
_thread_group.create_thread(std::bind(&ThreadPool::run, this));
}
}
run消费_queue中的任务,没有就等 get_task (wait)
void run() {
ThreadPool::setPriority(_priority);
Task::Ptr task;
while (true) {
startSleep();
if (!_queue.get_task(task)) {
//空任务,退出线程
break;
}
sleepWakeUp();
try {
(*task)();
task = nullptr;
} catch (std::exception &ex) {
ErrorL << "ThreadPool执行任务捕获到异常:" << ex.what();
}
}
}
shutdown
结束的操作很有趣,发出线程数量的空任务,run在get_task中取到了空任务,跳出while循环可以被join掉了
void shutdown()
{
_queue.push_exit(_thread_num);
}
线程池中线程的调度优先级
浅谈pthread_setschedparam的使用
struct sched_param params;
params.sched_priority = Priorities[priority];
return pthread_setschedparam(threadId, SCHED_OTHER, ¶ms) == 0;
总结
-
线程池的async执行方式,作为生产者添加任务到队列中
-
生产者消费者的实现,互斥量保证线程安全(不可同时访问),生产者(添加任务的线程)发信号量通知消费者(工作线程)进行同步(访问的先后顺序)
-
如何设置线程调度优先级pthread_setschedparam