人菜瘾大还是忍不住打了这场比赛,b卡了半小时,甚至还写了一个最长公共子序列然后喜提wa2,但是c,d还是过的比较快,最后排名rk175有惊无险的上分了,e题赛时一眼想出思路,但是我的实现能力有限,没能在赛时通过,赛后补了这道题,狠狠抽打了我自己的码力,马上要ec了,未来的队友还需要我去当代码手实现思路,在这里狠狠拷打一下我自己。
简要题意 给你一颗树,问你划分成若干条颜色段,颜色段必须联通,并且颜色段每个点的深度不同,问你颜色段最小值的最大值是多少。
看到这个题,第一反应就是做贪心,我们可以比较套路性地想到我们可以从底往上做,我们先处理子树,再处理当前节点。根据题意,我们不难发现,这个颜色段一定是一条链,而且是从上到下平铺在树上,即链上的任意两点的lca为
l
c
a
(
u
,
v
)
=
=
u
或
l
c
a
(
u
,
v
)
=
=
u
lca(u , v) == u 或 lca(u , v) == u
lca(u,v)==u或lca(u,v)==u。
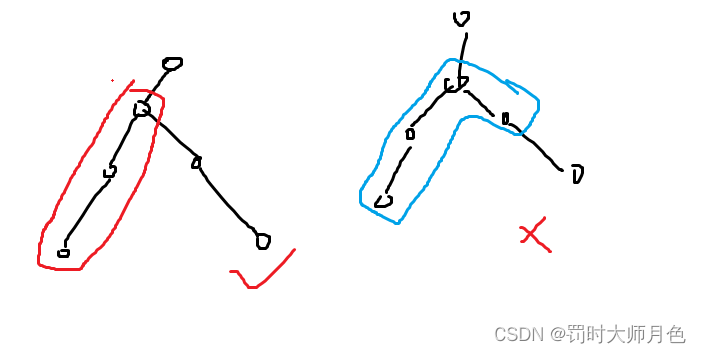
然后我们考虑由下到上贪心,我们对于一个点
u
u
u,我们维护两个值,一个是节点u所在的颜色段的长度,当前子树颜色段的最小值。
接下来考虑转移我们对于一个节点
u
u
u,我们可以从儿子所在的链种选择一条链,然后接上节点u。
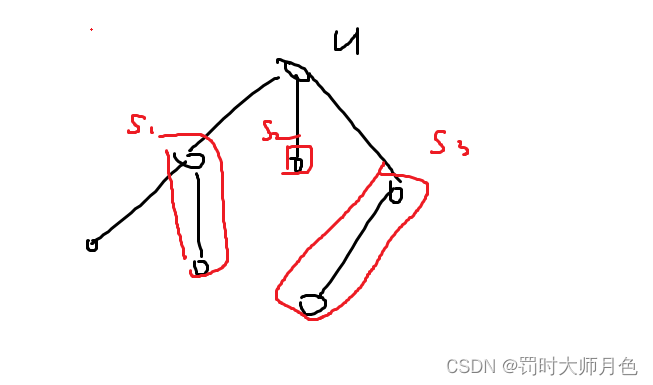
如上图所示,我们对于一个节点u,我们可以从三个儿子维护的链中选择一个接上u,如果我们采取接上s1,则为下图所示。
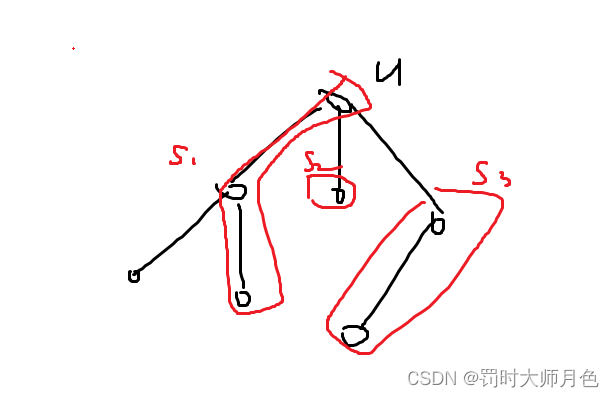
然后我们现在有若干个儿子,我们该如何去接儿子呢,我们先对儿子的链大小进行排序,我们应该去接长度最短的链。原因:考虑贪心地让最小值最大,如果我们考虑不接长度最短的,答案一定小于等于长度最短的链,若接到长度最短的链,答案就小于等于次小值,答案更大,更优,所以我们一定接在最短的一条链上, 然后没有被接到
u
u
u的链,我们把他放到u子树颜色段的最小值去维护(即第二关键字),然后我们确定一个根,然后
d
f
s
dfs
dfs一遍我们就可以得到某个点为根时的答案了,我们如何求全局最小值,我们考虑暴力地把每个根都跑一遍,时间复杂度是
O
(
n
2
)
O(n ^ 2)
O(n2),我们就考虑换根dp的思路去做,用换根dp的思路去维护这种转移即可。
代码实现难度比较大,我写了一个最小次小的封装类,然后维护不同的信息即可。
双倍经验!
代码的大致思路类似于1778E,可以参考我之前写的博文。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define x first
#define y second
#define int long long
using namespace std ;
int read(){
int res = 0 , flag = 1 ;
char c = getchar() ;
while(!isdigit(c)){
if(c == '-') flag = -1 ;
c = getchar() ;
}
while(isdigit(c)){
res = (res << 1) + (res << 3) + (c ^ 48) ;
c = getchar() ;
}
return res * flag ;
}
void write(int x){
if(x < 0) {
putchar('-') ;
x = - x ;
}
if(x >= 10) write(x / 10) ;
putchar('0' + x % 10) ;
}
void write(int x , char c){
write(x) ;
putchar(c) ;
}
const int N = 2e5 + 10 ;
typedef pair<int , int> pii ;
typedef pair<double ,double> pdd ;
const int mod = 998244353 ;
const int inf = 1e9 + 10 ;
const int M = 2 * N ;
struct T{
int a[2] = {inf , inf} ;
void insert(int x){
if(a[0] >= x) a[1] = a[0] , a[0] = x ;
else a[1] = min(a[1] , x) ;
}
void r(){
if(a[0] > a[1]) swap(a[0] , a[1]) ;
}
T operator+(T& b)const{
T c ;
c.a[0] = a[0] ;
c.a[1] = a[1] ;
c.insert(b.a[0]) ;
c.insert(b.a[1]) ;
return c;
}
T(){
}
T(int x , int y){
a[0] = x , a[1] = y ;
}
} ;
int h[N] , e[M] , ne[M] , idx ;
void add(int a , int b){
e[idx] = b , ne[idx] = h[a] , h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
pii dp[N] , f[N] ;
void dfs(int u , int v){
T t ;
int res = inf ;
for(int i = h[u] ; ~i ; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i] ;
if(j == v) continue ;
dfs(j , u) ;
t.insert(dp[j].x) ;
res = min(res , dp[j].y) ;
}
if(t.a[0] == inf) dp[u].x = 1 ;
else dp[u].x = t.a[0] + 1 ;
dp[u].y = min(t.a[1] , res) ;
}
int ans ;
void dfs1(int u , int v){
T t ;
// cout << u << " " << v << " " << f[v].x << " " << f[v].y << endl ;
int res = inf ;
for(int i = h[u] ; ~i ; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i] ;
if(j == v) continue ;
t.insert(dp[j].x) ;
res = min(res , dp[j].y) ;
}
t.insert(f[v].x) ;
res = min(res , f[v].y) ;
// cout << "res" << res << endl ;
ans = max(ans , min(t.a[0] + 1 , min(res , t.a[1]))) ;
vector<T> pre(1) , suf(1) ;
vector<int> p(1 , inf) , s(1 , inf) ;
int cnt = 0 ;
for(int i = h[u] ; ~i ; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i] ;
if(j == v) continue ;
++ cnt ;
p.push_back(dp[j].y) ;
s.push_back(dp[j].y) ;
pre.push_back(T(dp[j].x , inf)) ;
suf.push_back(T(dp[j].x , inf)) ;
}
pre.push_back(T(inf , inf)) ;
suf.push_back(T(inf , inf)) ;
p.push_back(inf) ;
s.push_back(inf) ;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= cnt ; i ++){
pre[i] = pre[i] + pre[i - 1] ;
p[i] = min(p[i] , p[i - 1]) ;
}
for(int i = cnt ; i ; i --){
suf[i] = suf[i + 1] + suf[i] ;
s[i] = min(s[i] , s[i + 1]) ;
}
cnt = 0 ;
for(int i = h[u] ; ~i ; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i] ;
if(j == v) continue ;
++ cnt ;
T tt ;
int rr = inf ;
rr = min(rr , f[v].y) ;
rr = min(p[cnt - 1] , rr) ;
rr = min(s[cnt + 1] , rr) ;
tt.insert(f[v].x) ;
tt = tt + pre[cnt - 1] ;
tt = tt + suf[cnt + 1] ;
rr = min(tt.a[1] , rr) ;
if(tt.a[0] == inf) f[u] = {1 , rr} ;
else
f[u] = {tt.a[0] + 1 , rr} ;
dfs1(j , u) ;
}
}
void solve() {
int n = read() ;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) h[i] = -1 ;
idx = 0 ;
for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++){
int a = read() , b = read() ;
add(a , b) , add(b , a) ;
}
dfs(1 , 1) ;
f[0] = {inf , inf} ;
ans = 0 ;
dfs1(1 , 0) ;
// cout << min(dp[1].x , dp[1].y) << endl ;
write(ans , '\n') ;
}
signed main(void){
int T = read() ;
while(T --)
solve() ;
}