本文属于「征服LeetCode」系列文章之一,这一系列正式开始于2021/08/12。由于LeetCode上部分题目有锁,本系列将至少持续到刷完所有无锁题之日为止;由于LeetCode还在不断地创建新题,本系列的终止日期可能是永远。在这一系列刷题文章中,我不仅会讲解多种解题思路及其优化,还会用多种编程语言实现题解,涉及到通用解法时更将归纳总结出相应的算法模板。
为了方便在PC上运行调试、分享代码文件,我还建立了相关的仓库。在这一仓库中,你不仅可以看到LeetCode原题链接、题解代码、题解文章链接、同类题目归纳、通用解法总结等,还可以看到原题出现频率和相关企业等重要信息。如果有其他优选题解,还可以一同分享给他人。
由于本系列文章的内容随时可能发生更新变动,欢迎关注和收藏征服LeetCode系列文章目录一文以作备忘。
Given a callable function f(x, y) with a hidden formula and a value z, reverse engineer the formula and return all positive integer pairs x and y where f(x,y) == z. You may return the pairs in any order.
While the exact formula is hidden, the function is monotonically increasing, i.e.:
f(x, y) < f(x + 1, y)f(x, y) < f(x, y + 1)
The function interface is defined like this:
interface CustomFunction {
public:
// Returns some positive integer f(x, y) for two positive integers x and y based on a formula.
int f(int x, int y);
};
We will judge your solution as follows:
- The judge has a list of
9hidden implementations ofCustomFunction, along with a way to generate an answer key of all valid pairs for a specificz. - The judge will receive two inputs: a
function_id(to determine which implementation to test your code with), and the targetz. - The judge will call your
findSolutionand compare your results with the answer key. - If your results match the answer key, your solution will be
Accepted.
题意:给你一个函数 f(x, y) 和一个目标结果 z,函数公式未知,计算方程 f(x,y) == z 所有可能的正整数 数对 x 和 y。满足条件的结果数对可以按任意顺序返回。尽管函数的具体式子未知,但它是单调递增函数,也就是说:
f(x, y) < f(x + 1, y)f(x, y) < f(x, y + 1)
解法1 双重循环
由于数据不大,可以直接暴力循环。
- 时间复杂度: O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)
- 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> findSolution(CustomFunction& customfunction, int z) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
for (int x = 1; x <= 1000; ++x) {
for (int y = 1; y <= 1000; ++y) {
if (customfunction.f(x, y) == z) ans.push_back({x, y});
}
}
return ans;
}
};
解法2 二分
类似LeetCode 15 三数之和,循环遍历 x x x ,然后对单调递增的 y y y 进行二分搜索。
- 时间复杂度: O ( n log n ) O(n\log n) O(nlogn) 。
- 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> findSolution(CustomFunction& customfunction, int z) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
for (int x = 1; x <= 1000; ++x) {
int yl = 1, yh = 1000;
while (yl <= yh) {
int mid = (yl + yh) / 2, tz = customfunction.f(x, mid);
if (tz == z) {
ans.push_back({x, mid});
break;
}
else if (tz > z) yh = mid - 1; // 说明y太大了
else yl = mid + 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
解法3 抽象BST
官解告诉我们这是240题搜索二维矩阵II的变形题,如果题目读不懂,不妨看看本题前身240题搜索二维矩阵II是一道怎样的题目——这道题的题目含义就非常清晰了。最关键的信息在于,对于给定的
m
×
n
m \times n
m×n 矩阵 matrix ,存在以下性质:
- 每行的元素从左到右升序排列
- 每列的元素从上到下升序排列
用数学语言来表达的话,就是对于下标为 ( x , y ) (x, y) (x,y) 的元素 m a t r i x [ x ] [ y ] matrix[x][y] matrix[x][y] ,(在不越界的情况下)一定存在以下两个关系:
- m a t r i x [ x ] [ y ] < m a t r i x [ x ] [ y + 1 ] matrix[x][y] < matrix[x][y+1] matrix[x][y]<matrix[x][y+1] ,即同一行的元素从左往右单调递增
-
m
a
t
r
i
x
[
x
]
[
y
]
<
m
a
t
r
i
x
[
x
+
1
]
[
y
]
matrix[x][y] < matrix[x+1][y]
matrix[x][y]<matrix[x+1][y] ,即同一列的元素从上往下单调递增
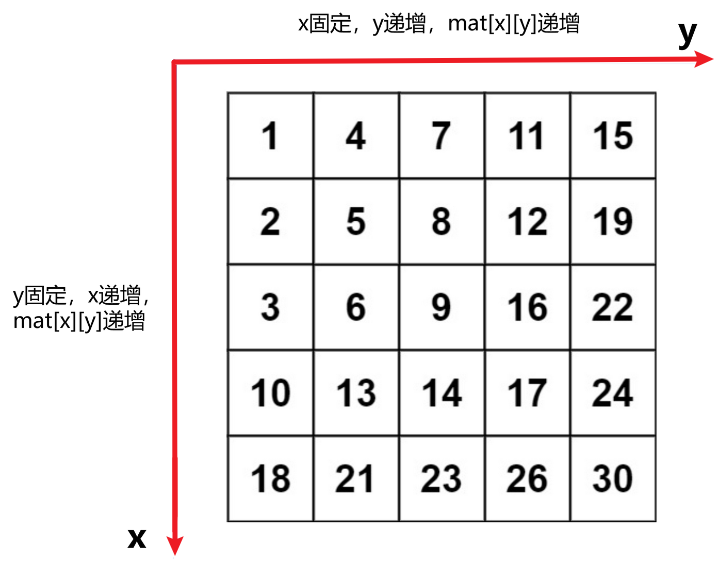
我们对240题的搜索过程如下所示:
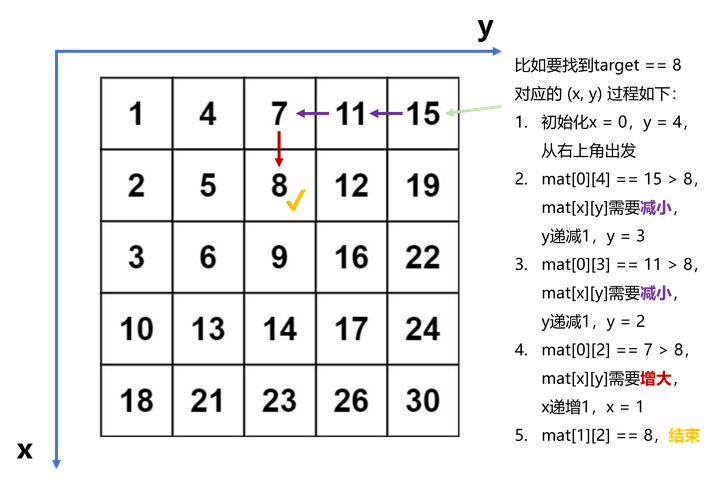
如果我们把整个矩阵matrix看作是一棵二叉树,每一个值都是一个节点,把起始点 ( 0 , n − 1 ) (0, n-1) (0,n−1) 看作根节点,左边的值看作是左节点,下面的值看作是右节点,那么这个二维矩阵可以抽象成一颗二叉搜索树BST。我们的搜寻过程,其实也遵循BST的搜索原则。
从而对于本题,我们也可以这么做:
- 把解也就是
x和y类似上图一样,看做一个二维矩阵,高宽均是1000(取值范围) - 从二维数组右上角开始,即 x = 1 , y = 1000 x = 1, y = 1000 x=1,y=1000 为起始点,将这个起始点看为二叉搜索树的根节点
- 由于函数方程具有单调性,也就是任一点向左 ( y − 1 ) (y - 1) (y−1) 结果递减,任一点向下 ( x + 1 ) (x+1) (x+1) 结果递增
- 从起始点来看,向左对应二叉搜索树的左子结点,向下对应二叉搜索树的右子结点
- 从起始点逐个得到当前 x x x 和 y y y 的方程结果,比目标值大则向左移动,比目标值小则向下移动
- 特别处理:如果已经找到了当前方程的解之一,怎么移动都可以,往左或往下或往左下都行。
完整代码如下所示:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n) 。
- 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) 。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> findSolution(CustomFunction& customfunction, int z) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
int x = 1, y = 1000; // x向右,f=(x,y)递增,y向下,f(x,y)递减
while (x <= 1000 && y >= 1) {
int tz = customfunction.f(x, y);
if (tz == z) { // x,y合适
ans.push_back({x, y});
++x; // 或者--y
} else if (tz < z) ++x; // tz太小,增加x以增加tz
else --y; // tz太大,减少y以减少tz
}
return ans;
}
};