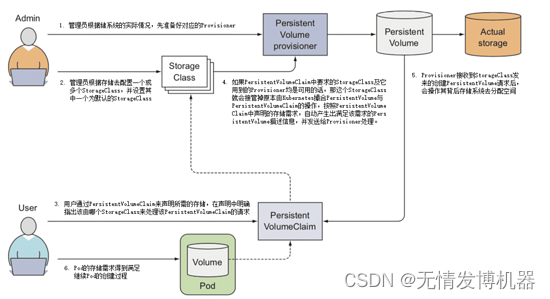
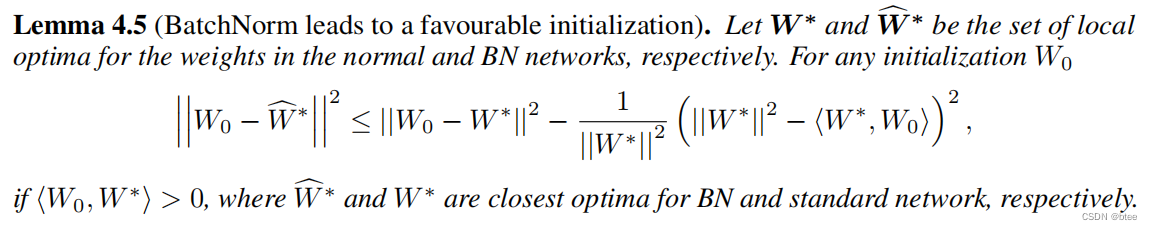
原文地址:http://blog.jboost.cn/trick-logback-prop.html
当使用logback来记录Web应用的日志时,我们通过在logback.xml中配置appender来指定日志输出格式及输出文件路径,这在一台主机或一个文件系统上部署单个实例没有问题,但是如果部署多个实例(比如通过容器的方式),多个实例同时往同一文件写日志可能就会引起问题。这时可以将每个实例的日志文件加以区分,如IP或UUID,或两者结合的形式。这其实就涉及如何在logback.xml中自定义动态属性的问题。
可以有4种方式来实现logback.xml中获取自定义变量值:
- 通过设置环境变量或传递系统属性(比如在程序启动时通过-D传递)的方式,两者是可以直接在logback.xml中通过
${变量名}获取的。 - 自定义logback.xml的加载时机,在其加载前将需要设置的属性注入到logback的context中,这种方式相对复杂,本文不讨论。
- 通过实现PropertyDefiner接口来提供属性值设置
- 通过实现LoggerContextListener接口来设置属性值
第一种方式简单,但不能通过程序生成属性值
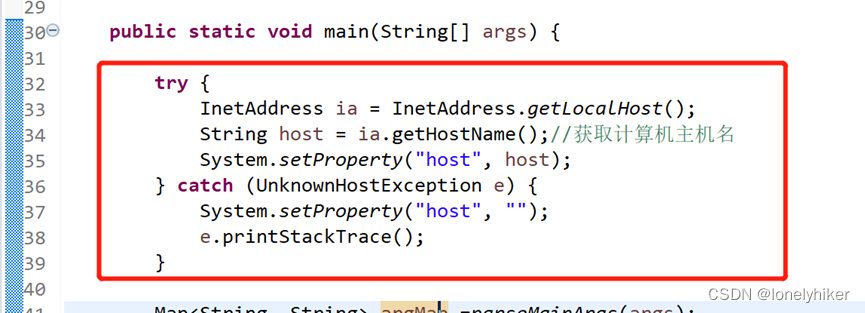
需要在spring-boot启动类中加入设置环境变量的代码,如下:
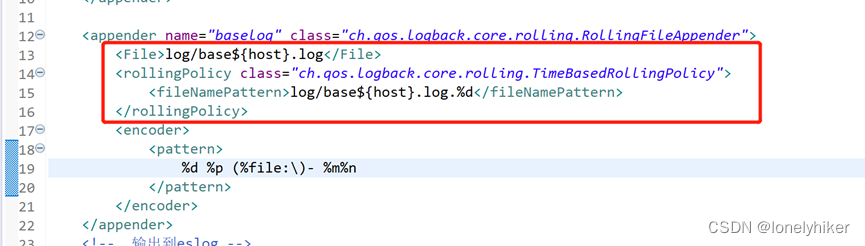
修改logback.xml中的代码如下:
第二种方式稍显复杂,本文主要介绍后两种方式
PropertyDefiner方式
首先定义一个类,实现PropertyDefiner接口,可以通过继承PropertyDefinerBase会更方便
import ch.qos.logback.core.PropertyDefinerBase; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.UnknownHostException; import java.util.UUID; /\*\*\*
\* 将本地IP拼接到日志文件名中,以区分不同实例,避免存储到同一位置时的覆盖冲突问题
\* @Author ronwxy
\* @Date 2019/8/20 16:17 \*/
public class IPLogDefiner extends PropertyDefinerBase { private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(IPLogDefiner.class); private String getUniqName() {
String localIp \= null; try {
localIp \= InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
LOG.error("fail to get ip...", e);
}
String uniqName \= UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", ""); if (localIp != null) {
uniqName \= localIp + "-" + uniqName;
} return uniqName;
}
@Override public String getPropertyValue() { return getUniqName();
}
}
然后在logback.xml中,添加 <define> 配置,指定属性名(本例中为localIP)及获取属性值的实现类,这样就可以在配置中通过 ${localIP}来引用该属性值了。在实现方法 getPropertyValue 中返回你需要生成的值,本例中是返回 本地IP-UUID 的形式。
<configuration>
<define name="localIP" class="cn.jboost.common.IPLogDefiner"/>
<appender name="interfaceLogFile"
class\="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
<File>D:\\\\logs\\\\elk\\\\interface\-${localIP}.log</File>
<filter class\="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.ThresholdFilter">
<level>INFO</level>
</filter> # 省略了其它配置
LoggerContextListener方式
定义一个实现LoggerContextListener接口的类,在start方法中,将需要设置的属性设置到logback的Context中,
import ch.qos.logback.classic.Level; import ch.qos.logback.classic.Logger; import ch.qos.logback.classic.LoggerContext; import ch.qos.logback.classic.spi.LoggerContextListener; import ch.qos.logback.core.Context; import ch.qos.logback.core.spi.ContextAwareBase; import ch.qos.logback.core.spi.LifeCycle; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.UnknownHostException; import java.util.UUID; /\*\*\*
\* 第二种实现方式
\* @Author ronwxy
\* @Date 2019/8/20 18:45 \*/
public class LoggerStartupListener extends ContextAwareBase implements LoggerContextListener, LifeCycle { private boolean started = false;
@Override public void start() { if (started) { return;
}
Context context \= getContext();
context.putProperty("localIP", getUniqName());
started \= true;
} private String getUniqName() {
String localIp \= null; try {
localIp \= InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) { //LOG.error("fail to get ip...", e);
}
String uniqName \= UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", ""); if (localIp != null) {
uniqName \= localIp + "-" + uniqName;
} return uniqName;
} //省略了其它函数
然后在logback.xml中,配置如上监听器类,这样就可以通过 ${localIP} 获取到上面 context.putProperty("localIP", getUniqName()); 设置的值了。
<configuration>
<!--<define name="localIP" class\="com.cnbot.common.IPLogDefiner"/>-->
<contextListener class="cn.jboost.common.LoggerStartupListener"/>
<define name="localIP" class\="com.cnbot.common.IPLogDefiner"/>
<appender name="interfaceLogFile"
class\="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
<File>D:\\\\logs\\\\elk\\\\interface\-${localIP}.log</File>
<filter class\="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.ThresholdFilter">
<level>INFO</level>
</filter> # 省略了其它配置
这种方式能设置任意个数的属性值,比前一种方式灵活。
总结
在logback.xml中获取自定义属性值,主要是需要在加载前将对应的属性值进行设置,这样加载时才能有效获取。本文虽是自定义日志文件名称,但不局限于此,所有需要动态获取的变量都可以按这种方式实现。