文章目录
- 38. 外观数列:
- 样例 1:
- 样例 2:
- 提示:
- 分析:
- 题解:
- rust
- go
- c++
- python
- java
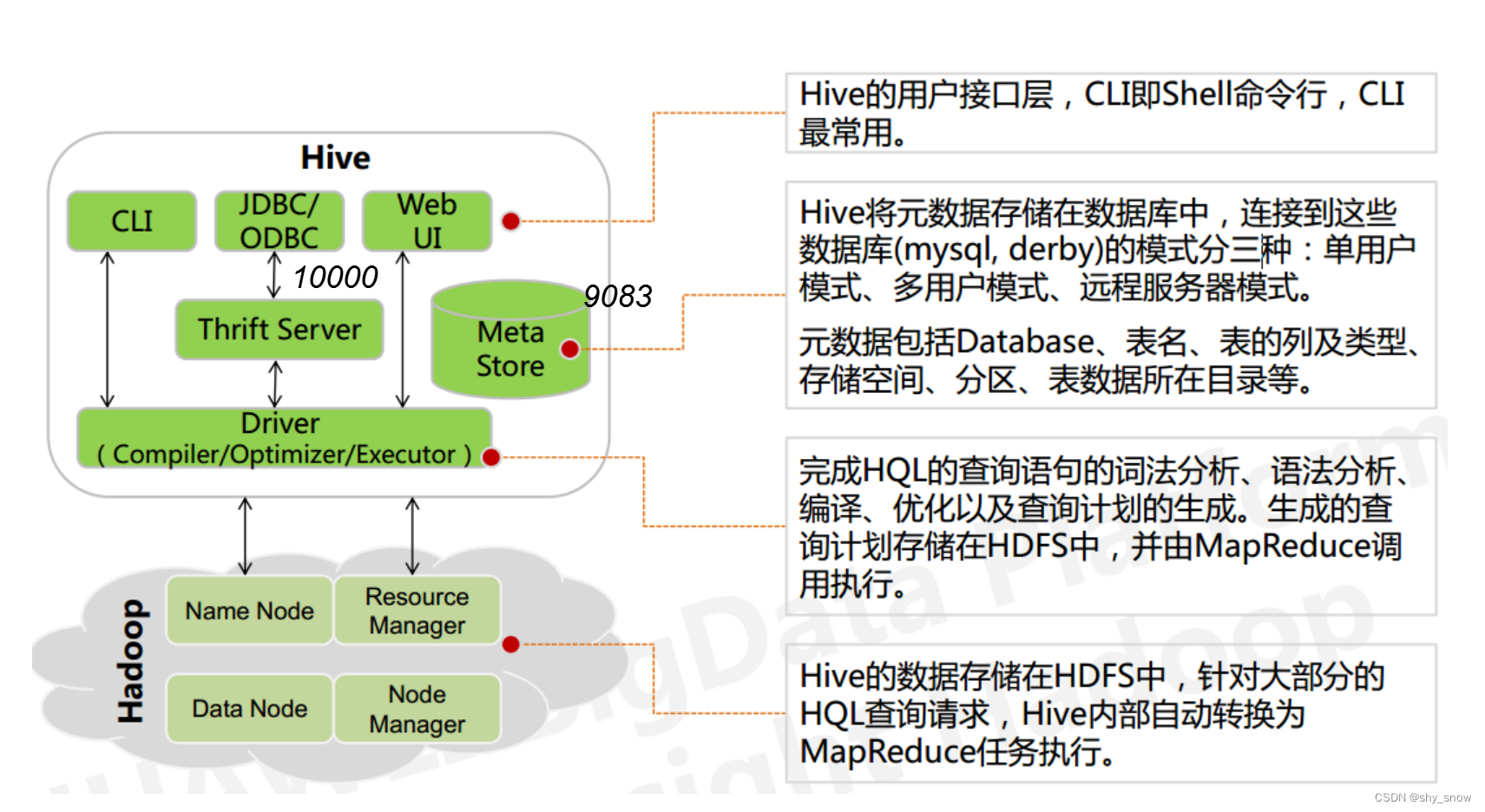
38. 外观数列:
给定一个正整数 n ,输出外观数列的第 n 项。
「外观数列」是一个整数序列,从数字 1 开始,序列中的每一项都是对前一项的描述。
你可以将其视作是由递归公式定义的数字字符串序列:
countAndSay(1) = "1"countAndSay(n)是对countAndSay(n-1)的描述,然后转换成另一个数字字符串。
前五项如下:
1. 1
2. 11
3. 21
4. 1211
5. 111221
第一项是数字 1
描述前一项,这个数是 1 即 “ 一 个 1 ”,记作 "11"
描述前一项,这个数是 11 即 “ 二 个 1 ” ,记作 "21"
描述前一项,这个数是 21 即 “ 一 个 2 + 一 个 1 ” ,记作 "1211"
描述前一项,这个数是 1211 即 “ 一 个 1 + 一 个 2 + 二 个 1 ” ,记作 "111221"
要 描述 一个数字字符串,首先要将字符串分割为 最小 数量的组,每个组都由连续的最多 相同字符 组成。然后对于每个组,先描述字符的数量,然后描述字符,形成一个描述组。要将描述转换为数字字符串,先将每组中的字符数量用数字替换,再将所有描述组连接起来。
例如,数字字符串 “3322251” 的描述如下图:

样例 1:
输入:
n = 1
输出:
"1"
解释:
这是一个基本样例。
样例 2:
输入:
n = 4
输出:
"1211"
解释:
countAndSay(1) = "1"
countAndSay(2) = 读 "1" = 一 个 1 = "11"
countAndSay(3) = 读 "11" = 二 个 1 = "21"
countAndSay(4) = 读 "21" = 一 个 2 + 一 个 1 = "12" + "11" = "1211"
提示:
1 <= n <= 30
分析:
- 面对这道算法题目,二当家的陷入了沉思。
- 很明显需要循环或者递归,模拟题意即可。
- 由于题目规定的参数取值范围很有限,打表可以高效通关,没什么技术含量,但是可以应试。
题解:
rust
impl Solution {
pub fn count_and_say(n: i32) -> String {
let mut ans = vec![b'1'];
(2..n + 1).for_each(|i| {
let mut cur = Vec::new();
let mut start = 0;
let mut pos = 0;
while pos < ans.len() {
while pos < ans.len() && ans[pos] == ans[start] {
pos += 1;
}
cur.push((pos - start) as u8 + b'0');
cur.push(ans[start]);
start = pos;
}
ans = cur;
});
return String::from_utf8(ans).unwrap();
}
}
go
func countAndSay(n int) string {
ans := "1"
for i := 2; i <= n; i++ {
cur := &strings.Builder{}
for pos, start := 0, 0; pos < len(ans); start = pos {
for pos < len(ans) && ans[pos] == ans[start] {
pos++
}
cur.WriteString(strconv.Itoa(pos - start))
cur.WriteByte(ans[start])
}
ans = cur.String()
}
return ans
}
c++
class Solution {
public:
string countAndSay(int n) {
string ans = "1";
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
string cur = "";
int start = 0;
int pos = 0;
while (pos < ans.size()) {
while (pos < ans.size() && ans[pos] == ans[start]) {
++pos;
}
cur += to_string(pos - start) + ans[start];
start = pos;
}
ans = cur;
}
return ans;
}
};
python
class Solution:
def countAndSay(self, n: int) -> str:
ans = "1"
for i in range(n - 1):
cur = ""
pos = 0
start = 0
while pos < len(ans):
while pos < len(ans) and ans[pos] == ans[start]:
pos += 1
cur += str(pos - start) + ans[start]
start = pos
ans = cur
return ans
java
class Solution {
public String countAndSay(int n) {
String ans = "1";
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int start = 0;
int pos = 0;
while (pos < ans.length()) {
while (pos < ans.length() && ans.charAt(pos) == ans.charAt(start)) {
pos++;
}
sb.append(Integer.toString(pos - start)).append(ans.charAt(start));
start = pos;
}
ans = sb.toString();
}
return ans;
}
}
非常感谢你阅读本文~
欢迎【点赞】【收藏】【评论】~
放弃不难,但坚持一定很酷~
希望我们大家都能每天进步一点点~
本文由 二当家的白帽子:https://le-yi.blog.csdn.net/ 博客原创~