栈的接口实现(附图解和源码)
文章目录
- 栈的接口实现(附图解和源码)
- 前言
- 一、定义结构体
- 二、接口实现(附图解+源码)
- 1.初始化栈
- 2.销毁栈
- 3.入栈
- 4.判断栈是否为空
- 5.出栈
- 6.获取栈顶元素
- 7.获取栈中元素个数
- 三、源代码展示
- (1)test.c(测试+主函数)
- (2)Stack.h(接口函数的声明)
- (3)Stack.c(接口函数的实现)
- 总结
前言
本文主要介绍双向链表中增删查改等接口实现,结尾附总源码!这里我们采用数组栈的方式。
一、定义结构体

二、接口实现(附图解+源码)
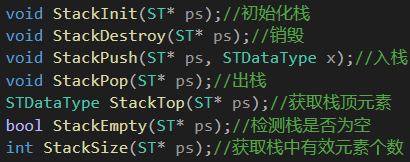
这里一共7个接口,我会我都会一 一为大家讲解(图解+源码)
1.初始化栈
这里初始化和顺序表一样,详细的可以参考顺序表!
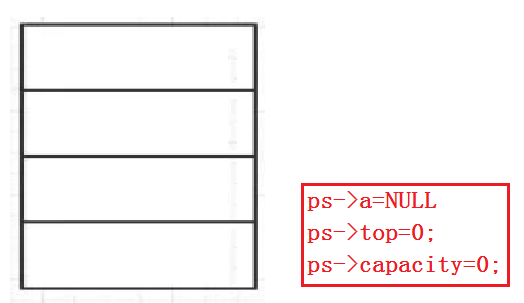
代码如下(示例):
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
2.销毁栈
销毁栈也可以直接参考顺序表,在这里不做过多介绍!
代码如下(示例):
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
3.入栈
这里要考虑增容的问题:
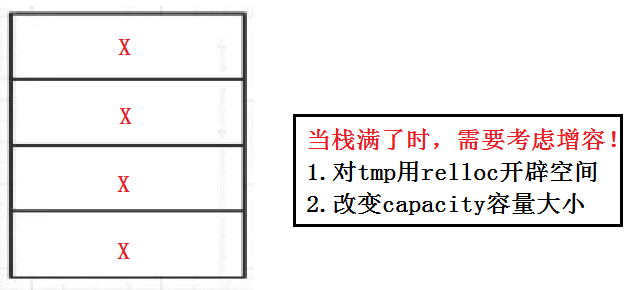
代码如下(示例):
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
4.判断栈是否为空
如果ps->top=0即栈为空!这里也可以用if语句,我这里是直接返回 true of false
代码如下(示例):
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
5.出栈
这里要注意:需要用 StackEmpty 判断一下栈是否为空,因为空了之后就不需要出栈!

代码如下(示例):
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
--ps->top;
}
6.获取栈顶元素
这里也要注意:需要用 StackEmpty 判断一下栈是否为空,因为空了之后就不可以获取栈顶元素!
 我初始化时 top 用的0,所以在获取栈顶数据时,直接 ps->a[ps->top - 1]
我初始化时 top 用的0,所以在获取栈顶数据时,直接 ps->a[ps->top - 1]
代码如下(示例):
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
7.获取栈中元素个数
直接返回 top 即可,这里不做过多的介绍!
代码如下(示例):
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
三、源代码展示
(1)test.c(测试+主函数)
代码如下(示例):
//#include <stdio.h>
//
//int f(int n)
//{
// return n == 1 ? 1 : f(n - 1) + n;
//}
//
//int main()
//{
// printf("%d\n", f(10000));
//
// return 0;
//}
#include <stdio.h>
#include "Stack.h"
#include "Queue.h"
// 解耦 -- 低耦合 高内聚
// 数据结构建议不要直接访问结构数据,一定要通过函数接口访问
void TestStack()
{
ST st;
StackInit(&st);
StackPush(&st, 1);
StackPush(&st, 2);
StackPush(&st, 3);
printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackPop(&st);
printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackPop(&st);
StackPush(&st, 4);
StackPush(&st, 5);
while (!StackEmpty(&st))
{
printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackPop(&st);
}
printf("\n");
}
void TestQueue()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
int main()
{
//TestStack();
TestQueue();
return 0;
}
(2)Stack.h(接口函数的声明)
代码如下(示例):
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
//#define N 100
//typedef int STDataType;
//struct Stack
//{
// STDataType a[N];
// int top;
//};
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
void StackInit(ST* ps);//初始化栈
void StackDestroy(ST* ps);//销毁
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);//入栈
void StackPop(ST* ps);//出栈
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);//获取栈顶元素
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);//检测栈是否为空
int StackSize(ST* ps);//获取栈中有效元素个数
(3)Stack.c(接口函数的实现)
代码如下(示例):
#include "Stack.h"
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
--ps->top;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文介绍栈的接口实现(附图解和源码)!
如果我的博客对你有所帮助记得三连支持一下,感谢大家的支持!





![[Java代码审计]—命令执行失效问题](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5535f815b8aa4cfeb5704ee19cdfb646.png#pic_center)