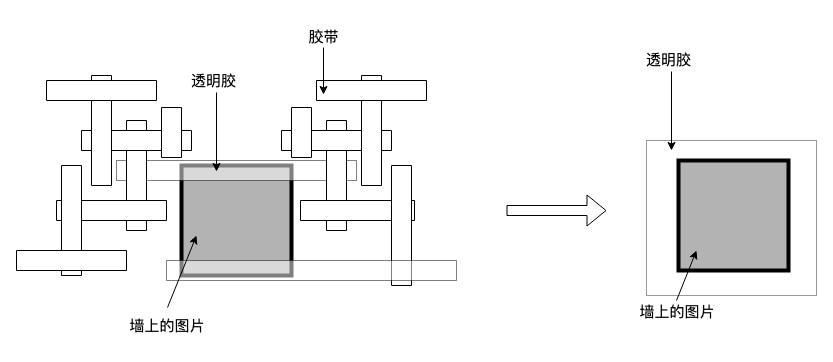
概览
org.apache.dubbo包下META-INF/dubbo/internal/org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.LoadBalance中内部spi实现类有以下几种:
random=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.loadbalance.RandomLoadBalance
roundrobin=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.loadbalance.RoundRobinLoadBalance
leastactive=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.loadbalance.LeastActiveLoadBalance
consistenthash=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.loadbalance.ConsistentHashLoadBalance
shortestresponse=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.loadbalance.ShortestResponseLoadBalance
通过ConsumerConfig可设置负载均衡策略:
...
//<editor-fold desc="consumer 配置">
// 负载均衡策略
// * random - 随机;
// * roundrobin - 轮询;
// * leastactive - 最少活跃调用;
// * consistenthash - 哈希一致 (2.1.0以上版本);
// * shortestresponse - 最短响应 (2.7.7以上版本);
ConsumerConfig consumerConfig = new ConsumerConfig();
consumerConfig.setLoadbalance("roundrobin");
//</editor-fold>
...
另外,对于加权随机,加权轮询等策略都集成自以上的策略中,consumer会检查注册中心中provider是否提供weight参数自动开启加权负载均衡。除了哈希一致策略,其他的均有加权版本(不提供weight参数即权重一样)。
在provider端,我们可以设置ServiceConfig中设置weight,注意:在RegistryConfig中也可以设置weight,不过这是在多注册中心的环境下对该注册中心负载均衡的权重,不是某个服务调用的负载均衡权重。
//<editor-fold desc="服务配置">
ServiceConfig<GreetingsService> hiConfig = new ServiceConfig<>();
hiConfig.setInterface(GreetingsService.class);
hiConfig.setRef(new GreetingsServiceImpl());
// 权重
hiConfig.setWeight(2);
//</editor-fold>
//<editor-fold desc="registry配置">
RegistryConfig registryConfig = new RegistryConfig();
registryConfig.setAddress("zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181");
// 多个registry时,该registry的权重
registryConfig.setWeight(2);
//</editor-fold>
此时,zk为例注册的服务如下:
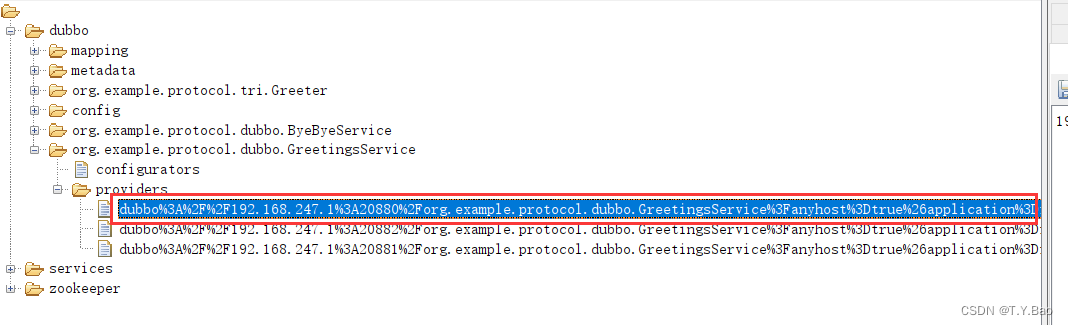
该节点名称最后会显示weight参数:
dubbo%3A%2F%2F192.168.247.1%3A20880%2Forg.example.protocol.dubbo.GreetingsService%3Fanyhost%3Dtrue%26application%3Dfirst-dubbo-provider%26application.version%3D1.0.0%26background%3Dfalse%26deprecated%3Dfalse%26dubbo%3D2.0.2%26dynamic%3Dtrue%26generic%3Dfalse%26interface%3Dorg.example.protocol.dubbo.GreetingsService%26methods%3DsayHi%26owner%3Dbty%26pid%3D2716%26release%3D3.1.6%26service-name-mapping%3Dtrue%26side%3Dprovider%26timestamp%3D1677208111268%26weight%3D2
AbstractLoadBalance
该abstract类只有一个作用:获取provider的权重,提升代码复用率。
注:如果provider没有提供weight参数,则默认为100.
其中,random和roundrobin加权时每次都起作用;而leastactive和shortestresponse是在存在符合选取条件的provider有多个时使用加权随机在其中选一个;consistenthash没用到。
RandomLoadBalance
public class RandomLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
// invokers代表需要负载均衡的provider列表
// URL代表该consumer的metadata,和zk中/dubbo/metadata/com.xxx.service/consumer/xxx-consumer节点内容相同
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
// Number of invokers
int length = invokers.size();
// 根据从registry拿到的参数中寻找是否有weight参数或timestamp参数来判断
// 是否需要加权操作
if (!needWeightLoadBalance(invokers, invocation)) {
// 没有直接random选取
return invokers.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(length));
}
// 标志位,权重是否都一样
boolean sameWeight = true;
// weights序列,不过 weights[i]是0到i的provider节点实际weight的和
// 如:
// 节点索引i : 0 1 2
// 节点i的weight: 2 3 5
// weights[i] : 2 2+3=5 2+3+5=10
// 应该叫weightSum更合适
// 这是为了后面随机选取节点用,随机数大小落入哪个区间,就选哪个节点
int[] weights = new int[length];
// The sum of weights
int totalWeight = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
// Sum
totalWeight += weight;
// save for later use
weights[i] = totalWeight;
// 如果当前weight不是之前weight的和的索引倍数,则清空same标志
// 索引: 0 1 2
// w: 3 3 2
// total: 3 6 8
// w*(i+1) 3 6 6
// same? √ √ ×
if (sameWeight && totalWeight != weight * (i + 1)) {
sameWeight = false;
}
}
// 如果权重不等 且 至少有一个invoker的权重大于0
if (totalWeight > 0 && !sameWeight) {
// 根据权重和计算随机offset
int offset = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
// Return a invoker based on the random value.
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
// 选取第一个小于offset的节点i做调用
if (offset < weights[i]) {
return invokers.get(i);
}
}
}
// 权重相等
return invokers.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(length));
}
}
ThreadLocalRandom随机数生成
RandomLoadBalance中随机数生成使用ThreadLocalRandom,该类始于JDK1.7,由Doug Lea操刀编写。
优点:When applicable, use of ThreadLocalRandom rather than shared Random objects in concurrent programs will typically encounter much less overhead and contention.
用法:ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextX(…) (where X is Int, Long, etc).
缺点:Instances of ThreadLocalRandom are not cryptographically secure. Consider instead using java.security.SecureRandom in security-sensitive applications. Additionally, default-constructed instances do not use a cryptographically random seed unless the system property java.util.secureRandomSeed is set to true.
RoundRobinLoadBalance
public class RoundRobinLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
protected static class WeightedRoundRobin {
private int weight;
private AtomicLong current = new AtomicLong(0);
private long lastUpdate;
...
// 每次加一个权值
public long increaseCurrent() {
return current.addAndGet(weight);
}
}
...
// 接口名称:<providerId:WeightedRoundRobin>
// 如:
// org.example.protocol.dubbo.GreetingsService.sayHi : < dubbo://192.168.247.1:20882/org.example.protocol.dubbo.GreetingsService , WeightedRoundRobin >
private ConcurrentMap<String, ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin>> methodWeightMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin>>();
...
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
// <接口.方法>,如org.example.protocol.dubbo.GreetingsService.sayHi
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
// 初始化
ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin> map = methodWeightMap.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
// 权重和
int totalWeight = 0;
// 记录当前最大值
long maxCurrent = Long.MIN_VALUE;
// 记录更新时间,一个接口的所有provider的时间都一样。
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 选中的
Invoker<T> selectedInvoker = null;
// 选中的
WeightedRoundRobin selectedWRR = null;
// 每次都会循环一遍,不会中途退出
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
// dubbo://192.168.247.1:20882/org.example.protocol.dubbo.GreetingsService
String identifyString = invoker.getUrl().toIdentityString();
// 获取权重,如果没有权重,则默认权重都一样,均为100
int weight = getWeight(invoker, invocation);
// 没有缓存,则为GreetingsService的这个provider设置weight,生成WeightedRoundRobin对象
// 缓存了直接获取
WeightedRoundRobin weightedRoundRobin = map.computeIfAbsent(identifyString, k -> {
WeightedRoundRobin wrr = new WeightedRoundRobin();
wrr.setWeight(weight);
return wrr;
});
// 缓存的WeightedRoundRobin可能会过时,这里判定以下,保持最新的weight
if (weight != weightedRoundRobin.getWeight()) {
//weight changed
weightedRoundRobin.setWeight(weight);
}
// 更新
// 每次每个provider都会先增加自己权重的值
long cur = weightedRoundRobin.increaseCurrent();
// 标记更新时间
weightedRoundRobin.setLastUpdate(now);
// 如果当前值大于最大值,则选取
if (cur > maxCurrent) {
maxCurrent = cur;
selectedInvoker = invoker;
selectedWRR = weightedRoundRobin;
}
//
totalWeight += weight;
}
if (invokers.size() != map.size()) {
map.entrySet().removeIf(item -> now - item.getValue().getLastUpdate() > RECYCLE_PERIOD);
}
if (selectedInvoker != null) {
// 注意,选中的weightedRoundRobin的current会减去totalWeight;
selectedWRR.sel(totalWeight);
return selectedInvoker;
}
// should not happen here
return invokers.get(0);
}
}
轮询算法流程
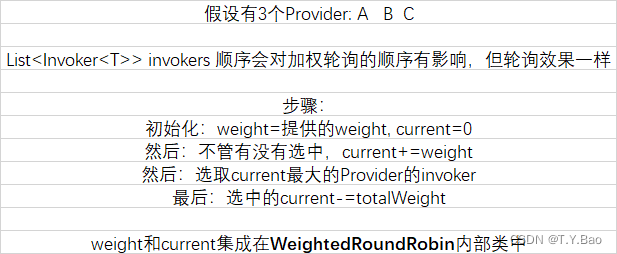
| 轮次 | 结果 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 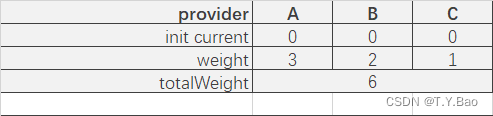 |
| 1 | 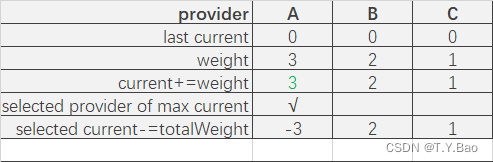 |
| 2 | 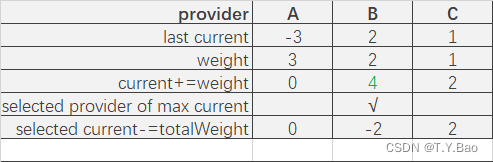 |
| 3 | 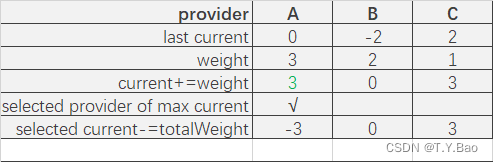 |
| 4 | 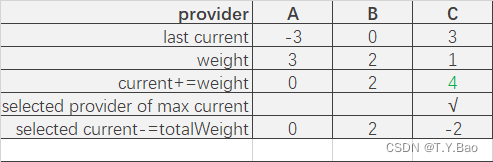 |
| 5 | 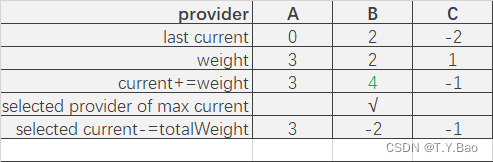 |
| 6 | 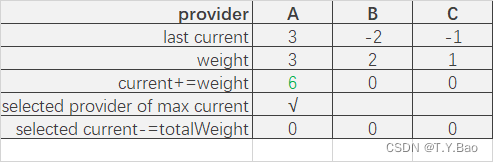 |
可以看到调用顺序为:A → \rightarrow →B → \rightarrow →A → \rightarrow →C → \rightarrow →B → \rightarrow →A。
LeastActiveLoadBalance
按照最小调用次数优先的方式选provider,如果存在多个则加权随机选取。
Active等参数由RpcStatus提供,记录RpcStatus的工作由ActiveLimitFilter完成
public class LeastActiveLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
// Number of invokers
int length = invokers.size();
// The least active value of all invokers
int leastActive = -1;
// The number of invokers having the same least active value (leastActive)
int leastCount = 0;
// 存储所有具有相同least active value的invoker的index,数组长度==leastCount
int[] leastIndexes = new int[length];
// the weight of every invokers
int[] weights = new int[length];
// The sum of the warmup weights of all the least active invokers
int totalWeight = 0;
// The weight of the first least active invoker
int firstWeight = 0;
// Every least active invoker has the same weight value?
boolean sameWeight = true;
// 过滤找到调用次数最少的provider,可能存在多个provider
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Invoker<T> invoker = invokers.get(i);
// Get the active number of the invoker
int active = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName()).getActive();
// 获取权重参数,provider没有提供则默认100
int afterWarmup = getWeight(invoker, invocation);
weights[i] = afterWarmup;
// 如果是第一次调用,或当前active小于最小的,设置新的leastActive
if (leastActive == -1 || active < leastActive) {
...
} else
// 多个leastActive
if (active == leastActive) {
...
}
}
// 如果符合最少调用次数的provider只有一个,直接返回
if (leastCount == 1) {
return invokers.get(leastIndexes[0]);
}
//
if (!sameWeight && totalWeight > 0) {
// 权重不等且totalWeight>0则利用权重随机选取
int offsetWeight = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
// Return a invoker based on the random value.
for (int i = 0; i < leastCount; i++) {
// 找到相同权重的provider第一个比随机选取的offsetWeight大的provider
int leastIndex = leastIndexes[i];
offsetWeight -= weights[leastIndex];
if (offsetWeight < 0) {
return invokers.get(leastIndex);
}
}
}
// 如果所有provider的weight相同或totalWeight==0则随机选取.
return invokers.get(leastIndexes[ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(leastCount)]);
}
}
ShortestResponseLoadBalance
同上,利用RpcStatus中获取的参数选取响应最低的provider(滑动时间窗口内),存在多个则加权随机选取。
ConsistentHashLoadBalance
public class ConsistentHashLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
// 对每一个接口方法缓存一个ConsistentHashSelector
// key为interface.methodName
private final ConcurrentMap<String, ConsistentHashSelector<?>> selectors = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, ConsistentHashSelector<?>>();
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + methodName;
// 用来代表List<Invoker<T>>,如果内容变化,则该hashcode也变化,为了保持缓存一致性
int invokersHashCode = invokers.hashCode();
ConsistentHashSelector<T> selector = (ConsistentHashSelector<T>) selectors.get(key);
// 缓存的ConsistentHashSelector为空,或已经过期
if (selector == null || selector.identityHashCode != invokersHashCode) {
selectors.put(key, new ConsistentHashSelector<T>(invokers, methodName, invokersHashCode));
selector = (ConsistentHashSelector<T>) selectors.get(key);
}
return selector.select(invocation);
}
private static final class ConsistentHashSelector<T> {
// 虚拟节点和Invoker对应关系
private final TreeMap<Long, Invoker<T>> virtualInvokers;
// 一致性哈希,哈希环虚拟节点个数
private final int replicaNumber;
private final int identityHashCode;
// select时候以方法的那个参数为key进行hash映射到hash环,默认第一个参数
private final int[] argumentIndex;
ConsistentHashSelector(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, String methodName, int identityHashCode) {
this.virtualInvokers = new TreeMap<Long, Invoker<T>>();
this.identityHashCode = identityHashCode;
URL url = invokers.get(0).getUrl();
// 如果hash.nodes没有指定,默认每个provider160个节点
this.replicaNumber = url.getMethodParameter(methodName, HASH_NODES, 160);
String[] index = COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url.getMethodParameter(methodName, HASH_ARGUMENTS, "0"));
argumentIndex = new int[index.length];
for (int i = 0; i < index.length; i++) {
argumentIndex[i] = Integer.parseInt(index[i]);
}
// 为每个invoker分配哈希环160个虚拟节点
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
String address = invoker.getUrl().getAddress();
for (int i = 0; i < replicaNumber / 4; i++) {
byte[] digest = Bytes.getMD5(address + i);
for (int h = 0; h < 4; h++) {
long m = hash(digest, h);
virtualInvokers.put(m, invoker);
}
}
}
}
public Invoker<T> select(Invocation invocation) {
boolean isGeneric = invocation.getMethodName().equals($INVOKE);
// 获取此次invocation的hash的key
String key = toKey(invocation.getArguments(),isGeneric);
byte[] digest = Bytes.getMD5(key);
// 映射
return selectForKey(hash(digest, 0));
}
}
}