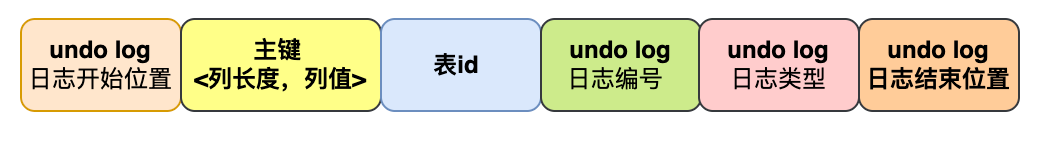
一、数据准备
数据使用的不同处理土壤样品的微生物组成数据,包含物种丰度,分类单元和样本分组数据。此数据为虚构,可用于练习,请不要作他用。
# 1.1 设置工作路径
#knitr::opts_knit$set(root.dir="D:\\EnvStat\\PCA")# 使用Rmarkdown进行程序运行
Sys.setlocale('LC_ALL','C') # Rmarkdown全局设置
#options(stringsAsFactors=F)# R中环境变量设置,防止字符型变量转换为因子
setwd("D:\\EnvStat\\alluvial_map")
# 1.2 读入数据
## 物种组成数据
spetax <- read.table("spetax.csv", header=T, row.names=1, sep=",", comment.char="",stringsAsFactors = TRUE,quote = "")
head(spetax)
## 将物种分类单元注释信息与丰度数据分开
spe <- spetax[-c(1:7)]
tax <- spetax[1:7]
head(spe)
head(tax)
## 样本分组数据
group <- read.table("group.csv", header=T, row.names=1, sep=",", comment.char="",stringsAsFactors = TRUE,quote = "")
group$grazing <- factor(group$grazing,levels = c("CK","LG","MG","HG"))
group

图1|物种丰度及分类单元注释信息,spetax.csv。

图2|样本分组信息,group.csv。
二、 物种组成冲积图
使用ggalluvial包在门水平绘制物种组成冲积图,可以绘制绝对丰度冲积图,也可以使用相对丰度绘制冲积图。
2.1 绝对丰度物种组成冲积图
# 2.1.1 物种组成数据按照门进行汇总
## spe和tax数据表中物种排序一致
library(tidyverse)
phy <- spe %>%
group_by(tax$Phylum) %>% # 使用tax中的门水平进行分类
summarise_all(sum) %>%
rename(Phylum = `tax$Phylum`) %>%
gather(key="Samples",value = "abun",-Phylum) %>% # 数据形式转换:“宽”转“长”
left_join(group,by=c("Samples"="name")) %>%
select(grazing,depth,Phylum,abun) %>%
group_by(grazing,depth,Phylum) %>% # 求均值
summarise_all(mean)
dim(phy)
head(phy)
# 2.1.2 颜色
library(ggsci)
col=pal_d3("category20")(20)
col2 = pal_d3("category20",alpha = 0.5)(20)
mypal=c(col,col2[-8])

图3|按门汇总的各处理物种丰度均值数据,phy。long format数据形式可直接用于ggplot2绘图。
# 2.1.3 物种组成冲积图-绝对丰度
abs_allu <- ggplot(data = phy,
aes(x = depth, y = abun, fill = reorder(Phylum,-abun),
stratum = reorder(Phylum,-abun),
alluvium = reorder(Phylum,-abun))) +
geom_alluvium()+
geom_stratum(width=0.45, size=0.1) +
geom_bar(aes(fill = reorder(Phylum,-abun)),stat='identity', width=0.45) +
scale_y_continuous(expand=c(0, 0))+
theme_bw() +
facet_grid( ~ grazing,scales = "fixed")+
scale_fill_manual(values = mypal,name="Phylum") +
scale_color_manual(values = mypal) +
theme(legend.position = "top",
panel.grid=element_blank(),
panel.spacing.x = unit(0,units = "cm"),
strip.background = element_rect(
color="white", fill="white",
linetype="solid",size=0.8),
strip.placement = "outside",
axis.line.y.left = element_line(color="black",size=0.8),
axis.line.x.bottom = element_line(color="black",size=0.8),
strip.text.x = element_text(size = 14,face = "bold"),
axis.text = element_text(face = "bold",
size = 12,color="black"),
axis.title = element_text(face = "bold",
size = 14,colour = "black"),
legend.title = element_text(face = "bold",
size =12,color="black"),
legend.text = element_text(face = "bold", size =12,color="black"),
axis.ticks.x = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.y = element_line(size = 0.3),
)+
labs(x = "Depth",y= "Relative Abundance of Phylum (%)")
abs_allu
ggsave("abs_allu.pdf",abs_allu,device = "pdf",width = 12,height = 8,family="Times")
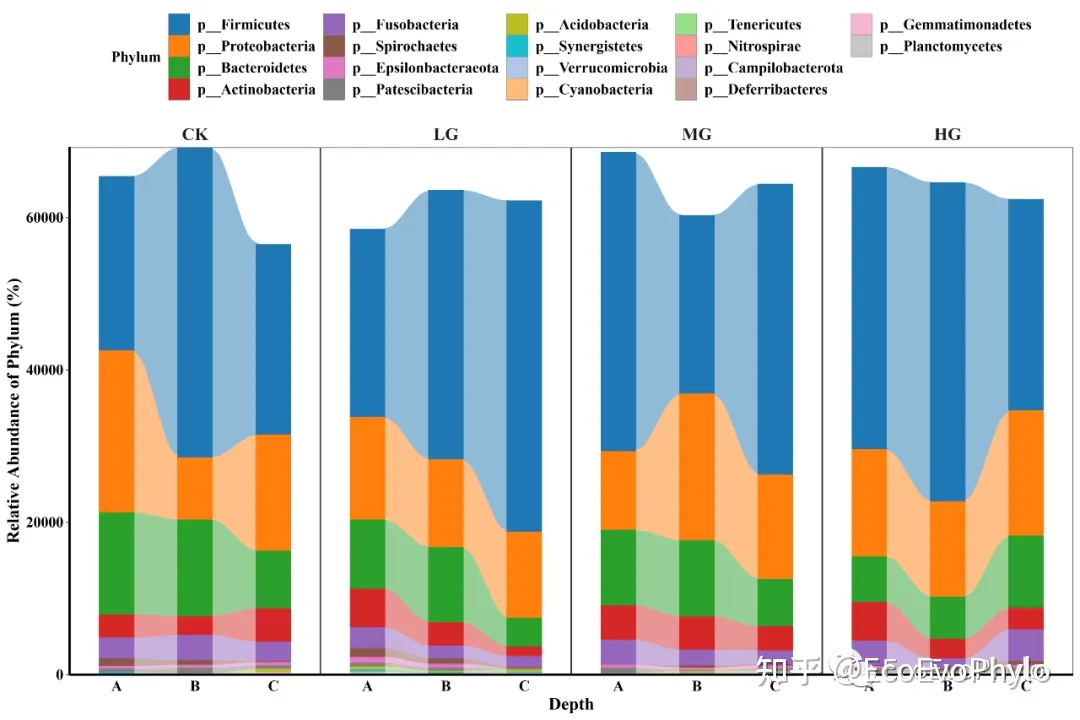
图4|绝对丰度冲积图,abs_allu.pdf。
2.2 相对丰度物种组成冲积图
# 2.2.1 需要先计算相对丰度
rel_spe <- sweep(spe,2,colSums(spe),'/')*100
head(rel_spe)
# 2.2.2 物种组成数据按照门进行汇总
## spe和tax数据表中物种排序一致
rel_phy <- rel_spe %>%
group_by(tax$Phylum) %>% # 使用tax中的门水平进行分类
summarise_all(sum) %>%
rename(Phylum = `tax$Phylum`) %>%
gather(key="Samples",value = "abun",-Phylum) %>% # 数据形式转换:“宽”转“长”
left_join(group,by=c("Samples"="name")) %>%
select(grazing,depth,Phylum,abun) %>%
group_by(grazing,depth,Phylum) %>% # 求均值
summarise_all(mean)
dim(rel_phy)
head(rel_phy)

图5|按门汇总的各处理物种相对丰度数据,rel_phy。
# 2.2.3 物种组成冲积图-相对丰度
rel_allu <- ggplot(data = rel_phy,
aes(x = depth, y = abun, fill = reorder(Phylum,-abun),
stratum = reorder(Phylum,-abun),
alluvium = reorder(Phylum,-abun))) +
geom_alluvium()+
geom_stratum(width=0.45, size=0.1) +
geom_bar(aes(fill = reorder(Phylum,-abun)),stat='identity', width=0.45) +
scale_y_continuous(expand=c(0, 0))+
theme_bw() +
facet_grid( ~ grazing,scales = "fixed")+
scale_fill_manual(values = mypal,name="Phylum") +
scale_color_manual(values = mypal) +
theme(legend.position = "top",
panel.grid=element_blank(),
panel.spacing.x = unit(0,units = "cm"),
strip.background = element_rect(
color="white", fill="white",
linetype="solid",size=0.8),
strip.placement = "outside",
axis.line.y.left = element_line(color="black",size=0.8),
axis.line.x.bottom = element_line(color="black",size=0.8),
strip.text.x = element_text(size = 14,face = "bold"),
axis.text = element_text(face = "bold",
size = 12,color="black"),
axis.title = element_text(face = "bold",
size = 14,colour = "black"),
legend.title = element_text(face = "bold",
size =12,color="black"),
legend.text = element_text(face = "bold", size =12,color="black"),
axis.ticks.x = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.y = element_line(size = 0.3),
)+
labs(x = "Depth",y= "Relative Abundance of Phylum (%)")
rel_allu
ggsave("rel_allu.pdf",rel_allu,device = "pdf",width = 12,height = 8,family="Times")

图6|相对丰度冲积图,rel_allu.pdf。
原始数据和代码EcoEvoPhylo公众号后台发送“alluvial_map”获取。
原文链接:R统计绘图 | 物种组成冲积图(绝对/相对丰度,ggalluvial) (qq.com)
推荐阅读
R绘图-物种、环境因子相关性网络图(简单图、提取子图、修改图布局参数、物种-环境因子分别成环径向网络图)
R统计绘图-分子生态相关性网络分析(拓扑属性计算,ggraph绘图)
R统计绘图-变量分组相关性网络图(igraph)
机器学习-分类随机森林分析(randomForest模型构建、参数调优、特征变量筛选、模型评估和基础理论等)
R统计绘图-随机森林分类分析及物种丰度差异检验组合图
机器学习-多元分类/回归决策树模型(tree包)
R统计绘图-环境因子相关性+mantel检验组合图(linkET包介绍1)
R统计绘图-NMDS、环境因子拟合(线性和非线性)、多元统计(adonis2和ANOSIM)及绘图(双因素自定义图例)
R统计绘图-RDA分析、Mantel检验及绘图
R绘图-RDA排序分析R统计绘图-VPA(方差分解分析)
R统计绘图-PCA详解1(princomp/principal/rcomp/rda等)
R统计-PCA/PCoA/db-RDA/NMDS/CA/CCA/DCA等排序分析教程R统计绘图-PCA分析绘图及结果解读(误差线,多边形,双Y轴图、球形检验、KMO和变量筛选等)R统计-微生物群落结构差异分析及结果解读
R统计绘图-PCA分析及绘制双坐标轴双序图R统计绘图-分子生态相关性网络分析
R中进行单因素方差分析并绘图R统计-多变量单因素参数、非参数检验及多重比较
R绘图-相关性分析及绘图
R绘图-相关性系数图
R统计绘图-环境因子相关性热图
R统计绘图-corrplot绘制热图及颜色、字体等细节修改
R统计绘图-corrplot热图绘制细节调整2(更改变量可视化顺序、非相关性热图绘制、添加矩形框等)
R数据可视化之美-节点链接图R统计绘图-rgbif包下载GBIF数据及绘制分布图
R统计绘图 | 物种组成堆叠柱形图(绝对/相对丰度)
R统计-单因素ANOVA/Kruskal-Wallis置换检验R统计-正态性分布检验[Translation]
R统计-数据正态分布转换[Translation]
R统计-方差齐性检验[Translation]
R统计-Mauchly球形检验[Translation]R统计绘图-单、双、三因素重复测量方差分析[Translation]
R统计绘图-混合方差分析[Translation]
R统计绘图-协方差分析[Translation]
R统计绘图-One-Way MANOVA