来源0x3f:https://space.bilibili.com/206214
文章目录
- 二叉树
- [104. 二叉树的最大深度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
- [111. 二叉树的最小深度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
- [129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和](https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/)
- 二叉树变体(判断相同、平衡、对称)
- [100. 相同的树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/same-tree/)
- [101. 对称二叉树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/symmetric-tree/)
- [110. 平衡二叉树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/balanced-binary-tree/)
- [199. 二叉树的右视图](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/)
- [226. 翻转二叉树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/invert-binary-tree/)
- 二叉搜索树相关(中序遍历二叉搜索树等于遍历有序数组)
- [98. 验证二叉搜索树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/)
- [230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素](https://leetcode.cn/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/)
- [501. 二叉搜索树中的众数](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-mode-in-binary-search-tree/)
- 暴力(List转int数组:list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();)
- 利用二叉搜索树的性质一次遍历
- [530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-absolute-difference-in-bst/)
- [700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索](https://leetcode.cn/problems/search-in-a-binary-search-tree/)
- 二叉树的最近公共祖先相关
- [236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/)
- [235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/)
- 二叉树的层序遍历(BFS)
- [102. 二叉树的层序遍历](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
- [103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-zigzag-level-order-traversal/)
- [513. 找树左下角的值](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-bottom-left-tree-value/)
二叉树
104. 二叉树的最大深度
难度简单1507
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最大深度 3 。
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int left = maxDepth(root.left);
int right = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}
}
111. 二叉树的最小深度
难度简单928
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
**说明:**叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
输出:5
提示:
- 树中节点数的范围在
[0, 105]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
class Solution {
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
dfs(root,0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode node, int depth){
if(node.left == null && node.right == null){
res = Math.min(res, depth+1);
return;
}
if(node.left != null) dfs(node.left, depth+1);
if(node.right != null) dfs(node.right, depth+1);
return;
}
}
129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和
难度中等609
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,树中每个节点都存放有一个 0 到 9 之间的数字。
每条从根节点到叶节点的路径都代表一个数字:
- 例如,从根节点到叶节点的路径
1 -> 2 -> 3表示数字123。
计算从根节点到叶节点生成的 所有数字之和 。
叶节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
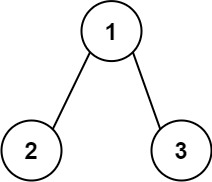
输入:root = [1,2,3]
输出:25
解释:
从根到叶子节点路径 1->2 代表数字 12
从根到叶子节点路径 1->3 代表数字 13
因此,数字总和 = 12 + 13 = 25
示例 2:
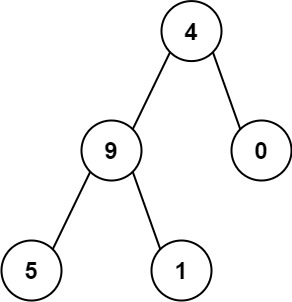
输入:root = [4,9,0,5,1]
输出:1026
解释:
从根到叶子节点路径 4->9->5 代表数字 495
从根到叶子节点路径 4->9->1 代表数字 491
从根到叶子节点路径 4->0 代表数字 40
因此,数字总和 = 495 + 491 + 40 = 1026
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[1, 1000]内 0 <= Node.val <= 9- 树的深度不超过
10
class Solution {
int res = 0;
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, 0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode node, int num){
if(node.left == null && node.right == null){
res += num * 10 + node.val;
return;
}
if(node.left != null) dfs(node.left, num * 10 + node.val);
if(node.right != null) dfs(node.right, num * 10 + node.val);
return;
}
}
二叉树变体(判断相同、平衡、对称)
100. 相同的树
难度简单967
给你两棵二叉树的根节点 p 和 q ,编写一个函数来检验这两棵树是否相同。
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
示例 1:
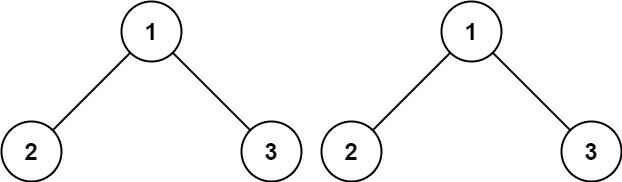
输入:p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3]
输出:true
示例 2:
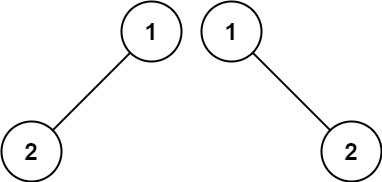
输入:p = [1,2], q = [1,null,2]
输出:false
示例 3:
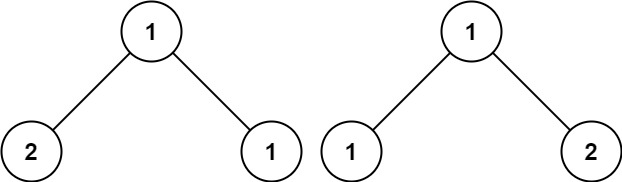
输入:p = [1,2,1], q = [1,1,2]
输出:false
提示:
- 两棵树上的节点数目都在范围
[0, 100]内 -104 <= Node.val <= 104
class Solution {
boolean same = true;
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p == null && q == null) return true;
else if(p == null && q != null) return false;
else if(p != null && q == null) return false;
else{
return (p.val == q.val) && isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
}
}
}
101. 对称二叉树
难度简单2278
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
示例 1:
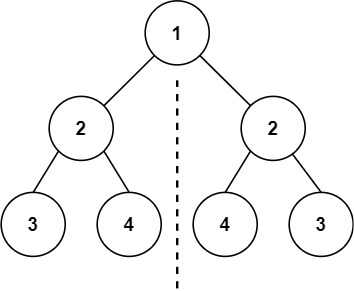
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
输出:true
示例 2:
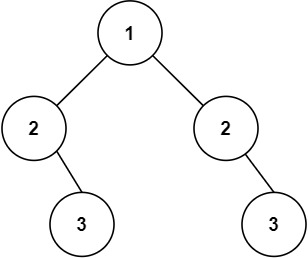
输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3]
输出:false
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[1, 1000]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
**进阶:**你可以运用递归和迭代两种方法解决这个问题吗?
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return true;
return iscopy(root.left, root.right);
}
public boolean iscopy(TreeNode node1, TreeNode node2){
if(node1 == null && node2 == null)
return true;
if(node1 == null || node2 == null)
return false;
return node1.val == node2.val
&& iscopy(node1.left, node2.right)
&& iscopy(node1.right, node2.left);
}
}
110. 平衡二叉树
难度简单1245
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:
一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 。
示例 1:
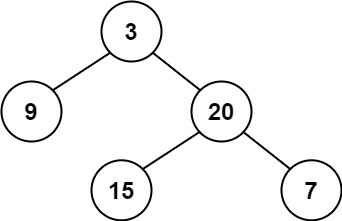
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:true
示例 2:
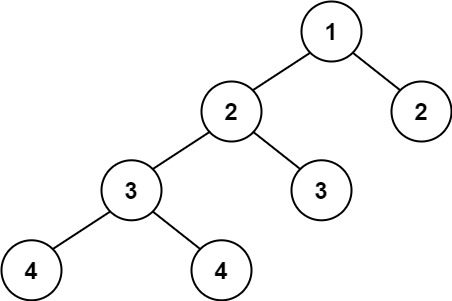
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]
输出:false
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:true
提示:
- 树中的节点数在范围
[0, 5000]内 -104 <= Node.val <= 104
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return true;
return get_height(root) > 0 ? true : false;
}
public int get_height(TreeNode node){
if(node == null) return 0;
int leftheight = get_height(node.left);
if(leftheight == -1) return -1;
int rightheight = get_height(node.right);
if(rightheight == -1) return -1;
if(Math.abs(leftheight - rightheight) > 1) return -1;
return Math.max(leftheight, rightheight) + 1;
}
}
199. 二叉树的右视图
难度中等814
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
示例 1:

输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
输出: [1,3,4]
示例 2:
输入: [1,null,3]
输出: [1,3]
示例 3:
输入: []
输出: []
提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是
[0,100] -100 <= Node.val <= 100
class Solution {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, 0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode node, int depth){
if(node == null) return;
if(depth == res.size()){
res.add(node.val);
}
dfs(node.right, depth+1);
dfs(node.left, depth+1);
return;
}
}
226. 翻转二叉树
难度简单1505
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
示例 1:

输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
示例 2:
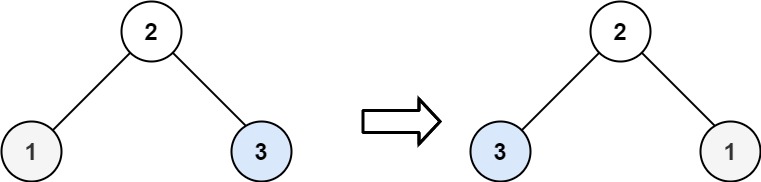
输入:root = [2,1,3]
输出:[2,3,1]
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点数目范围在
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return root;
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
root.right = invertTree(root.right);
root.left = invertTree(root.left);
return root;
}
}
二叉搜索树相关(中序遍历二叉搜索树等于遍历有序数组)
中序遍历二叉搜索树等于遍历有序数组
中序遍历二叉搜索树等于遍历有序数组
中序遍历二叉搜索树等于遍历有序数组
98. 验证二叉搜索树
难度中等1894
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
- 节点的左子树只包含 小于 当前节点的数。
- 节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
示例 1:

输入:root = [2,1,3]
输出:true
示例 2:

输入:root = [5,1,4,null,null,3,6]
输出:false
解释:根节点的值是 5 ,但是右子节点的值是 4 。
提示:
- 树中节点数目范围在
[1, 104]内 -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
法一:前序遍历(额外传递判断范围)
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return isBST(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
public boolean isBST(TreeNode node, long left, long right){
if(node == null) return true;
long x = node.val;
boolean valid = (left < x) && (x < right);
return valid && isBST(node.left, left, x) && isBST(node.right, x, right);
}
}
法二:中序遍历(从小到大的顺序,即判断是否大于前一个结点值)
class Solution {
long pre = Long.MIN_VALUE;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return true;
if(!isValidBST(root.left)) return false;
if(root.val <= pre) return false;
pre = root.val;
return isValidBST(root.right);
}
}
法三:后序遍历(返回最大和最小值,然后最后判断当前节点是否合法)
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root)[1] != Long.MAX_VALUE;
}
public long[] dfs(TreeNode node){
if(node == null) return new long[]{Long.MAX_VALUE, Long.MIN_VALUE};
long[] left = dfs(node.left);
long[] right = dfs(node.right);
long x = node.val;
// 小于等于左边最大值 或者 大于等于右边最小值 : 都是不合法的
if(x <= left[1] || x >= right[0]){
return new long[]{Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE};
}
// 返回左边最小值和右边最大值
return new long[]{Math.min(left[0], x), Math.max(right[1], x)};
}
}
230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
难度中等706
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,和一个整数 k ,请你设计一个算法查找其中第 k 个最小元素(从 1 开始计数)。
示例 1:
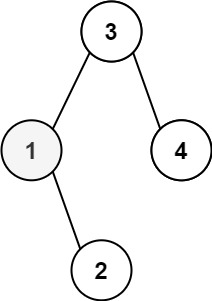
输入:root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
输出:1
示例 2:
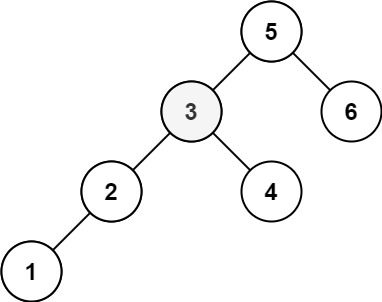
输入:root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
输出:3
提示:
- 树中的节点数为
n。 1 <= k <= n <= 1040 <= Node.val <= 104
**进阶:**如果二叉搜索树经常被修改(插入/删除操作)并且你需要频繁地查找第 k 小的值,你将如何优化算法?
法一:树的遍历+排序
class Solution {
//先对二叉树进行一次完整遍历,将所有节点存入列表中,最后对列表排序后返回目标值
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
dfs(root);
Collections.sort(list);
return list.get(k-1);
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
list.add(root.val);
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
}
法二:树的遍历+优先队列
- 第K小的元素用大根堆
class Solution {
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b-a);
Deque<TreeNode> dq = new ArrayDeque<>();
dq.addLast(root);
while(!dq.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = dq.pollFirst();
if(pq.size() < k){
pq.add(node.val);
}else if(pq.peek() > node.val){
pq.poll();
pq.add(node.val);
}
if(node.left != null) dq.addLast(node.left);
if(node.right != null) dq.addLast(node.right);
}
return pq.peek();
}
}
法三:中序遍历
上述两种节点,都没有利用该树为二叉搜索树的特性。
而我们知道,二叉搜索树的中序遍历是有序的,因此我们只需要对二叉搜索树执行中序遍历,并返回第 k 小的值即可。
class Solution {
int k, res = 0;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int _k) {
k = _k;
dfs(root);
return res;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root == null || k <= 0) return;
dfs(root.left);
if(--k == 0) res = root.val;
dfs(root.right);
}
}
501. 二叉搜索树中的众数
难度简单588
给你一个含重复值的二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root ,找出并返回 BST 中的所有 众数(即,出现频率最高的元素)。
如果树中有不止一个众数,可以按 任意顺序 返回。
假定 BST 满足如下定义:
- 结点左子树中所含节点的值 小于等于 当前节点的值
- 结点右子树中所含节点的值 大于等于 当前节点的值
- 左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树
示例 1:
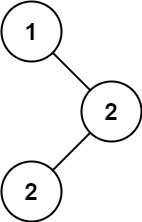
输入:root = [1,null,2,2]
输出:[2]
示例 2:
输入:root = [0]
输出:[0]
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[1, 104]内 -105 <= Node.val <= 105
**进阶:**你可以不使用额外的空间吗?(假设由递归产生的隐式调用栈的开销不被计算在内)
暴力(List转int数组:list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();)
class Solution {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int max = -1;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()){
if(entry.getValue() == max)
list.add(entry.getKey());
}
return list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
public void dfs(TreeNode node){
if(node == null) return;
int x = node.val;
map.put(x, map.getOrDefault(x, 0) + 1);
max = Math.max(max, map.get(x));
dfs(node.left);
dfs(node.right);
return;
}
}
利用二叉搜索树的性质一次遍历
思路:二叉搜索树的中序遍历是一个升序序列,逐个比对当前结点(root)值与前驱结点(pre)值。更新当前节点值出现次数(curTimes)及最大出现次数(maxTimes),更新规则:若curTimes=maxTimes,将root->val添加到结果向量(res)中;若curTimes>maxTimes,清空res,将root->val添加到res,并更新maxTimes为curTimes。
class Solution {
int pre = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int maxcnt = 0, curcnt = 0;
List<Integer> res;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(root);
return res.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
// 二叉搜索树中序遍历是递增顺序
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return;
dfs(root.left);
//判断当前值与上一个值的关系, 更新 curcnt 和 pre
if(pre == root.val){
curcnt++;
}else{
pre = root.val;
curcnt = 1;
}
//判断当前数量与最大数量的关系, 更新 list 和 maxTimes
if(curcnt == maxcnt){
res.add(root.val);
}else{
if(curcnt > maxcnt){
res = new ArrayList<>();
maxcnt = curcnt;
res.add(root.val);
}
}
dfs(root.right);
}
}
530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
难度简单433
给你一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,返回 树中任意两不同节点值之间的最小差值 。
差值是一个正数,其数值等于两值之差的绝对值。
示例 1:
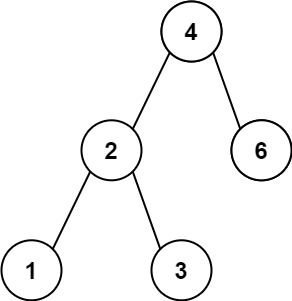
输入:root = [4,2,6,1,3]
输出:1
示例 2:
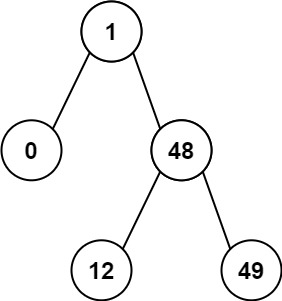
输入:root = [1,0,48,null,null,12,49]
输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是
[2, 104] 0 <= Node.val <= 105
class Solution {
int pre = (int)-1e5;
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return res == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : res;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode node){
if(node == null) return;
dfs(node.left);
res = Math.min(res, node.val - pre);
pre = node.val;
dfs(node.right);
}
}
700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
难度简单365
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和一个整数值 val。
你需要在 BST 中找到节点值等于 val 的节点。 返回以该节点为根的子树。 如果节点不存在,则返回 null 。
示例 1:
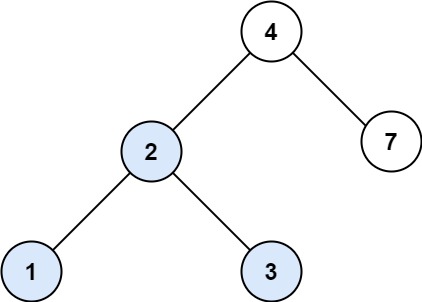
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 2
输出:[2,1,3]
示例 2:
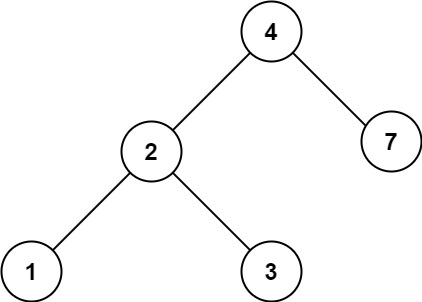
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5
输出:[]
提示:
- 数中节点数在
[1, 5000]范围内 1 <= Node.val <= 107root是二叉搜索树1 <= val <= 107
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root == null) return root;
if(root.val == val) return root;
else if(root.val > val) return searchBST(root.left, val);
else return searchBST(root.right, val);
}
}
二叉树的最近公共祖先相关
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
难度中等2153
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
输出:3
解释:节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3 。
示例 2:

输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
输出:5
解释:节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5 。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2
输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[2, 105]内。 -109 <= Node.val <= 109- 所有
Node.val互不相同。 p != qp和q均存在于给定的二叉树中。
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root == q){
return root;
}
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(left != null && right != null){
return root;
}
if(left != null)
return left;
else
return right;
}
}
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
难度中等1022
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
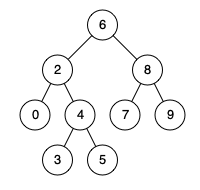
示例 1:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
输出: 6
解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
示例 2:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
输出: 2
解释: 节点 2 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是 2, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
- 所有节点的值都是唯一的。
- p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉搜索树中。
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p.val > q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root, q, p);
if(root.val >= p.val && root.val <= q.val) return root;
else if(root.val > q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
else return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
}
}
二叉树的层序遍历(BFS)
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
难度中等1580
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 层序遍历 。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
示例 2:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[[1]]
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 2000]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return res;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while(size-- > 0){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
res.add(list);
}
return res;
}
}
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
难度中等737
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 锯齿形层序遍历 。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[[3],[20,9],[15,7]]
示例 2:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[[1]]
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 2000]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return res;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean even = false;
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while(size-- > 0){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
if(even) Collections.reverse(list);
even = !even;
res.add(list);
}
return res;
}
}
513. 找树左下角的值
难度中等437
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例 1:
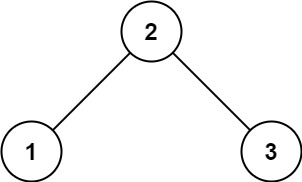
输入: root = [2,1,3]
输出: 1
示例 2:
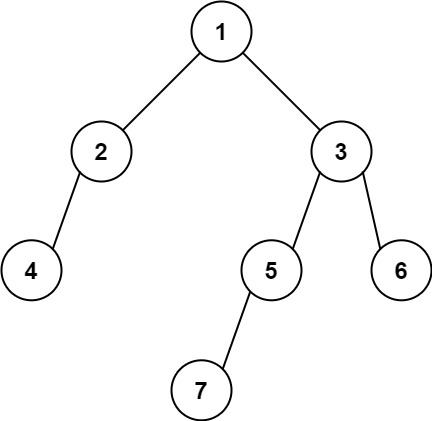
输入: [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7]
输出: 7
提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是
[1,104] -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
记录遍历的节点,从右往左遍历每层,最后一个出队列的节点就是答案
class Solution {
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(-1);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
while(size-- > 0){
node = queue.poll();
if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
}
}
return node.val;
}
}