目录
- 一.整体的设计结构图
- 二.各个组件代码详解
- 2.1 DUT
- 2.2 bus_driver
- 2.3 bus_sequencer
- 2.4 bus_monitor
- 2.5 bus_agent
- 2.6 bus_transaction
- 2.7 bus_if
- 2.8 my_if
- 2.9 my_transaction
- 2.10 my_sequencer
- 2.11 my_driver
- 2.12 my_monitor
- 2.13 my_agent
- 2.14 my_scoreboard
- 2.15 my_env
- 2.16 my_model
- 2.17 base_test
- 2.18 reg_model
- 2.19 my_adapter
- 2.20 my_vsqr
- 2.21 my_case0
一.整体的设计结构图
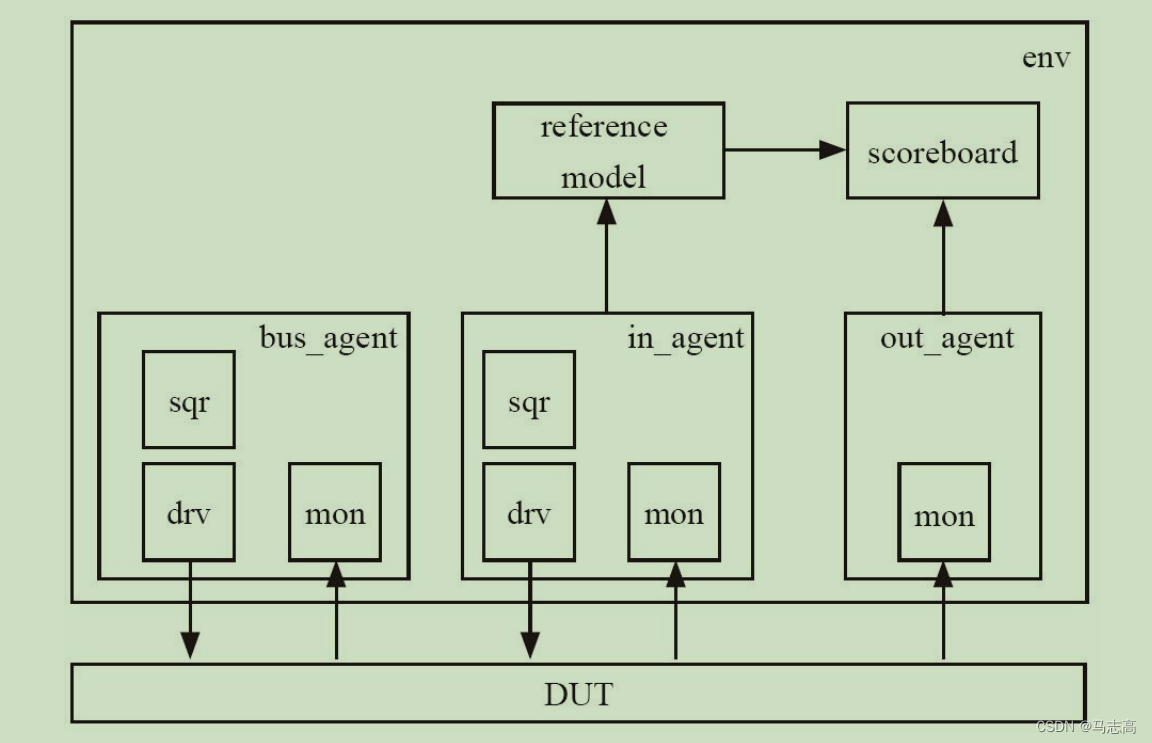
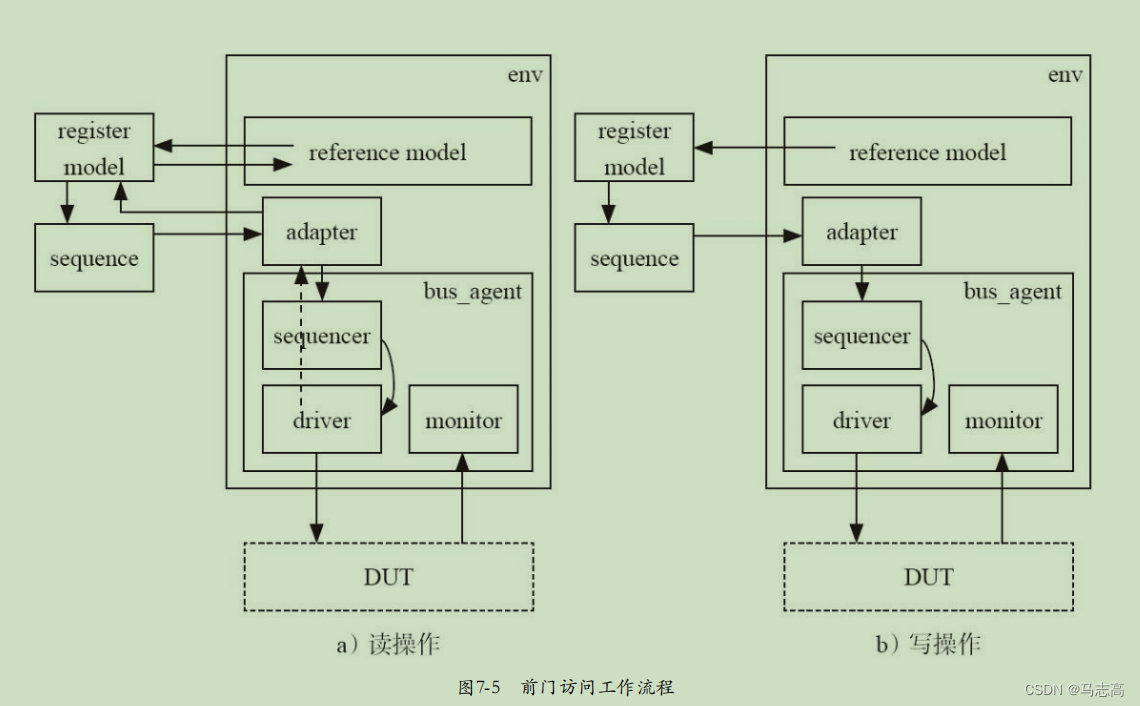
第二章例子的DUT,只有一组输入输出口,而没有行为控制口,这样的DUT几乎没有任何的价值,通常来说,DUT中会有一组控制端口,通过控制端口,可以配置DUT中的寄存器,DUT可以根据寄存器的值来改变其行为。这组端口就是寄存器配置总线。可以发现结构图中多了bus_agent,但实际上bus_agent的构成并不陌生,依然是由sequencer,driver,monitor组成。
二.各个组件代码详解
2.1 DUT
module dut(clk,rst_n,bus_cmd_valid,bus_op,bus_addr,bus_wr_data,bus_rd_data,rxd,rx_dv,txd,tx_en);
input clk;
input rst_n;
input bus_cmd_valid;//为1时表示数据有效,只持续一个时钟
input bus_op;//1时为写。0时为读
input [15:0] bus_addr;//地址
input [15:0] bus_wr_data;//读取的数据
output [15:0] bus_rd_data;//写入的数据
input [7:0] rxd;
input rx_dv;
output [7:0] txd;
output tx_en;
reg[7:0] txd;
reg tx_en;
reg invert;
//如果invert为1翻转,否则直接输出
always @(posedge clk) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
txd <= 8'b0;
tx_en <= 1'b0;
end
else if(invert) begin
txd <= ~rxd;
tx_en <= rx_dv;
end
else begin
txd <= rxd;
tx_en <= rx_dv;
end
end
always @(posedge clk) begin
if(!rst_n)
invert <= 1'b0;
else if(bus_cmd_valid && bus_op) begin
case(bus_addr)
16'h9: begin
invert <= bus_wr_data[0];
end
default: begin
end
endcase
end
end
reg [15:0] bus_rd_data;
always @(posedge clk) begin
if(!rst_n)
bus_rd_data <= 16'b0;
else if(bus_cmd_valid && !bus_op) begin
case(bus_addr)
16'h9: begin
bus_rd_data <= {15'b0, invert};
end
default: begin
bus_rd_data <= 16'b0;
end
endcase
end
end
endmodule
2.2 bus_driver
`ifndef BUS_DRIVER__SV
`define BUS_DRIVER__SV
class bus_driver extends uvm_driver#(bus_transaction);
virtual bus_if vif;
`uvm_component_utils(bus_driver)
function new(string name = "bus_driver", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
if(!uvm_config_db#(virtual bus_if)::get(this, "", "vif", vif))
`uvm_fatal("bus_driver", "virtual interface must be set for vif!!!")
endfunction
extern task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern task drive_one_pkt(bus_transaction tr);
endclass
task bus_driver::run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
vif.bus_cmd_valid <= 1'b0;
vif.bus_op <= 1'b0;
vif.bus_addr <= 15'b0;
vif.bus_wr_data <= 15'b0;
while(!vif.rst_n)
@(posedge vif.clk);
while(1) begin
seq_item_port.get_next_item(req);
drive_one_pkt(req);
seq_item_port.item_done();
end
endtask
task bus_driver::drive_one_pkt(bus_transaction tr);
`uvm_info("bus_driver", "begin to drive one pkt", UVM_LOW);
repeat(1) @(posedge vif.clk);
vif.bus_cmd_valid <= 1'b1;
vif.bus_op <= ((tr.bus_op == BUS_RD) ? 0 : 1);
vif.bus_addr = tr.addr;
vif.bus_wr_data <= ((tr.bus_op == BUS_RD) ? 0 : tr.wr_data);
@(posedge vif.clk);
vif.bus_cmd_valid <= 1'b0;
vif.bus_op <= 1'b0;
vif.bus_addr <= 15'b0;
vif.bus_wr_data <= 15'b0;
@(posedge vif.clk);
if(tr.bus_op == BUS_RD) begin
tr.rd_data = vif.bus_rd_data;
//$display("@%0t, rd_data is %0h", $time, tr.rd_data);
end
//`uvm_info("bus_driver", "end drive one pkt", UVM_LOW);
endtask
`endif
可以发现bus_driver和my_driver其实没有什么差别,就是在driver_one_pkt中的赋值过程稍有差别。
2.3 bus_sequencer
`ifndef BUS_SEQUENCER__SV
`define BUS_SEQUENCER__SV
class bus_sequencer extends uvm_sequencer #(bus_transaction);
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
`uvm_component_utils(bus_sequencer)
endclass
`endif
sequencer的化发现就名字发生了变化,其他的过程不变,这里可以总结一下,sequencer是通用的,以后改代码,就名字注意一下即可。
2.4 bus_monitor
`ifndef BUS_MONITOR__SV
`define BUS_MONITOR__SV
class bus_monitor extends uvm_monitor;
virtual bus_if vif;
uvm_analysis_port #(bus_transaction) ap;
`uvm_component_utils(bus_monitor)
function new(string name = "bus_monitor", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
if(!uvm_config_db#(virtual bus_if)::get(this, "", "vif", vif))
`uvm_fatal("bus_monitor", "virtual interface must be set for vif!!!")
ap = new("ap", this);
endfunction
extern task main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern task collect_one_pkt(bus_transaction tr);
endclass
task bus_monitor::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
bus_transaction tr;
while(1) begin
tr = new("tr");
collect_one_pkt(tr);
ap.write(tr);
end
endtask
task bus_monitor::collect_one_pkt(bus_transaction tr);
while(1) begin
@(posedge vif.clk);
if(vif.bus_cmd_valid) break;
end
tr.bus_op = ((vif.bus_op == 0) ? BUS_RD : BUS_WR);
tr.addr = vif.bus_addr;
tr.wr_data = vif.bus_wr_data;
@(posedge vif.clk);
tr.rd_data = vif.bus_rd_data;
`uvm_info("bus_monitor", "end collect one pkt", UVM_LOW);
endtask
`endif
这里的bus_monitor同样也是和my_monitor在collect_one_pkt有所区别,其他基本一致。
2.5 bus_agent
`ifndef BUS_AGENT__SV
`define BUS_AGENT__SV
class bus_agent extends uvm_agent ;
bus_sequencer sqr;
bus_driver drv;
bus_monitor mon;
uvm_analysis_port #(bus_transaction) ap;
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
extern virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_component_utils(bus_agent)
endclass
function void bus_agent::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
if (is_active == UVM_ACTIVE) begin
sqr = bus_sequencer::type_id::create("sqr", this);
drv = bus_driver::type_id::create("drv", this);
end
mon = bus_monitor::type_id::create("mon", this);
endfunction
function void bus_agent::connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.connect_phase(phase);
if (is_active == UVM_ACTIVE) begin
drv.seq_item_port.connect(sqr.seq_item_export);
end
ap = mon.ap;
endfunction
`endif
bus_agent和my_agent相似度极高可以按照之理解
2.6 bus_transaction
`ifndef BUS_TRANSACTION__SV
`define BUS_TRANSACTION__SV
typedef enum{BUS_RD, BUS_WR} bus_op_e;
class bus_transaction extends uvm_sequence_item;
rand bit[15:0] rd_data;
rand bit[15:0] wr_data;
rand bit[15:0] addr;
rand bus_op_e bus_op;
`uvm_object_utils_begin(bus_transaction)
`uvm_field_int(rd_data, UVM_ALL_ON)
`uvm_field_int(wr_data, UVM_ALL_ON)
`uvm_field_int(addr , UVM_ALL_ON)
//(1)`uvm_field_enum的用法
`uvm_field_enum(bus_op_e, bus_op, UVM_ALL_ON)
`uvm_object_utils_end
function new(string name = "bus_transaction");
super.new();
endfunction
endclass
`endif
(1)`uvm_field_enum的用法
define uvm_field_enum(T,ARG,FLAG)会比其他的域的自动化多一个变量T,
2.7 bus_if
`ifndef BUS_IF__SV
`define BUS_IF__SV
interface bus_if(input clk, input rst_n);
logic bus_cmd_valid;
logic bus_op;
logic [15:0] bus_addr;
logic [15:0] bus_wr_data;
logic [15:0] bus_rd_data;
endinterface
`endif
bus_if和my_if理解很类似
2.8 my_if
`ifndef MY_IF__SV
`define MY_IF__SV
interface my_if(input clk, input rst_n);
logic [7:0] data;
logic valid;
endinterface
`endif
my_if与第二章保持一致
2.9 my_transaction
`ifndef MY_TRANSACTION__SV
`define MY_TRANSACTION__SV
class my_transaction extends uvm_sequence_item;
rand bit[47:0] dmac;
rand bit[47:0] smac;
rand bit[15:0] ether_type;
rand byte pload[];
rand bit[31:0] crc;
constraint pload_cons{
pload.size >= 46;
pload.size <= 1500;
}
function bit[31:0] calc_crc();
return 32'h0;
endfunction
function void post_randomize();
crc = calc_crc;
endfunction
`uvm_object_utils_begin(my_transaction)
`uvm_field_int(dmac, UVM_ALL_ON)
`uvm_field_int(smac, UVM_ALL_ON)
`uvm_field_int(ether_type, UVM_ALL_ON)
`uvm_field_array_int(pload, UVM_ALL_ON)
`uvm_field_int(crc, UVM_ALL_ON)
`uvm_object_utils_end
function new(string name = "my_transaction");
super.new();
endfunction
endclass
`endif
my_transaction和第二章保持一致
2.10 my_sequencer
`ifndef MY_SEQUENCER__SV
`define MY_SEQUENCER__SV
class my_sequencer extends uvm_sequencer #(my_transaction);
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
`uvm_component_utils(my_sequencer)
endclass
`endif
2.11 my_driver
`ifndef MY_DRIVER__SV
`define MY_DRIVER__SV
class my_driver extends uvm_driver#(my_transaction);
virtual my_if vif;
`uvm_component_utils(my_driver)
function new(string name = "my_driver", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
if(!uvm_config_db#(virtual my_if)::get(this, "", "vif", vif))
`uvm_fatal("my_driver", "virtual interface must be set for vif!!!")
endfunction
extern task main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern task drive_one_pkt(my_transaction tr);
endclass
task my_driver::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
vif.valid <= 1'b0;
vif.data <= 8'b0;
while(!vif.rst_n)
@(posedge vif.clk);
while(1) begin
seq_item_port.get_next_item(req);
drive_one_pkt(req);
seq_item_port.item_done();
end
endtask
task my_driver::drive_one_pkt(my_transaction tr);
byte unsigned data_q[];
int data_size;
data_size = tr.pack_bytes(data_q) / 8;
//`uvm_info("my_driver", "begin to drive one pkt", UVM_LOW);
repeat(3) @(posedge vif.clk);
for ( int i = 0; i < data_size; i++ ) begin
@(posedge vif.clk);
vif.valid <= 1'b1;
vif.data <= data_q[i];
end
@(posedge vif.clk);
vif.valid <= 1'b0;
//`uvm_info("my_driver", "end drive one pkt", UVM_LOW);
endtask
`endif
2.12 my_monitor
`ifndef MY_MONITOR__SV
`define MY_MONITOR__SV
class my_monitor extends uvm_monitor;
virtual my_if vif;
uvm_analysis_port #(my_transaction) ap;
`uvm_component_utils(my_monitor)
function new(string name = "my_monitor", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
if(!uvm_config_db#(virtual my_if)::get(this, "", "vif", vif))
`uvm_fatal("my_monitor", "virtual interface must be set for vif!!!")
ap = new("ap", this);
endfunction
extern task main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern task collect_one_pkt(my_transaction tr);
endclass
task my_monitor::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
my_transaction tr;
while(1) begin
tr = new("tr");
collect_one_pkt(tr);
ap.write(tr);
end
endtask
task my_monitor::collect_one_pkt(my_transaction tr);
byte unsigned data_q[$];
byte unsigned data_array[];
logic [7:0] data;
logic valid = 0;
int data_size;
while(1) begin
@(posedge vif.clk);
if(vif.valid) break;
end
//`uvm_info("my_monitor", "begin to collect one pkt", UVM_LOW);
while(vif.valid) begin
data_q.push_back(vif.data);
@(posedge vif.clk);
end
data_size = data_q.size();
data_array = new[data_size];
for ( int i = 0; i < data_size; i++ ) begin
data_array[i] = data_q[i];
end
tr.pload = new[data_size - 18]; //da sa, e_type, crc
data_size = tr.unpack_bytes(data_array) / 8;
//`uvm_info("my_monitor", "end collect one pkt", UVM_LOW);
endtask
`endif
2.13 my_agent
`ifndef MY_AGENT__SV
`define MY_AGENT__SV
class my_agent extends uvm_agent ;
my_sequencer sqr;
my_driver drv;
my_monitor mon;
uvm_analysis_port #(my_transaction) ap;
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
extern virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_component_utils(my_agent)
endclass
function void my_agent::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
if (is_active == UVM_ACTIVE) begin
sqr = my_sequencer::type_id::create("sqr", this);
drv = my_driver::type_id::create("drv", this);
end
mon = my_monitor::type_id::create("mon", this);
endfunction
function void my_agent::connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.connect_phase(phase);
if (is_active == UVM_ACTIVE) begin
drv.seq_item_port.connect(sqr.seq_item_export);
end
ap = mon.ap;
endfunction
`endif
2.14 my_scoreboard
`ifndef MY_SCOREBOARD__SV
`define MY_SCOREBOARD__SV
class my_scoreboard extends uvm_scoreboard;
my_transaction expect_queue[$];
uvm_blocking_get_port #(my_transaction) exp_port;
uvm_blocking_get_port #(my_transaction) act_port;
`uvm_component_utils(my_scoreboard)
extern function new(string name, uvm_component parent = null);
extern virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern virtual task main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
endclass
function my_scoreboard::new(string name, uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void my_scoreboard::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
exp_port = new("exp_port", this);
act_port = new("act_port", this);
endfunction
task my_scoreboard::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
my_transaction get_expect, get_actual, tmp_tran;
bit result;
super.main_phase(phase);
fork
while (1) begin
exp_port.get(get_expect);
expect_queue.push_back(get_expect);
end
while (1) begin
act_port.get(get_actual);
if(expect_queue.size() > 0) begin
tmp_tran = expect_queue.pop_front();
result = get_actual.compare(tmp_tran);
if(result) begin
`uvm_info("my_scoreboard", "Compare SUCCESSFULLY", UVM_LOW);
end
else begin
`uvm_error("my_scoreboard", "Compare FAILED");
$display("the expect pkt is");
tmp_tran.print();
$display("the actual pkt is");
get_actual.print();
end
end
else begin
`uvm_error("my_scoreboard", "Received from DUT, while Expect Queue is empty");
$display("the unexpected pkt is");
get_actual.print();
end
end
join
endtask
`endif
2.15 my_env
`ifndef MY_ENV__SV
`define MY_ENV__SV
class my_env extends uvm_env;
my_agent i_agt;
my_agent o_agt;
bus_agent bus_agt;
my_model mdl;
my_scoreboard scb;
reg_model p_rm;
uvm_tlm_analysis_fifo #(my_transaction) agt_scb_fifo;
uvm_tlm_analysis_fifo #(my_transaction) agt_mdl_fifo;
uvm_tlm_analysis_fifo #(my_transaction) mdl_scb_fifo;
function new(string name = "my_env", uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
i_agt = my_agent::type_id::create("i_agt", this);
o_agt = my_agent::type_id::create("o_agt", this);
i_agt.is_active = UVM_ACTIVE;
o_agt.is_active = UVM_PASSIVE;
bus_agt = bus_agent::type_id::create("bus_agt", this);
bus_agt.is_active = UVM_ACTIVE;
mdl = my_model::type_id::create("mdl", this);
scb = my_scoreboard::type_id::create("scb", this);
agt_scb_fifo = new("agt_scb_fifo", this);
agt_mdl_fifo = new("agt_mdl_fifo", this);
mdl_scb_fifo = new("mdl_scb_fifo", this);
endfunction
extern virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_component_utils(my_env)
endclass
function void my_env::connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.connect_phase(phase);
i_agt.ap.connect(agt_mdl_fifo.analysis_export);
mdl.port.connect(agt_mdl_fifo.blocking_get_export);
mdl.ap.connect(mdl_scb_fifo.analysis_export);
scb.exp_port.connect(mdl_scb_fifo.blocking_get_export);
o_agt.ap.connect(agt_scb_fifo.analysis_export);
scb.act_port.connect(agt_scb_fifo.blocking_get_export);
mdl.p_rm = this.p_rm;
endfunction
`endif
主要增加了关于bus_agent的例化和is_active的赋值,还有reg_model的内容,区别不大
2.16 my_model
`ifndef MY_MODEL__SV
`define MY_MODEL__SV
class my_model extends uvm_component;
uvm_blocking_get_port #(my_transaction) port;
uvm_analysis_port #(my_transaction) ap;
reg_model p_rm;
extern function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
extern function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern virtual task main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern virtual function void invert_tr(my_transaction tr);
`uvm_component_utils(my_model)
endclass
function my_model::new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void my_model::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
port = new("port", this);
ap = new("ap", this);
endfunction
function void my_model::invert_tr(my_transaction tr);
tr.dmac = tr.dmac ^ 48'hFFFF_FFFF_FFFF;
tr.smac = tr.smac ^ 48'hFFFF_FFFF_FFFF;
tr.ether_type = tr.ether_type ^ 16'hFFFF;
tr.crc = tr.crc ^ 32'hFFFF_FFFF;
for(int i = 0; i < tr.pload.size; i++)
tr.pload[i] = tr.pload[i] ^ 8'hFF;
endfunction
task my_model::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
my_transaction tr;
my_transaction new_tr;
uvm_status_e status;
uvm_reg_data_t value;
super.main_phase(phase);
p_rm.invert.read(status, value, UVM_FRONTDOOR);
while(1) begin
port.get(tr);
new_tr = new("new_tr");
new_tr.copy(tr);
//`uvm_info("my_model", "get one transaction, copy and print it:", UVM_LOW)
//new_tr.print();
if(value)
invert_tr(new_tr);
ap.write(new_tr);
end
endtask
`endif
2.17 base_test
`ifndef BASE_TEST__SV
`define BASE_TEST__SV
class base_test extends uvm_test;
my_env env;
my_vsqr v_sqr;
//(2)成员变量的理解
reg_model rm;
my_adapter reg_sqr_adapter;
function new(string name = "base_test", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction
extern virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern virtual function void report_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_component_utils(base_test)
endclass
function void base_test::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
env = my_env::type_id::create("env", this);
v_sqr = my_vsqr::type_id::create("v_sqr", this);
//(1)如何理解reg_model的实例化过程
rm = reg_model::type_id::create("rm", this);
rm.configure(null, "");
rm.build();
rm.lock_model();
rm.reset();
rm.set_hdl_path_root("top_tb.my_dut");
reg_sqr_adapter = new("reg_sqr_adapter");
env.p_rm = this.rm;
endfunction
//(3)connect_phase的理解
function void base_test::connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.connect_phase(phase);
v_sqr.p_my_sqr = env.i_agt.sqr;
v_sqr.p_bus_sqr = env.bus_agt.sqr;
v_sqr.p_rm = this.rm;
rm.default_map.set_sequencer(env.bus_agt.sqr, reg_sqr_adapter);
rm.default_map.set_auto_predict(1);
endfunction
function void base_test::report_phase(uvm_phase phase);
uvm_report_server server;
int err_num;
super.report_phase(phase);
server = get_report_server();
err_num = server.get_severity_count(UVM_ERROR);
if (err_num != 0) begin
$display("TEST CASE FAILED");
end
else begin
$display("TEST CASE PASSED");
end
endfunction
`endif
(1)如何理解reg_model的实例化过程
第一是调用configure函数,其第一个参数是parent block,由于最顶层的reg_block,因此填写null,第二个参数是后门访问路径,这里传入一个空的字符串。
第二是调用build函数,将所有的寄存器实例化。
第三是调用lock_model函数,调用此函数后,reg_model中就不能加入新的寄存器了。
第四是调用reset函数,如果不调用此函数,那么reg_model中所有寄存器的值都是0,调用此函数后,所有寄存器的值都将变为设置的复位值。
(2)成员变量的理解
要将一个寄存器模型集成到base_test中,那么至少需要base_test中定义两个成员变量,一个reg_model,另外一个是reg_sqr_adapter。
(3)connect_phase的理解
寄存器模型的前门访问操作最终都将由uvm_reg_map完成,因此在connect_phase中,需要将转换器和bus_sequencer通过set_sequencer函数告知reg_model的default_map,并将default_map设置为自动预测状态。
2.18 reg_model
`ifndef REG_MODEL__SV
`define REG_MODEL__SV
//uvm_reg是比较小的单位,一个寄存器中至少包含一个uvm_reg_field
class reg_invert extends uvm_reg;
//uvm_reg_filed是寄存器模型中的最小单位
rand uvm_reg_field reg_data;
//build的理解
virtual function void build();
reg_data = uvm_reg_field::type_id::create("reg_data");
// parameter: parent, size, lsb_pos, access, volatile, reset value, has_reset, is_rand, individually accessible
//(4)configure的参数理解
reg_data.configure(this, 1, 0, "RW", 1, 0, 1, 1, 0);
endfunction
`uvm_object_utils(reg_invert)
function new(input string name="reg_invert");
//parameter: name, size, has_coverage
//(3)new函数的理解
super.new(name, 16, UVM_NO_COVERAGE);
endfunction
endclass
class reg_counter extends uvm_reg;
rand uvm_reg_field reg_data;
virtual function void build();
reg_data = uvm_reg_field::type_id::create("reg_data");
// parameter: parent, size, lsb_pos, access, volatile, reset value, has_reset, is_rand, individually accessible
reg_data.configure(this, 32, 0, "W1C", 1, 0, 1, 1, 0);
endfunction
`uvm_object_utils(reg_counter)
function new(input string name="reg_counter");
//parameter: name, size, has_coverage
super.new(name, 32, UVM_NO_COVERAGE);
endfunction
endclass
//uvm_reg_block它是一个较大的单位,在其中可以加入很多的uvm_reg,也可以加入其他的uvm_reg_block
class reg_model extends uvm_reg_block;
rand reg_invert invert;
rand reg_counter counter;
virtual function void build();
//(5)uvm_reg_map
default_map = create_map("default_map", 0, 2, UVM_BIG_ENDIAN, 0);
//(6)实例化invert并调用invert.configure函数
invert = reg_invert::type_id::create("invert", , get_full_name());
invert.configure(this, null, "invert");
invert.build();
//(7)default_map
default_map.add_reg(invert, 'h9, "RW");
counter= reg_counter::type_id::create("counter", , get_full_name());
counter.configure(this, null, "counter");
counter.build();
default_map.add_reg(counter, 'h5, "RW");
endfunction
`uvm_object_utils(reg_model)
function new(input string name="reg_model");
super.new(name, UVM_NO_COVERAGE);
endfunction
endclass
`endif
(1)uvm_reg,uvm_reg_field,uvm_reg_block,uvm_reg_map四者的关系
uvm_reg_block>uvm_reg>uvm_reg_field,在每个block中至少包含一个uvm_reg_map。
(2)uvm_reg_map:每一个寄存器在加入寄存器模型时都有其地址,uvm_reg_map就是存储这些地址,并将其转化为可以访问的物理地址。
(3)new函数的理解
在new函数中,要将invert寄存器的宽度作为参数传递给super.new函数。这里的宽度并不是指这个寄存器的有效宽度,而是指寄存器中总共的位数。如对于一个16位的寄存器,其中可能只使用了8位,那么这里要填写的是16,而不是8。这个数字一般与系统总线的宽度一致。super.new中另外一个参数是是否要加入覆盖率的支持,这里选择UVM_NO_COVERAGE,即不支持。
(4)build的理解
每一个派生自uvm_reg的类都有一个build,这个build与uvm_component的build_phase并不一样,它不会自动执行,而需要手工调用,与build_phase相似的是所有的uvm_reg_field都在这里实例化。当reg_data实例化后,要调用reg_data_configure函数来配置这个字段。
(5)configure的参数理解
第一个参数就是此域(uvm_reg_filed)的父辈,也即此域位于那个寄存器中,这里当然是填写this了。
第二个参数是此域的宽度,由于DUT中的invert的宽度为1,所以这里为1。
第三个参数是此域的最低在整个寄存器中的位置,从0开始计数。
第四个参数表示此字段的存取方式。
第五个字段表示是否是易失的,这个参数一般不会使用。
第六个参数表示此域上电复位后的默认值。
第七个参数表示此域是否复位,一般的寄存器或者寄存器的域都有上电复位值,因此这里一般也填写1。
第八个参数表示这个域是否可以随机化
第九个参数表示这个域是否可以单独存取
(5)uvm_reg_map
一个uvm_reg_block中一定要定义一个uvm_reg_map,系统已经有一个声明好的default_map,只需要在build中将其实例化,这个实例化的过程并不是直接调用uvm_reg_map的new函数,而是通过调用uvm_reg_block的create_map来实现,create_map有众多的参数,
第一个参数是名字,
第二个参数是基地址,
第三个参数则是系统总线的宽度,这里的单位是byte而不是bit,
第四个参数是大小端,
最后一个参数表示是否能够按照byte寻址,
(6)实例化invert并调用invert.configure函数
这个函数的主要功能是指定寄存器进行后门访问操作时的路径,
第一个参数是此寄存器所在的uvm_reg_block的指针,这里填写this
第二个参数是reg_file的指针
第三个参数是此寄存器的后门访问路径,这里暂且为空
当调用完configure时,需要手动调用invert的build函数,将invert中的域进行实例化
(7)default_map
将寄存器加入default_map中,uvm_reg_map的作用是存储所有寄存器的地址,因此必须将实例化的寄存器加入default_map中,否则无法进行前门访问操作。
add_reg函数的第一个参数是要加入寄存器
第二个参数是寄存器的地址,这里是16’h9
第三个参数是寄存器的存取方式
2.19 my_adapter
`ifndef MY_ADAPTER__SV
`define MY_ADAPTER__SV
//(1)adapter的作用
class my_adapter extends uvm_reg_adapter;
string tID = get_type_name();
`uvm_object_utils(my_adapter)
function new(string name="my_adapter");
super.new(name);
endfunction : new
//reg2bus,其作用为寄存器模型通过sequence发出的uvm_reg_bus_op型的变量转换成bus_sequencer能够接收的形式
function uvm_sequence_item reg2bus(const ref uvm_reg_bus_op rw);
bus_transaction tr;
tr = new("tr");
tr.addr = rw.addr;
tr.bus_op = (rw.kind == UVM_READ) ? BUS_RD: BUS_WR;
if (tr.bus_op == BUS_WR)
tr.wr_data = rw.data;
return tr;
endfunction : reg2bus
//bus2reg,其作用为当监测到总线上有操作时,它将收集来的transaction转换成寄存器模型能够接受的形式,以便寄存器模型能够更新相应的寄存器的值。
function void bus2reg(uvm_sequence_item bus_item, ref uvm_reg_bus_op rw);
bus_transaction tr;
if(!$cast(tr, bus_item)) begin
`uvm_fatal(tID,
"Provided bus_item is not of the correct type. Expecting bus_transaction")
return;
end
rw.kind = (tr.bus_op == BUS_RD) ? UVM_READ : UVM_WRITE;
rw.addr = tr.addr;
rw.byte_en = 'h3;
rw.data = (tr.bus_op == BUS_RD) ? tr.rd_data : tr.wr_data;
rw.status = UVM_IS_OK;
endfunction : bus2reg
endclass : my_adapter
`endif
(1)adapter的作用
寄存器的前门访问操作可以分为读和写两种,无论是读或者写,寄存器模型都会通过sequence产生一个uvm_reg_bus_op的变量,此变量中存储这操作类型(读还是写)和操作地址,如果是写操作,还会有要写入的数据。此变量中的信息要经过一个转换器(adapter)转换后交给bus_sequencer,随后交给bus_driver,由bus_driver实现最终的前门访问读写操作。
2.20 my_vsqr
`ifndef MY_VSQR__SV
`define MY_VSQR__SV
class my_vsqr extends uvm_sequencer;
my_sequencer p_my_sqr;
bus_sequencer p_bus_sqr;
reg_model p_rm;
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
`uvm_component_utils(my_vsqr)
endclass
`endif
2.21 my_case0
`ifndef MY_CASE0__SV
`define MY_CASE0__SV
class case0_sequence extends uvm_sequence #(my_transaction);
my_transaction m_trans;
function new(string name= "case0_sequence");
super.new(name);
endfunction
virtual task body();
repeat (10) begin
`uvm_do(m_trans)
end
endtask
`uvm_object_utils(case0_sequence)
endclass
class case0_cfg_vseq extends uvm_sequence;
`uvm_object_utils(case0_cfg_vseq)
`uvm_declare_p_sequencer(my_vsqr)
function new(string name= "case0_cfg_vseq");
super.new(name);
endfunction
virtual task body();
uvm_status_e status;
uvm_reg_data_t value;
bit[31:0] counter;
uvm_reg_block blks[$];
reg_model p_rm;
if(starting_phase != null)
starting_phase.raise_objection(this);
uvm_reg_block::get_root_blocks(blks);
if(blks.size() == 0)
`uvm_fatal("case0_cfg_vseq", "can't find root blocks")
else begin
if(!$cast(p_rm, blks[0]))
`uvm_fatal("case0_cfg_vseq", "can't cast to reg_model")
end
p_rm.invert.read(status, value, UVM_FRONTDOOR);
`uvm_info("case0_cfg_vseq", $sformatf("invert's initial value is %0h", value), UVM_LOW)
p_rm.invert.write(status, 1, UVM_FRONTDOOR);
p_rm.invert.read(status, value, UVM_FRONTDOOR);
`uvm_info("case0_cfg_vseq", $sformatf("after set, invert's value is %0h", value), UVM_LOW)
p_rm.counter.read(status, value, UVM_FRONTDOOR);
counter = value;
`uvm_info("case0_cfg_vseq", $sformatf("counter's initial value(FRONTDOOR) is %0h", counter), UVM_LOW)
p_rm.counter.poke(status, 32'hFFFD);
p_rm.counter.read(status, value, UVM_FRONTDOOR);
counter = value;
`uvm_info("case0_cfg_vseq", $sformatf("after poke, counter's value(FRONTDOOR) is %0h", counter), UVM_LOW)
p_rm.counter.peek(status, value);
counter = value;
`uvm_info("case0_cfg_vseq", $sformatf("after poke, counter's value(BACKDOOR) is %0h", counter), UVM_LOW)
if(starting_phase != null)
starting_phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask
endclass
class case0_vseq extends uvm_sequence;
`uvm_object_utils(case0_vseq)
`uvm_declare_p_sequencer(my_vsqr)
function new(string name= "case0_vseq");
super.new(name);
endfunction
virtual task body();
case0_sequence dseq;
uvm_status_e status;
uvm_reg_data_t value;
if(starting_phase != null)
starting_phase.raise_objection(this);
#10000;
dseq = case0_sequence::type_id::create("dseq");
dseq.start(p_sequencer.p_my_sqr);
if(starting_phase != null)
starting_phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask
endclass
class my_case0 extends base_test;
function new(string name = "my_case0", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction
extern virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_component_utils(my_case0)
endclass
function void my_case0::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
uvm_config_db#(uvm_object_wrapper)::set(this,
"v_sqr.configure_phase",
"default_sequence",
case0_cfg_vseq::type_id::get());
uvm_config_db#(uvm_object_wrapper)::set(this,
"v_sqr.main_phase",
"default_sequence",
case0_vseq::type_id::get());
endfunction
`endif