事件处理
1.通过onXxx属性指定事件处理函数(注意大小写)
React使用的是自定义(合成)事件, 而不是使用的原生DOM事件 —— 为了更好的兼容性;React中的事件是通过事件委托方式处理的(委托给组件最外层的元素) ——为了的高效。
2.通过event.target得到发生事件的DOM元素对象 ——不要过度使用ref。
高阶函数和函数的柯里化
高阶函数:如果一个函数符合下面2个规范中的任何一个,那该函数就是高阶函数。
1.若A函数,接收的参数是一个函数,那么A就可以称之为高阶函数。
2.若A函数,调用的返回值依然是一个函数,那么A就可以称之为高阶函数。
常见的高阶函数有:Promise、setTimeout、arr.map()等等
函数的柯里化:通过函数调用继续返回函数的方式,实现多次接收参数最后统一处理的函数编码形式。
function sum(a){
return(b)=>{
return (c)=>{
return a+b+c
}
}
}
React生命周期
React组件从创建到死亡它会经历一些特定的阶段。React组件中包含一系列勾子函数(生命周期回调函数), 会在特定的时刻调用。在定义组件时,会在特定的生命周期回调函数中,做特定的工作。
生命周期的三个阶段(旧)
- 初始化阶段: 由ReactDOM.render()触发-----------初次渲染
constructor()
componentWillMount()
render()必须使用的一个
componentDidMount()常用,一般在这个钩子中做一些初始化的事,例如:开启定时器、发送网络请求、订阅消息 - 更新阶段: 由组件内部this.setState()或父组件重新render触发
shouldComponentUpdate()
componentWillUpdate()
render()
componentDidUpdate() - 卸载组件: 由ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode()触发
componentWillUnmount()常用,一般在这个钩子中做一些收尾的事,例如:关闭定时器、取消订阅消息。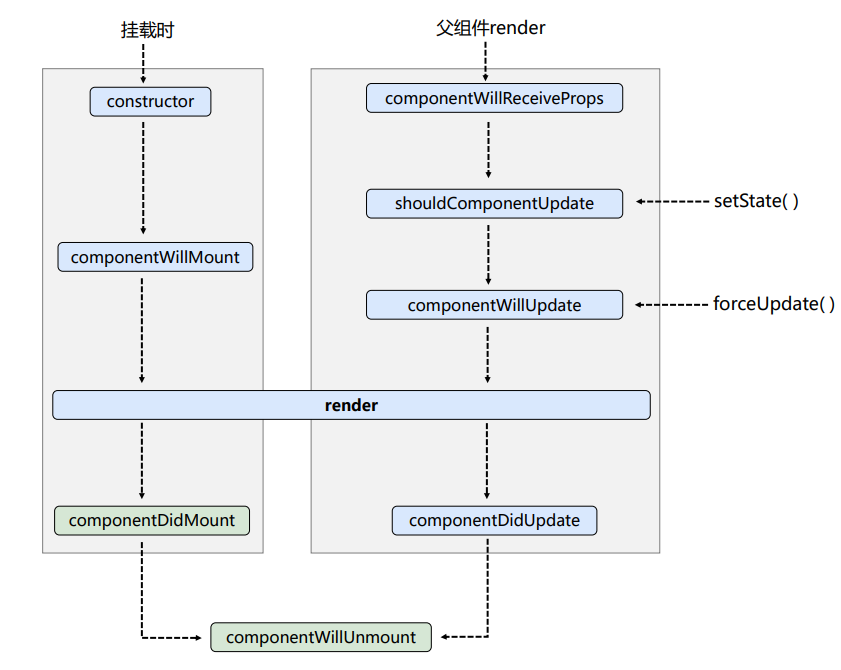
重要的钩子
- render:初始化渲染或更新渲染调用
- componentDidMount:开启监听, 发送ajax请求
- componentWillUnmount:做一些收尾工作, 如: 清理定时器
即将废弃的钩子
- componentWillMount
- componentWillReceiveProps
- componentWillUpdate
16版本使用会出现警告,17版本大版本需要加上UNSAFE_前缀才能使用,以后可能会被彻底废弃,不建议使用。
生命周期演示
class Count extends React.Component{
//构造器
constructor(props){
console.log('Count---constructor');
super(props)
//初始化状态
this.state = {count:0}
}
//加1按钮的回调
add = ()=>{
//获取原状态
const {count} = this.state
//更新状态
this.setState({count:count+1})
}
//卸载组件按钮的回调
death = ()=>{
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('test'))
}
//强制更新按钮的回调
force = ()=>{// 没有改变状态,只是强制更新一下
this.forceUpdate()
}
//组件将要挂载的钩子
componentWillMount(){
console.log('Count---componentWillMount');
}
//组件挂载完毕的钩子
componentDidMount(){
console.log('Count---componentDidMount');
}
//组件将要卸载的钩子
componentWillUnmount(){
console.log('Count---componentWillUnmount');
}
//控制组件更新的“阀门”
shouldComponentUpdate(){
console.log('Count---shouldComponentUpdate');
return true// 必须返回true或false
}
//组件将要更新的钩子
componentWillUpdate(){
console.log('Count---componentWillUpdate');
}
//组件更新完毕的钩子
componentDidUpdate(){
console.log('Count---componentDidUpdate');
}
render(){
console.log('Count---render');
const {count} = this.state
return(
<div>
<h2>当前求和为:{count}</h2>
<button onClick={this.add}>点我+1</button>
<button onClick={this.death}>卸载组件</button>
<button onClick={this.force}>不更改任何状态中的数据,强制更新一下</button>
</div>
)
}
}
//父组件A
class A extends React.Component{
//初始化状态
state = {carName:'奔驰'}
changeCar = ()=>{
this.setState({carName:'奥拓'})
}
render(){
return(
<div>
<div>我是A组件</div>
<button onClick={this.changeCar}>换车</button>
<B carName={this.state.carName}/>
</div>
)
}
}
//子组件B
class B extends React.Component{
//组件将要接收新的props的钩子,第一次不调,更新了才调
componentWillReceiveProps(props){
console.log('B---componentWillReceiveProps',props);
}
//控制组件更新的“阀门”
shouldComponentUpdate(){
console.log('B---shouldComponentUpdate');
return true
}
//组件将要更新的钩子
componentWillUpdate(){
console.log('B---componentWillUpdate');
}
//组件更新完毕的钩子
componentDidUpdate(){
console.log('B---componentDidUpdate');
}
render(){
console.log('B---render');
return(
<div>我是B组件,接收到的车是:{this.props.carName}</div>
)
}
}
//渲染组件
ReactDOM.render(<Count/>,document.getElementById('test'))
ReactDOM.render(<A/>,document.getElementById('test'))
定时器结合生命周期使用:
<div id="test"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
class Life extends React.Component{
state = {opacity:1}
death = ()=>{
//卸载组件
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('test'))
}
//组件挂载完毕
componentDidMount(){
console.log('componentDidMount');
this.timer = setInterval(() => {
let {opacity} = this.state// 获取原状态
opacity -= 0.1// 减小0.1
if(opacity <= 0) opacity = 1
this.setState({opacity})//设置新的透明度
}, 200);
}
//组件将要卸载
componentWillUnmount(){
clearInterval(this.timer)
}
//初始化渲染、状态更新之后
render(){
console.log('render');
return(
<div>
<h2 style={{opacity:this.state.opacity}}>React学不会怎么办?</h2>
<button onClick={this.death}>不活了</button>
</div>
)
}
}
//渲染组件
ReactDOM.render(<Life/>,document.getElementById('test'))
</script>
生命周期的三个阶段(新)
- 初始化阶段: 由ReactDOM.render()触发—初次渲染
constructor()
getDerivedStateFromProps
render()
componentDidMount() - 更新阶段: 由组件内部this.setSate()或父组件重新render触发
getDerivedStateFromProps
shouldComponentUpdate()
render()
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
componentDidUpdate() - 卸载组件: 由ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode()触发
componentWillUnmount()
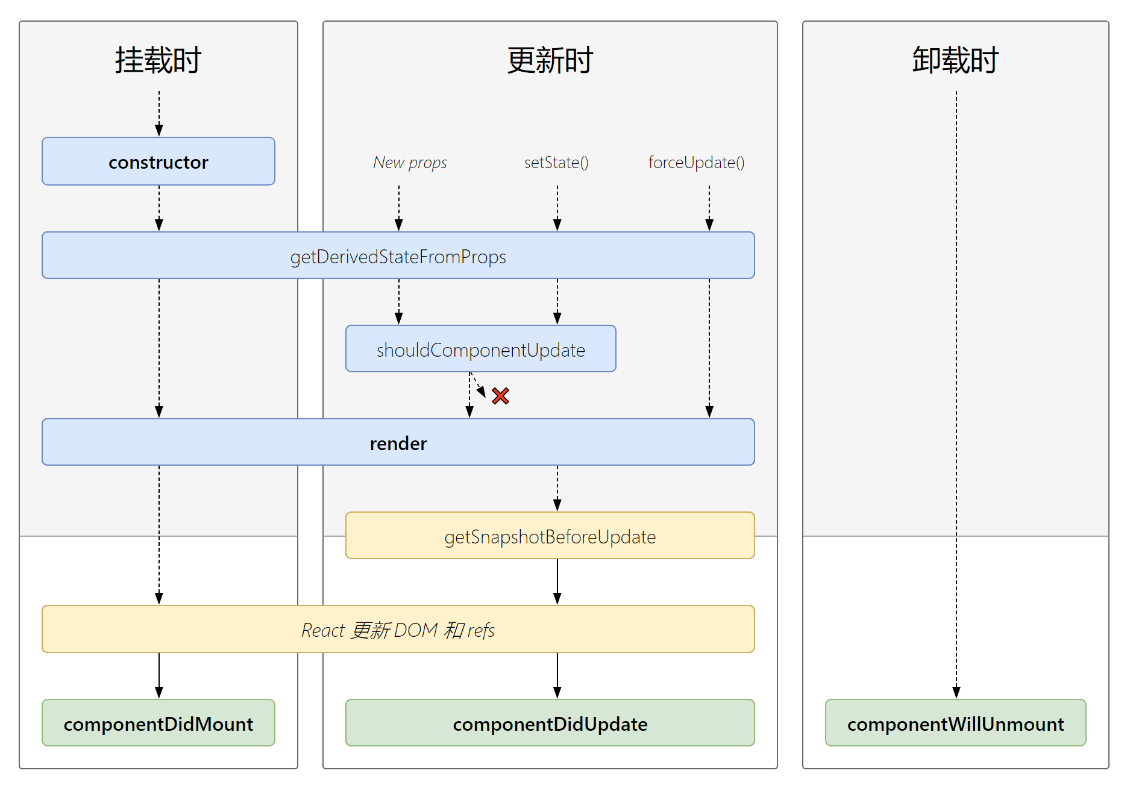
生命周期演示
//若state的值在任何时候都取决于props,那么可以使用getDerivedStateFromProps
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props,state){
console.log('getDerivedStateFromProps',props,state);
return null// 返回状态对象或null
}
//在更新之前获取快照
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(){
console.log('getSnapshotBeforeUpdate');
return 'zagiee'
}
//组件更新完毕的钩子
componentDidUpdate(preProps,preState,snapshotValue){// snapshotValue ='zagiee'
console.log('Count---componentDidUpdate',preProps,preState,snapshotValue);
}
DOM的diffing算法
虚拟DOM中key的作用
1). 简单的说: key是虚拟DOM对象的标识, 在更新显示时key起着极其重要的作用。
2). 详细的说: 当状态中的数据发生变化时,react会根据【新数据】生成【新的虚拟DOM】,随后React进行【新虚拟DOM】与【旧虚拟DOM】的diff比较,比较规则如下:
a. 旧虚拟DOM中找到了与新虚拟DOM相同的key:
(1).若虚拟DOM中内容没变, 直接使用之前的真实DOM
(2).若虚拟DOM中内容变了, 则生成新的真实DOM,随后替换掉页面中之前的真实DOM
b. 旧虚拟DOM中未找到与新虚拟DOM相同的key:
根据数据创建新的真实DOM,随后渲染到到页面
用index作为key可能会引发的问题:
- 若对数据进行:逆序添加、逆序删除等破坏顺序操作:
会产生没有必要的真实DOM更新 ==> 界面效果没问题, 但效率低。 - 如果结构中还包含输入类的DOM:
会产生错误DOM更新 ==> 界面有问题。 - 注意!如果不存在对数据的逆序添加、逆序删除等破坏顺序操作,仅用于渲染列表用于展示,使用index作为key是没有问题的。
开发中如何选择key?:
1.最好使用每条数据的唯一标识作为key, 比如id、手机号、身份证号、学号等唯一值。
2.如果确定只是简单的展示数据,用index也是可以的。

使用index索引值作为key
初始数据:
{id:1,name:'小张',age:18},
{id:2,name:'小李',age:19},
初始的虚拟DOM:
<li key=0>小张---18<input type="text"/></li>
<li key=1>小李---19<input type="text"/></li>
更新后的数据:
{id:3,name:'小王',age:20},
{id:1,name:'小张',age:18},
{id:2,name:'小李',age:19},
更新数据后的虚拟DOM:
<li key=0>小王---20<input type="text"/></li>key相同,内容变了,创建新的真实DOM
<li key=1>小张---18<input type="text"/></li>
<li key=2>小李---19<input type="text"/></li>
-----------------------------------------------------------------
使用id唯一标识作为key
初始数据:
{id:1,name:'小张',age:18},
{id:2,name:'小李',age:19},
初始的虚拟DOM:
<li key=1>小张---18<input type="text"/></li>
<li key=2>小李---19<input type="text"/></li>
更新后的数据:
{id:3,name:'小王',age:20},
{id:1,name:'小张',age:18},
{id:2,name:'小李',age:19},
更新数据后的虚拟DOM:
<li key=3>小王---20<input type="text"/></li>
<li key=1>小张---18<input type="text"/></li>
<li key=2>小李---19<input type="text"/></li>