目录
一、环境搭建
创建项目
编码 IDE
修改端口
配置代理
项目架构
二、Vue组件
main.ts
属性绑定
事件绑定
表单绑定
计算属性
xhr
axios
环境变量
baseURL
拦截器
条件和列表
监听器
vueuse
useRequest
usePagination(分页)
子组件
一、环境搭建
创建项目
采用 vite 作为前端项目的打包,构建工具
npm init vite@latest
按照提示操作

cd 项目目录
npm install
npm run dev
编码 IDE
推荐采用微软的 VSCode 作为开发工具,到它的官网 Visual Studio Code - Code Editing. Redefined 下载安装即可。

要对 *.vue 做语法支持,还要安装一个 Volar 插件

修改端口
打开项目根目录下 vite.config.ts
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import vue from '@vitejs/plugin-vue'
// https://vitejs.dev/config/
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [vue()],
server: {
port: 7070
}
})-
文档地址:配置 Vite {#configuring-vite} | Vite中文网 (vitejs.cn)
配置代理
为了避免前后端服务器联调时, fetch、xhr 请求产生跨域问题,需要配置代理,同样是修改项目根目录下 vite.config.ts
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import vue from '@vitejs/plugin-vue'
// https://vitejs.dev/config/
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [vue()],
server: {
port: 7070,
proxy: {
'/api': {
target: 'http://localhost:8080',
changeOrigin: true
}
}
}
})项目架构

-
index.html 为主页面
-
package.json npm 配置文件
-
tsconfig.json typescript 配置文件
-
vite.config.ts vite 配置文件
-
public 静态资源
-
src/components 可重用组件
-
src/model 模型定义
-
src/router 路由
-
src/store 共享存储
-
src/views 视图组件
二、Vue组件
ue 的组件文件以 .vue 结尾,每个组件由三部分组成
<script setup lang="ts"></script>
<template></template>
<style scoped></style>-
script 代码部分,控制模板的数据来源和行为
-
template 模板部分,由它生成 html 代码
-
style 样式部分
根组件是 src/App.vue,先来个 Hello,world 例子
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from "vue";
let msg = ref("hello"); // 把数据变成响应式的
function change() {
msg.value = "world";
console.log(msg);
}
</script>
<template>
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
<input type="button" value="修改msg" @click="change" />
</template>-
{{msg}} 用来把一个变量绑定到页面上某个位置
-
绑定的变量必须用 ref 函数来封装
-
ref 返回的是【响应式】数据,即数据一旦变化,页面展示也跟着变化
-
main.ts
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import './style.css'
import App from './App.vue'
createApp(App)
.mount('#app')-
createApp 是创建一个 Vue 应用程序,它接收的参数 App 即之前我们看到的根组件
-
mount 就是把根组件生成的 html 代码片段【挂载】到 index.html 中 id 为 app 的 html 元素上
可以修改自己的组件文件,挂载到主页面。
新建 src/views/E0.vue,内容如下
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from 'vue'
const msg = ref('Hello, World!!')
</script>
<template>
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
</template>修改 main.ts 将自己的组件文件挂载
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import './style.css'
// import App from './App.vue'
import E0 from './views/E0.vue'
createApp(E0).mount('#app')打开浏览器控制台,进入 Vue 的开发工具,尝试做如下修改

当把 msg 的值由 "Hello, World" 改为 "你好" 时,会发现页面展示同步发生了变化 ,这个就是响应式。
属性绑定
-
【:属性名】用来将标签属性与【响应式】变量绑定 v-bind
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from 'vue'
const path = ref('/src/assets/vue.svg')
</script>
<template>
<img :src="path" alt="">
</template>事件绑定
-
【@事件名】用来将标签属性与函数绑定,事件发生后执行函数内代码
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from 'vue'
const count = ref(0)
function dec() {
count.value--
}
function inc() {
count.value++
}
</script>
<template>
<input type="button" value="-" @click="dec">
<h2>{{count}}</h2>
<input type="button" value="+" @click="inc">
</template>表单绑定
-
用 v-model 实现双向绑定,即
-
javascript 数据可以同步到表单标签
-
反过来用户在表单标签输入的新值也会同步到 javascript 这边
-
-
双向绑定只适用于表单这种带【输入】功能的标签,其它标签的数据绑定,单向就足够了
-
复选框这种标签,双向绑定的 javascript 数据类型一般用数组
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from "vue";
const user = ref({
name:'张三',
age:18,
sex:'男',
fav:['游泳','打球']
})
function saveUser() {
console.log(user.value)
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="outer">
<div>
<label for="">请输入姓名</label>
<input type="text" v-model="user.name"/>
</div>
<div>
<label for="">请输入年龄</label>
<input type="text" v-model="user.age"/>
</div>
<div>
<label for="">请选择性别</label>
男 <input type="radio" value="男" v-model="user.sex"/>
女 <input type="radio" value="女" v-model="user.sex"/>
</div>
<div>
<label for="">请选择爱好</label>
游泳 <input type="checkbox" value="游泳" v-model="user.fav"/>
打球 <input type="checkbox" value="打球" v-model="user.fav"/>
健身 <input type="checkbox" value="健身" v-model="user.fav"/>
</div>
<div>
<input type="button" value="保存" @click="saveUser">
</div>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
div {
margin-bottom: 8px;
}
.outer {
width: 100%;
position: relative;
padding-left: 80px;
}
label {
text-align: left;
width: 100px;
display: inline-block;
position: absolute;
left :0;
}
</style>计算属性
有时在数据展示时要做简单的计算
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from 'vue'
const firstName = ref('三')
const lastName = ref('张')
</script>
<template>
<h2>{{lastName + firstName}}</h2>
<h3>{{lastName + firstName}}</h3>
<h4>{{lastName + firstName}}</h4>
</template>看起来较为繁琐,可以用计算属性改进
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, computed } from 'vue'
const firstName = ref('三')
const lastName = ref('张')
const fullName = computed(() => {
console.log('enter')
return lastName.value + firstName.value
})
</script>
<template>
<h2>{{fullName}}</h2>
<h3>{{fullName}}</h3>
<h4>{{fullName}}</h4>
</template>-
fullName 即为计算属性,它具备缓存功能,即 firstName 和 lastName 的值发生了变化,才会重新计算
-
如果用函数实现相同功能,则没有缓存功能。
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from 'vue'
const firstName = ref('三')
const lastName = ref('张')
function fullName() {
console.log('enter')
return lastName.value + firstName.value
}
</script>
<template>
<h2>{{fullName()}}</h2>
<h3>{{fullName()}}</h3>
<h4>{{fullName()}}</h4>
</template>xhr
浏览器中有两套 API 可以和后端交互,发送请求、接收响应,fetch api 前面我们已经介绍过了,另一套 api 是 xhr,基本用法如下。
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.onload = function() {
console.log(xhr.response)
}
xhr.open('GET', 'http://localhost:8080/api/students')
xhr.responseType = "json"
xhr.send()xhr.onload函数会在xhr接收到响应后才执行方法。
但这套 api 虽然功能强大,但比较老,不直接支持 Promise,因此有必要对其进行改造。
function get(url: string) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.onload = function() {
if(xhr.status === 200){
resolve(xhr.response)
} else if(xhr.status === 404) {
reject(xhr.response)
} // 其它情况也需考虑,这里简化处理
}
xhr.open('GET', url)
xhr.responseType = 'json'
xhr.send()
})
}-
Promise 对象适合用来封装异步操作,并可以配合 await 一齐使用
-
Promise 在构造时,需要一个箭头函数,箭头函数有两个参数 resolve 和 reject
-
resolve 是异步操作成功时被调用,把成功的结果传递给它,最后会作为 await 的结果返回
-
reject 在异步操作失败时被调用,把失败的结果传递给它,最后在 catch 块被捉住
-
-
await 会一直等到 Promise 内调用了 resolve 或 reject 才会继续向下运行
走代理和不走代理速度比较
调用示例1:同步接收结果,不走代理
try {
const resp = await get("http://localhost:8080/api/students")
console.log(resp)
} catch (e) {
console.error(e)
}调用示例2:走代理
try {
const resp = await get('/api/students')
console.log(resp)
} catch(e) {
console.log(e)
}会发现,走代理明显速度慢不少。
axios
axios 就是对 xhr api 的封装,手法与前面例子类似。
安装
npm install axios一个简单的例子
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, onMounted } from "vue";
import axios from "axios";
let count = ref(0);
async function getStudents() {
try {
const resp = await axios.get("/api/students");
count.value = resp.data.data.length;
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
}
}
onMounted(() => {
getStudents()
})
</script>
<template>
<h2>学生人数为:{{ count }}</h2>
</template>-
onMounted 指 vue 组件生成的 html 代码片段,挂载完毕后被执行
再来看一个 post 例子
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from "vue";
import axios from "axios";
const student = ref({
name: '',
sex: '男',
age: 18
})
async function addStudent() {
console.log(student.value)
const resp = await axios.post('/api/students', student.value)
console.log(resp.data.data)
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<div>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入姓名" v-model="student.name"/>
</div>
<div>
<label for="">请选择性别</label>
男 <input type="radio" value="男" v-model="student.sex"/>
女 <input type="radio" value="女" v-model="student.sex"/>
</div>
<div>
<input type="number" placeholder="请输入年龄" v-model="student.age"/>
</div>
<div>
<input type="button" value="添加" @click="addStudent"/>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
div {
font-size: 14px;
}
</style>环境变量
-
开发环境下,联调的后端服务器地址是
http://localhost:8080, -
上线改为生产环境后,后端服务器地址为
http://itheima.com
这就要求我们区分开发环境和生产环境,这件事交给构建工具 vite 来做
默认情况下,vite 支持上面两种环境,需要我们分别在对应根目录下创建两个配置文件
-
.env.development - 开发环境
-
.env.production - 生产环境
针对以上需求,分别在两个文件中加入
VITE_BACKEND_API_BASE_URL = 'http://localhost:8080'和
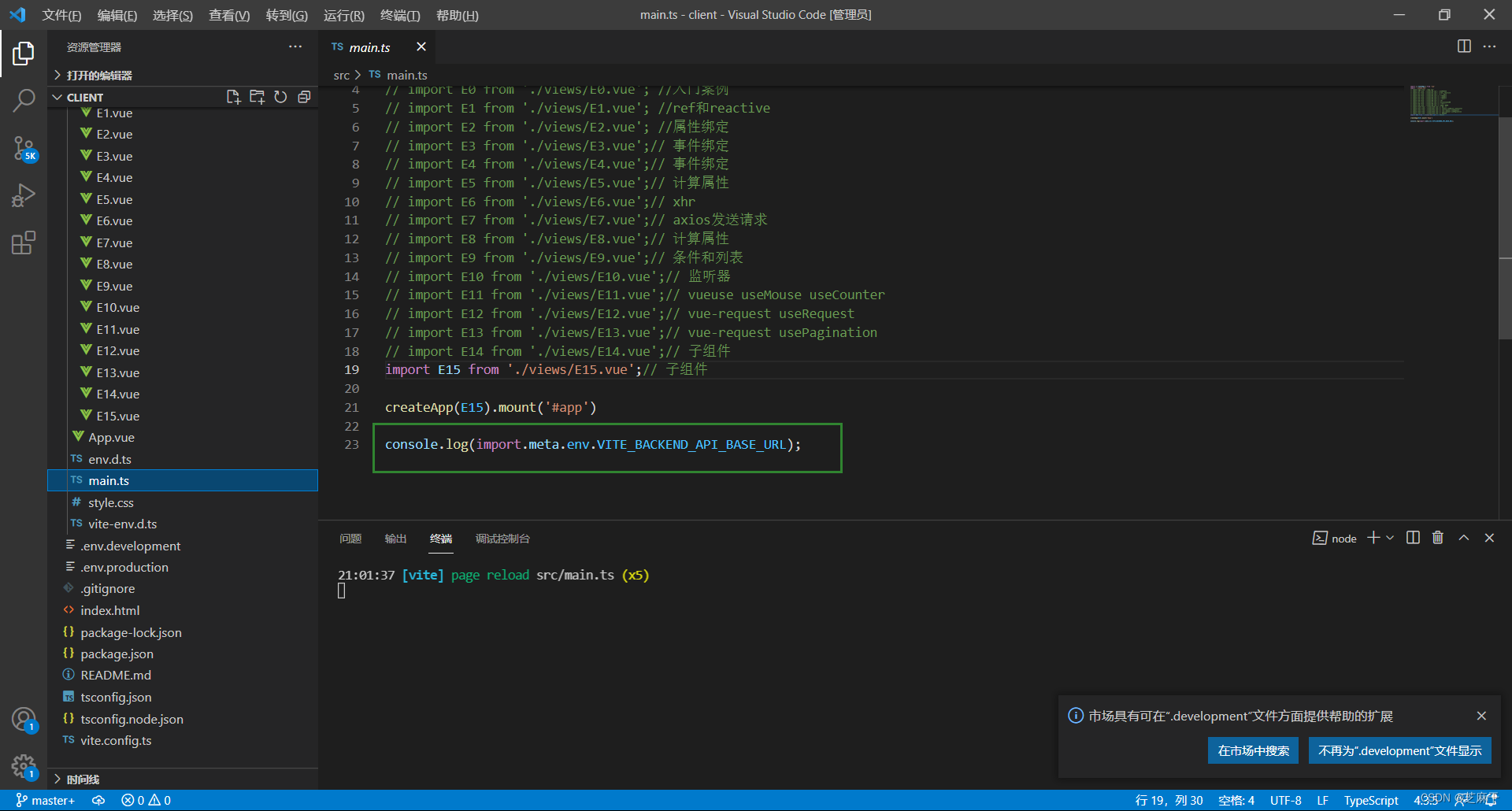
VITE_BACKEND_API_BASE_URL = 'http://itheima.com' 然后在代码中使用 vite 给我们提供的特殊对象 import.meta.env,就可以获取到 VITE_BACKEND_API_BASE_URL 在不同环境下的值
import.meta.env.VITE_BACKEND_API_BASE_URL默认情况下,不能智能提示自定义的环境变量,做如下配置:新增文件 src/env.d.ts 并添加如下内容
/// <reference types="vite/client" />
interface ImportMetaEnv {
readonly VITE_BACKEND_API_BASE_URL: string
// 更多环境变量...
}
interface ImportMeta {
readonly env: ImportMetaEnv
}-
参考文档地址 环境变量和模式 | Vite 官方中文文档 (vitejs.dev)
baseURL
可以自己创建一个 axios 对象,方便添加默认设置,新建文件 /src/api/request.ts
// 创建新的 axios 对象
import axios from 'axios'
const _axios = axios.create({
baseURL: import.meta.env.VITE_BACKEND_API_BASE_URL
})
export default _axios然后在其它组件中引用这个 ts 文件,例如 /src/views/E8.vue,就不用自己拼接路径前缀了
<script setup lang="ts">
import axios from '../api/request'
// ...
await axios.post('/api/students', ...)
</script>拦截器
// 创建新的 axios 对象
import axios from 'axios'
const _axios = axios.create({
baseURL: import.meta.env.VITE_BACKEND_API_BASE_URL
})
// 请求拦截器
_axios.interceptors.request.use(
(config)=>{ // 统一添加请求头
config.headers = {
Authorization: 'aaa.bbb.ccc'
}
return config
},
(error)=>{ // 请求出错时的处理
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
// 响应拦截器
_axios.interceptors.response.use(
(response)=>{ // 状态码 2xx
// 这里的code是自定义的错误码
if(response.data.code === 200) {
return response
}
else if(response.data.code === 401) {
// 情况1
return Promise.resolve({})
}
// ...
},
(error)=>{ // 状态码 > 2xx, 400,401,403,404,500
console.error(error) // 处理了异常
if(error.response.status === 400) {
// 情况1
} else if(error.response.status === 401) {
// 情况2
}
// ...
return Promise.resolve({})
}
)
export default _axios处理响应时,又分成两种情况
-
后端返回的是标准响应状态码,这时会走响应拦截器第二个箭头函数,用 error.response.status 做分支判断
-
后端返回的响应状态码总是200,用自定义错误码表示出错,这时会走响应拦截器第一个箭头函数,用 response.data.code 做分支判断
另外
-
Promise.reject(error) 类似于将异常继续向上抛出,异常由调用者(Vue组件)来配合 try ... catch 来处理
-
Promise.resolve({}) 表示错误已解决,返回一个空对象,调用者中接到这个空对象时,需要配合 ?. 来避免访问不存在的属性。
条件和列表
首先,新增模型数据 src/model/Model8080.ts
export interface Student {
id: number;
name: string;
sex: string;
age: number;
}
// 如果 spring 错误,返回的对象格式
export interface SpringError {
timestamp: string,
status: number,
error: string,
message: string,
path: string
}
// 如果 spring 成功,返回 list 情况
export interface SpringList<T> {
data: T[],
message?: string,
code: number
}
// 如果 spring 成功,返回 page 情况
export interface SpringPage<T> {
data: { list: T[], total: number },
message?: string,
code: number
}
// 如果 spring 成功,返回 string 情况
export interface SpringString {
data: string,
message?: string,
code: number
}
import { AxiosResponse } from 'axios'
export interface AxiosRespError extends AxiosResponse<SpringError> { }
export interface AxiosRespList<T> extends AxiosResponse<SpringList<T>> { }
export interface AxiosRespPage<T> extends AxiosResponse<SpringPage<T>> { }
export interface AxiosRespString extends AxiosResponse<SpringString> { }其中
-
AxiosRespPage 代表分页时的响应类型
-
AxiosRespList 代表返回集合时的响应类型
-
AxiosRespString 代表返回字符串时的响应类型
-
AxiosRespError 代表 Spring 出错时时的响应类
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { ref, onMounted } from "vue";
import axios from "../api/request";
import { Student, SpringList } from "../model/Model8080";
// 说明 students 数组类型为 Student[]
const students = ref<Student[]>([]);
async function getStudents() {
// 说明 resp.data 类型是 SpringList<Student>
const resp = await axios.get<SpringList<Student>>("/api/students");
console.log(resp.data.data);
students.value = resp.data.data;
}
onMounted(() => getStudents());
</script>
<template>
<div class="outer">
<div class="title">学生列表</div>
<div class="thead">
<div class="row bold">
<div class="col">编号</div>
<div class="col">姓名</div>
<div class="col">性别</div>
<div class="col">年龄</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="tbody">
<div v-if="students.length === 0">暂无数据</div>
<template v-else>
<div class="row" v-for="s of students" :key="s.id">
<div class="col">{{ s.id }}</div>
<div class="col">{{ s.name }}</div>
<div class="col">{{ s.sex }}</div>
<div class="col">{{ s.age }}</div>
</div>
</template>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
.outer {
font-family: 华文行楷;
font-size: 20px;
width: 500px;
}
.title {
margin-bottom: 10px;
font-size: 30px;
color: #333;
text-align: center;
}
.row {
background-color: #fff;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.col {
border: 1px solid #f0f0f0;
width: 15%;
height: 35px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 35px;
}
.bold .col {
background-color: #f1f1f1;
}
</style>-
加入泛型是为了更好的提示
-
v-if 与 v-else 不能和 v-for 处于同一标签
-
template 标签还有一个用途,就是用它少生成一层真正 html 代码
-
可以看到将结果封装为响应式数据还是比较繁琐的,后面会使用 useRequest 改进
监听器
利用监听器,可以在【响应式】的基础上添加一些副作用,把更多的东西变成【响应式的】
-
原本只是数据变化 => 页面更新
-
watch 可以在数据变化时 => 其它更新
下述代码就可以通过watch监听事件和sessionStorage 来实现响应式数据。
watch监听当数据发生变化是,存入sessionStorage,然后在通过sessionStorage获取新值
<template>
<input type="text" v-model="name" />
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, watch } from "vue";
function useStorage(name: string) {
const data = ref(sessionStorage.getItem(name) ?? "");
watch(data, (newValue) => {
sessionStorage.setItem(name, newValue);
});
return data;
}
const name = useStorage("name");
</script>-
名称为 useXXXX 的函数,作用是返回带扩展功能的【响应式】数据
-
localStorage 即使浏览器关闭,数据还在
-
sessionStorage 数据工作在浏览器活动期间
vueuse
安装
npm install @vueuse/core一些函数的用法
useMouse:鼠标移动、useCount:数字运算、useStorage: 存取数据
<template>
<h3>X: {{x}}</h3>
<h3>Y: {{y}}</h3>
<h3>{{count}}</h3>
<input type="button" @click="inc()" value="+">
<input type="button" @click="dec()" value="-">
<input type="text" v-model="name">
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { useMouse, useCounter, useStorage } from '@vueuse/core'
const {x, y} = useMouse()
const {count, inc, dec} = useCounter()
const name = useStorage("name", "")
</script>useRequest
响应式的 axios 封装,官网地址 一个 Vue 请求库 | VueRequest (attojs.org)
首先安装 vue-request
npm install vue-request@next组件
<template>
<h3 v-if="students.length === 0">暂无数据</h3>
<ul v-else>
<li v-for="s of students" :key="s.id">
<span>{{s.name}}</span>
<span>{{s.sex}}</span>
<span>{{s.age}}</span>
</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import axios from "../api/request"
import { useRequest } from 'vue-request'
import { computed } from 'vue'
import { AxiosRespList, Student } from '../model/Model8080'
// data 代表就是 axios 的响应对象
const { data } = useRequest<AxiosRespList<Student>>(() => axios.get('/api/students'))
const students = computed(()=>{
return data?.value?.data.data || []
})
</script>
<style scoped>
ul li {
list-style: none;
font-family: "华文行楷";
}
li span:nth-child(1) {
font-size: 24px;
}
li span:nth-child(2) {
font-size: 12px;
color: crimson;
vertical-align: bottom;
}
li span:nth-child(3) {
font-size: 12px;
color: darkblue;
vertical-align: top;
}
</style>-
data.value 的取值一开始是 undefined,随着响应返回变成 axios 的响应对象
-
用 computed 进行适配
usePagination(分页)
在 src/model/Model8080.ts 中补充类型说明
export interface StudentQueryDto {
name?: string,
sex?: string,
age?: string, // 18,20
page: number,
size: number
}-
js 中类似于 18,20 这样以逗号分隔字符串,会在 get 传参时转换为 java 中的整数数组
编写组件
<template>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入姓名" v-model="dto.name">
<select v-model="dto.sex">
<option value="" selected>请选择性别</option>
<option value="男">男</option>
<option value="女">女</option>
</select>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入年龄范围" v-model="dto.age">
<br>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入页码" v-model="dto.page">
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入页大小" v-model="dto.size">
<input type="button" value="搜索" @click="search">
<hr>
<h3 v-if="students.length === 0">暂无数据</h3>
<ul v-else>
<li v-for="s of students" :key="s.id">
<span>{{s.name}}</span>
<span>{{s.sex}}</span>
<span>{{s.age}}</span>
</li>
</ul>
<hr>
总记录数{{total}} 总页数{{totalPage}}
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import axios from "../api/request"
import { usePagination } from 'vue-request'
import { computed, ref } from 'vue'
import { AxiosRespPage, Student, StudentQueryDto } from '../model/Model8080'
const dto = ref<StudentQueryDto>({name:'', sex:'', age:'', page:1, size:5})
// data 代表就是 axios 的响应对象
// 泛型参数1: 响应类型
// 泛型参数2: 请求类型
const { data, total, totalPage, run } = usePagination<AxiosRespPage<Student>, StudentQueryDto[]>(
(d) => axios.get('/api/students/q', {params: d}), // 箭头函数
{
defaultParams: [ dto.value ], // 默认参数, 会作为参数传递给上面的箭头函数
pagination: {
currentKey: 'page', // 指明当前页属性
pageSizeKey: 'size', // 指明页大小属性
totalKey: 'data.data.total' // 指明总记录数属性
}
} // 选项
)
const students = computed(()=>{
return data?.value?.data.data.list || []
})
function search() {
run(dto.value) // 会作为参数传递给usePagination的箭头函数
}
</script>
<style scoped>
ul li {
list-style: none;
font-family: "华文行楷";
}
li span:nth-child(1) {
font-size: 24px;
}
li span:nth-child(2) {
font-size: 12px;
color: crimson;
vertical-align: bottom;
}
li span:nth-child(3) {
font-size: 12px;
color: darkblue;
vertical-align: top;
}
input,select {
width: 100px;
}
</style>usePagination 只需要定义一次,后续还想用它内部的 axios 发请求,只需调用 run 函数子组件
例1
定义子组件 Child1
<template>
<div class="container">
<div class="card">
<div>
<p class="name">{{name}}</p>
<p class="location">{{country}}</p>
</div>
<img :src="avatar || '/src/assets/vue.svg'"/>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
// 定义属性, 编译宏
defineProps<{name:string,country:string,avatar?:string}>()
</script>
<style scoped>
.container {
width: 100%;
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
justify-content: space-evenly;
flex-direction: row-reverse;
}
.name {
font-weight: bold;
}
.location {
font-size: 0.8em;
color: #6d597a;
}
.card {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-evenly;
padding: 1em;
margin: 1rem;
border-radius: 5px;
background: #fff;
width: 200px;
box-shadow: 0 14px 28px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.25), 0 10px 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.22);
}
.card:hover {
transform: rotate(-5deg);
}
.card img {
margin-left: 1em;
border-radius: 50%;
max-width: 55px;
max-height: 55px;
}
</style>父组件引用
<template>
<Child1 name="张三" country="中国" avatar="/src/assets/vue.svg"></Child1>
<Child1 name="李四" country="印度" avatar="/vite.svg"></Child1>
<Child1 name="王五" country="韩国" ></Child1>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import Child1 from '../components/Child1.vue';
</script>例2
首先添加类型说明 model/ModelRandomUser.ts
import { AxiosResponse } from "axios";
export interface AxiosRespResults extends AxiosResponse<Results>{}
export interface Results {
info: {
page: number,
results: number
},
results: Result[]
}
export interface Result {
gender: 'male' | 'female',
name: {
first: string,
last: string
},
location: {
country: string
},
picture: {
medium: string
},
login: {
username: string
}
}子组件不变,父组件使用子组件
<!-- 父组件 -->
<template>
<Child1 v-for="u of users"
:name="u.name.first"
:country="u.location.country"
:avatar="u.picture.medium"
:key="u.login.username"></Child1>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import axios from "axios";
import { useRequest } from "vue-request";
import { computed } from "vue";
import { AxiosRespResults } from '../model/ModelRandomUser'
import Child1 from "../components/Child1.vue";
const { data } = useRequest<AxiosRespResults>(
()=>axios.get('https://randomuser.me/api/?results=3')
)
const users = computed(()=>{
return data.value?.data.results || []
})
</script>如果觉得 Result 数据结构嵌套太复杂,还可以做一个类型映射
<!-- 父组件 -->
<template>
<Child1 v-for="u of users"
:name="u.name"
:country="u.country"
:avatar="u.avatar"
:key="u.username"></Child1>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import axios from "axios";
import { useRequest } from "vue-request";
import { computed } from "vue";
import { AxiosRespResults, Result } from '../model/ModelRandomUser'
import Child1 from "../components/Child1.vue";
const { data } = useRequest<AxiosRespResults>(
()=>axios.get('https://randomuser.me/api/?results=3')
)
const users = computed(()=>{
return data.value?.data.results.map(resultToUser) || []
})
interface User {
name: string,
country: string,
avatar: string,
username: string
}
function resultToUser(r:Result):User {
return {
name: r.name.first,
country: r.location.country,
avatar: r.picture.medium,
username: r.login.username
}
}
</script>-
resultToUser 将 Result 类型映射为 User 类型






![[黑马程序员SSM框架教程]03 spring核心概念](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ff8ffdba0f884faeb97345ab61069741.png)