vector
- vector 容器
- vector 基本使用
- vector 定义
- 库中各类接口的使用
- 迭代器
- 容量相关接口
- 元素访问相关接口
- 元素修改相关接口
- 模拟实现 vector
- 前期准备
- 构造与析构
- 赋值运算符重载
- 迭代器相关
- 容量相关
- 元素访问相关
- 元素的修改相关
- 二维数组的创建
- 对于自定义类型数据的测试
vector 容器
C++ STL 中的 vector 就类似于 C 语言当中的数组,但是 vector 又拥有很多数组没有的接口,使用起来会更加的方便。
相比于 STL 中的 string ,vector 可以定义不同的数据类型
vector 基本使用
vector 定义
template < class T, class Alloc = allocator > class vector;
方式一:创建 vector 对象,不进行初始化
vector (const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
方式二:创建 vector 对象,容量为 n,并赋值为 val
vector (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type(),
const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
方式三:创建 vector 对象,并采用区间赋值
vector (InputIterator first, InputIterator last,
const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
方式四:拷贝构造
vector (const vector& x);
代码演示:
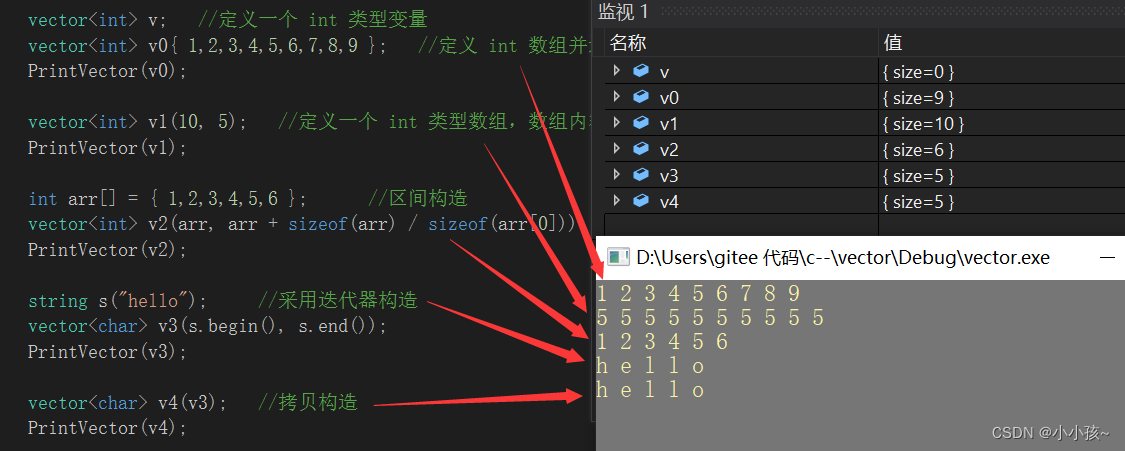
vector<int> v; //定义一个 int 类型变量
vector<int> v0{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 }; //定义 int 数组并进行列表赋值
PrintVector(v0);
vector<int> v1(10, 5); //定义一个 int 类型数组,数组内容为 10 个 5
PrintVector(v1);
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 }; //区间构造
vector<int> v2(arr, arr + sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));
PrintVector(v2);
string s("hello"); //采用迭代器构造
vector<char> v3(s.begin(), s.end());
PrintVector(v3);
vector<char> v4(v3); //拷贝构造
PrintVector(v4);
定义一个打印函数可以很明显的观察到定义结果:
template<class T>
void PrintVector(const vector<T>& v)
{
for (auto e : v)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
}
库中各类接口的使用
迭代器
迭代器的本质是指针,其指针指向如下图:
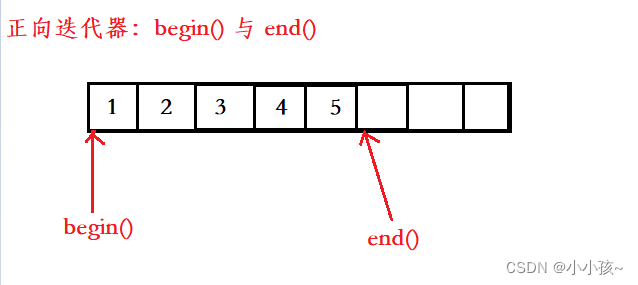
begin() 指向空间起始位置,end() 指向最后一个有效元素的下一个位置
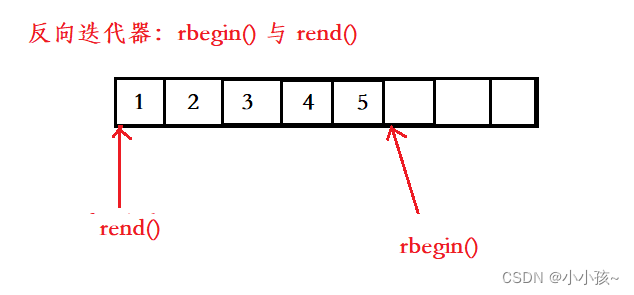
rbegin() 指向最后一个有效元素的下一个位置,rend() 指向空间的起始位置。
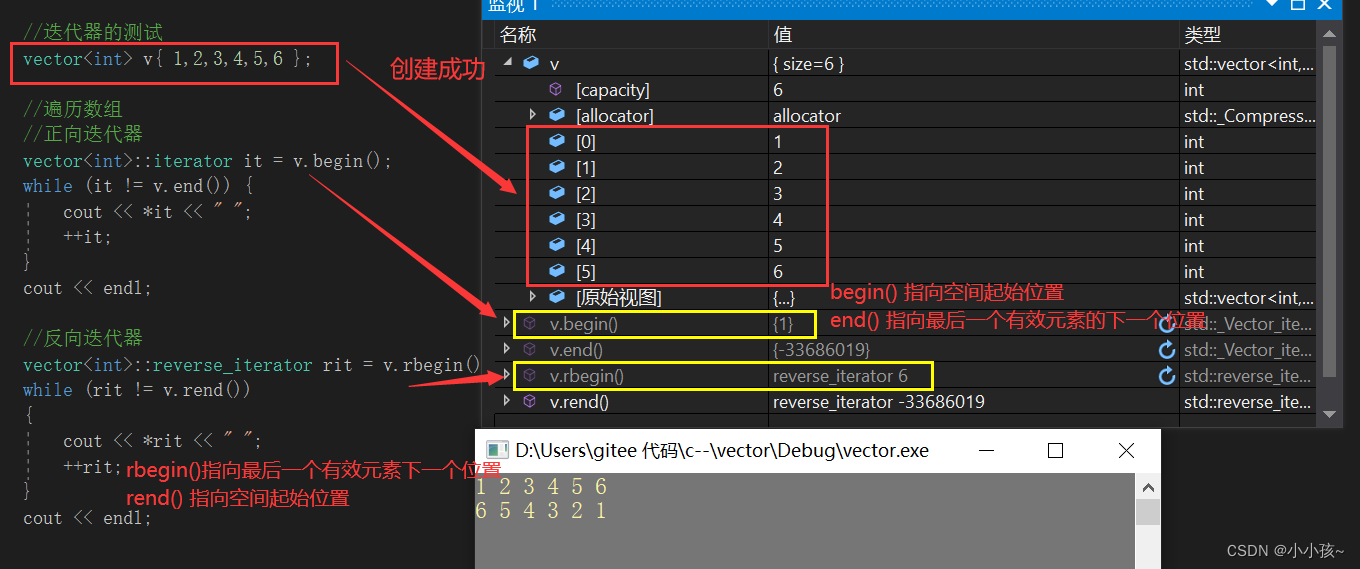
代码演示:
容量相关接口

代码演示:
(1)测试 size() 、capacity()、以及 resize()
vector<int> v{ 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
PrintVector(v);
cout << "v.size() = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "v.capacity() = " << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "----------------------------------------------------" << endl;
//resize 修改有效元素个数
v.resize(10, 0); //将有效元素个数修改为 10,多余空间用 0 来进行填充
PrintVector(v);
cout << "v.size() = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "v.capacity() = " << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "----------------------------------------------------" << endl;
v.resize(20);
cout << "v.size() = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "v.capacity() = " << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "----------------------------------------------------" << endl;
v.resize(4); //有效元素个数缩小为 4
PrintVector(v);
cout << "v.size() = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "v.capacity() = " << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "----------------------------------------------------" << endl;
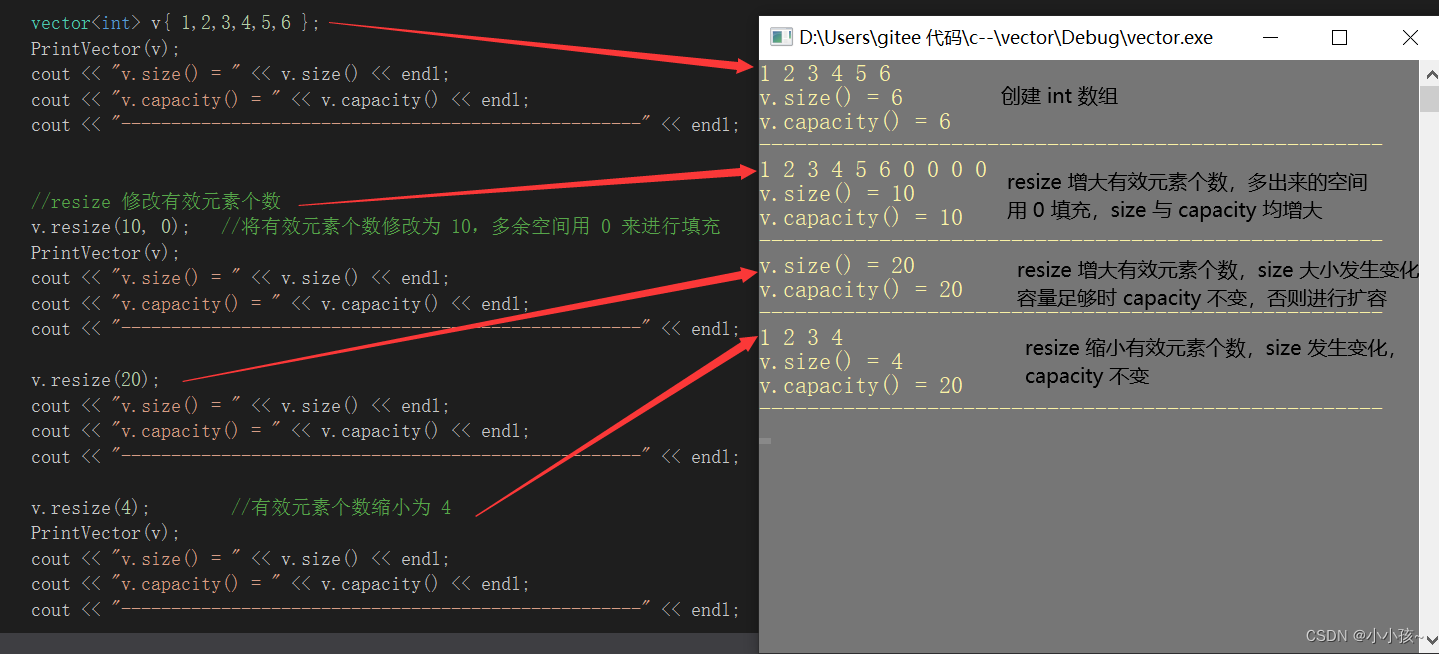
可以发现:
resize 修改有效元素个数时,size 会进行相应的扩大或缩小变化,capacity 不一定会变化(有效元素增多时,若容量足够则capacity不变,否则会扩容;有效元素减少时,capacity 不变)
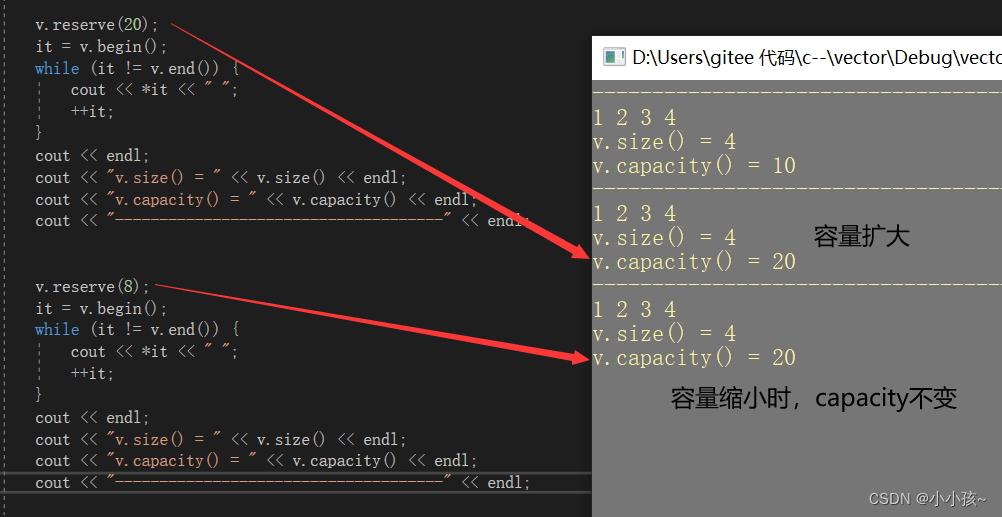
(2)测试 reserve
vector<int> v{ 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
PrintVector(v);
cout << "v.size() = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "v.capacity() = " << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "----------------------------------------------------" << endl;
//reserve 修改容量
v.reserve(10);
PrintVector(v);
cout << "v.size() = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "v.capacity() = " << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "----------------------------------------------------" << endl;
v.reserve(30);
PrintVector(v);
cout << "v.size() = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "v.capacity() = " << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "----------------------------------------------------" << endl;
v.reserve(10);
PrintVector(v);
cout << "v.size() = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "v.capacity() = " << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "----------------------------------------------------" << endl;
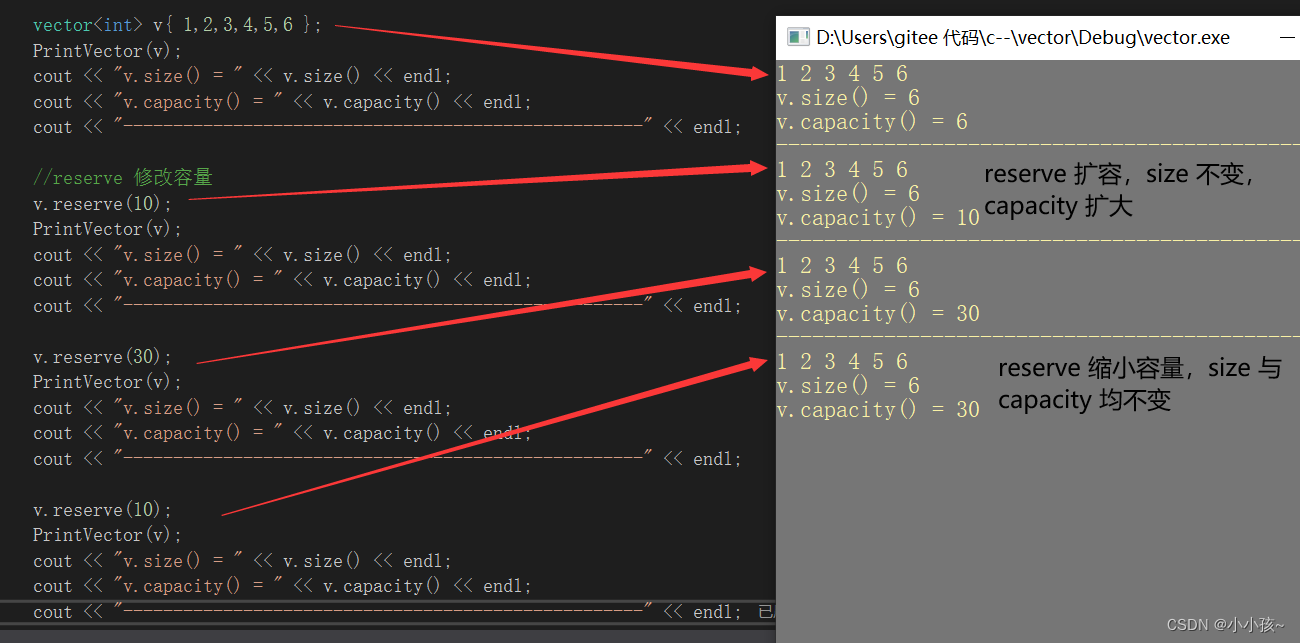
可以发现:
reserve 修改容量时,size 是不会发生变化的(因为有效元素个数不变),若空间容量扩大则 capacity 会相应的进行扩大,若空间容量缩小时 capacity 是不会发生变化的
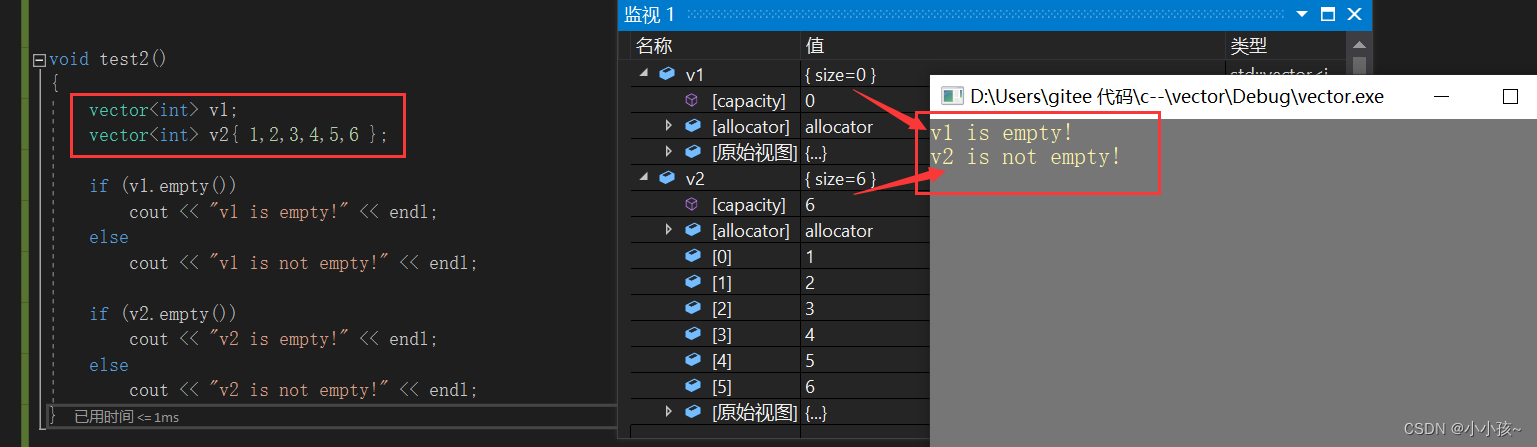
(3)测试 empty
empty 是进行判空的接口
元素访问相关接口
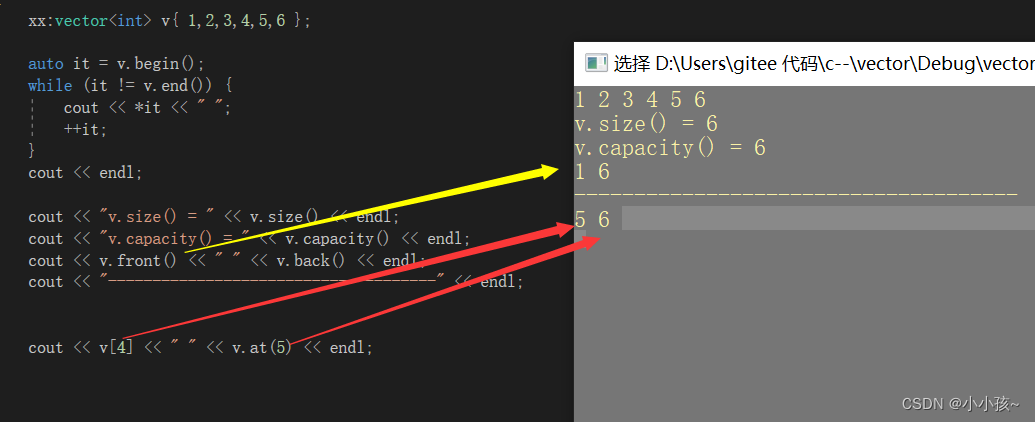
(1)下标运算符访问 operator[]
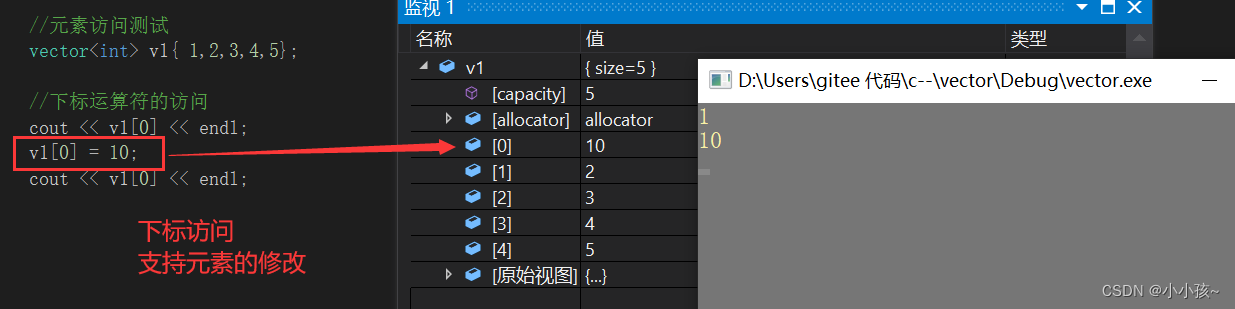
越界测试:越界触发 assert 异常

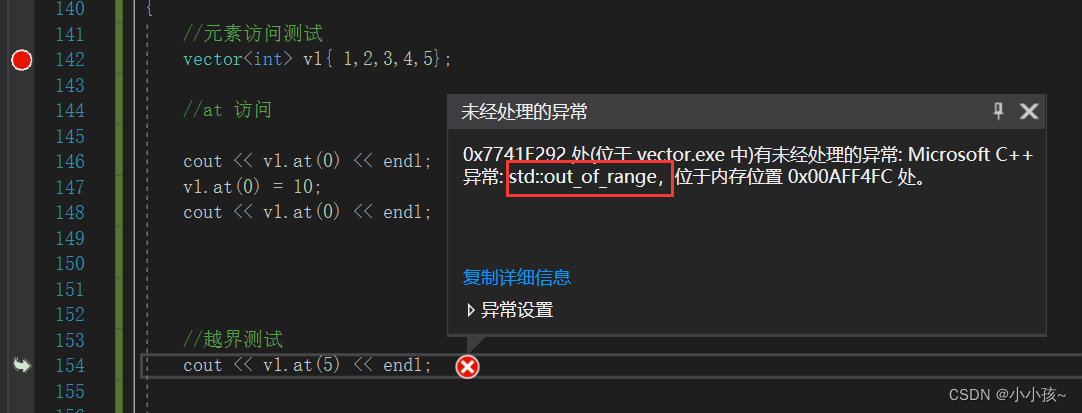
(2)at 访问
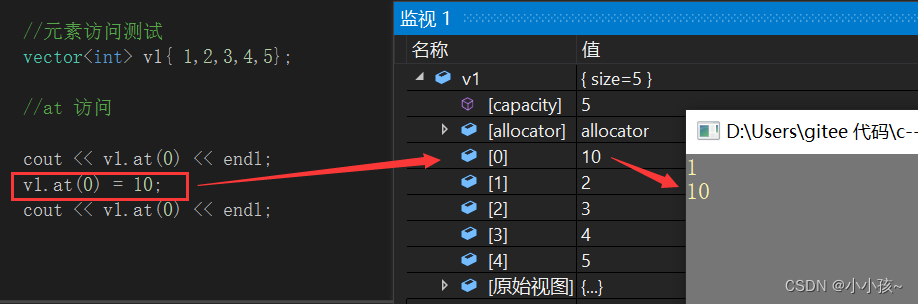
越界测试:越界抛出 out_of_range 异常
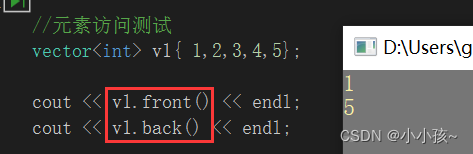
(3)获取首尾元素 front back
元素修改相关接口
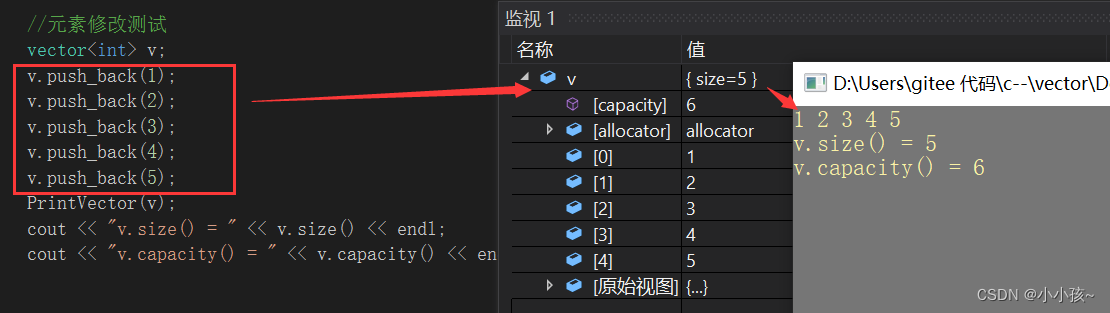
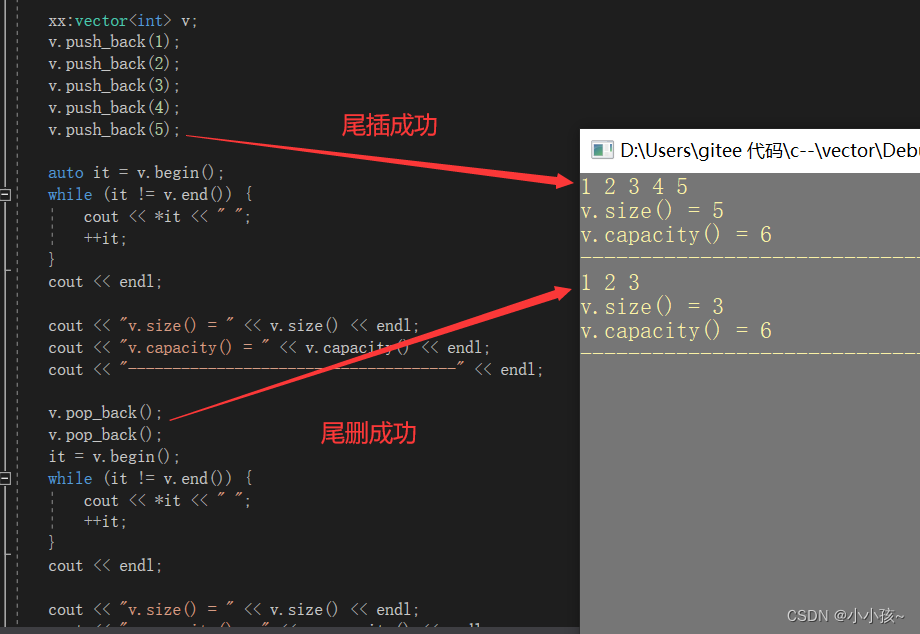
(1)尾插 push_back
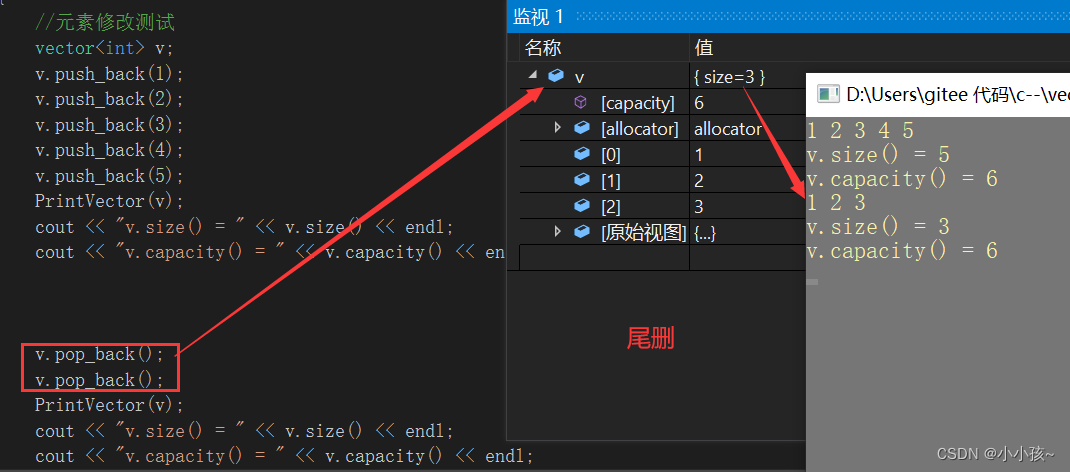
(2)尾删 pop_back
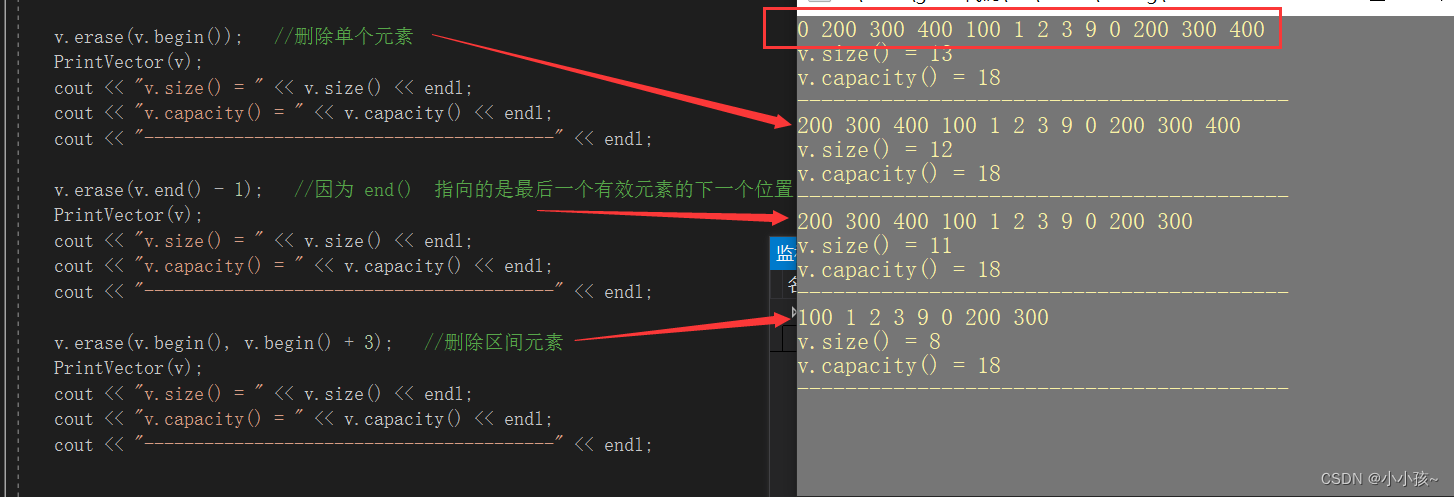
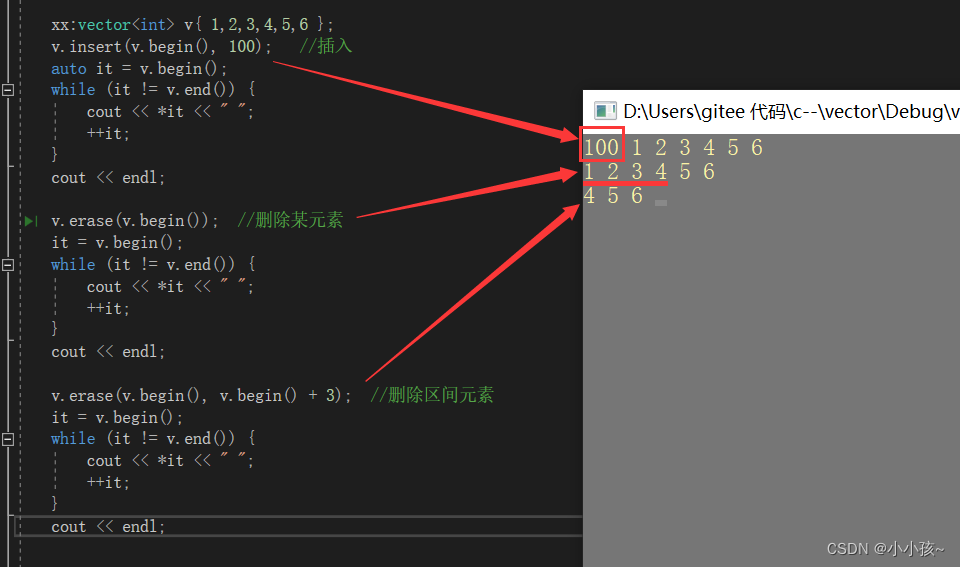
(3)任意位置插入 insert
vector<int> v{ 1,2,3 };
cout << "v.size() = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "v.capacity() = " << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "-----------------------------------------" << endl;
v.insert(v.begin(), 100); //在起始位置插入 100
PrintVector(v);
cout << "v.size() = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "v.capacity() = " << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "-----------------------------------------" << endl;
int arr[] = { 0,200,300,400 };
v.insert(v.begin(), arr, arr + sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0])); //起始位置插入arr数组中元素
PrintVector(v);
cout << "v.size() = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "v.capacity() = " << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "-----------------------------------------" << endl;
v.insert(v.end(), 9); //尾部插入元素 9----------------同理也可以插入数组 arr
PrintVector(v);
cout << "v.size() = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "v.capacity() = " << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "-----------------------------------------" << endl;
v.insert(v.end(), arr, arr + sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0])); //尾部插入arr数组中元素
PrintVector(v);
cout << "v.size() = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "v.capacity() = " << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "-----------------------------------------" << endl;

(4)任意位置删除 erase
(5)清空 clear
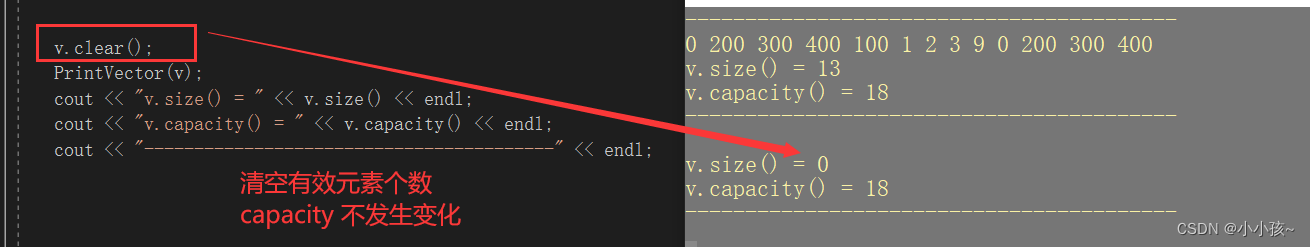
模拟实现 vector
前期准备
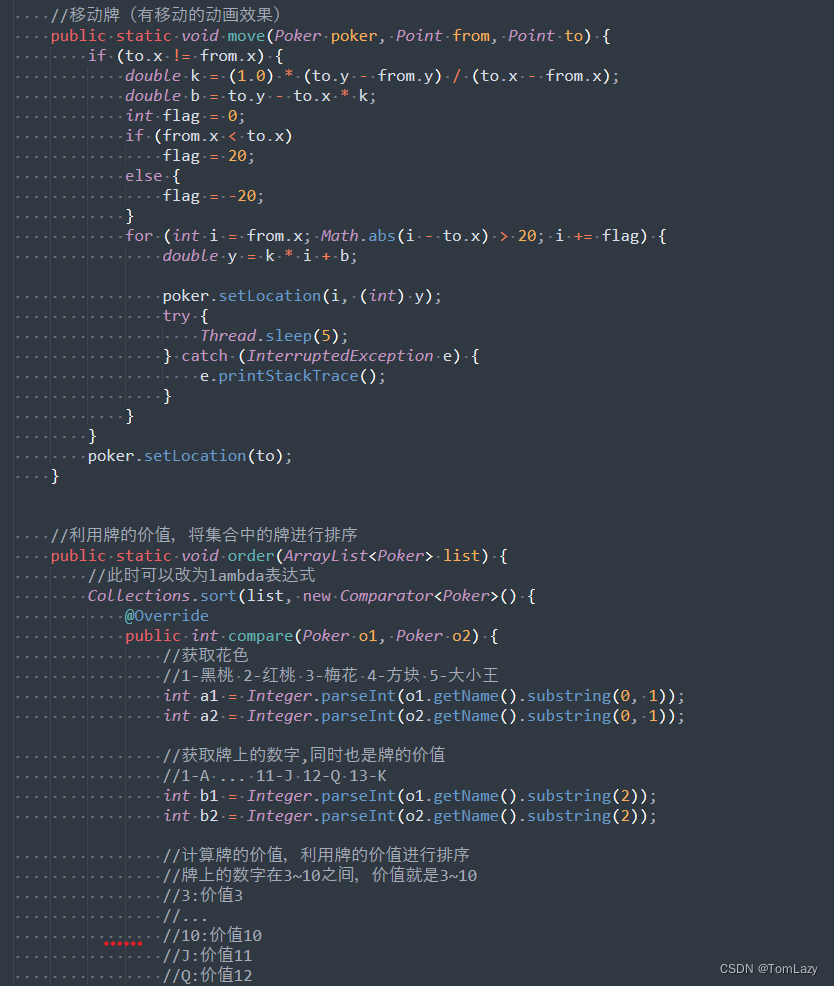
迭代器的本质就是指针,模拟实现 vector 容器,我们需要定义三个指针 :指向起始位置 start,指向最后一个有效元素的下一个位置 finish ,指向容器最后一个位置 endofstorage:
namespace xx { //自定义命名空间
template<class T> //定义模板类型
class vector{
public:
typedef T* iterator; //迭代器 等价于 T 类型指针
private:
iterator start; //空间起始位置
iterator finish; //最后一个有效元素的下一个位置
iterator endofstorage; //最后一个容量空间位置
};
}
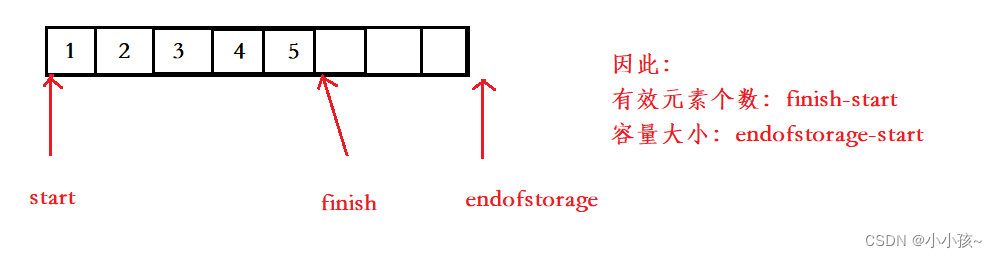
构造与析构
构造函数
(1)默认无参构造
vector() :start(nullptr), finish(nullptr), endofstorage(nullptr)
{}
(2)构造具有 n 个对象值为 val 的容器 (数据类型为模板类型 T)
vector(int n, const T& val = T())
{
start = new T[n]; //创建新空间
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
start[i] = val; //对空间进行赋值操作
}
finish = start + n; //修改 finish 指向---最后一个有效元素的下一个位置
endofstorage = finish; //修改容量指针
}
注意:
第二个参数 val 是一个缺省参数,对于内置类型,T() 的值为 0;对于自定义类型, T() 调用的是该自定义类型的默认构造函数
因此,对于自定义类型一定要有默认的构造函数,否则会报错
(3)使用迭代器进行构造
template<class Iterator>
vector(Iterator first, Iterator last) //区间构造
{
auto it = first;
size_t n = 0;
while (it != last) {
++it;
n++; //统计区间中元素个数
}
start = new T[n]; //开辟空间
finish = start;
while (first != last) { //进行赋值
*finish = *first;
++first; ++finish;
}
endofstorage = finish; //修改容量指针
}
(4)拷贝构造
vector(const vector<T>& v)
{
size_t n = v.size(); //记录 v 中元素个数
start = new T[n]; //创建新空间
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
start[i] = v[i]; //进行赋值操作
}
finish = start + n; //修改指向
endofstorage = finish;
}
新写法(参考上一篇博客深浅拷贝问题)
vector(const vector<T>& v)
{
vector<T> tmp(v.begin(),v.end()); //定义临时对象--调用迭代器构造方法
this->swap(tmp); //进行资源交换
}
析构函数
~vector()
{
if (start) {
delete[] start;
start = finish = endofstorage = nullptr;
}
}
测试代码
void MyvectorTest0()
{
xx::vector<int> v1;
xx::vector<int> v2(10, 5);
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 }; //区间构造
xx::vector<int> v3(arr, arr + sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));
xx::vector<int> v4(v2); //拷贝构造
//遍历一:
for (int i = 0; i < v2.size(); ++i) {
cout << v2[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//遍历二:
for (auto e : v3)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
//遍历三:
auto it = v4.begin();
while (it != v4.end()) {
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
会发现在运行代码时候出现的问题:
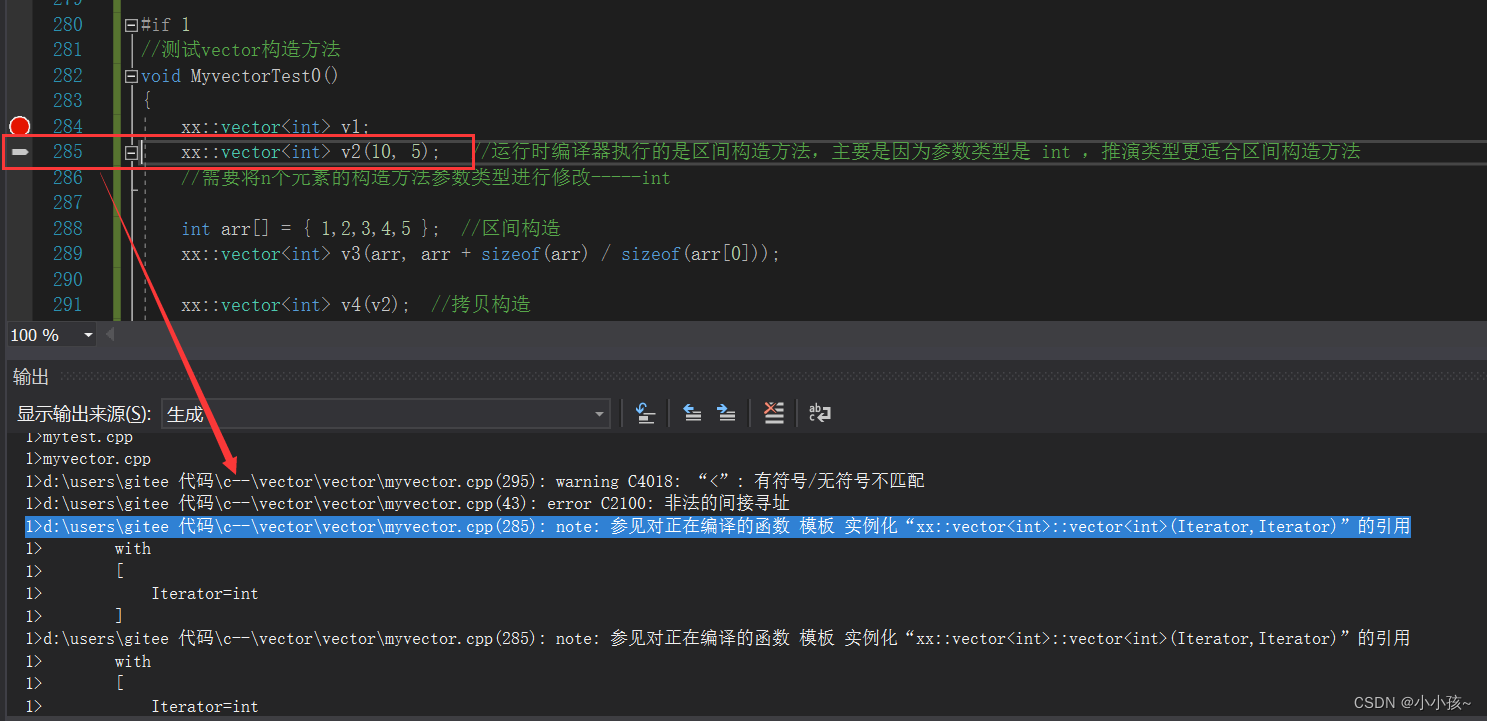
分析:
在构造 v2 时候,会调用区间构造方法,进行参数类型的推演,由于构造 v2 的两个参数都是 int 类型,故编译器会根据类型推演的结果来选择合适的构造方法,又因为构造 n 个值为 val 的构造方法中参数类型为 size_t , int,所以编译器认为类型不匹配,排除该构造方法,选用了迭代器区间的构造方法(参数类型实例化之后都为 int 类型),因此,为了实现构造 n 个值为 val 的空间构造,我们需要对构造函数进行一定的修改,使得其调用更准确:

赋值运算符重载
vector<T>& operator=(vector<T> v) {
//因为参数是传值类型,故在传参过程中会进行一次拷贝构造的调用
//赋值运算符重载
this->swap(v); //直接进行交换(可以参考上一篇博客中深浅拷贝内容)
return *this;
}
迭代器相关
//迭代器
iterator begin()
{
return start;
}
iterator end()
{
return finish;
}
容量相关
(1)size、capacity、empty 的实现
size_t size()const {
return finish - start;
}
size_t capacity()const {
return endofstorage - start;
}
bool empty()const {
return finish == start;
}
(2)resize :修改有效元素个数
void resize(size_t newsize, const T&val = T())
{
size_t oldsize = size();
if (newsize <= oldsize) { //缩小有效元素
finish = start + newsize; //容量不变
}
else {//有效元素增大
//需要扩容
size_t cap = capacity();
if(newsize > cap)
reserve(newsize);
for (size_t i = oldsize; i < newsize; ++i) {
//多出来的空间填充
start[i] = val;
}
finish = start + newsize;
//endofstorage = finish;
}
}
(3)reserve:修改容量
void reserve(size_t newcapacity)
{
size_t oldcapacity = capacity();
if (newcapacity > oldcapacity) {
//开辟新空间
T* tmp = new T[newcapacity];
if (start) {
拷贝元素:memcpy(内存拷贝--------将一段空间中的内容原封不动的拷贝到新空间----浅拷贝) 按字节拷贝
涉及到资源管理时,memcpy 属于浅拷贝
//memcpy(tmp, start, sizeof(T)*size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < size(); ++i) {
tmp[i] = start[i];
}
//释放旧空间
delete[] start;
}
size_t sz = size();
start = tmp;
finish = start + sz; //**********
endofstorage = start + newcapacity;
}
}
代码测试:
(1)测试 resize (含 size, capacity 的测试)
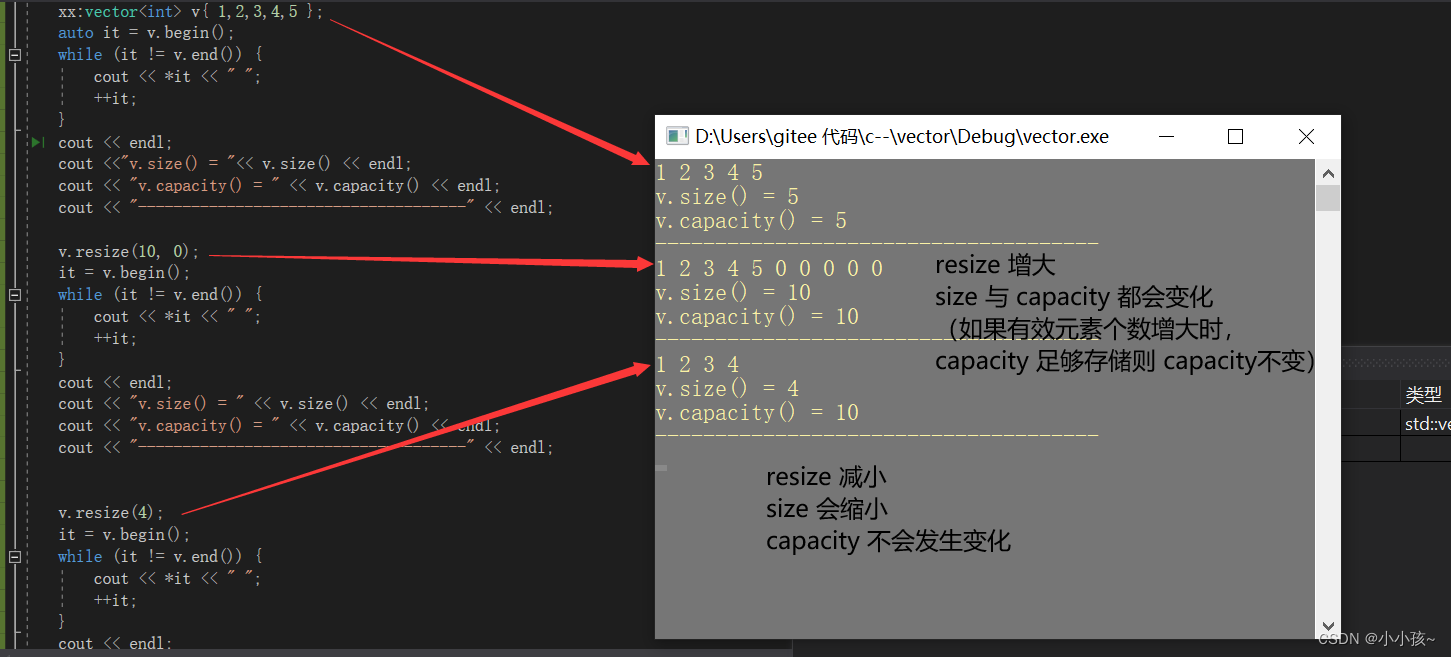
(2)测试 reserve
元素访问相关
(1)获取首尾元素 front back
T& front()
{
return *start;
}
const T& front()const
{
return *start;
}
T& back()
{
return *(finish - 1);
}
const T& back()const
{
return *(finish - 1);
}
(2)下标访问
T& operator[](size_t index)
{
assert(index < size()); //注意区分异常处理方式
return start[index];
}
const T& operator[](size_t index)const
{
assert(index < size());
return start[index];
}
(3)at 访问
T& at(size_t index)
{
if (index >= size())
throw out_of_range("vector at method: index out_of_range"); //抛出异常
return start[index];
}
const T& at(size_t index)const
{
if (index >= size())
throw out_of_range("vector at method: index out_of_range");
return start[index];
}
代码测试:
元素的修改相关
(1)尾插
void push_back(const T& val)
{
//进行尾插,判断容量是否足够
if (finish == endofstorage) {
reserve(capacity() * 2 + 3); //按照2倍进行扩容
}
*finish = val;
++finish;
}
(2)尾删
void pop_back()
{
//进行尾删
if (empty())
return;
--finish; //直接修改尾指针
}
(3)任意位置插入
//insert 插入元素的时间复杂度 O(n)
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T&val)
{
//判断插入位置的合法性
if (pos < begin() || pos > end())
return end();
//任意位置进行插入
if (finish == endofstorage)
reserve(capacity() * 2); //扩容
auto it = finish - 1;
while (it >= pos) { //元素后移
*(it + 1) = *it;
--it;
}
*it = val; //当前 it 指向的就是 pos 的位置
++finish;
return it; //返回新插入的元素的位置
}
(4)任意位置删除
删除单个元素:
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
//删除任意位置元素
if (empty())
return end();
if (pos < begin() || pos >= end())
return end();
//位置合理
auto it = pos;
while (it != end() - 1) //end() 表示最后一个有效元素的下一个位置
{
*it = *(it + 1); //元素前移
--it;
}
--finish; //删除元素需要修改尾指针位置
return pos;
}
删除区间元素:
iterator erase(iterator start, iterator last)
{
if (empty())
return end();
if (start < begin() || start >= end())
return end();
//位置合法, 删除区间
auto beg = start;
auto en = last;
int n = last - start; //要删除的元素个数
while (en != end()){
*beg = *en;
++beg; ++en;
//--finish;
}
finish -= n;
return start; //返回删除的区间首元素位置
}
(5)清空
void clear()
{
erase(begin(), end());
}
(6)交换函数
void swap(vector<T>& v)
{
std::swap(start, v.start);
std::swap(finish, v.finish);
std::swap(endofstorage, v.endofstorage);
}
测试代码:
(1)测试尾插尾删:
(2)测试任意位置的插入删除:
(3)清空:
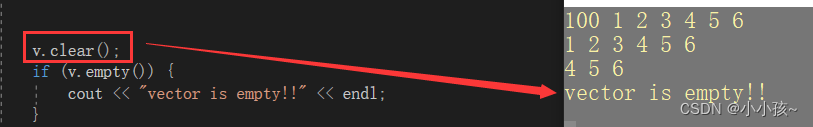
二维数组的创建
创建一个五行六列数组,数组中元素值都为 8:
void MyvectorTest3()
{
xx::vector<xx::vector<int>> vv(5, xx::vector<int>(6, 8));
//创建有 5 个元素的数组,数组中元素用 vector<int>(6,8) 来进行填充
for (size_t i = 0; i < vv.size(); ++i)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < vv[i].size(); ++j)
cout << vv[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}

对于自定义类型数据的测试
上述的测试我们都是基于内置类型int数据的测试,发现代码可以正确运行没有报错,那针对于自定义类型数据是否正确呢?
(1)定义一个日期类:
class Date {
public:
Date(int year = 1990, int month = 1, int day = 20)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
Date(const Date& d)
{//拷贝构造
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
~Date() {}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
void MyvectorTest4()
{
xx::vector<Date> d; //定义 Date 类型数组
d.push_back(Date(2023, 1, 1)); //插入元素--------Date 构造函数必须为带缺省值的构造方法
d.push_back(Date(2023, 1, 2));
d.push_back(Date(2023, 1, 3));
d.push_back(Date(2023, 1, 4));
d.push_back(Date(2023, 1, 5));
cout << d.size() << endl;
}
运行改代码显式可以正确运行,因为 Date 类不存在资源的处理,那针对于 string 类是否正常?
我们来试试:
(2)定义 string 类:
class String {
public:
String(const char* str=""):_str(nullptr)
{
//构造
if (nullptr == str)
str = "";
_str = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
String(const String& s):_str(new char[strlen(s._str)+1])
{
//拷贝构造
strcpy(_str, s._str);
}
String& operator=(const String& s)
{
if (this != &s) {
//不是给自己的赋值
char* tmp = new char[strlen(s._str) + 1];
strcpy(tmp, s._str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
}
return *this;
}
//String& operator=(const String s)
//{
// if (this != &s) {
// //新写法
// this->swap(s._str);
// }
// return *this;
//}
~String()
{
if (_str) {
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
}
private:
char* _str;
};
void MyvectorTest5()
{
xx::vector<String> s;
s.push_back("hello");
s.push_back("welcom");
s.push_back("come on");
cout << s.size() << endl;
s.push_back("hahahha"); //此时需要进行扩容发生报错----------memcpy是属于浅拷贝
}
运行发现,在最后一次尾插时发生了错误,我们来看看是什么原因导致的:
因为在第四次尾插时候需要进行扩容,因此产生了错误
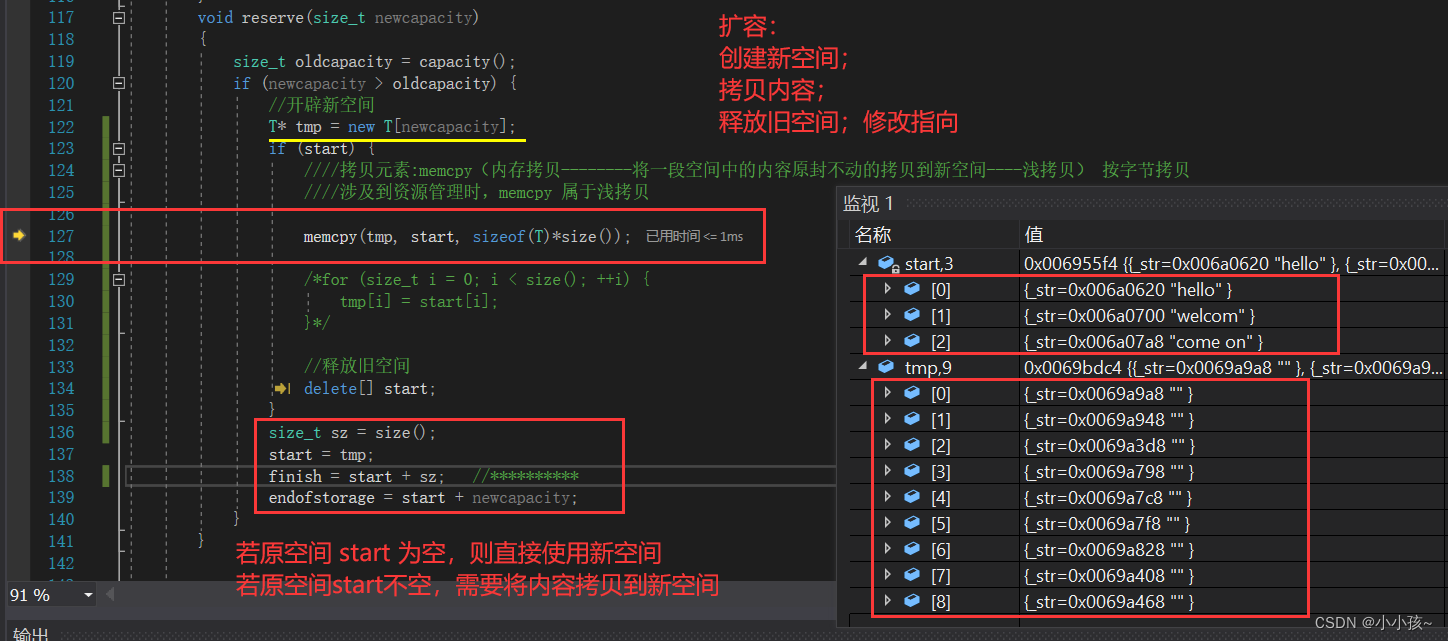
往下运行一步就会发现问题所在了:
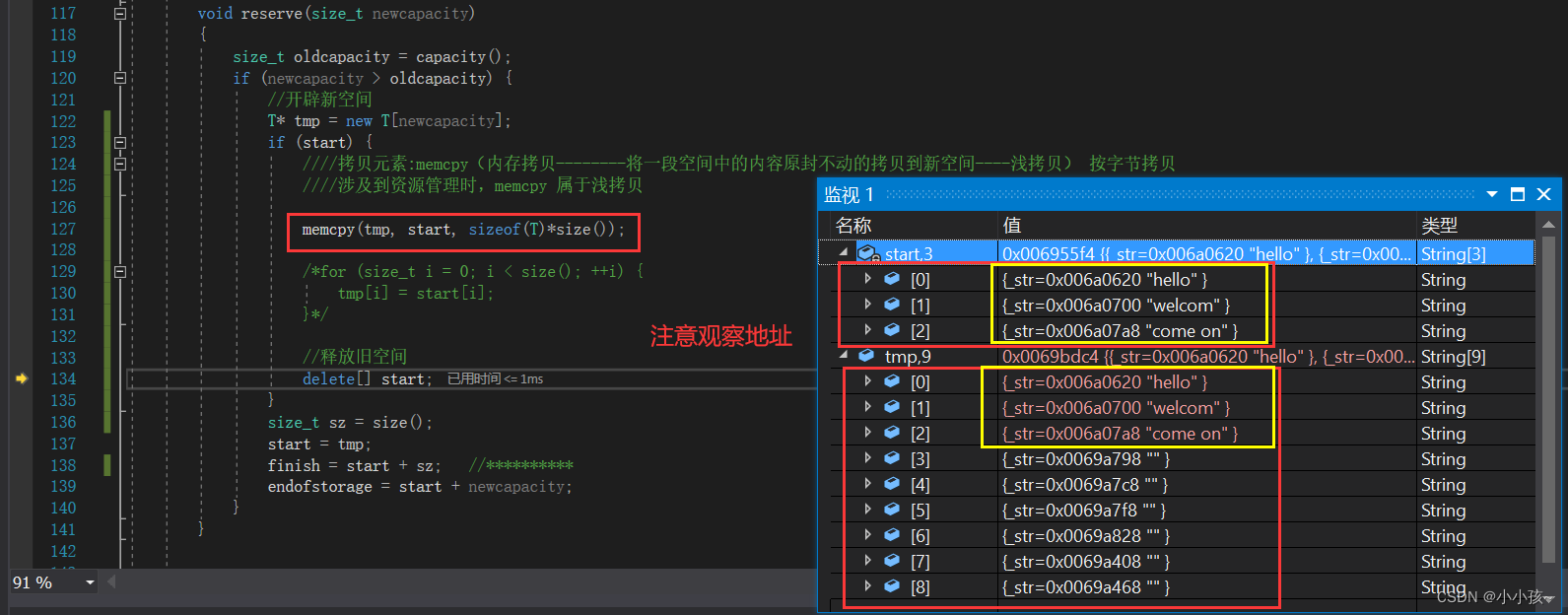
发现,在进行 memcpy 拷贝时候发生了浅拷贝,即将原空间内容原封不动的拷贝到新空间,这就导致了新空间共享旧空间的地址,会造成内存泄漏
因此,在扩容时候我们需要按元素将旧空间中元素交给新空间,而不是将地址空间也赋给新空间
进行修改:
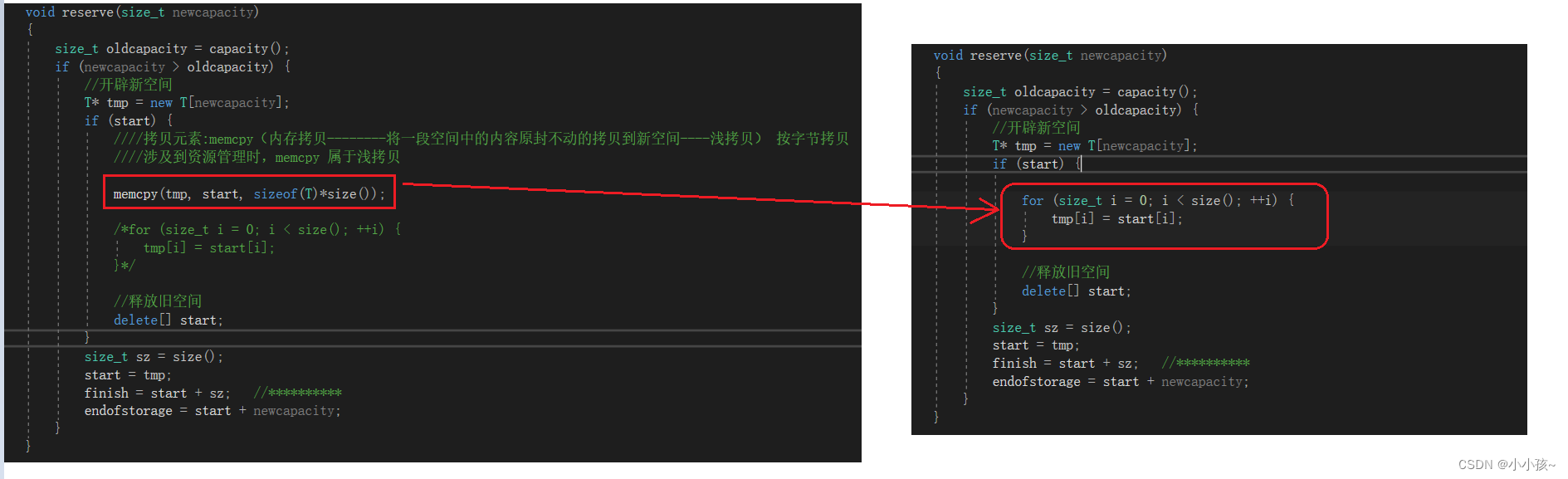
修改之后程序可以正常运行。
_CrtDumpMemoryLeaks(); //检测内存泄漏
该章节完整代码:
添加链接描述
本篇内容就分享到这里啦!!!
学习编程的道路很长,要注重自我实践与验证,欢迎读者评论探讨~

![[qiankun]实战问题汇总](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/290e7d4aa9354eb88bff7a32e1327ac7.png)