前言:大家好,我是前端獭子。高效优雅是我的创作方式。学习是一个渐进的过程,要把知识串联起来才能解决某一方面的问题。
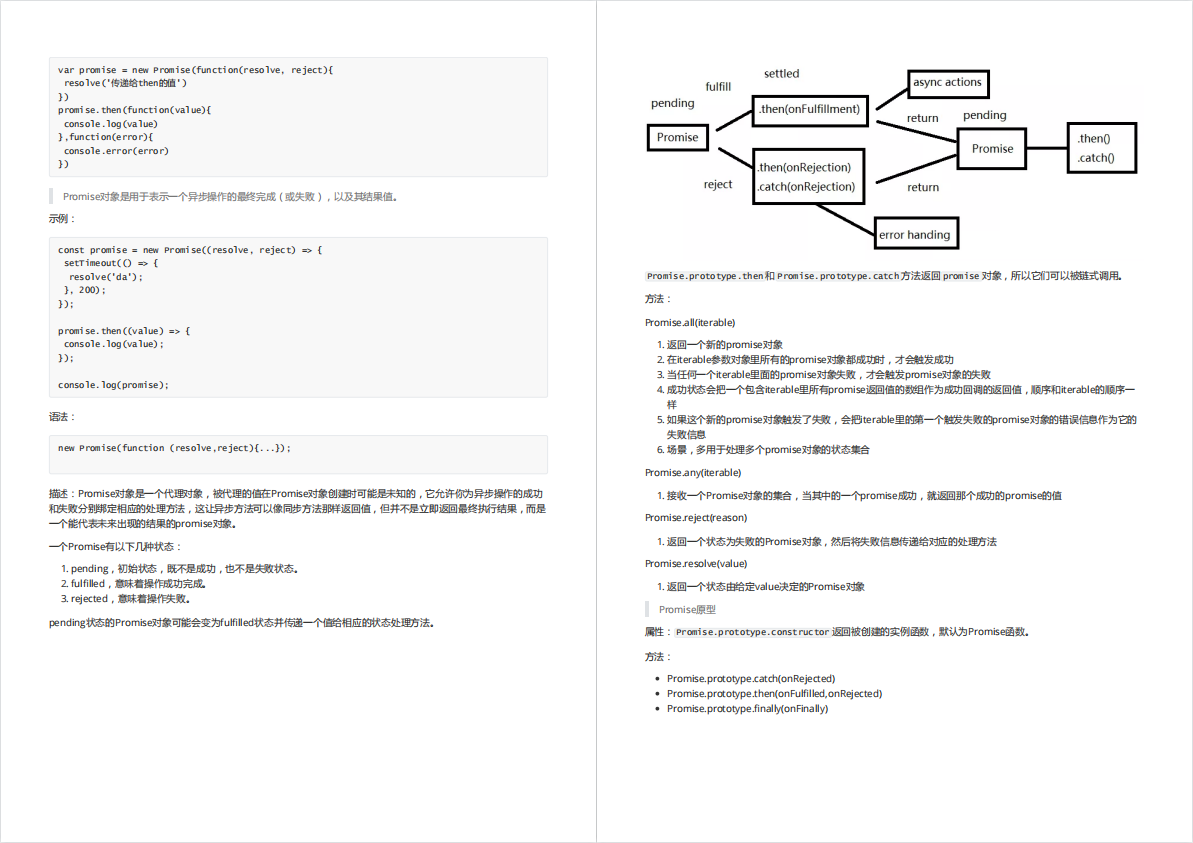
Promise 构造函数
我们先来写 Promise 构造函数的属性和值,以及处理new Promise()时会传入的两个回调函数。如下:
class myPromise {constructor(func) {this.state = 'pending' // Promise状态this.value = undefined // 成功的值this.reason = undefined // 错误的值this.resolveCallbacks = [] // 收集解决回调函数this.rejectCallbacks = [] // 收集错误回调函数try { // 对传入的函数进行try...catch...做容错处理func(this.resolve, this.reject) // 执行传入的两个回调函数} catch (e) {this.reject(e)}}
}
三个状态(pending、rejected和fulfilled)
pending:待定状态。待定 Promise 。只有在then方法执行后才会保持此状态。
rejected:拒绝状态。终止 Promise 。只有在reject方法执行后才会由 pending 更改为此状态。
fulfilled:解决状态。终止 Promise 。只有在resolve方法执行后才会由 pending 更改为此状态。
注意:其中只有 pedding 状态可以变更为 rejected 或 fulfilled 。rejected 或 fulfilled 不能更改其他任何状态。
三个方法(resolve、reject和then)
resolve方法实现要点
1.状态由pending为fulfilled。
2.resolve方法传入的value参数赋值给this.value
3.按顺序执行resolveCallbacks里面所有解决回调函数
4.利用call方法将解决回调函数内部的 this 绑定为undefined
坑点 1:resolve方法内部 this 指向会丢失,进而造成this.value丢失。
解决办法:我们将resolve方法定义为箭头函数。在构造函数执行后,箭头函数可以绑定实例对象的 this 指向。
// 2.1. Promise 状态
resolve = (value) => { // 在执行构造函数时内部的this通过箭头函数绑定实例对象if (this.state === 'pending') {this.state = 'fulfilled' // 第一点this.value = value // 第二点while (this.resolveCallbacks.length > 0) { // 第三点this.resolveCallbacks.shift().call(undefined) // 第四点}}
}
reject方法实现要点
1.状态由pending为rejected
2.reject方法传入的reason参数赋值给this.reason
3.按顺序执行rejectCallbacks里面所有拒绝回调函数
4.利用call方法将拒绝回调函数内部的 this 绑定为undefined
坑点 1: reject 方法内部 this 指向会丢失,进而造成this.reason丢失。
解决办法:我们将reject方法定义为箭头函数。在构造函数执行后,箭头函数可以绑定实例对象的 this 指向。
// 2.1. Promise 状态
reject = (reason) => { // 在执行构造函数时内部的this通过箭头函数绑定实例对象if (this.state === 'pending') {this.state = 'rejected' // 第一点this.reason = reason // 第二点while (this.rejectCallbacks.length > 0) {// 第三点this.rejectCallbacks.shift().call(undefined) // 第四点}}
}
then方法实现要点
1.判断then方法的两个参数onRejected和onFulfilled是否为function。1.1 onRejected和onFulfilled都是function,继续执行下一步。1.2 onRejected不是function,将onRejected赋值为箭头函数,参数为reason执行throw reason1.3 onFulfilled不是function,将onFulfilled赋值为箭头函数,参数为value执行return value2.当前Promise状态为rejected:2.1 onRejected方法传入this.reason参数,异步执行。2.2 对执行的onRejected方法做容错处理,catch错误作为reject方法参数执行。3.当前Promise状态为fulfilled:3.1 onFulfilled方法传入this.value参数,异步执行。3.2 对执行的onFulfilled方法做容错处理,catch错误作为reject方法参数执行。4.当前Promise状态为pending:4.1 收集onFulfilled和onRejected两个回调函数分别push给resolveCallbacks和rejectCallbacks。4.2 收集的回调函数同样如上所述,先做异步执行再做容错处理。5.返回一个 Promise 实例对象。```
// 2.2. then 方法
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === ‘function’ ? onFulfilled : value => value // 第一点 onRejected = typeof onRejected === ‘function’ ? onRejected : reason => { throw reason } // 第一点 const p2 = new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {if (this.state === ‘rejected’) { // 第二点queueMicrotask(() => {try {onRejected(this.reason)} catch (e) {reject(e)}})} else if (this.state === ‘fulfilled’) { // 第三点queueMicrotask(() => {try {onFulfilled(this.value)} catch (e) {reject(e)}})} else if (this.state === ‘pending’) { // 第四点this.resolveCallbacks.push(() => {queueMicrotask(() => {try {onFulfilled(this.value)} catch (e) {reject(e)}})})this.rejectCallbacks.push(() => {queueMicrotask(() => {try {onRejected(this.reason)} catch (e) {reject(e)}})})}})return p2 // 第五点
}
* * *
Promise 解决程序(resolvePromise方法)
------------------------------
旁白:其实这个解决程序才是实现核心Promise最难的一部分。因为Promise A+规范对于这部分说的比较绕。
我们直击其实现要点,能跑通所有官方用例就行。如下:
1.如果x和promise引用同一个对象:1.1 调用`reject`方法,其参数为`new TypeError()`2.如果x是一个promise或x是一个对象或函数:2.1 定义一个`called`变量用于记录`then.call`参数中两个回调函数的调用情况。2.2 定义一个`then`变量等于`x.then`2.3 `then`是一个函数。使用`call`方法绑定`x`对象,传入**解决回调函数**和**拒绝回调函数**作为参数。同时利用`called`变量记录`then.call`参数中两个回调函数的调用情况。2.4 `then`不是函数。调用`resolve`方法解决Promise,其参数为`x`2.5 对以上 **2.2** 检索属性和 **2.3** 调用方法的操作放在一起做容错处理。`catch`错误作为`reject`方法参数执行。同样利用`called`变量记录`then.call`参数中两个回调函数的调用情况。3.如果x都没有出现以上两种状况:调用`resolve`方法解决Promise,其参数为`x````
// 2.3 Promise解决程序
function resolvePromise(p2, x, resolve, reject) {if (x === p2) {// 2.3.1 如果promise和x引用同一个对象reject(new TypeError())} else if ((x !== null && typeof x === 'object') || typeof x === 'function') {// 2.3.2 如果x是一个promise// 2.3.3 如果x是一个对象或函数let calledtry {let then = x.then // 检索x.then属性,做容错处理if (typeof then === 'function') {then.call(x, // 使用call绑定会立即执行then方法,做容错处理(y) => { // y也可能是一个Promise,递归调用直到y被resolve或rejectif (called) { return }called = trueresolvePromise(p2, y, resolve, reject)},(r) => {if (called) { return }called = truereject(r)})} else {resolve(x)}} catch (e) {if (called) { return }called = truereject(e)}} else {resolve(x)}
}
called变量的作用:记录then.call传入参数(两个回调函数)的调用情况。
根据Promise A+ 2.3.3.3.3规范:两个参数作为函数第一次调用优先,以后的调用都会被忽略。
因此我们在以上两个回调函数中这样处理:
1.已经调用过一次:此时called已经为true,直接return忽略
2.首次调用:此时called为undefined,调用后called设为true
注意:2.3 中的catch可能会发生(两个回调函数)已经调用但出现错误的情况,因此同样按上述说明处理。
运行官方测试用例
在完成上面的代码后,我们最终整合如下:
class myPromise {constructor(func) {this.state = 'pending'this.value = undefinedthis.reason = undefinedthis.resolveCallbacks = []this.rejectCallbacks = []try {func(this.resolve, this.reject)} catch (e) {this.reject(e)}}resolve = (value) => {if (this.state === 'pending') {this.state = 'fulfilled'this.value = valuewhile (this.resolveCallbacks.length > 0) {this.resolveCallbacks.shift().call(undefined)}}}reject = (reason) => {if (this.state === 'pending') {this.state = 'rejected'this.reason = reasonwhile (this.rejectCallbacks.length > 0) {this.rejectCallbacks.shift().call(undefined)}}}then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : value => valueonRejected = typeof onRejected === 'function' ? onRejected : reason => { throw reason }const p2 = new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {if (this.state === 'rejected') {queueMicrotask(() => {try {const x = onRejected(this.reason)resolvePromise(p2, x, resolve, reject)} catch (e) {reject(e)}})} else if (this.state === 'fulfilled') {queueMicrotask(() => {try {const x = onFulfilled(this.value)resolvePromise(p2, x, resolve, reject)} catch (e) {reject(e)}})} else if (this.state === 'pending') {this.resolveCallbacks.push(() => {queueMicrotask(() => {try {const x = onFulfilled(this.value)resolvePromise(p2, x, resolve, reject)} catch (e) {reject(e)}})})this.rejectCallbacks.push(() => {queueMicrotask(() => {try {const x = onRejected(this.reason)resolvePromise(p2, x, resolve, reject)} catch (e) {reject(e)}})})}})return p2}
}
function resolvePromise(p2, x, resolve, reject) {if (x === p2) {reject(new TypeError())} else if ((x !== null && typeof x === 'object') || typeof x === 'function') {let calledtry {let then = x.thenif (typeof then === 'function') {then.call(x,(y) => {if (called) { return }called = trueresolvePromise(p2, y, resolve, reject)},(r) => {if (called) { return }called = truereject(r)})} else {resolve(x)}} catch (e) {if (called) { return }called = truereject(e)}} else {resolve(x)}
}
// 新加入部分
myPromise.deferred = function () {let result = {};result.promise = new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {result.resolve = resolve;result.reject = reject;});return result;
}
module.exports = myPromise;
新建一个文件夹,放入我们的 myPromise.js 并在终端执行以下命令:
npm init -y
npm install promises-aplus-tests
package.json 文件修改如下:
{"name": "promise","version": "1.0.0","description": "","main": "myPromise.js","scripts": {"test": "promises-aplus-tests myPromise"},"keywords": [],"author": "","license": "ISC","devDependencies": {"promises-aplus-tests": "^2.1.2"}
}
开始测试我们的手写 Promise,在终端执行以下命令即可:
npm test
Promise 其他方法补充
容错处理方法
Promise.prototype.catch()
catch(onRejected) {return this.then(undefined, onRejected)
}
Promise.prototype.finally()
finally(callback) {return this.then(value => {return myPromise.resolve(callback()).then(() => value)},reason => {return myPromise.resolve(callback()).then(() => { throw reason })})
}
静态方法
Promise.resolve()
static resolve(value) {if (value instanceof myPromise) {return value// 传入的参数为Promise实例对象,直接返回} else {return new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {resolve(value)})}
}
Promise.reject()
static reject(reason) {return new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {reject(reason)})
}
Promise.all()
static all(promises) {return new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {let countPromise = 0 // 记录传入参数是否为Promise的次数let countResolve = 0 // 记录数组中每个Promise被解决次数let result = [] // 存储每个Promise的解决或拒绝的值if (promises.length === 0) { // 传入的参数是一个空的可迭代对象resolve(promises)}promises.forEach((element, index) => {if (element instanceof myPromise === false) { // 传入的参数不包含任何 promise++countPromiseif (countPromise === promises.length) {queueMicrotask(() => {resolve(promises)})}} else {element.then(value => {++countResolveresult[index] = valueif (countResolve === promises.length) {resolve(result)}},reason => {reject(reason)})}})})
}
Promise.race()
static race(promises) {return new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {if (promises.length !== 0) {promises.forEach(element => {if (element instanceof myPromise === true)element.then(value => {resolve(value)},reason => {reject(reason)})})}})
}
上述所有实现代码已放置我的Github仓库。可自行下载测试,做更多优化。
最后
最近还整理一份JavaScript与ES的笔记,一共25个重要的知识点,对每个知识点都进行了讲解和分析。能帮你快速掌握JavaScript与ES的相关知识,提升工作效率。


有需要的小伙伴,可以点击下方卡片领取,无偿分享

![[论文阅读笔记19]SiamMOT: Siamese Multi-Object Tracking](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/58e4f8b9aae048a78dfc74a80500a785.png)