文章目录
- 一、栈的概念及使用
- 1.1 概念
- 1.2 栈的使用
- 1.3 栈的模拟实现
- 二、队列的概念及使用
- 2.1 概念
- 2.2 队列的使用
- 2.3 双端队列(Deque)
- 三、相关OJ题
- 3.1 用队列实现栈。
- 3.2 用栈实现队列。
- 总结
一、栈的概念及使用
1.1 概念
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵循后进先出的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈,出数据在栈顶。
1.2 栈的使用
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| Stack() | 构造一个空的栈 |
| E push(E e) | 将e入栈,并返回e |
| E pop() | 将栈顶元素出栈并返回 |
| E peek() | 获取栈顶元素 |
| int size() | 获取栈中有效元素个数 |
| boolean empty() | 检测栈是否为空 |
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack();
s.push(1);
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
s.push(4);
System.out.println(s.size()); // 获取栈中有效元素个数---> 4
System.out.println(s.peek()); // 获取栈顶元素---> 4
s.pop(); // 4出栈,栈中剩余1 2 3,栈顶元素为3
System.out.println(s.pop()); // 3出栈,栈中剩余1 2 栈顶元素为3
if(s.empty()){
System.out.println("栈空");
}else{
System.out.println(s.size());
}
}
1.3 栈的模拟实现
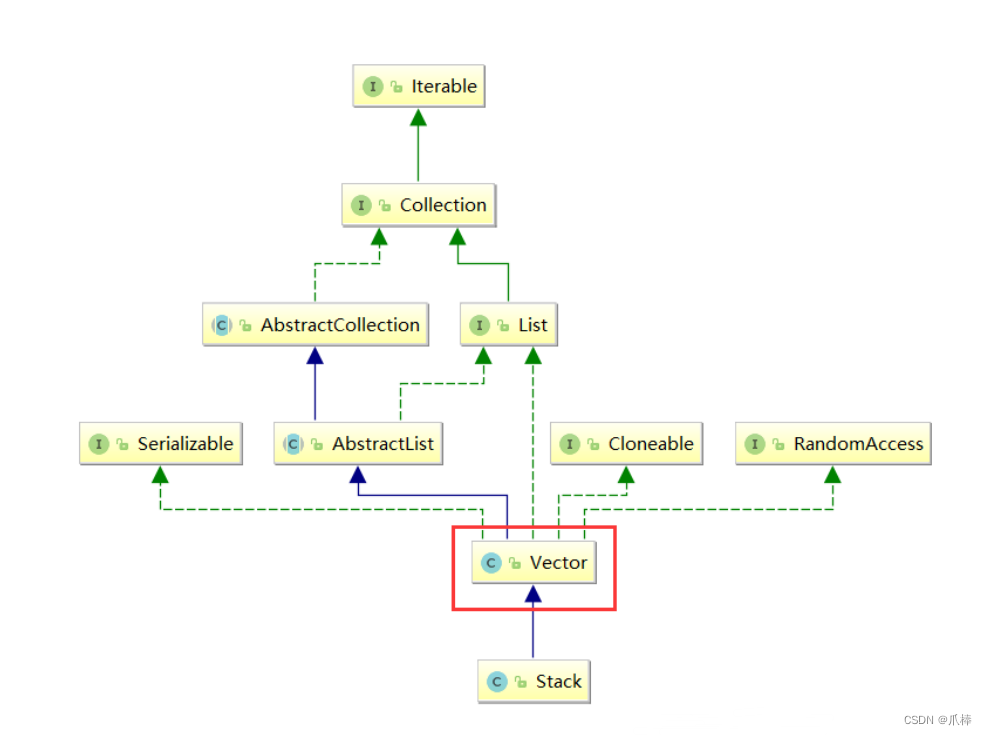
从上图中可以看到,Stack继承了Vector,Vector和ArrayList类似,都是动态的顺序表,不同的是Vector是线程安全的。
public class MyStack {
int[] array;
int size;
public MyStack(){
array = new int[3];
}
public int push(int e){
ensureCapacity();
array[size++] = e;
return e;
}
public int pop(){
int e = peek();
size--;
return e;
}
public int peek(){
if(empty()){
throw new RuntimeException("栈为空,无法获取栈顶元素");
}
return array[size-1];
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
public boolean empty(){
return 0 == size;
}
private void ensureCapacity(){
if(size == array.length){
array = Arrays.copyOf(array, size*2);
}
}
}
二、队列的概念及使用
2.1 概念
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出的特点。
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾。
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头。
2.2 队列的使用
在java中,Queue是个接口,底层是通过链表实现的。
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| boolean offer(E e) | 入队列 |
| E pool() | 出队列 |
| peek() | 获取队头元素 |
| int size() | 获取队列中有效元素个数 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 检测元素是否为空 |
注意:Queue是个接口,在实例化时必须实例化LinkedList的对象,因为LinkedList实现了Queue接口。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(1);
q.offer(2);
q.offer(3);
q.offer(4);
q.offer(5); // 从队尾入队列
System.out.println(q.size());
System.out.println(q.peek()); // 获取队头元素
q.poll();
System.out.println(q.poll()); // 从队头出队列,并将删除的元素返回
if(q.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("队列空");
}else{
System.out.println(q.size());
}
}
2.3 双端队列(Deque)
双端队列(deque)是指允许两端都可以进行入队和出队操作的队列,deque是"double ended queue"的简称。那就说明元素可以从队头出队和入队,也可以从队尾出队和入队。
Deque是一个接口,使用时必须创建LinkedList的对象。
在实际工程中,使用Deque接口是比较多的,栈和队列均可以使用该接口。
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>(); //双端队列的线性实现
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); //双端队列的链式实现
三、相关OJ题
3.1 用队列实现栈。
OJ链接
代码如下:
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> qu1;
private Queue<Integer> qu2;
public MyStack() {
qu1 = new LinkedList<>();
qu2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {
qu1.offer(x);
}else if (!qu2.isEmpty()) {
qu2.offer(x);
}else {
qu1.offer(x);
}
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {
int size = qu1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size-1; i++) {
int val = qu1.poll();
qu2.offer(val);
}
return qu1.poll();
}else {
int size = qu2.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size-1; i++) {
int val = qu2.poll();
qu1.offer(val);
}
return qu2.poll();
}
}
public int top() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {
int size = qu1.size();
int val = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
val = qu1.poll();
qu2.offer(val);
}
return val;
}else {
int size = qu2.size();
int val = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
val = qu2.poll();
qu1.offer(val);
}
return val;
}
}
public boolean empty() {
return qu1.isEmpty() && qu2.isEmpty();
}
}
3.2 用栈实现队列。
OJ链接
代码如下:
class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> stack1;
private Stack<Integer> stack2;
public MyQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<>();
stack2 = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(stack2.empty()) {
while (!stack1.empty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(stack2.empty()) {
while (!stack1.empty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty();
}
}
总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文仅仅简单介绍了栈与队列的概念及其使用,栈与队列在解决实际问题中有着很大的作用,我们需要多练习,熟能生巧。