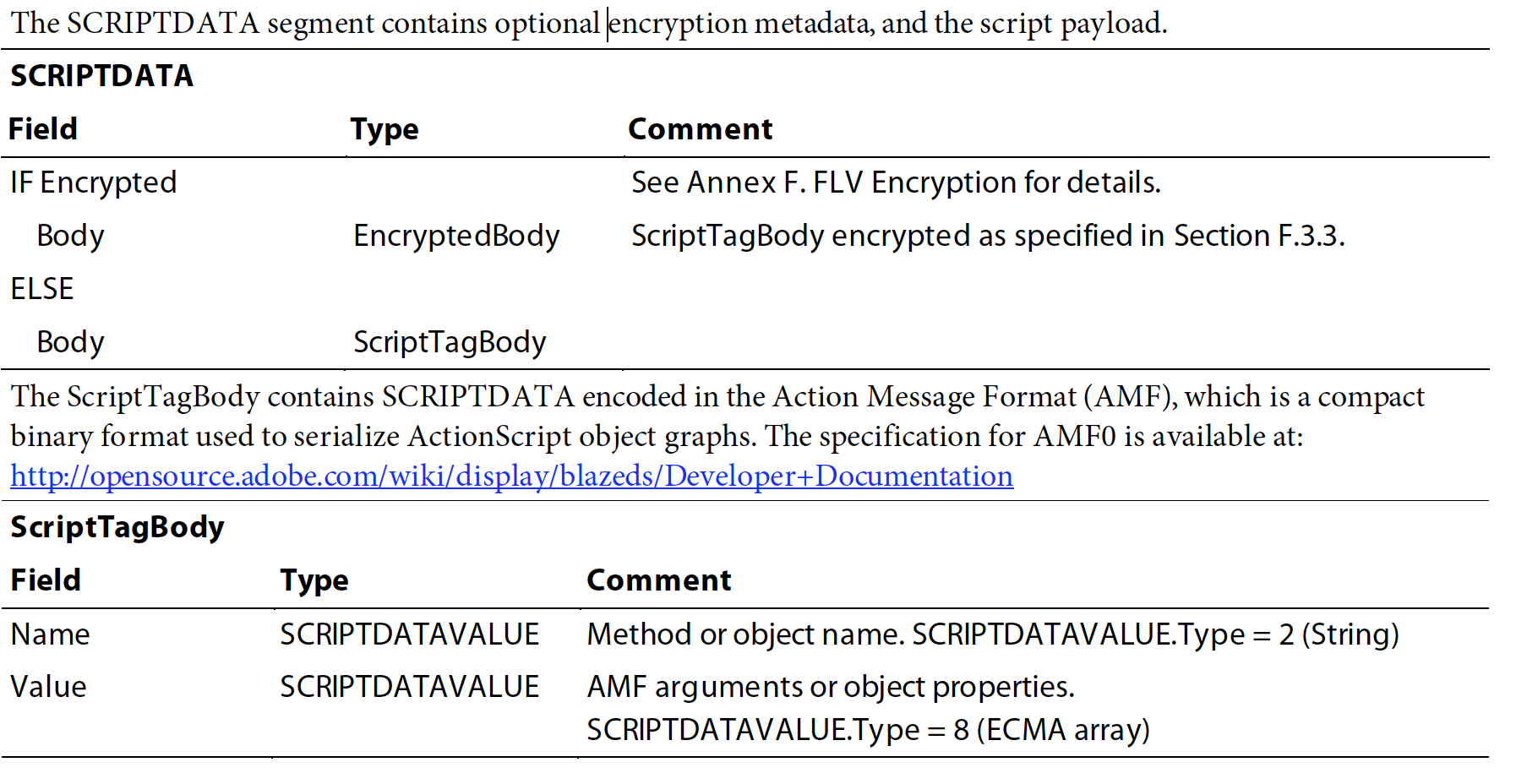
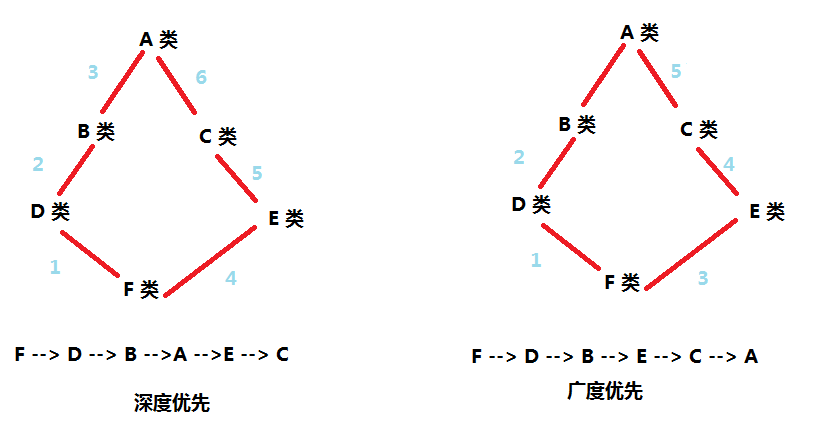
文章目录
- 程序设计要素
- 1.可读性
- 2.健壮性
- 3.优化
- 4.复用性
- 5.可扩展性
- 设计类的关系遵循的原则
- 1、 高内聚低耦合
- 2、面向对象开发中 “针对接口编程优于针对实现编程”,”组合优于继承” 的总体设计
- 类与类之间的关系(即事物关系)
- A is-a B 泛化(继承,实现)
- A has-a B 包含(紧密程度:组合 > 聚合 > 关联)
- A need-a B 依赖(依赖)
- Java程序体现的形式为
程序设计要素
1.可读性
- 名字 缩进 注释
2.健壮性
- 判断严谨
3.优化
- 结构 性能 内存
4.复用性
- 抽取方法 类
5.可扩展性
- 抽象 接口 面向配置文件
设计类的关系遵循的原则
1、 高内聚低耦合
耦合度:紧密程度 从强到弱依次是: 继承>实现>组合>聚合>关联>依赖
2、面向对象开发中 “针对接口编程优于针对实现编程”,”组合优于继承” 的总体设计

类与类之间的关系(即事物关系)
类与类之间关系(即事物关系)有如下6种
继承(Generalization,又叫作泛化)关系、
实现(Realization)关系
组合(Composition )关系
聚合(Aggregate)关系
关联(Association)关系
依赖(Dependency)关系
A is-a B 泛化(继承,实现)
1、在 继承关系 中,子类继承父类的所有功能,父类所具有的属性、方法,子类都应该有。除了与父类一致的信息,子类中还包括额外的信息。例如,公交车、出租车都是车
2、接口(包括抽象类)是方法的集合,在 实现关系 中,类实现了接口,类中的方法实现了接口声明的所有方法。例如,人、动物都吃饭都睡觉
A has-a B 包含(紧密程度:组合 > 聚合 > 关联)
3、 关联关系 是类与类之间最常用的一种关系,表示一类对象与另一类对象之间有联系。组合、聚合也属于关联关系,只是关联关系的类间关系比其他两种关系要弱。比如说,人有汽车,人有电脑;整体和部分的关系,可以分割,后来形成在一起
关联关系有4种:
双向关联、
单向关联、
自关联、
多重性关联
例如汽车和司机,一辆汽车对应特定的司机,一个司机也可以开多辆车
Association is a relation between two separate classes which establishes through their Objects. Association can be
1、one-to-one,
2、one-to-many, i.e. Bank can have many employees
3、many-to-one,
4、many-to-many.
In Object-Oriented programming, an Object communicates to another object to use functionality and services provided by that object.
Composition and Aggregation are the two forms of association.
4、 聚合关系 也表示类之间整体与部分的关系,成员对象是整体对象的一部分,但是成员对象可以脱离整体对象独立存在。例如,工人和工作服是整体与部分的关系,但是可以分开,没有共同的生命周期。工作服可以穿在别的司机身上,工人也可以换别人的工作服。再比如说,汽车和车轮,电脑和主板。
It is a special form of Association where:
1、It represents Has-A’s relationship.
2、It is a unidirectional association i.e. a one-way relationship.
For example, a department can have students but vice versa is not possible and thus unidirectional in nature.
3、In Aggregation, both the entries can survive individually which means ending one entity will not affect the other entity.
When do we use Aggregation ??
Code reuse is best achieved by aggregation.
5、 组合关系 表示类之间整体与部分的关系,整体与部分有一致的生存期。一旦整体对象不存在,部分对象也将不存在,整体和部分是同生共死的关系。 皮之不存,毛将焉附 例如,人和脑袋,人和大脑,人和心脏
Composition is a restricted form of Aggregation in which two entities are highly dependent on each other.
1、It represents part-of relationship.
2、In composition, both entities are dependent on each other.
3、When there is a composition between two entities, the composed object cannot exist without the other entity.
For example, Book is Part-of Library. If Library gets destroyed then All books within that particular library will be destroyed. i.e. books can not exist without libraries. That’s why it is composition.
Aggregation vs Composition
1. Dependency: Aggregation implies a relationship where the child can exist independently of the parent. For example, Bank and Employee, delete the Bank and the Employee still exist. whereas Composition implies a relationship where the child cannot exist independent of the parent. Example: Human and heart, heart don’t exist separate to a Human
2. Type of Relationship: Aggregation relation is “has-a” and composition is “part-of” relation.
3. Type of association: Composition is a strong Association whereas Aggregation is a weak Association.
A need-a B 依赖(依赖)
6、 依赖关系 是一种“使用”关系,特定事物的改变有可能会影响到使用该事物的其他事物,当需要表示一个事物使用另一个事物时,使用依赖关系。
在大多数情况下,依赖关系体现在某个类的方法使用另一个类的对象作为参数。例如,汽车依赖汽油,如果没有汽油,则汽车将无法行驶。
在这6种类关系中,
组合、聚合和关联的代码结构一样,可以从关系的强弱来理解,
各类关系从强到弱依次是: 继承>实现>组合>聚合>关联>依赖
-----------------------------------------------------摘自《设计模式就该这样学:基于经典框架源码和真实业务场景》(谭勇德)
------------------------------------------------------------------------摘自Article–《Association, Composition and Aggregation in Java》
Java程序体现的形式为
has a :一个类的对象当做另一个类的属性来存储
对于赋值 :
- 可以在构造方法里赋值
- 可以通过set方法赋值;
need a:一个类的方法中使用到了另一个类的对象
对于赋值:
- 可以在方法中自己创建
- 可以在方法中传递进来
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------自己总结