一,前言
前两篇,购买了 3 台阿里云服务器并完成了 ci-server 构建服务器的环境安装与配置;
三台服务器规划如下:
| 服务 | 配置 | 内网IP | 外网IP | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ci-server | 2c4g | 172.17.178.104 | 182.92.4.158 | Jenkins + Nexus + Docker |
| k8s-master | 2c4g | 172.17.178.105 | 47.93.9.45 | Kubernetes + Docker |
| k8s-node | 2c1g | 172.17.178.106 | 39.105.58.35 | Kubernetes + Docker |
本篇,配置 k8s-master 和 k8s-node 两台服务器,搭建 k8s 集群;
备注:考虑服务器成本使用 1 主+1 从的集群配置,有条件也可以使用 1 主 + 2 从;
二,Kubernetes 简介
1,k8s 简介
- kubernetes 简称 K8s,其中数字 8 指代中间的 8 个字符
ubernete; - K8s 是一个开源的,用于管理云平台上多个主机上的容器化的应用;
- K8s 的目标是让部署容器化的应用简单并且高效;
- K8s 提供了应用部署,规划,更新,维护的一种机制;
- K8s 是一个部署镜像的平台,可以用来调度多台机器上的的镜像部署操作;
K8s 可以使用集群来组织服务器,集群中存在 1 个 Master 集群控制节点,负责调度集群中其他服务器的资源;除 master 之外的其他节点称为 Node;
2,为什么要使用 k8s
大型互联网公司(如 Google),拥有上亿级别的 docker 容器,
容器维护涉及启动、停止、销毁、负载均衡、灾备、扩容等诸多问题需要解决,
因此传统的手工部署的方式就不切实际了,需要使用容器编排工具,而 k8s 目前是这个领域事实上的标准;
部署一个网站会涉及多个容器,可以通过 k8s 配置容器的部署、启动、关闭以及实现负载均衡;
三,k8s 集群搭建
以下配置,如未做特殊说明,则 k8s-master 和 k8s-node 默认都需要进行配置;
1,关闭 Swap 交换分区
swap 分区:虚拟内存分区;
Swap 分区:是 Linux 的交换分区,当系统资源不足时,Swap 分区将会启用;
比如,1c1g 配置的服务器,当需要 2g 内存时,便会从硬盘借用空间当做内存使用(但速度会比内存慢);
搭建 k8s 集群:1 个 master + n 个 node;
当 master 资源不足时,新任务将自动调度到集群中的其他 node 节点处理,实现负载均衡,所以无需启用虚拟内存分区;
#关闭swap分区
swapoff -a
备注:k8s 虽然是一个集群架构,但单从表现上看和一台服务器是一样的:内存资源可以互相共享;
2,关闭 Selinux
- 关闭 Selinux:达到支持容器访问宿主机的文件系统;
# 暂时关闭 selinux
setenforce 0
# 永久关闭
vi /etc/sysconfig/selinux
# 修改以下参数,设置为disable
SELINUX=disabled
Linux 部分权限比较严格,不方便操作
[root@k8s-master ~]# setenforce 0
setenforce: SELinux is disabled
3,统一系统时间和时区
使用 ntpdate 统一系统的时间和时区,服务器时间与阿里云服务器保持一致;
# 统一时区,为上海时区
ln -snf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
bash -c "echo 'Asia/Shanghai' > /etc/timezone"
# 统一使用阿里服务器进行时间更新
ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com
实际操作:
// ln:软连接,创建软连接,从 /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai 到 /etc/localtime
[root@k8s-master ~]# ln -snf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
// bash -c:执行 shell 脚本,将 Asia/Shanghai 写入到 /etc/timezone 中,使用亚洲/上海时区
[root@k8s-master ~]# bash -c "echo 'Asia/Shanghai' > /etc/timezone"
// 让服务器时间与阿里云标准时间对齐
[root@k8s-master ~]# ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com
20 Dec 16:03:31 ntpdate[1608]: adjust time server 120.25.115.20 offset -0.003746 sec
备注:需要确保服务器之间的时间和时区一致,以避免执行定时任务时产生误差;
4,安装 Docker
在 kubernetes 中,组件、服务均能够以 Docker 镜像的方式进行部署,需要 docker 环境支持;
// 安装 docker 依赖的基础库
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
device-mapper-persistent-data:存储驱动,Linux 上的许多高级卷管理技术;
lvm:逻辑卷管理器,用于创建逻辑磁盘分区使用;
在安装 docker 前,需要先配置 docker 安装源:
// 添加阿里云的 docker 安装源
[root@k8s-node ~]# sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
已加载插件:fastestmirror
adding repo from: http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
grabbing file http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo to /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo
repo saved to /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo
安装 docker-ce:
yum install docker-ce -y
启动 docker 并设置为开机启动:
// 启动 docker
[root@k8s-master yum.repos.d]# systemctl start docker
// 设置开机启动
[root@k8s-master yum.repos.d]# systemctl enable docker
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/docker.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service.
设置安装镜像源,使用阿里云镜像源:
// 创建配置目录
sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker
// 创建文件 daemon.json
sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF'
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://fwvjnv59.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
}
EOF
实际操作:
[root@k8s-master yum.repos.d]# sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker
[root@k8s-master yum.repos.d]# sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF'
> {
> "registry-mirrors": ["https://fwvjnv59.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
> }
> EOF
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://fwvjnv59.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
}
重启 docker,完成配置文件的重新加载:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart docker.service
这样,docker 获取镜像时就会通过阿里云镜像仓库拉取,速度会快一些;
5,安装 Kubernetes 组件
1,切换 k8s 下载源
\
指定 yum 安装 k8s 的下载地址为“阿里云”源:
cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg
http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
2,安装 Kubernetes 核心组件
k8s 的三个核心组件:
- kubelet:Kubernetes 核心组件。运行在集群所有节点上,负责创建、启动服务容器;
- kubectl:Kubernetes 的命令行工具。可以用来管理,删除,创建资源;
- kubeadm:用来初始化集群,子节点加入的工具;
// 安装最新版本,会导致安装问题
yum install -y kubelet kubectl kubeadm
// 建议指定版本安装
yum install -y kubelet-1.20.4 kubectl-1.20.4 kubeadm-1.20.4
注意:在不指定组件版本的情况下,默认会安装最新版本(此时最新版本为 1.23.1)
这样可能导致 k8s 初始化报错:
执行:
kubeadm init --config init-kubeadm.conf
报错:
[kubelet-check] It seems like the kubelet isn’t running or healthy.
[kubelet-check] The HTTP call equal to 'curl -sSL http://localhost:10248/healthz’ failed with error: Get "http://localhost:10248/healthz": dial tcp [::1]:10248: connect: connection refused.
解决办法:
网上的解决办法均未实现,指定 1.20.4 版本安装无此问题,建议使用 1.20.4 版本;
3,kubeadm 介绍
k8s 与 mysql 组件功能对照
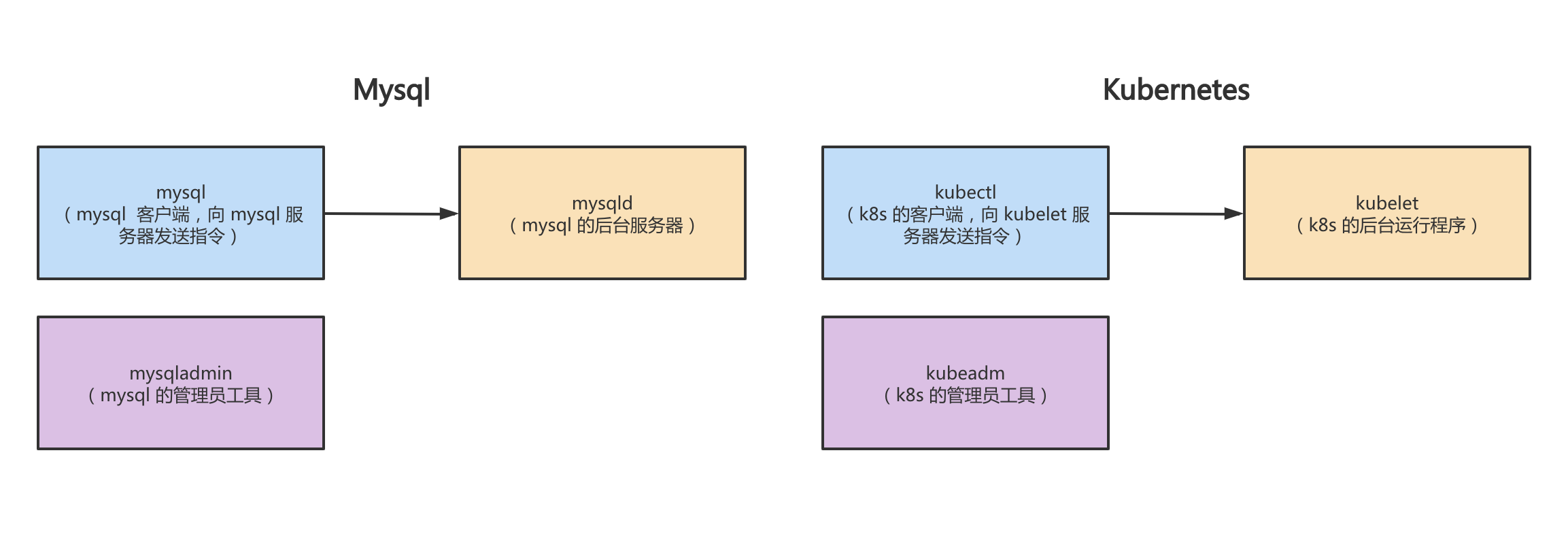
| mysql组件 | 组件功能 | 对标 K8s 组件 | 组件功能 |
|---|---|---|---|
| mysqld | mysql 的后台服务器; | kubelet | k8s 的后台运行程序; |
| mysql | mysql 的客户端,作为命令行工具向 mysql 服务器发送指令; | kubectl | k8s 的客户端,作为命令行工具向 kubelet 服务器发送指令,用于管理、创建、删除 k8s 资源; |
| mysqladmin | mysql 的管理员工具,如:重启、关闭服务器; | kubeadm | k8s 的管理员工具,用于初始化集群、提供配置文件等; |
4,启动 kubelet
# 启动 kubelet 并配置为开机启动
[root@k8s-master ~]# systemctl enable kubelet && systemctl start kubelet
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/kubelet.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/kubelet.service.
5,设置 bridge-nf-call-iptables
开启 bridge-nf-call-iptables,配置内核参数,将桥接的 IPV4 浏览传递到 iptables 链
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/bridge/bridge-nf-call-iptables
6,配置 Master 服务器(修改主机名:k8s-master)
Master 节点:负责集群中的任务调度;
hostnamectl set-hostname k8s-master
查看 hosts 文件
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat /etc/hosts
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
172.17.178.105 k8s-master k8s-master
7,配置 Node 服务器(修改主机名:k8s-node)
Node 节点:负责接收调度,运行服务容器;
hostnamectl set-hostname k8s-node
查看 hosts 文件:
[root@k8s-node ~]# cat /etc/hosts
cat /etc/hosts
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
172.17.178.106 k8s-node k8s-node
8,配置 Master(hosts 添加 k8s-node)
在 k8s-master 中,添加 k8s-node:
[root@k8s-master ~]# vi /etc/hosts
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
172.17.178.105 k8s-master
172.17.178.106 k8s-node
在 k8s-master 执行 ping k8s-node,测试主从通信:
[root@k8s-master ~]# ping k8s-node
PING k8s-node (172.17.178.106) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from k8s-node (172.17.178.106): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.492 ms
64 bytes from k8s-node (172.17.178.106): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.307 ms
64 bytes from k8s-node (172.17.178.106): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.299 ms
64 bytes from k8s-node (172.17.178.106): icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.296 ms
64 bytes from k8s-node (172.17.178.106): icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.328 ms
^C
--- k8s-node ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 5 received, 0% packet loss, time 4000ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.296/0.344/0.492/0.076 ms
9,配置 Node(hosts 添加 k8s-master)
在 k8s-node 中,添加 k8s-master:
[root@k8s-node ~]# vi /etc/hosts
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
172.17.178.106 k8s-node
172.17.178.105 k8s-master
在 k8s-node 中执行 ping k8s-master ,测试主从通信:
[root@k8s-node ~]# ping k8s-master
PING k8s-master (172.17.178.105) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from k8s-master (172.17.178.105): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.361 ms
64 bytes from k8s-master (172.17.178.105): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.01 ms
64 bytes from k8s-master (172.17.178.105): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.314 ms
^C
--- k8s-master ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2013ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.314/0.564/1.018/0.321 ms
完成测试,目前主从两台服务器可以相互 ping 通
10,生成 Kubernetes 初始化文件(仅 master 操作即可)
init-defaults:输出一份默认初始化配置文件;
// 执行 init-defaults 命令,并将输出结果写入 init-kubeadm.conf 中
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubeadm config print init-defaults > init-kubeadm.conf
// 修改配置:镜像仓库
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat init-kubeadm.conf
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3
bootstrapTokens:
- groups:
- system:bootstrappers:kubeadm:default-node-token
token: abcdef.0123456789abcdef
ttl: 24h0m0s
usages:
- signing
- authentication
kind: InitConfiguration
localAPIEndpoint:
advertiseAddress: 1.2.3.4
bindPort: 6443
nodeRegistration:
criSocket: /var/run/dockershim.sock
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: node
taints: null
---
apiServer:
timeoutForControlPlane: 4m0s
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3
certificatesDir: /etc/kubernetes/pki
clusterName: kubernetes
controllerManager: {}
dns: {}
etcd:
local:
dataDir: /var/lib/etcd
imageRepository: k8s.gcr.io
kind: ClusterConfiguration
kubernetesVersion: 1.23.0
networking:
dnsDomain: cluster.local
serviceSubnet: 10.96.0.0/12
scheduler: {}
11,修改 init-kubeadm.conf 配置项
需要修改以下三处配置
1,配置 k8s 拉取 docker 镜像的地址为阿里云镜像源;
2,本地 api 端点:广播地址,需修改为 k8s-master 的 ip;
3,添加 network 中的 pod 子网配置;
// 镜像仓库地址
imageRepository: k8s.gcr.io
imageRepository: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers // 更换 k8s 镜像仓库
// 本地 api 端点
localAPIEndpoint:
advertiseAddress: 1.2.3.4
bindPort: 6443
localAPIEndpoint:
advertiseAddress: 172.17.178.105 // 广播地址,需修改为 k8s-master 的 ip
bindPort: 6443
// 添加 network
networking:
dnsDomain: cluster.local
serviceSubnet: 10.96.0.0/12
networking:
dnsDomain: cluster.local // dns 域名
serviceSubnet: 10.96.0.0/12 // 服务子网
podSubnet: 10.244.0.0/16 // pod 子网配置
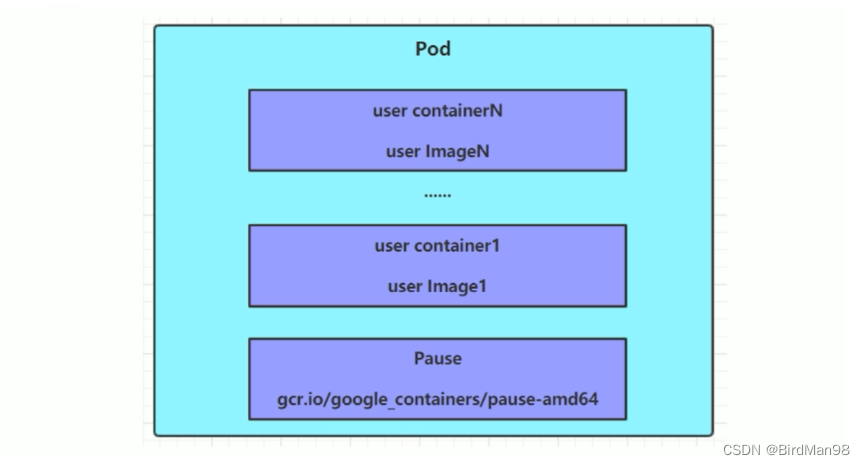
了解 podSubnet 需要先了解 k8s 架构,详见附:k8s 架构;
12,查看并拉取缺少的组件
配置文件中的镜像列表:目前已经安装了 k8s 的 3 个核心组件,还差 7 个组件
// 查看缺少的组件(缺少以下 7 个组件)
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubeadm config images list --config init-kubeadm.conf
registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-apiserver:v1.20.0
registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-controller-manager:v1.20.0
registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-scheduler:v1.20.0
registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-proxy:v1.20.0
registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause:3.2
registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/etcd:3.4.13-0
registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/coredns:1.7.0
// 拉取缺少的 7 个组件
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubeadm config images pull --config init-kubeadm.conf
[config/images] Pulled registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-apiserver:v1.20.0
[config/images] Pulled registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-controller-manager:v1.20.0
[config/images] Pulled registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-scheduler:v1.20.0
[config/images] Pulled registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-proxy:v1.20.0
[config/images] Pulled registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause:3.2
[config/images] Pulled registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/etcd:3.4.13-0
[config/images] Pulled registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/coredns:1.7.0
6,初始化 Kubernetes
1,通过 init-kubeadm.conf 初始化 k8s
- kubeadm join 可以快速将 Node 节点加入到 Master 集群内
- 将默认的 Kubernetes 认证文件拷贝到 .kube 文件夹内,默认使用该配置文件
在 Master 节点执行 k8s 集群初始化命令:
// 通过 init-kubeadm.conf 初始化 k8s
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubeadm init --config init-kubeadm.conf
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.20.0
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[WARNING IsDockerSystemdCheck]: detected "cgroupfs" as the Docker cgroup driver. The recommended driver is "systemd". Please follow the guide at https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/cri/
[WARNING SystemVerification]: this Docker version is not on the list of validated versions: 20.10.12. Latest validated version: 19.03
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-master kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [10.96.0.1 172.17.178.105]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-master localhost] and IPs [172.17.178.105 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-master localhost] and IPs [172.17.178.105 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "sa" key and public key
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s
[kubelet-check] Initial timeout of 40s passed.
[apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 64.005020 seconds
[upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config-1.20" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster
[upload-certs] Skipping phase. Please see --upload-certs
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node k8s-master as control-plane by adding the labels "node-role.kubernetes.io/master=''" and "node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane='' (deprecated)"
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node k8s-master as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule]
[bootstrap-token] Using token: abcdef.0123456789abcdef
[bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to get nodes
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[kubelet-finalize] Updating "/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" to point to a rotatable kubelet client certificate and key
[addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 172.17.178.105:6443 --token abcdef.0123456789abcdef \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:31e43ceaaf17f2c0d738ba6efa7fa71c6b5ad0d818a900a10b3e76bc397b5f7a
安装完成后的提示,注意以下两部分:
// 1,创建目录、添加配置、修改权限
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
// 2,在 node 节点执行以下命令,加入到 k8s 集群汇中:
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 172.17.178.105:6443 --token abcdef.0123456789abcdef \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:31e43ceaaf17f2c0d738ba6efa7fa71c6b5ad0d818a900a10b3e76bc397b5f7a
2,创建配置文件
根据安装完成后的提示,创建目录、拷贝 k8s 配置、修改权限
[root@k8s-master ~]# mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
[root@k8s-master ~]# sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
[root@k8s-master ~]# sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
3,查看节点启动情况
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8s-master NotReady control-plane,master 15m v1.20.4
可以发现,k8s-master 节点,目前还是 NotReady 状态;
7,安装 Flannel
flannel 主要的作用是通过创建一个虚拟网络,让不同节点下的服务具有全局唯一的 IP 地址,且服务之见可以互相访问和连接;集群内网网络通信协议通信模式采用了 Flannel 协议;
1,安装 Flannel 内网通讯协议
// 下载 kube-flannel.yml
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
// 拉取镜像
docker pull quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.13.0-rc2
备注:raw.githubusercontent.com被墙可以网上下载文件内容
查看 kube-flannel.yml 内容
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat kube-flannel.yml
---
apiVersion: policy/v1beta1
kind: PodSecurityPolicy
metadata:
name: psp.flannel.unprivileged
annotations:
seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/allowedProfileNames: docker/default
seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: docker/default
apparmor.security.beta.kubernetes.io/allowedProfileNames: runtime/default
apparmor.security.beta.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: runtime/default
spec:
privileged: false
volumes:
- configMap
- secret
- emptyDir
- hostPath
allowedHostPaths:
- pathPrefix: "/etc/cni/net.d"
- pathPrefix: "/etc/kube-flannel"
- pathPrefix: "/run/flannel"
readOnlyRootFilesystem: false
# Users and groups
runAsUser:
rule: RunAsAny
supplementalGroups:
rule: RunAsAny
fsGroup:
rule: RunAsAny
# Privilege Escalation
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
defaultAllowPrivilegeEscalation: false
# Capabilities
allowedCapabilities: ['NET_ADMIN', 'NET_RAW']
defaultAddCapabilities: []
requiredDropCapabilities: []
# Host namespaces
hostPID: false
hostIPC: false
hostNetwork: true
hostPorts:
- min: 0
max: 65535
# SELinux
seLinux:
# SELinux is unused in CaaSP
rule: 'RunAsAny'
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: flannel
rules:
- apiGroups: ['extensions']
resources: ['podsecuritypolicies']
verbs: ['use']
resourceNames: ['psp.flannel.unprivileged']
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes
verbs:
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes/status
verbs:
- patch
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: flannel
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: flannel
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: flannel
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: flannel
namespace: kube-system
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: kube-flannel-cfg
namespace: kube-system
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
data:
cni-conf.json: |
{
"name": "cbr0",
"cniVersion": "0.3.1",
"plugins": [
{
"type": "flannel",
"delegate": {
"hairpinMode": true,
"isDefaultGateway": true
}
},
{
"type": "portmap",
"capabilities": {
"portMappings": true
}
}
]
}
net-conf.json: |
{
"Network": "10.244.0.0/16",
"Backend": {
"Type": "vxlan"
}
}
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: kube-flannel-ds
namespace: kube-system
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: flannel
template:
metadata:
labels:
tier: node
app: flannel
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/os
operator: In
values:
- linux
hostNetwork: true
priorityClassName: system-node-critical
tolerations:
- operator: Exists
effect: NoSchedule
serviceAccountName: flannel
initContainers:
- name: install-cni
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.13.1-rc2
command:
- cp
args:
- -f
- /etc/kube-flannel/cni-conf.json
- /etc/cni/net.d/10-flannel.conflist
volumeMounts:
- name: cni
mountPath: /etc/cni/net.d
- name: flannel-cfg
mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/
containers:
- name: kube-flannel
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.13.1-rc2
command:
- /opt/bin/flanneld
args:
- --ip-masq
- --kube-subnet-mgr
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "50Mi"
limits:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "50Mi"
securityContext:
privileged: false
capabilities:
add: ["NET_ADMIN", "NET_RAW"]
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
volumeMounts:
- name: run
mountPath: /run/flannel
- name: flannel-cfg
mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/
volumes:
- name: run
hostPath:
path: /run/flannel
- name: cni
hostPath:
path: /etc/cni/net.d
- name: flannel-cfg
configMap:
name: kube-flannel-cfg
注意以下两个部分:
// 1,
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.13.1-rc2
// 2,
net-conf.json: |
{
// 初始化时配置的 Pod 子网,三个 pod 互相通信,依靠 Flannel 协议组成子网
"Network": "10.244.0.0/16",
"Backend": {
"Type": "vxlan"
}
}
2,启动 Flannel
// 启动
kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml
// 实际执行
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml
podsecuritypolicy.policy/psp.flannel.unprivileged created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/flannel created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/flannel created
serviceaccount/flannel created
configmap/kube-flannel-cfg created
daemonset.apps/kube-flannel-ds created
3,查看节点启动情况
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8s-master Ready control-plane,master 13h v1.20.4
可以发现,k8s-master节点,目前已经是 Ready 状态;
8, node 节点配置
1,拷贝 Master 节点配置文件到 node
将 k8s-master 节点的配置文件拷贝到 k8s-node 节点
// 将当前 $HOME/.kube/config 文件,拷贝到指定 IP 的 HOME 中
[root@k8s-master ~]# scp $HOME/.kube/config root@172.17.178.106:~/
The authenticity of host '172.17.178.106 (172.17.178.106)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:59P14/vci6LQz7+cksAjPYi5IuYnC6FxaCPVBe+I2p8.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:8e:bd:91:34:fa:c2:34:69:07:ae:33:cf:9a:7d:6d:c3.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '172.17.178.106' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
root@172.17.178.106's password:
config 100% 5566 8.5MB/s 00:00
到 k8s-node 上,查看拷贝结果:
[root@k8s-node ~]# ls
config kube-flannel.yml
在 k8s-node 节点上,归档配置文件
// 创建目录 $HOME/.kube
[root@k8s-node ~]# mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
// 将拷贝的 config 移动到 $HOME/.kube 中
[root@k8s-node ~]# sudo mv $HOME/config $HOME/.kube/config
// 修改权限
[root@k8s-node ~]# sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
2,将 node 节点加入到集群
根据安装完成后的提示,在 node 节点中执行命令,
// 让 k8s-node 节点加入到 k8s-master 集群内
[root@k8s-node ~]# kubeadm join 172.17.178.105:6443 --token abcdef.0123456789abcdef \
> --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:31e43ceaaf17f2c0d738ba6efa7fa71c6b5ad0d818a900a10b3e76bc397b5f7a
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[WARNING IsDockerSystemdCheck]: detected "cgroupfs" as the Docker cgroup driver. The recommended driver is "systemd". Please follow the guide at https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/cri/
[WARNING SystemVerification]: this Docker version is not on the list of validated versions: 20.10.12. Latest validated version: 19.03
[preflight] Reading configuration from the cluster...
[preflight] FYI: You can look at this config file with 'kubectl -n kube-system get cm kubeadm-config -o yaml'
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[kubelet-start] Waiting for the kubelet to perform the TLS Bootstrap...
This node has joined the cluster:
* Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and a response was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
Run 'kubectl get nodes' on the control-plane to see this node join the cluster.
备注:当前的 node 节点,在前面已经完成了 3 个 k8s 核心组件的安装;
如果加入集群的命令丢失了,可以在 master 上使用 kubeadm token create 重新生成一条命令:
kubeadm token create --print-join-command
3,查看节点启动情况
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8s-master Ready control-plane,master 13h v1.20.4
k8s-node Ready <none> 12h v1.20.4
两个节点均已 Ready,k8s 集群配置完成;
四,结尾
本篇,完成了 k8s 两台服务器 k8s-master、k8s-node 的安装与配置;
下一篇,k8s 部署:直接部署和 yaml 部署