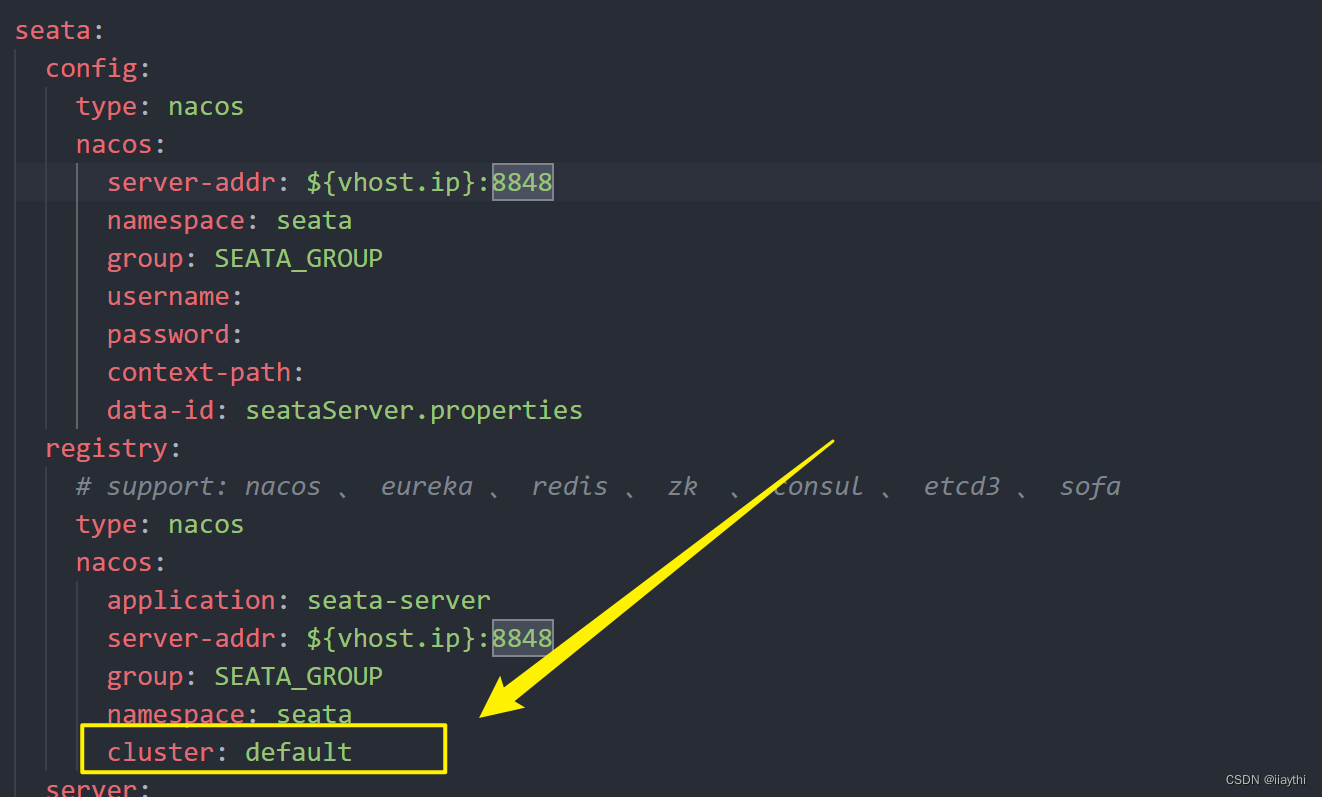
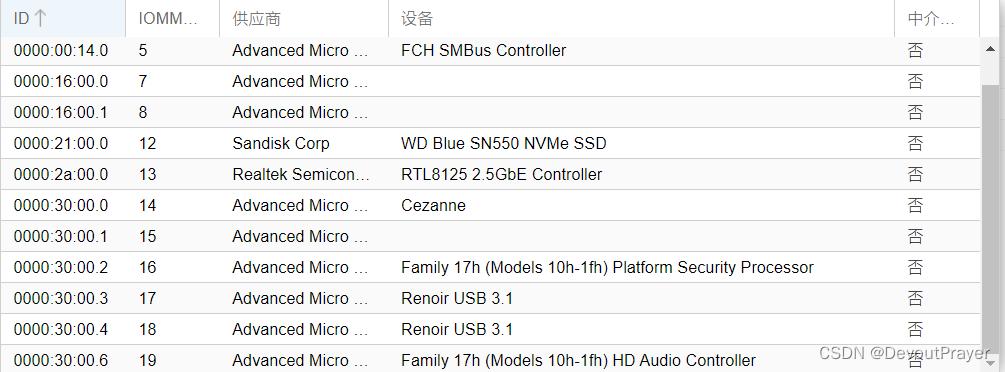
为了确保能够真正地了解线程块的分配,接下来我们写一个简短的内核程序来输出线程块、线程、线程束和线程全局标号到屏幕上。现在,除非你使用的是 3.2 版本以上的 SDK否则内核中是不支持 printf的。因此,我们可以将数据传送回 CPU 端然后输出到控制台窗口,内核的代码如下:
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <conio.h>
__global__ void what_is_my_id(unsigned int* const block,
unsigned int* const thread,
unsigned int* const warp,
unsigned int* const calc_thread) {
/* Thread id is block index * block size + thread offset into the block */
const unsigned int thread_idx = (blockIdx.x * blockDim.x) + threadIdx.x;
block[thread_idx] = blockIdx.x; thread[thread_idx] = threadIdx.x;
/* Calculate warp using buit in variable warpSize */
warp[thread_idx] = threadIdx.x / warpSize;
calc_thread[thread_idx] = thread_idx;
}
#define ARRAY_SIZE 128
#define ARRAY_SIZE_IN_BYTES (sizeof(unsigned int)* (ARRAY_SIZE))
/* Declare statically four arrays of ARRAY_SIZE each */
unsigned int cpu_block[ARRAY_SIZE];
unsigned int cpu_thread[ARRAY_SIZE];
unsigned int cpu_warp[ARRAY_SIZE];
unsigned int cpu_calc_thread[ARRAY_SIZE];
int main(void) {
/* Total thread count =2*64=128 */
const unsigned int num_blocks = 2;
const unsigned int num_threads = 64;
char ch;
/* Declare pointers for GPU based params */
unsigned int* gpu_block;
unsigned int* gpu_thread;
unsigned int* gpu_warp;
unsigned int* gpu_calc_thread;
/* Declare loop counter for use later */
unsigned int i;
/* Allocate four arrays on the GPU */
cudaMalloc((void**)&gpu_block, ARRAY_SIZE_IN_BYTES);
cudaMalloc((void**)&gpu_thread, ARRAY_SIZE_IN_BYTES);
cudaMalloc((void**)&gpu_warp, ARRAY_SIZE_IN_BYTES);
cudaMalloc((void**)&gpu_calc_thread, ARRAY_SIZE_IN_BYTES);
/* Execute our kerne] */
what_is_my_id <<<num_blocks, num_threads>>>(gpu_block, gpu_thread, gpu_warp, gpu_calc_thread);
/* Copy back the gpu results to the CPU */
cudaMemcpy(cpu_block, gpu_block, ARRAY_SIZE_IN_BYTES, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaMemcpy(cpu_thread, gpu_thread, ARRAY_SIZE_IN_BYTES, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaMemcpy(cpu_warp, gpu_warp, ARRAY_SIZE_IN_BYTES, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaMemcpy(cpu_calc_thread, gpu_calc_thread, ARRAY_SIZE_IN_BYTES, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
/* Free the arrays on the GPU as now we're done with them */
cudaFree(gpu_block);
cudaFree(gpu_thread);
cudaFree(gpu_warp);
cudaFree(gpu_calc_thread);
/* Iterate through the arrays and print */
for (i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++) {
printf("Calculated Thread: %3u - Block:%2u - Warp %2u - Thread %3u\n", cpu_calc_thread[i], cpu_block[i], cpu_warp[i], cpu_thread[i]);
}
ch = getch();
}在这个例子中,我们可以看到线程块按照线程块的编号紧密相连。由于处理的是一维数组,所以我们对线程块采用相同的布局便可简单解决问题。以下是此程序的输出结果:

正如我们计算的那样,线程索引是0~ 127。一共有两个线块,每个线程块包含 64个线程,每个线程块内部线程的索引为0~63。一个线程块包含两个线束。
渗透测试](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c25687b6276f47a4953f04fff0d90787.png)