从web.xml说起
在开始 Spring MVC 的分析之前,先来聊一聊 Java 初学者接触的最多的 Java Web 基础。还记得我的第一个 Web 工程是由 Servlet、Velocity 和 Filter 来完成的,那时几乎所有人都是根据 Servlet、JSP 和 Filter 来编写自己的第一个 Hello World 工程。那时,还离不开 web.xml 配置文件,需要对 Servlet 和 Filter 进行配置,相对来说比较繁琐。随着 Spring 体系的快速发展,配置逐渐演变成了 Java Configuration 和 XML 配置两种方式的共存。现如今,Spring Boot 和 Spring Cloud 在许多中大型企业中被普及,Java Configuration 成为了主流,XML 配置的方式也逐渐“消失”在我们的视野里面。不知道现在的小伙伴是否还记得那个 web.xml 文件,这中间都发生过什么变化,其中的 Servlet 和 Filter 配置项被什么取代了?
Servlet:Java Servlet 为 Web 开发人员提供了一种简单,一致的机制,以扩展 Web 服务器的功能并访问现有的业务系统。实现了 Servlet 接口的类在 Servlet 容器中可用于处理请求并发送响应。
Tomcat:Tomcat 是 Web 应用服务器,是一个 Servlet 容器,实现了对 Servlet 和 JSP 的支持。
如果应用程序是以 war 包的方式放入 Tomcat 的 webapps 文件夹下面,那么在 Tomcat 启动时会加载 war 包,生成对应的一个文件夹,Tomcat 则会去对 webapps 文件夹下面的每一个文件夹(我们的应用程序)生成一个部署任务,去解析对应的 WEB-INF/web.xml 文件,将配置的 Servlet 加载到 Servlet 容器中。当 Tomcat 监听到某端口的 HTTP 请求时,则会将请求解析成 Request 对象,然后交由相应的 Servlet 进行处理,最后将处理结果转换成 HTTP 响应。
为什么是 webapps 目录和 WEB-INF/web.xml 文件,可以看一下 Tomcat 的 conf/server.xml 和 conf/context.xml 两个配置文件,如下:
<!-- server.xml -->
<!-- appBase 属性指定应用程序所在目录 -->
<Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps" unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true">
<!-- context.xml -->
<Context>
<!-- Default set of monitored resources. If one of these changes, the web application will be reloaded. -->
<WatchedResource>WEB-INF/web.xml</WatchedResource>
<WatchedResource>WEB-INF/tomcat-web.xml</WatchedResource>
<WatchedResource>${catalina.base}/conf/web.xml</WatchedResource>
</Context>
Servlet3.0 以前的时代
为了体现出整个演进过程,先来回顾下当初我们是怎么写 Servlet 和 Filter 代码来完成自己的第一个 Hello World 工程
项目结构
.
├── pom.xml
├── src
├── main
│ ├── java
│ │ └── cn
│ │ └── edu
│ │ └── shopping
│ │ ├── filter
│ │ │ └── HelloWorldFilter.java
│ │ └── servlet
│ │ └── HelloWorldServlet.java
│ └── webapp
│ └── WEB-INF
│ └── web.xml
└── test
└── javacn.edu.shopping.servlet.HelloWorldServlet.java
public class HelloWorldServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/plain");
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("Hello World");
}
}
cn.edu.shopping.filter.HelloWorldFilter.java
public class HelloWorldFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("触发 Hello World 过滤器...");
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
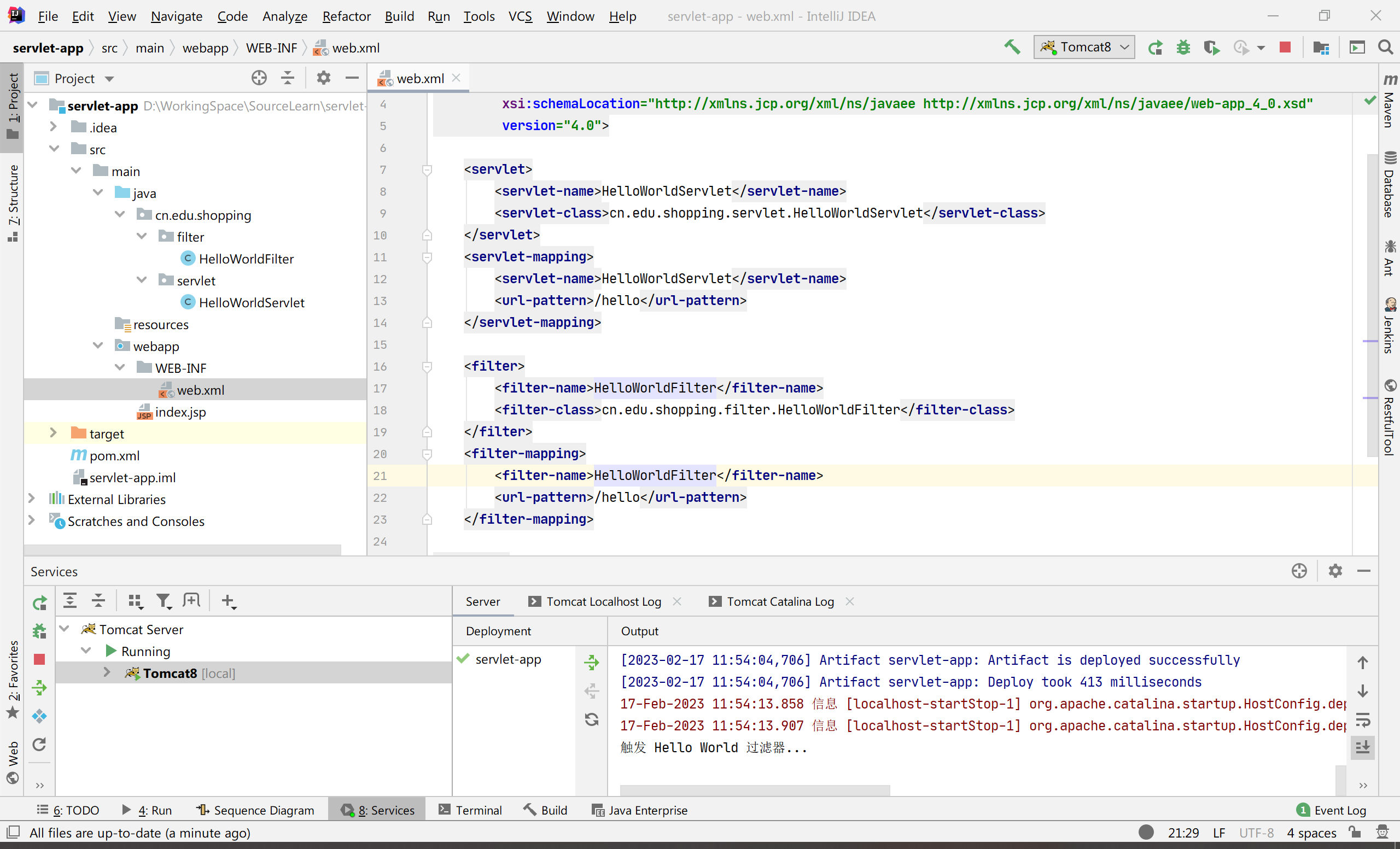
在 web.xml 中配置 Servlet 和 Filter
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>HelloWorldServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>cn.edu.shopping.servlet.HelloWorldServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>HelloWorldServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<filter>
<filter-name>HelloWorldFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>cn.edu.shopping.filter.HelloWorldFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HelloWorldFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
</web-app>
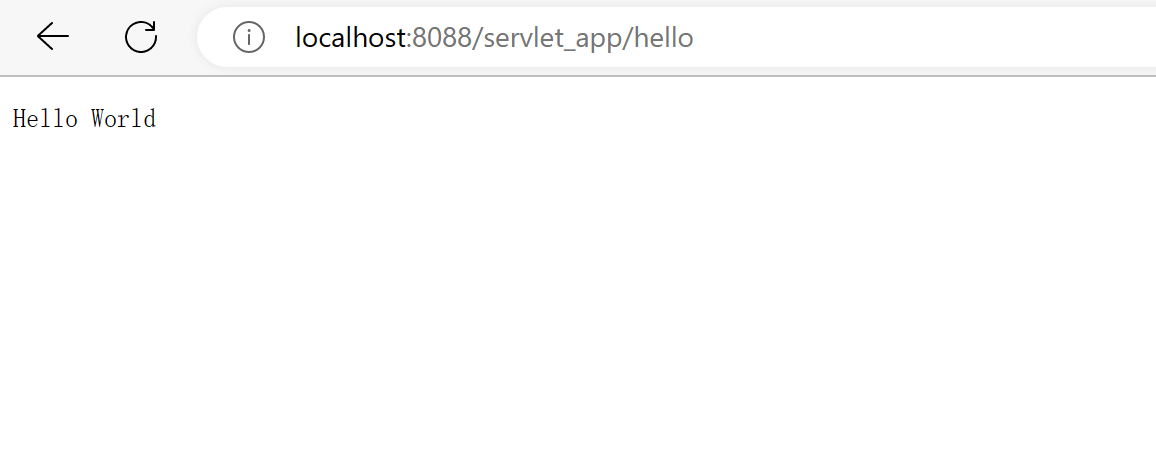
上述就是我当初第一个 Hello World 工程,配置 Tomcat 后启动,在浏览器里面输入 http://127.0.0.1:8080/hello 可看到 “Hello World”,在控制台会打印“触发 Hello World 过滤器...”
参考 IBM 的 Servlet 3.0 新特性详解 文章
Servlet 3.0 作为 Java EE 6 规范体系中一员,随着 Java EE 6 规范一起发布。该版本在前一版本(Servlet 2.5)的基础上提供了若干新特性用于简化 Web 应用的开发和部署。其中有几项特性的引入让开发者感到非常兴奋,同时也获得了 Java 社区的一片赞誉之声:
异步处理支持:有了该特性,Servlet 线程不再需要一直阻塞,直到业务处理完毕才能再输出响应,最后才结束该 Servlet 线程。在接收到请求之后,Servlet 线程可以将耗时的操作委派给另一个线程来完成,自己在不生成响应的情况下返回至容器。针对业务处理较耗时的情况,这将大大减少服务器资源的占用,并且提高并发处理速度。
新增的注解支持:该版本新增了若干注解,用于简化 Servlet、过滤器(Filter)和监听器(Listener)的声明,这使得 web.xml 部署描述文件从该版本开始不再是必选的了。
可插性支持:熟悉 Struts2 的开发者一定会对其通过插件的方式与包括 Spring 在内的各种常用框架的整合特性记忆犹新。将相应的插件封装成 JAR 包并放在类路径下,Struts2 运行时便能自动加载这些插件。现在 Servlet 3.0 提供了类似的特性,开发者可以通过插件的方式很方便的扩充已有 Web 应用的功能,而不需要修改原有的应用。
通过 Servlet3.0 首先提供了 @WebServlet、@WebFilter 和 @WebListener 等注解,可以替代 web.xml 文件中的 Servlet 和 Filter 等配置项
除了以上的新特性之外,ServletContext 对象的功能在新版本中也得到了增强。现在,该对象支持在运行时动态部署 Servlet、过滤器、监听器,以及为 Servlet 和过滤器增加 URL 映射等。以 Servlet 为例,过滤器与监听器与之类似。ServletContext 为动态配置 Servlet 增加了如下方法:
ServletRegistration.Dynamic addServlet(String servletName,Class<? extends Servlet> servletClass)
ServletRegistration.Dynamic addServlet(String servletName, Servlet servlet)
ServletRegistration.Dynamic addServlet(String servletName, String className)
T createServlet(Class clazz)
ServletRegistration getServletRegistration(String servletName)
Map<string,? extends servletregistration> getServletRegistrations()
其中前三个方法的作用是相同的,只是参数类型不同而已;通过 createServlet() 方法创建的 Servlet,通常需要做一些自定义的配置,然后使用 addServlet() 方法来将其动态注册为一个可以用于服务的 Servlet。两个 getServletRegistration() 方法主要用于动态为 Servlet 增加映射信息,这等价于在 web.xml( 抑或 web-fragment.xml) 中使用 标签为存在的 Servlet 增加映射信息。
以上 ServletContext 新增的方法要么是在 ServletContextListener 的 contexInitialized 方法中调用,要么是在 ServletContainerInitializer 的 onStartup() 方法中调用。
ServletContainerInitializer 也是 Servlet 3.0 新增的一个接口,容器在启动时使用 JAR 服务 API(JAR Service API) 来发现 ServletContainerInitializer 的实现类,并且容器将 WEB-INF/lib 目录下 JAR 包中的类都交给该类的 onStartup() 方法处理,我们通常需要在该实现类上使用 @HandlesTypes 注解来指定希望被处理的类,过滤掉不希望给 onStartup() 处理的类。
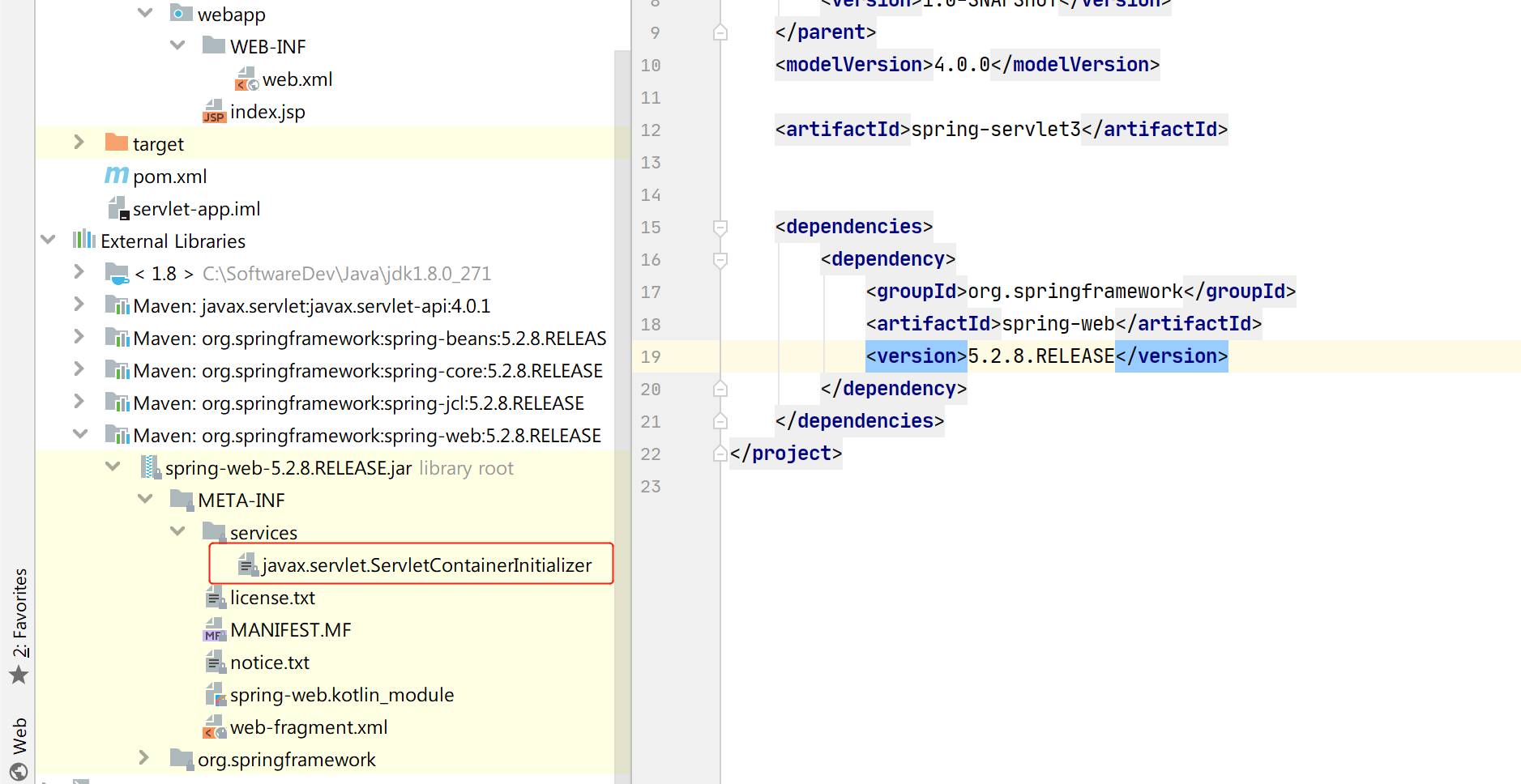
一个典型的 Servlet3.0+ 的 Web 项目结构如下:
.
├── pom.xml
├── src
├── main
│ ├── java
│ │ └── cn
│ │ └── edu
│ │ └── shopping
│ │ ├── CustomServletContainerInitializer.java
│ │ ├── filter
│ │ │ └── HelloWorldFilter.java
│ │ └── servlet
│ │ └── HelloWorldServlet.java
│ ├── resources
│ │ └── META-INF
│ │ └── services
│ │ └── javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer
│ └── webapp
│ └── WEB-INF
│ └── web.xml
└── test
└── javaHelloWorldFilter 和 HelloWorldServlet 没有变动,新增了一个 CustomServletContainerInitializer 对象,它实现了 javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer 接口,用来在 Web 容器启动时加载需要的 Servlet 和 Filter,代码如下
public class CustomServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> c, ServletContext ctx) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("创建 Hello World Servlet...");
javax.servlet.ServletRegistration.Dynamic servlet = ctx.addServlet(
HelloWorldServlet.class.getSimpleName(), HelloWorldServlet.class);
servlet.addMapping("/hello");
System.out.println("创建 Hello World Filter...");
javax.servlet.FilterRegistration.Dynamic filter = ctx.addFilter(HelloWorldFilter.class.getSimpleName(), HelloWorldFilter.class);
EnumSet<DispatcherType> dispatcherTypes = EnumSet.allOf(DispatcherType.class);
dispatcherTypes.add(DispatcherType.REQUEST);
dispatcherTypes.add(DispatcherType.FORWARD);
filter.addMappingForUrlPatterns(dispatcherTypes, true, "/hello");
}
}
在实现的 onStartup 方法中向 ServletContext 对象(Servlet 上下文)添加之前在 web.xml 中配置的 HelloWorldFilter 和 HelloWorldServlet,这样一来就可以去除 web.xml 文件了。
方法入参中的 Set<Class<?>> c 是和 @HandlesTypes 注解结合使用的,指定需要处理的 Calss 类,可以参考 Spring 中的 SpringServletContainerInitializer 使用方法
这么声明一个 ServletContainerInitializer 的实现类,Web 容器并不会识别它,需要借助 SPI 机制来指定该初始化类,通过在项目 ClassPath 路径下创建 META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer 文件来做到的,内容如下:
cn.edu.shopping.CustomServletContainerInitializer
这样一来,使用 ServletContainerInitializer 和 SPI 机制则可以拜托 web.xml 了。
Spring 是如何支持 Servlet3.0
回到 Spring 全家桶,你可能已经忘什么时候开始不写 web.xml 了,现在的项目基本看不到它了,Spring 又是如何支持 Servlet3.0 规范的呢?
在 Spring 的 spring-web 子工程的 ClassPath 下面的有一个 META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer 文件,如下:
org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer
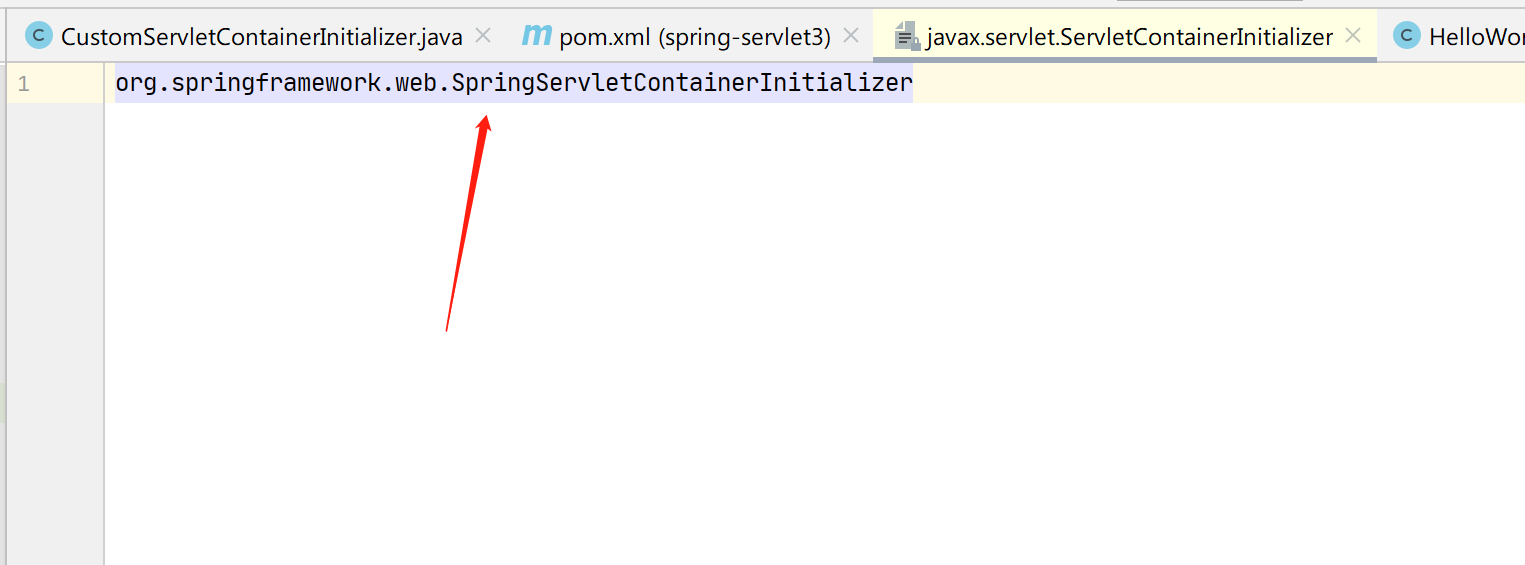
org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer 类,代码如下:
/**
* Servlet 3.0 {@link ServletContainerInitializer} designed to support code-based
* configuration of the servlet container using Spring's {@link WebApplicationInitializer}
* SPI as opposed to (or possibly in combination with) the traditional
* {@code web.xml}-based approach.
*/
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList<>();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes,
// no matter what @HandlesTypes says...
// <1>
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer)
ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
return;
}
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
// <2>
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
}
注意我在源码中标注两个序号,这对于我们理解 Spring 装配 Servlet 的流程来说非常重要
<1> 提示我们由于 Servlet 厂商实现的差异,onStartup 方法会加载我们本不想处理的 Class 对象,所以进行了判断。
<2> Spring 与我们上述提供的 Demo 不同,并没有在 SpringServletContainerInitializer 中直接对 Servlet 和 Filter 进行注册,而是委托给了一个陌生的类 WebApplicationInitializer ,这个类便是 Spring 用来初始化 Web 环境的委托者类,它的实现类:
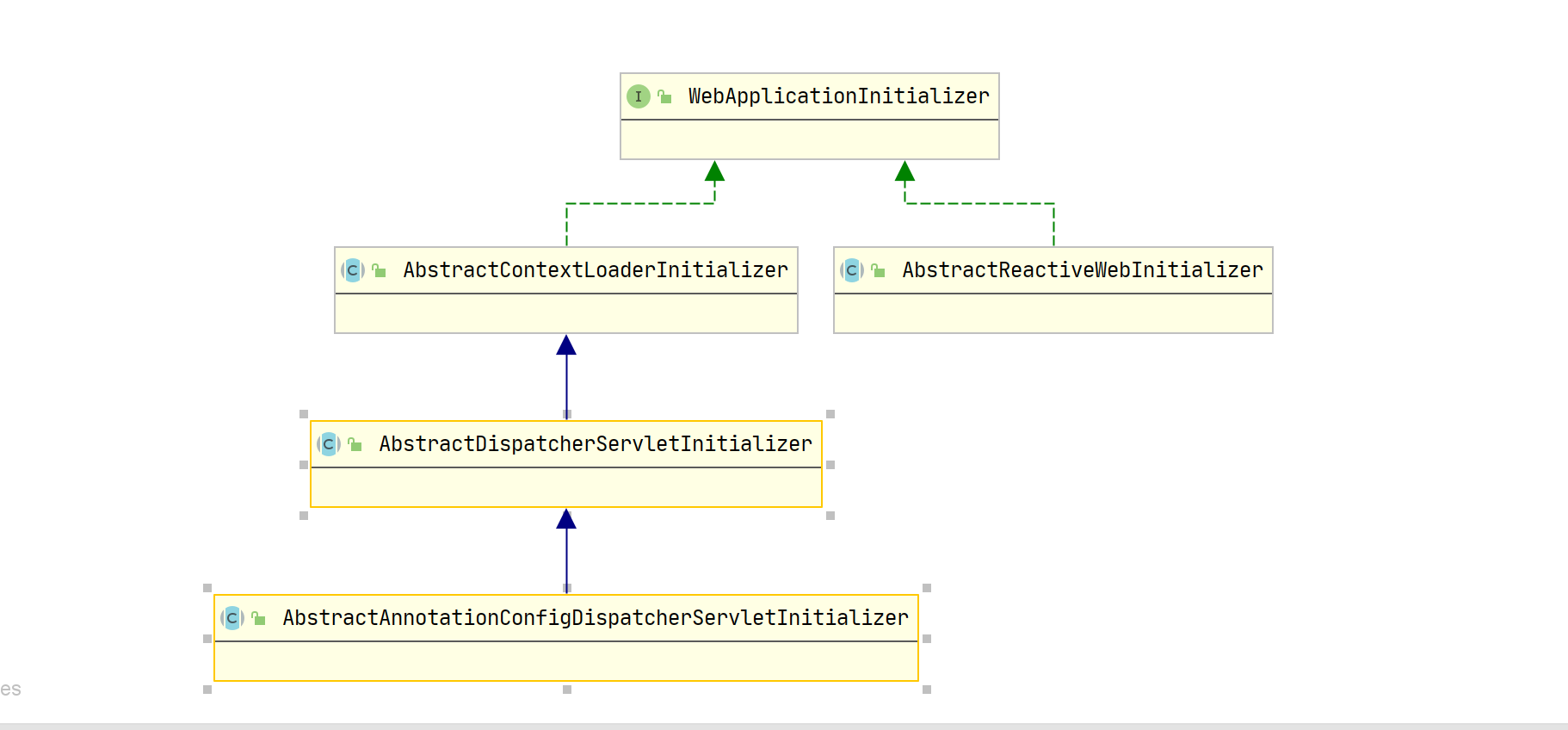
你一定不会对 DispatcherServlet 感到陌生,他就是 Spring MVC 中的核心类,AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer 便是无 web.xml 前提下,创建 DispatcherServlet 的关键类,代码如下:
public abstract class AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer extends AbstractContextLoaderInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
// 调用父类启动的逻辑
super.onStartup(servletContext);
// 注册 DispacherServlt
registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext);
}
protected void registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 获得 Servlet 名
String servletName = getServletName();
Assert.hasLength(servletName, "getServletName() must not return null or empty");
// <1> 创建 WebApplicationContext 对象
WebApplicationContext servletAppContext = createServletApplicationContext();
Assert.notNull(servletAppContext, "createServletApplicationContext() must not return null");
// <2> 创建 FrameworkServlet 对象
FrameworkServlet dispatcherServlet = createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
Assert.notNull(dispatcherServlet, "createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext) must not return null");
dispatcherServlet.setContextInitializers(getServletApplicationContextInitializers());
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet(servletName, dispatcherServlet);
if (registration == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to register servlet with name '" + servletName + "'. " +
"Check if there is another servlet registered under the same name.");
}
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping(getServletMappings());
registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported());
// <3> 注册过滤器
Filter[] filters = getServletFilters();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(filters)) {
for (Filter filter : filters) {
registerServletFilter(servletContext, filter);
}
}
customizeRegistration(registration);
}
}
<1> 处,调用 createServletApplicationContext() 方法,创建 WebApplicationContext 对象,代码如下:
// AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer.java
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
Class<?>[] configClasses = getServletConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
context.register(configClasses);
}
return context;
}该方法由子类 AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer 重写,并且创建的 WebApplicationContext 的子类 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext 对象
<2> 处,调用 createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext servletAppContext) 方法,创建 FrameworkServlet 对象,代码如下:
// AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer.java
protected FrameworkServlet createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext servletAppContext) {
return new DispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
}创建 FrameworkServlet 的子类 DispatcherServlet 对象
另外,比较有趣的是传入的 servletAppContext 方法参数,这就是该 DispatcherServlet 的 Servlet WebApplicationContext 容器
注意,上述这一切特性从 Spring 3 就已经存在了,而如今 Spring 5 已经伴随 SpringBoot 2.0 一起发行了
SpringBoot 如何配置 Servlet
读到这儿,你已经阅读了全文的 1/2。SpringBoot 对于 Servlet 的处理才是重头戏,因为 SpringBoot 使用范围很广,很少有人用 Spring 而不用 SpringBoot 了
是的,前面所讲述的 Servlet 的规范,无论是 web.xml 中的配置,还是 Servlet3.0 中的 ServletContainerInitializer 和 SpringBoot 的加载流程都没有太大的关联。按照惯例,先看看如何在 SpringBoot 中注册 Servlet 和 Filter,再来解释下 SpringBoot 的独特之处
注册方式一:Servlet3.0 注解 +@ServletComponentScan
SpringBoot 依旧兼容 Servlet 3.0 一系列以 @Web* 开头的注解:@WebServlet,@WebFilter,@WebListener
@WebFilter("/hello/*")
public class HelloWorldFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("触发 Hello World 过滤器...WebFilter");
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}@WebServlet("/hello")
public class HelloWorldServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
response.setContentType("text/plain");
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("Hello World"+": WebServlet");
}
}在启动类上面添加 @ServletComponentScan 注解去扫描到这些注解
@ServletComponentScan
@SpringBootApplication
public class BootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BootApplication.class, args);
}
}
这种方式相对来说比较简介直观,其中 org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.@ServletComponentScan 注解通过 @Import(ServletComponentScanRegistrar.class) 方式,它会将扫描到的 @WebServlet、@WebFilter、@WebListener 的注解对应的类,最终封装成 FilterRegistrationBean、ServletRegistrationBean、ServletListenerRegistrationBean 对象,注册到 Spring 容器中。也就是说,和注册方式二:RegistrationBean统一了
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import({ServletComponentScanRegistrar.class})
public @interface ServletComponentScan {
@AliasFor("basePackages")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] basePackages() default {};
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
}注册方式二:RegistrationBean
@Configuration
public class WebConfig {
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean<HelloWorldServlet> helloWorldServlet() {
ServletRegistrationBean<HelloWorldServlet> servlet = new ServletRegistrationBean<>();
servlet.addUrlMappings("/hello");
servlet.setServlet(new HelloWorldServlet());
return servlet;
}
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean<HelloWorldFilter> helloWorldFilter() {
FilterRegistrationBean<HelloWorldFilter> filter = new FilterRegistrationBean<>();
filter.addUrlPatterns("/hello/*");
filter.setFilter(new HelloWorldFilter());
return filter;
}
}ServletRegistrationBean 和 FilterRegistrationBean 都继成 RegistrationBean,它是 SpringBoot 中广泛应用的一个注册类,负责把 Servlet,Filter,Listener 给容器化,使它们被 Spring 托管,并且完成自身对 Web 容器的注册,这种注册方式值得推崇
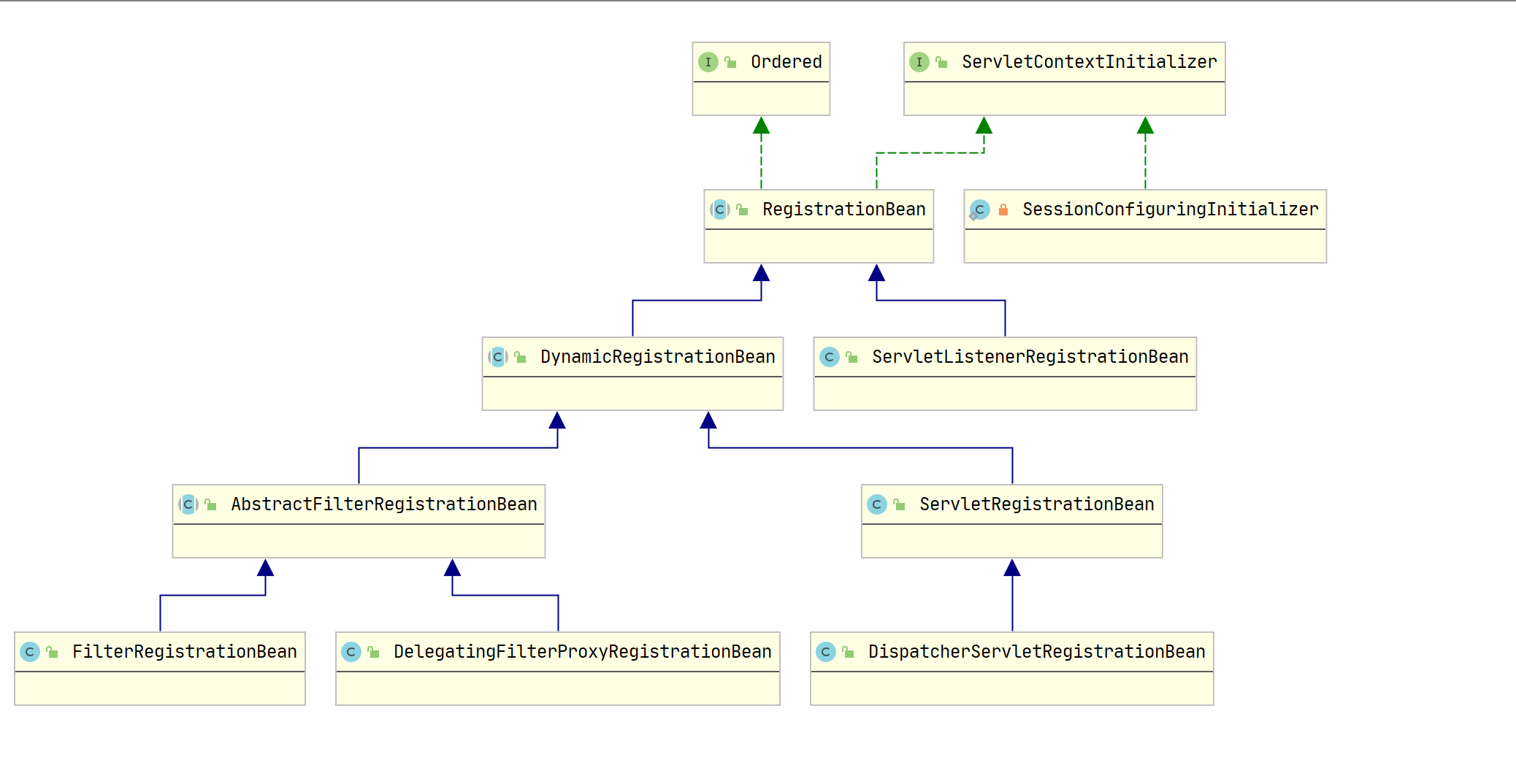
从图中可以看出 RegistrationBean 的地位,它的几个实现类作用分别是:
其中最底层有三个类分别帮助 Spring 容器注册 Filter,Servlet,Listener 对象
还有一个 DelegatingFilterProxyRegistrationBean,熟悉 Spring Security 的朋友应该不会感到陌生,SpringSecurityFilterChain 就是通过这个代理类来调用的
另外 RegistrationBean 实现了 ServletContextInitializer 接口,这个接口将会是下面分析的核心接口,大家先混个眼熟,了解下它有一个抽象实现 RegistrationBean 即可
SpringBoot 加载 Servlet 的流程
接下来开始讨论 SpringBoot 中 Servlet 的加载流程,讨论的前提是 SpringBoot 环境下使用内嵌的容器,比如最典型的 Tomcat
Initializer 被替换为 TomcatStarter
当使用内嵌的 Tomcat 时,你在 SpringServletContainerInitializer 上面打断点,会发现根本不会进入该类的内部,因为 SpringBoot 完全走了另一套初始化流程,而是进入了 org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatStarter 这个类
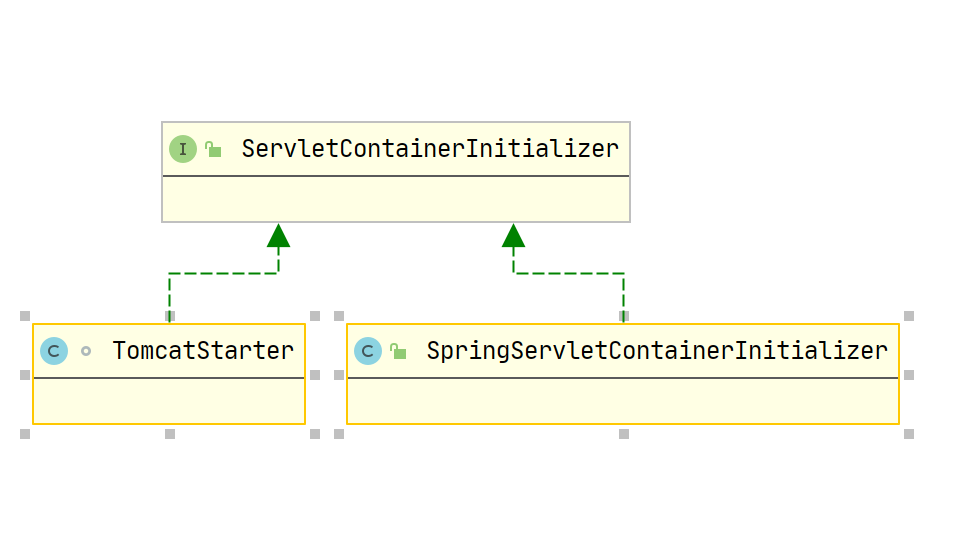
仔细扫一眼源码包,并没有发现有 SPI 文件对应到 TomcatStarter,也就是说没有通过 SPI 机制加载这个类,为什么没有这么做呢?可以翻阅 Spring Github 中的 issue,其中有 Spring 作者肯定的答复:https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/issues/321
This was actually an intentional design decision. The search algorithm used by the containers was problematic. It also causes problems when you want to develop an executable WAR as you often want a javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer for the WAR that is not executed when you run java -jar .
See the org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.ServletContextInitializer for an option that works with Spring Beans.
SpringBoot 这么做是有意而为之,我们在使用 SpringBoot 时,开发阶段一般都是使用内嵌 Tomcat 容器,但部署时却存在两种选择:一种是打成 jar 包,使用 java -jar 的方式运行;另一种是打成 war 包,交给外置容器去运行。
前者就会导致容器搜索算法出现问题,因为这是 jar 包的运行策略,不会按照 Servlet 3.0 的策略去加载 ServletContainerInitializer!
最后作者还提供了一个替代选项:ServletContextInitializer,它和 ServletContainerInitializer 长得特别像,别搞混淆了!
前者 ServletContextInitializer 是 org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletContextInitializer
后者 ServletContainerInitializer 是 javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer,前文提到的 RegistrationBean 就实现了 ServletContextInitializer 接口
TomcatStarter 中的 ServletContextInitializer 是关键
TomcatStarter 中 org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.ServletContextInitializer[] initializers 属性,是 SpringBoot 初始化 Servlet,Filter,Listener 的关键,代码如下:
class TomcatStarter implements ServletContainerInitializer {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(TomcatStarter.class);
private final ServletContextInitializer[] initializers;
private volatile Exception startUpException;
TomcatStarter(ServletContextInitializer[] initializers) {
this.initializers = initializers;
}
@Override
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> classes, ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
try {
for (ServletContextInitializer initializer : this.initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
this.startUpException = ex;
// Prevent Tomcat from logging and re-throwing when we know we can
// deal with it in the main thread, but log for information here.
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Error starting Tomcat context. Exception: "
+ ex.getClass().getName() + ". Message: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
public Exception getStartUpException() {
return this.startUpException;
}
}
在 onStartup(Set<Class<?>> classes, ServletContext servletContext) 方法中,负责调用一系列的 ServletContextInitializer 对象的 onStartup 方法
那么在 debug 的过程中,构造方法中的 ServletContextInitializer[] initializers 入参到底包含了哪些类呢?会不会有我们前面介绍的 RegistrationBean 呢?
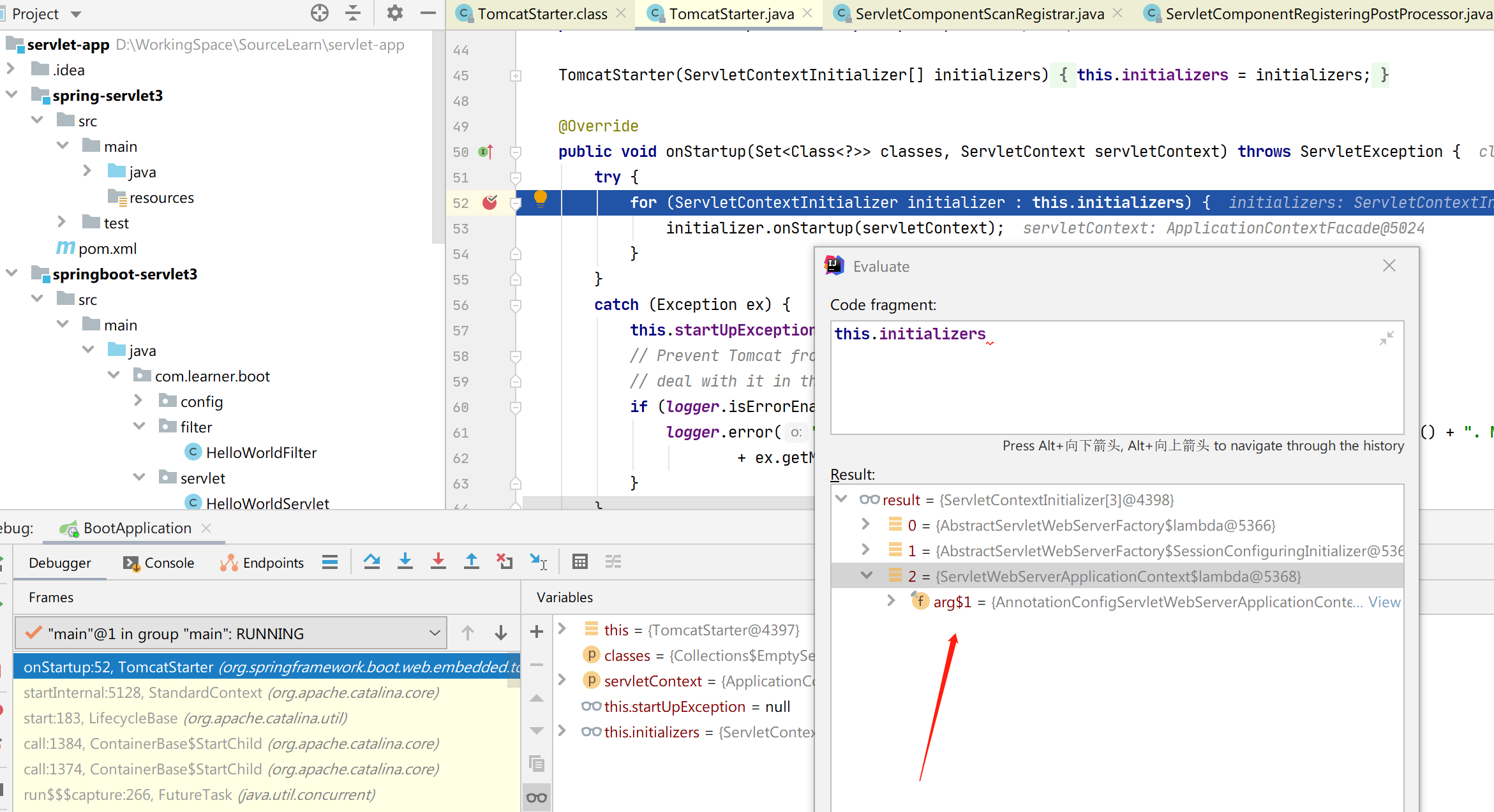
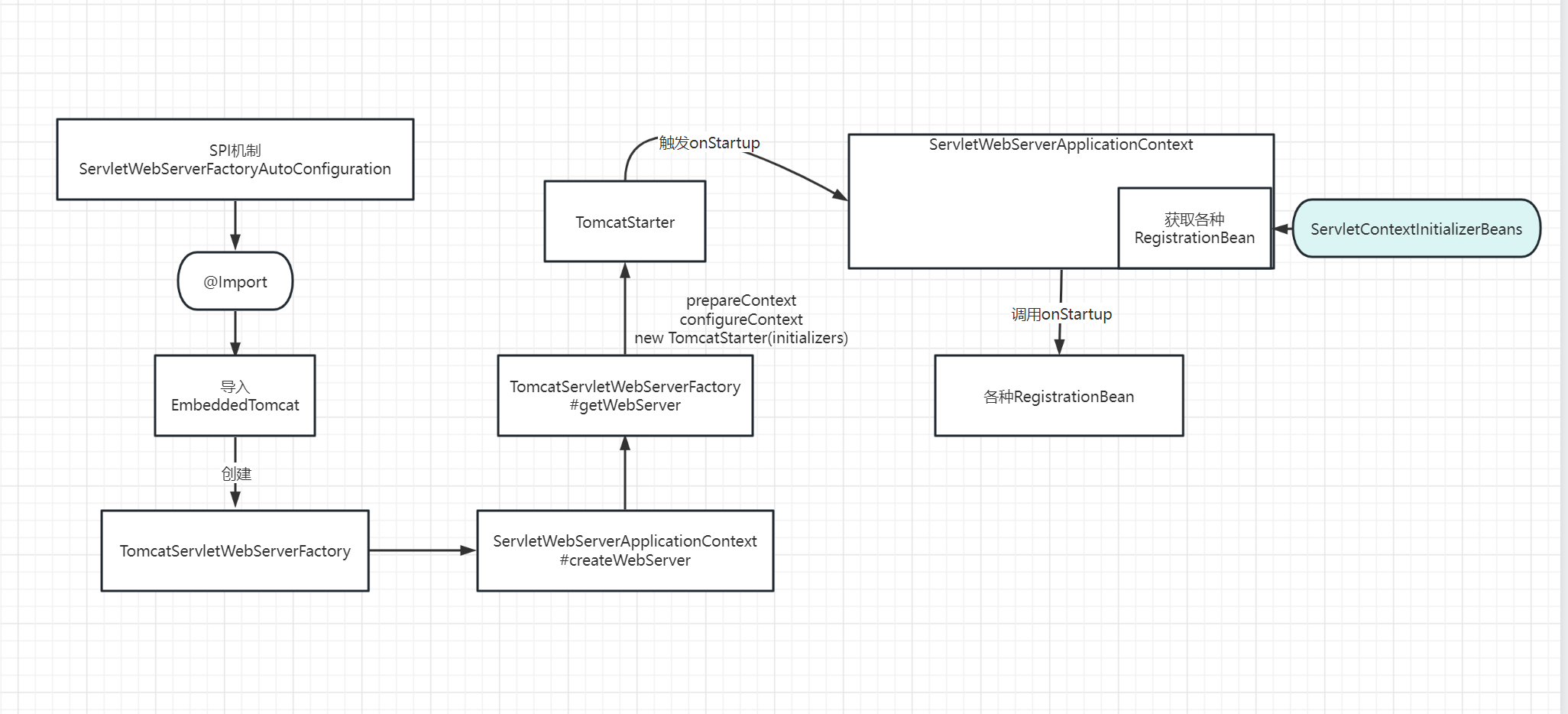
RegistrationBean 并没有出现在 TomcatStarter 的 debug 信息中,initializers 包含了三个类,其中只有第 3 个类看上去比较核心,ServletWebServerApplicationContext 的 子类 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext 对象,为了搞清楚 SpringBoot 如何加载 Filter、Servlet、Listener ,看来还得研究下 ServletWebServerApplicationContext 对象
上面是基于 SpringBoot 2.3.3.RELEASE 版本做的整体分析,如果是其他版本,可能会存在部分差异,不过原理都相同,不会有太大的变化
ServletWebServerApplicationContext 中的6层迭代加载
ApplicationContext 大家应该是比较熟悉的,这是 Spring 一个比较核心的类,一般我们可以从中获取到那些注册在容器中的托管 Bean,而这篇文章,主要分析的便是它在内嵌容器中的实现类:org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext ,重点分析它加载 Filter、Servlet 和 Listener 这部分的代码。
这里是整个代码中迭代层次最深的部分,做好心理准备起航,来看看 ServletWebServerApplicationContext 是怎么获取到所有的 Filter、Servlet 和 Listener 对象的,以下方法大部分出自于 ServletWebServerApplicationContext
第一层:onRefresh()
onRefresh() 方法,是 ApplicationContext 的生命周期方法,ServletWebServerApplicationContext 的实现非常简单,只干了一件事:
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer(); //第二层的入口
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}第二层:createWebServer()
看名字 Spring 是想创建一个内嵌的 Web 容器,代码如下:
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer()); // 第三层的入口
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context",
ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}凡是带有 Servlet,Initializer 字样的方法,都是我们需要留意的。其中 getSelfInitializer() 方法,便涉及到了我们最为关心的初始化流程,所以接着连接到了第三层
第三层:getSelfInitializer()
private org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletContextInitializer getSelfInitializer() {
return this::selfInitialize;
}
private void selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
prepareWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
ExistingWebApplicationScopes existingScopes = new ExistingWebApplicationScopes(
beanFactory);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory,
getServletContext());
existingScopes.restore();
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory,
getServletContext());
// 第四层的入口
for (ServletContextInitializer beans : getServletContextInitializerBeans()) {
beans.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}还记得前面 TomcatStarter 的 debug 信息中,第 3 个 ServletContextInitializer ServletWebServerApplicationContext 就是在 这里的 getSelfInitializer() 方法中创建的
解释下这里的 getSelfInitializer() 和 selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) 方法,为什么要这么设计?
这是典型的回调式方式,当匿名 ServletContextInitializer 类被 TomcatStarter 的 onStartup() 方法调用,设计上是触发了 selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) 方法的调用
所以这下就清晰了,为什么 TomcatStarter 中没有出现 RegistrationBean ,其实是隐式触发了 ServletWebServerApplicationContext 中的 selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) 方法。这样,在 selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) 方法中,调用 getServletContextInitializerBeans() 方法,获得 ServletContextInitializer 数组就成了关键
第四层:getServletContextInitializerBeans()
/**
* Returns {@link ServletContextInitializer}s that should be used with the embedded web server.
* By default this method will first attempt to find {@link ServletContextInitializer},
* {@link Servlet}, {@link Filter} and certain {@link EventListener} beans.
* @return the servlet initializer beans
*/
protected Collection<ServletContextInitializer> getServletContextInitializerBeans() {
return new ServletContextInitializerBeans(getBeanFactory()); //第五层的入口
}从注释中可以知晓这个 ServletContextInitializerBeans 类,就是用来加载 Servlet 和 Filter 、EventListener的
第五层:ServletContextInitializerBeans
org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletContextInitializerBeans
public ServletContextInitializerBeans(ListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.initializers = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
addServletContextInitializerBeans(beanFactory); // 第六层的入口
addAdaptableBeans(beanFactory);
List<ServletContextInitializer> sortedInitializers = this.initializers.values()
.stream()
.flatMap((value) -> value.stream()
.sorted(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
this.sortedList = Collections.unmodifiableList(sortedInitializers);
}第六层:addServletContextInitializerBeans(beanFactory)
// ServletContextInitializerBeans.java
private void addServletContextInitializerBeans(ListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
for (Entry<String, ServletContextInitializer> initializerBean : getOrderedBeansOfType(
beanFactory, ServletContextInitializer.class)) {
addServletContextInitializerBean(initializerBean.getKey(),
initializerBean.getValue(), beanFactory);
}
}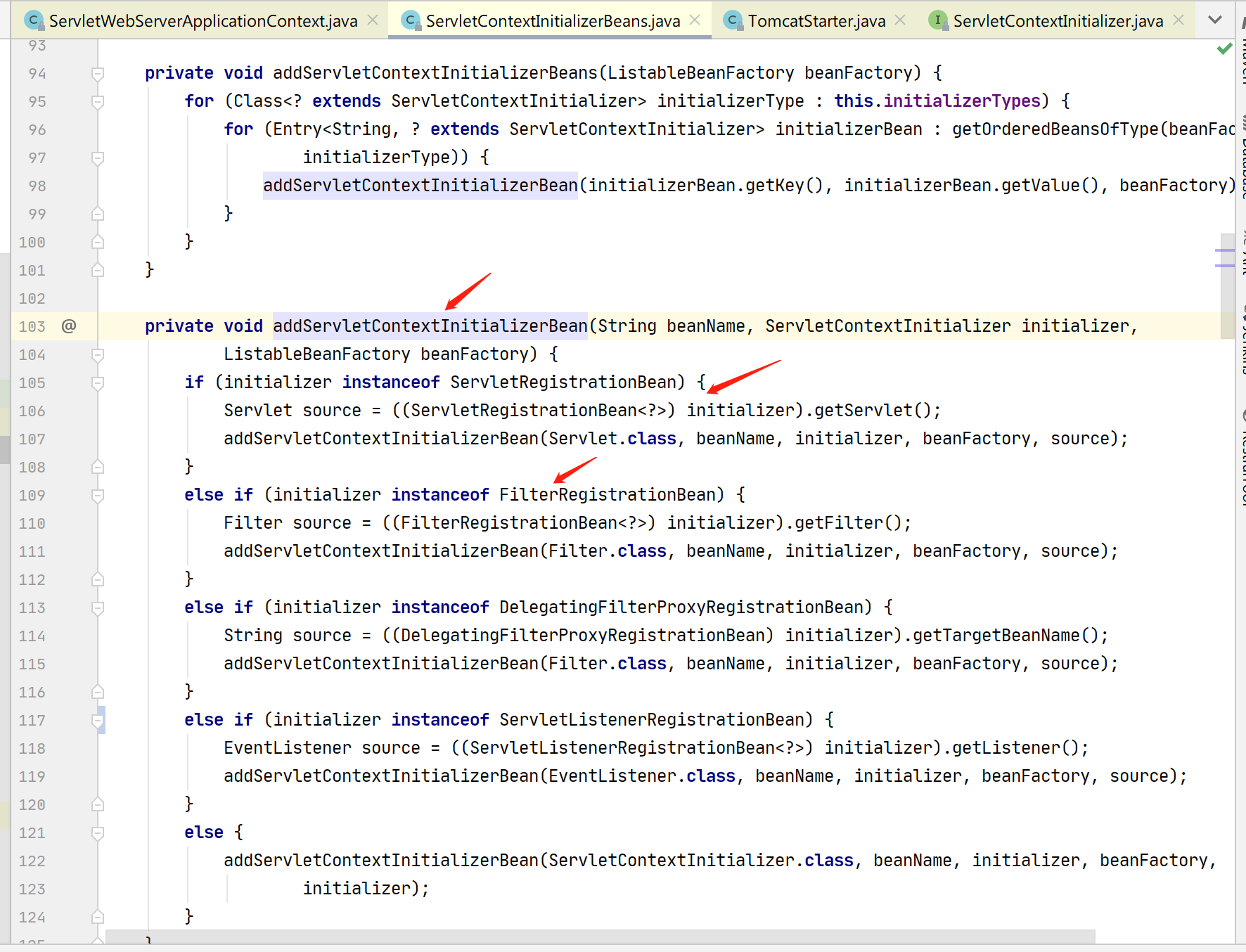
getOrderedBeansOfType(beanFactory, ServletContextInitializer.class) 方法,便是去 Spring 容器中寻找注册过的 ServletContextInitializer 对象们,这时候就可以把之前那些 RegistrationBean 全部加载出来了,并且 RegistrationBean 还实现了 Ordered 接口,在这儿用于排序
ServletWebServerApplicationContext 加载流程总结
如果你对具体的代码流程不感兴趣,可以跳过上述的 6 层分析,直接看本节的结论,总结如下:
ServletWebServerApplicationContext 的 onRefresh() 方法触发配置了一个匿名的 ServletContextInitializer
这个匿名的 ServletContextInitializer 的 onStartup 方法会去容器中搜索到了所有的 RegisterBean 并按照顺序加载到 ServletContext 中
这个匿名的 ServletContextInitializer 最终传递给 TomcatStarter,由 TomcatStarter 的 onStartup 方法去触发 ServletContextInitializer 的 onStartup 方法,最终完成装配
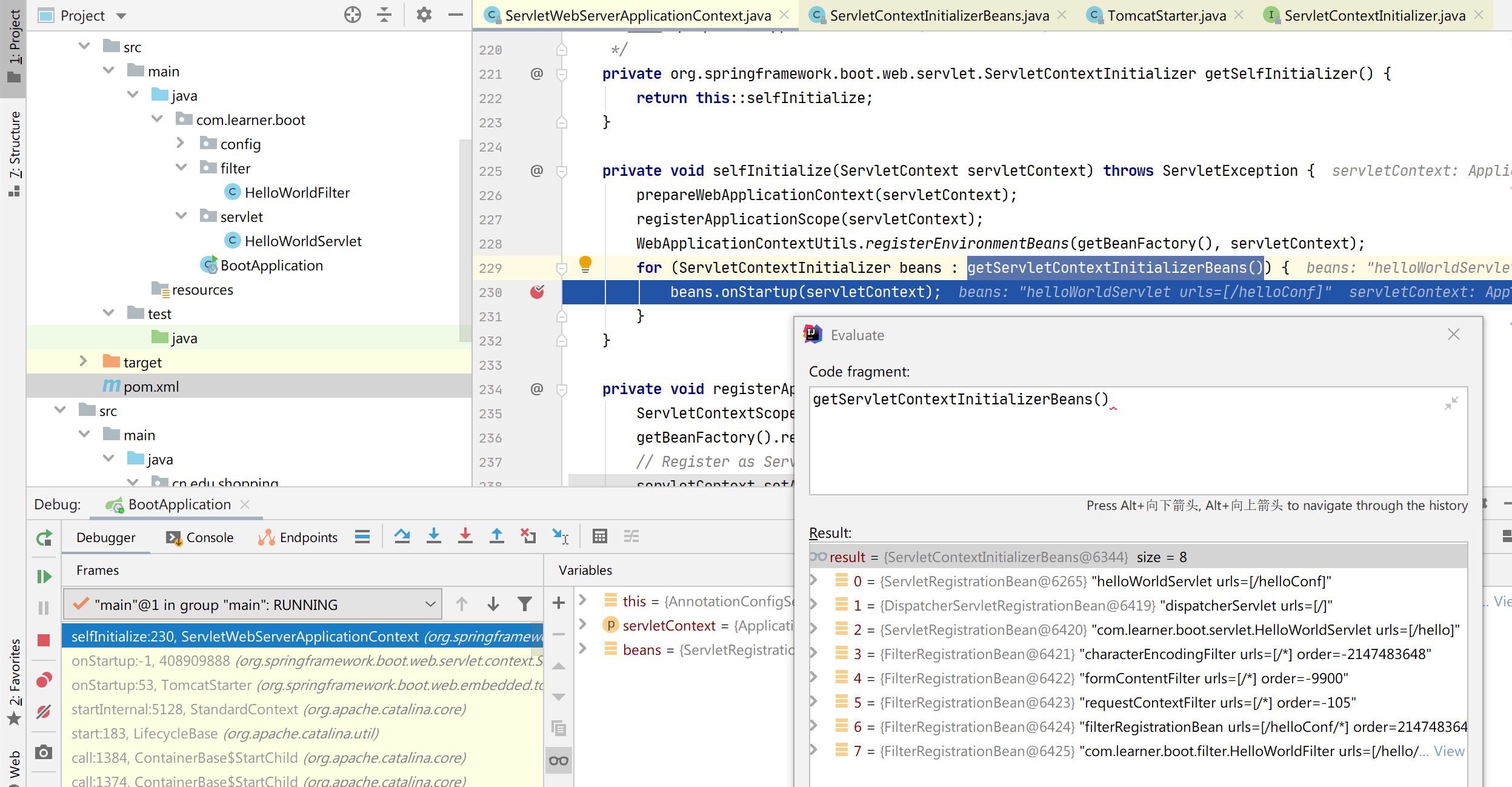
从上图中可以看到,我们配置的 Filter 和 Servlet 注册类都获取到了,然后调用其 onStartup 方法,进去后你会发现调用 ServletContext 对象的 addServlet 方法注册 Servlet,这个是 Servlet3.0 新特性
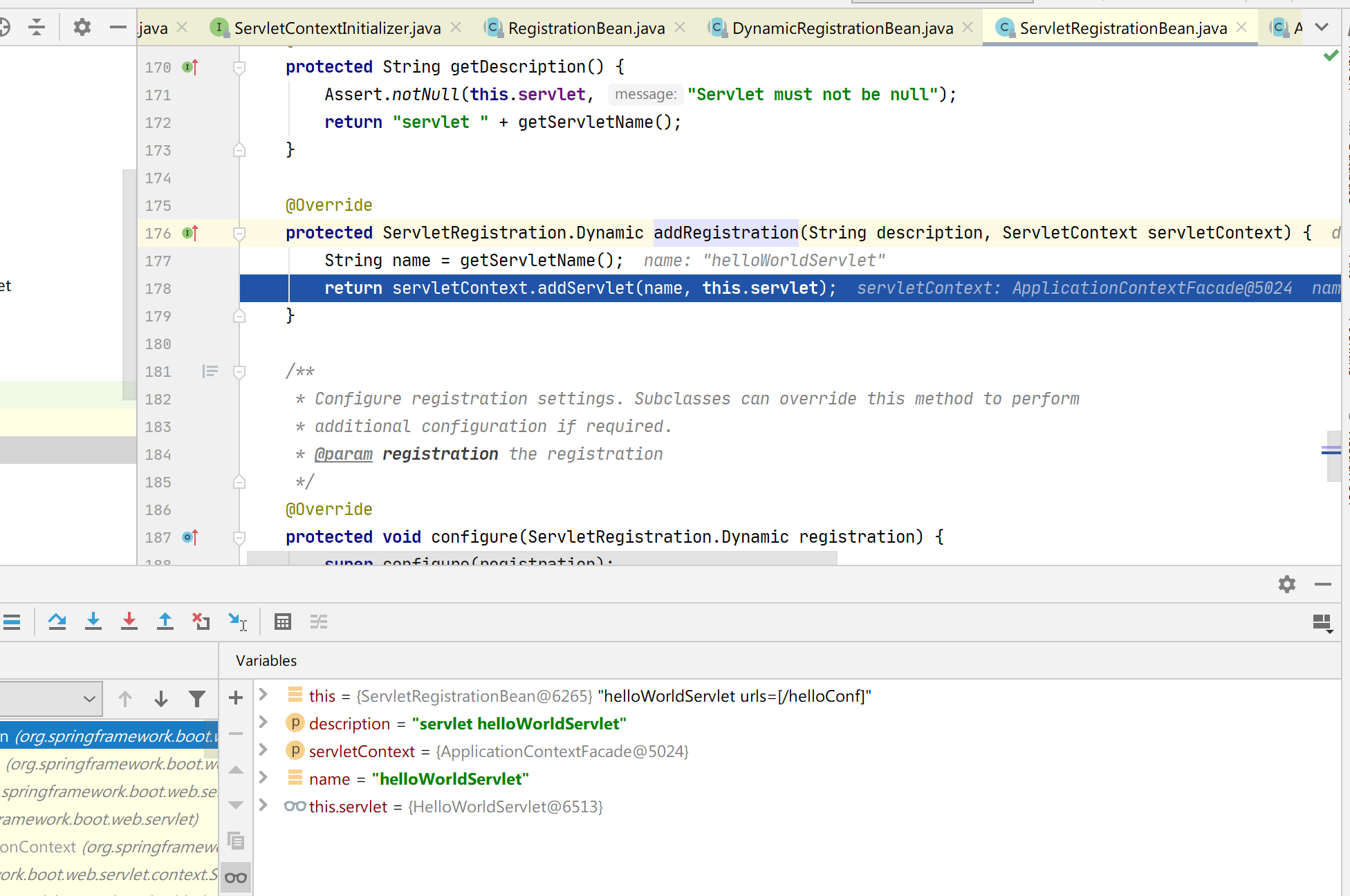
第三种注册 Servlet 的方式
研究完了上述 SpringBoot 加载 Servlet 的内部原理,可以发现 ServletContextInitializer 其实是 Spring 中 ServletContainerInitializer 的代理,虽然 SpringBoot 中 Servlet3.0 不起作用了,但它的代理还是会被加载的,于是我们有了第三种方式注册 servlet
@Configuration
public class CustomServletContextInitializer implements ServletContextInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("创建 Hello World Servlet...");
javax.servlet.ServletRegistration.Dynamic servlet = ctx.addServlet(
HelloWorldServlet.class.getSimpleName(), HelloWorldServlet.class);
servlet.addMapping("/hello");
System.out.println("创建 Hello World Filter...");
javax.servlet.FilterRegistration.Dynamic filter = ctx.addFilter(HelloWorldFilter.class.getSimpleName(), HelloWorldFilter.class);
EnumSet<DispatcherType> dispatcherTypes = EnumSet.allOf(DispatcherType.class);
dispatcherTypes.add(DispatcherType.REQUEST);
dispatcherTypes.add(DispatcherType.FORWARD);
filter.addMappingForUrlPatterns(dispatcherTypes, true, "/hello");
}
}
虽然 ServletCantainerInitializer 不能被内嵌容器加载,ServletContextInitializer 却能被 SpringBoot 的 ServletWebServerApplicationContext 加载到,从而装配其中的 Servlet 和 Filter。实际开发中,还是以一,二两种方式来注册为主,这里只是提供一个可能性,来让我们理解 SpringBoot 的加载流程
加载流程总结
TomcatStarter 既然不是通过 SPI 机制装配的,那是怎么被 Spring 使用的?
自然是被 new 出来的,在 TomcatServletWebServerFactory#configureContext 中可以看到,TomcatStarter 是被主动实例化出来的,并且还传入了 ServletContextInitializer 的数组,和上面分析的一样,一共有三个 ServletContextInitializer,包含了 ServletWebServerApplicationContext 中的匿名实现
protected void configureContext(Context context, ServletContextInitializer[] initializers) {
// <1>
TomcatStarter starter = new TomcatStarter(initializers);
// <2>
if (context instanceof TomcatEmbeddedContext) {
// Should be true
((TomcatEmbeddedContext) context).setStarter(starter);
}
// ... 省略相关代码
}<1> 处,创建了 TomcatStarter 对象。
<2> 处,通过 context instanceof TomcatEmbeddedContext 判断使用的是内嵌的 Tomcat ,所以将 TomcatStarter 作为 Initializer
如果对 <2> 处的逻辑感兴趣的胖友,可以在以下方法上打断点进行调试
TomcatServletWebServerFactory#getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers)
TomcatStarter#onStartup(Set<Class<?>> classes, ServletContext servletContext)
ServletWebServerApplicationContext#createWebServer
执行顺序:3、1、2
TomcatServletWebServerFactory 又是如何被声明的?
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRequest.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
// 这个就是我们 SpringBoot 中 application.yml 配置文件中 server.* 配置类,也就是 Tomcat 相关配置
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
@Import({ ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedJetty.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedUndertow.class })
public class ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
public ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer servletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(
ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return new ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(serverProperties);
}
@Bean
// 保证存在 Tomcat 的 Class 对象
@ConditionalOnClass(name = "org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat")
public TomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer tomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(
ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return new TomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(serverProperties);
}
// 省略 WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor 类
}其中 @Import 注解会注入 ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration 的几个静态内部类,如下:
class ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration {
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Tomcat.class, UpgradeProtocol.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public static class EmbeddedTomcat {
@Bean
public TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcatServletWebServerFactory() {
return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
}
}
// 省略 EmbeddedJetty、EmbeddedUndertow
}这样一来,只要 classpath 下存在 javax.servlet.Servlet、org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat、org.apache.coyote.UpgradeProtocol 类,并且不存在 ServletWebServerFactory 类型的 Bean 则会注入 EmbeddedTomcat 配置类,也就创建一个 TomcatServletWebServerFactory 类型的 Bean
总结
存在 web.xml 配置的 Java Web 项目,Servlet3.0 的 Java Web 项目,Spring Boot 内嵌容器的 Java Web 项目加载 Servlet,这三种项目,Servlet,Filter,Listener 的流程都是有所差异的。理解清楚这其中的由来,其实并不容易,至少得搞懂 Servlet3.0 的规范,SpringBoot 内嵌容器的加载流程等等前置逻辑
简化了整个 SpringBoot 加载 Servlet 的流程,如下图所示: