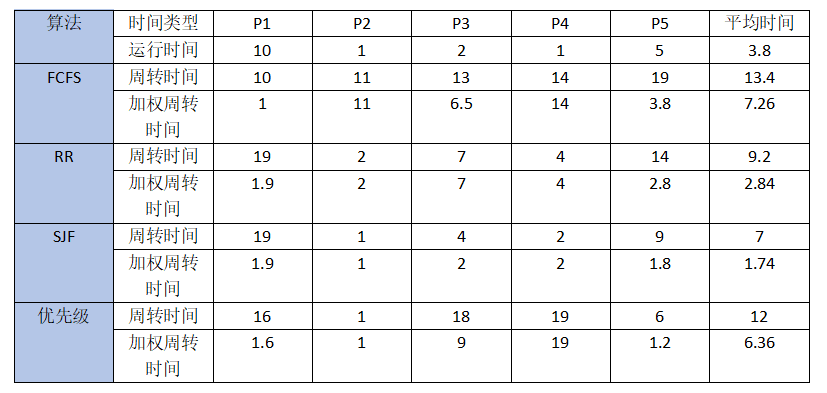
一、springboot 自动配置原理
先说说我们自己的应用程序中Bean加入容器的办法:
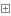
bean加入容器
我们在应用程序的入口设置了 @SpringBootApplication标签,默认情况下他会扫描所有次级目录。
如果增加了 scanBasePackages属性,就会扫描所有被指定的路径及其次级目录。
那么它在扫描的是什么东西呢?
是这个:@Component
所有被扫描到的 @Component,都会成为一个默认的singleton(单例,即一个容器里只有一个对象实体)加入到容器中。
认识到以上这点,便于我们理解springboot自动配置的机制。
接下来让我们看看在自己的应用程序中实现配置的方法。
如图:
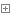
RestTemplateConfig
这里我们设置了一个配置,往容器中加入了一个RestTemplate。
首先说 @Configuration,这个标签继承了 @Component标签,我们可以在标签内容看到:
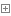
Configuration
可以看到其中是有 @Component标签的,所以,@Configuration会被 @SpringBootApplication扫描到,进而把它和它下面的 @Bean加入容器,于是我们 RestTemplate的内容就配置完成了,在后续的使用中,我们就可以直接从容器中拿出RestTemplate使用它。
对于在maven中引用的其他外部包加入容器的过程,需要用到spring.factories。
二、spring.factories文件的作用
在springboot运行时,SpringFactoriesLoader 类会去寻找
publicstatic final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
我们以mybatis-plus为例。
首先我们引入:
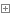
maven引包
然后去maven的依赖里看它的自动配置类MybatisPlusAutoConfiguration
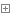
MybatisPlusAutoConfiguration
可以看到有上文提到的 @Configuration,还有从application.yml载入自动配置的 @EnableConfigurationProperties({MybatisPlusProperties.class})
这个注解的具体内容请查看我另一篇博文,对其进行了解释:
迅速学会@ConfigurationProperties的使用
也就是说,springboot只要能扫描到MybatisPlusAutoConfiguration类的 @Configuration注解,其中的所有配置就能自动加入到容器中,这一过程由上面提到的SpringFactoriesLoader 起作用,它会去寻找 “META-INF/spring.factories” 文件,我们可以在 mybatis-plus的依赖中找到它:
SpringFactoriesLoader为什么要读取它呢?因为它内部是这样的
factories
spring.factories用键值对的方式记录了所有需要加入容器的类,EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector的selectImports方法返回的类名,来自spring.factories文件内的配置信息,这些配置信息的key等于EnableAutoConfiguration,因为spring boot应用启动时使用了EnableAutoConfiguration注解,所以EnableAutoConfiguration注解通过import注解将EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector类实例化,并且将其selectImports方法返回的类名实例化后注册到spring容器。
以上内容是springboot获得这些类的方式,如果你想要实现自己的自动配置,就将你的类通过键值对的方式写在你的spring.factories即可,注意,值是你的自动配置类,键必须是org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration
三、spring.factories 的妙用
现象
在阅读 Spring-Boot 相关源码时,常常见到 spring.factories 文件,里面写了自动配置(AutoConfiguration)相关的类名,因此产生了一个疑问:“明明自动配置的类已经打上了 @Configuration 的注解,为什么还要写 spring.factories 文件?
用过 Spring Boot 的都知道
@ComponentScan 注解的作用是扫描 @SpringBootApplication 所在的 Application 类所在的包(basepackage)下所有的 @component 注解(或拓展了 @component 的注解)标记的 bean,并注册到 spring 容器中。
那么问题来了
在 Spring Boot 项目中,如果你想要被 Spring 容器管理的 bean 不在 Spring Boot 包扫描路径下,怎么办?
解决 Spring Boot 中不能被默认路径扫描的配置类的方式,有 2 种:
(1)在 Spring Boot 主类上使用 @Import 注解
(2)使用 spring.factories 文件
以下是对 使用 spring.factories 文件的简单理解
Spring Boot 的扩展机制之 Spring Factories
Spring Boot 中有一种非常解耦的扩展机制:Spring Factories。这种扩展机制实际上是仿照Java中的SPI扩展机制来实现的。
什么是 SPI 机制?
SPI 的全名为 Service Provider Interface.大多数开发人员可能不熟悉,因为这个是针对厂商或者插件的。在java.util.ServiceLoader的文档里有比较详细的介绍。
java SPI
java SPI 就是提供这样的一个机制:为某个接口寻找服务实现的机制。有点类似IOC的思想,就是将装配的控制权移到程序之外,在模块化设计中这个机制尤其重要。
Spring Boot 中的 SPI 机制
在 Spring 中也有一种类似与 Java SPI 的加载机制。它在 resources/META-INF/spring.factories 文件中配置接口的实现类名称,然后在程序中读取这些配置文件并实例化。
在 Spring 中也有一种类似与 Java SPI 的加载机制。它在 resources/META-INF/spring.factories 文件中配置接口的实现类名称,然后在程序中读取这些配置文件并实例化。
这种自定义的SPI机制是 Spring Boot Starter 实现的基础。
Spring Factories 实现原理是什么?
spring-core 包里定义了 SpringFactoriesLoader 类,这个类实现了检索 META-INF/spring.factories 文件,并获取指定接口的配置的功能。在这个类中定义了两个对外的方法:
实现
上面的两个方法的关键都是从指定的 ClassLoader 中获取 spring.factories 文件,并解析得到类名列表,具体代码如下
SpringFactoriesLoader
从代码中我们可以知道,在这个方法中会遍历整个 spring-boot 项目的 classpath 下 ClassLoader 中所有 jar 包下的 spring.factories文件。也就是说我们可以在自己的 jar 中配置 spring.factories 文件,不会影响到其它地方的配置,也不会被别人的配置覆盖。
Spring Factories 在 Spring Boot 中的应用
在 Spring Boot 的很多包中都能够找到 spring.factories 文件,接下来我们以 spring-boot-autoconfigure 包为例进行介绍
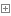
spring-boot-autoconfigure 包
结合前面的内容,可以看出 spring.factories 文件可以将 spring-boot 项目包以外的 bean(即在 pom 文件中添加依赖中的 bean)注册到 spring-boot 项目的 spring 容器。
由于@ComponentScan 注解只能扫描 spring-boot 项目包内的 bean 并注册到 spring 容器中,因此需要 @EnableAutoConfiguration 注解来注册项目包外的bean。
而 spring.factories 文件,则是用来记录项目包外需要注册的bean类名。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。