前面讲了如何离线构建yocto工程,这节讲如何创建自己的machine,在初始化yocto启动bitbake需要输入如下命令
DISTRO=fsl-imx-fb MACHINE=imx6ull14x14evk source imx-setup-release.sh -b build
其中DISTRO用来指定发行版本 MACHINE用来指定硬件平台 build为构建的目录名称
指定好以上两个参数后在运行imx-setup-release.sh脚本
imx-setup-release.sh脚本分析
在该脚本中主要执行以下内容
1.sources/meta-imx/tools/setup-utils.sh 执行setup-utils.sh脚本
2.设置了默认的machine和distro(用于没有指定machine和distro)
3.设置yocto的基本环境变量,执行以下命令
MACHINE=$MACHINE . ./$PROGNAME $BUILD_DIR 即执行以下命令
./setup-environment build
4.向$BUILD_DIR/conf/local.conf 和 $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf文件中写入重要参数
如我们要离线搭建yocoto工程local.conf中应该添加以下内容
#指定downloads路径
DL_DIR ?= "${BSPDIR}/downloads/"
# 指定SOURCE_MIRROR_URL路径
SOURCE_MIRROR_URL ?= "file://${DL_DIR}/"
#继承已有的mirror
INHERIT += "own-mirrors"
#禁止网络连接 只使用本地的源
BB_NO_NETWORK = "1"
即可以在 imx-setup-release.sh脚本中完成 如
echo "BB_NO_NETWORK = \"1\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/local.conf
#!/bin/sh
#
# i.MX Yocto Project Build Environment Setup Script
#
# Copyright (C) 2011-2016 Freescale Semiconductor
# Copyright 2017 NXP
#
# This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
# GNU General Public License for more details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
# along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
# Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
. sources/meta-imx/tools/setup-utils.sh
CWD=`pwd`
PROGNAME="setup-environment"
exit_message ()
{
echo "To return to this build environment later please run:"
echo " source setup-environment <build_dir>"
}
usage()
{
echo -e "\nUsage: source imx-setup-release.sh
Optional parameters: [-b build-dir] [-h]"
echo "
* [-b build-dir]: Build directory, if unspecified script uses 'build' as output directory
* [-h]: help
"
}
clean_up()
{
unset CWD BUILD_DIR FSLDISTRO
unset fsl_setup_help fsl_setup_error fsl_setup_flag
unset usage clean_up
unset ARM_DIR META_FSL_BSP_RELEASE
exit_message clean_up
}
# get command line options
OLD_OPTIND=$OPTIND
unset FSLDISTRO
while getopts "k:r:t:b:e:gh" fsl_setup_flag
do
case $fsl_setup_flag in
b) BUILD_DIR="$OPTARG";
echo -e "\n Build directory is " $BUILD_DIR
;;
h) fsl_setup_help='true';
;;
\?) fsl_setup_error='true';
;;
esac
done
shift $((OPTIND-1))
if [ $# -ne 0 ]; then
fsl_setup_error=true
echo -e "Invalid command line ending: '$@'"
fi
OPTIND=$OLD_OPTIND
if test $fsl_setup_help; then
usage && clean_up && return 1
elif test $fsl_setup_error; then
clean_up && return 1
fi
if [ -z "$DISTRO" ]; then
if [ -z "$FSLDISTRO" ]; then
FSLDISTRO='fsl-imx-xwayland'
fi
else
FSLDISTRO="$DISTRO"
fi
if [ -z "$BUILD_DIR" ]; then
BUILD_DIR='build'
fi
if [ -z "$MACHINE" ]; then
echo setting to default machine
MACHINE='imx6qpsabresd'
fi
case $MACHINE in
imx8*)
case $DISTRO in
*wayland)
: ok
;;
*)
echo -e "\n ERROR - Only Wayland distros are supported for i.MX 8 or i.MX 8M"
echo -e "\n"
return 1
;;
esac
;;
*)
: ok
;;
esac
# Cleanup previous meta-freescale/EULA overrides
cd $CWD/sources/meta-freescale
if [ -h EULA ]; then
echo Cleanup meta-freescale/EULA...
git checkout -- EULA
fi
if [ ! -f classes/fsl-eula-unpack.bbclass ]; then
echo Cleanup meta-freescale/classes/fsl-eula-unpack.bbclass...
git checkout -- classes/fsl-eula-unpack.bbclass
fi
cd -
# Override the click-through in meta-freescale/EULA
FSL_EULA_FILE=$CWD/sources/meta-imx/EULA.txt
# Set up the basic yocto environment
if [ -z "$DISTRO" ]; then
DISTRO=$FSLDISTRO MACHINE=$MACHINE . ./$PROGNAME $BUILD_DIR
else
MACHINE=$MACHINE . ./$PROGNAME $BUILD_DIR
fi
# Point to the current directory since the last command changed the directory to $BUILD_DIR
BUILD_DIR=.
if [ ! -e $BUILD_DIR/conf/local.conf ]; then
echo -e "\n ERROR - No build directory is set yet. Run the 'setup-environment' script before running this script to create " $BUILD_DIR
echo -e "\n"
return 1
fi
# On the first script run, backup the local.conf file
# Consecutive runs, it restores the backup and changes are appended on this one.
if [ ! -e $BUILD_DIR/conf/local.conf.org ]; then
cp $BUILD_DIR/conf/local.conf $BUILD_DIR/conf/local.conf.org
else
cp $BUILD_DIR/conf/local.conf.org $BUILD_DIR/conf/local.conf
fi
echo >> conf/local.conf
echo "# Switch to Debian packaging and include package-management in the image" >> conf/local.conf
echo "PACKAGE_CLASSES = \"package_deb\"" >> conf/local.conf
echo "EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES += \"package-management\"" >> conf/local.conf
if [ ! -e $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf.org ]; then
cp $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf.org
else
cp $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf.org $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
fi
META_FSL_BSP_RELEASE="${CWD}/sources/meta-imx/meta-bsp"
echo "" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
echo "# i.MX Yocto Project Release layers" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
hook_in_layer meta-imx/meta-bsp
hook_in_layer meta-imx/meta-sdk
hook_in_layer meta-imx/meta-ml
hook_in_layer meta-nxp-demo-experience
echo "" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
echo "BBLAYERS += \"\${BSPDIR}/sources/meta-browser\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
echo "BBLAYERS += \"\${BSPDIR}/sources/meta-rust\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
echo "BBLAYERS += \"\${BSPDIR}/sources/meta-clang\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
echo "BBLAYERS += \"\${BSPDIR}/sources/meta-openembedded/meta-gnome\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
echo "BBLAYERS += \"\${BSPDIR}/sources/meta-openembedded/meta-networking\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
echo "BBLAYERS += \"\${BSPDIR}/sources/meta-openembedded/meta-filesystems\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
echo "BBLAYERS += \"\${BSPDIR}/sources/meta-qt5\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
echo "BBLAYERS += \"\${BSPDIR}/sources/meta-python2\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
echo "BBLAYERS += \"\${BSPDIR}/sources/meta-bird-imx6ull\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
if [ -d ../sources/meta-ivi ]; then
echo -e "\n## Genivi layers" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
echo "BBLAYERS += \"\${BSPDIR}/sources/meta-gplv2\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
echo "BBLAYERS += \"\${BSPDIR}/sources/meta-ivi/meta-ivi\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
echo "BBLAYERS += \"\${BSPDIR}/sources/meta-ivi/meta-ivi-bsp\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
echo "BBLAYERS += \"\${BSPDIR}/sources/meta-ivi/meta-ivi-test\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
fi
echo "BB_NO_NETWORK = \"1\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/local.conf
echo BSPDIR=$BSPDIR
echo BUILD_DIR=$BUILD_DIR
# Support integrating community meta-freescale instead of meta-fsl-arm
if [ -d ../sources/meta-freescale ]; then
echo meta-freescale directory found
# Change settings according to environment
sed -e "s,meta-fsl-arm\s,meta-freescale ,g" -i conf/bblayers.conf
sed -e "s,\$.BSPDIR./sources/meta-fsl-arm-extra\s,,g" -i conf/bblayers.conf
fi
cd $BUILD_DIR
clean_up
unset FSLDISTRO
setup-environment分析
在该脚本中主要做了以下工作
1.判断是否为root
2.判断machine和distro是否设置
3.是否是第一次构建
4.添加一些信息到local.cof
5.最重要的是执行该命令
. $OEROOT/oe-init-build-env $CWD/$1 > /dev/null
即source/poky/下的oe-init-build-env
oe-init-build-env分析
该脚本首先判断了shell是采用那种方式调用的该脚本 . 还是 **./**或者是其他方式
This script needs to be sourced. Please run as '.
随后执行了
export OEROOT
. $OEROOT/scripts/oe-buildenv-internal &&
TEMPLATECONF="$TEMPLATECONF" $OEROOT/scripts/oe-setup-builddir || {
unset OEROOT
return 1
}
即执行$PWD/sources/poky目录下的子目录scripts中的oe-buildenv-internal和oe-setup-builddir脚本
[ -z "$BUILDDIR" ] || cd "$BUILDDIR"
判断oe-buildenv-internal和oe-setup-builddir脚本中是否设置了BUILDDIR变量,如果设置了,切换到他表示的目录里
① 检测OEROOT变量是否定义,如果没定义脚本立刻返回。OEROOT变量在oe-init-build-env脚本中设置,该变量表示oe-init-build-env脚本所在目录位置信息
② 检测主机安装python版本信息,Python2需大于2.7.3,Python3需大于3.4.0
③ 设置BUILDDIR变量等于构建目录的绝对路径信息。如果执行该脚本时没指定构建目录的路径为脚本的第一个参数的话,脚本设置使用"build"作为默认构建目录名
④ 令BITBAKEDIR="$OEROOT/bitbake,该路径是存放bitbake工具集和脚本的路径
⑤ 将"$BITBAKEDIR/bin" "$OEROOT/scripts"路径临时增加到PATH环境变量中,$BITBAKEDIR/bin路径存放的是bitbake工具,$OEROOT/scripts目录存放的是构建的脚本
⑥ 设置构建工具集使用的环境变量
回到正题
如何创建自己的machine
1.创建自己的meta-layer
在source目录下创建 meta-bird-imx6ull其结构如下
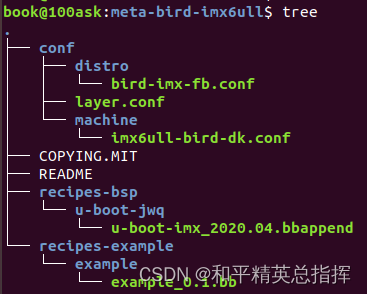
conf
该层中包含一个最重要的layer.conf和distro machine目录
conf中的layer.conf
layer.conf 定义了构建layer的参数配置 所需文件路径等 可以其他meta-layer中的layer.conf 移植而来
使用bitbake-layers show-layers可以查看所有的layer 及其编译时的 priority找到优先级最高的meta-layer对应的layer.conf 移植
即 fsl-yocto-release/sources/meta-imx/meta-bsp/conf/layer.conf
怎么修改?
1.修改 BBFILE_COLLECTIONS += "fsl-bsp-release" 为 BBFILE_COLLECTIONS += "meta-bird-imx6ull"
2.删除与imx6ull不相关的部分
conf中的machine
将/sources/metaimx/meta-bsp/conf/machine路径下的imx6ull14x14evk.conf文件拷贝至/sources/meta-birdimx6ull/machine路径下,并将其重命名为imx6ull-bird-dk.conf,作为我们构建系统所使用的硬件平台
的配置文件
conf中的distro
/sources/meta-imx/meta-sdk/conf/distro下的fsl-imx-fb.conf文件拷贝至/sources/meta-birdimx6ull/conf/distro/路径下,并将其重命名为bird-imx-fb.conf
使能meta-layer
添加BBLAYERS += "${BSPDIR}/sources/meta-bird-imx6ull"到bblayer.conf
即在imx-setup-relesas.sh中添加
echo "BBLAYERS += \"\${BSPDIR}/sources/meta-bird-imx6ull\"" >> $BUILD_DIR/conf/bblayers.conf
完成
完成后使用以下命令构建yocto
DISTRO=bird-imx-fb MACHINE=imx6ull-bird-dk source imx-setup-release.sh -b build
进入build后使用bitbake-layers show-layers可以查看到meta-bird-imx6ull