Java调用ChatGPT的小插件
- 1. 申请ChatGPT账号
- 2. 配置阶段
- 2.1 依赖引入
- 2.2 配置application.yml文件
- 2.3 @EnableChatGPT注解
- 3. 使用
- 4. 测试
1. 申请ChatGPT账号
CSDN上面有很多申请ChatGPT账号的教程,可以直接搜索chatgpt账号注册,然后按照高赞的几个回答注册就好了。
申请到ChatGPT帐号之后打开openai的官网去创建API KEYS,链接:https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys。
注意:这里的API KEYS创建好以后一定要妥善保存,创建以后,第二次就无法再查看了,想要再看,只能删除了API KEYS然后重新创建。
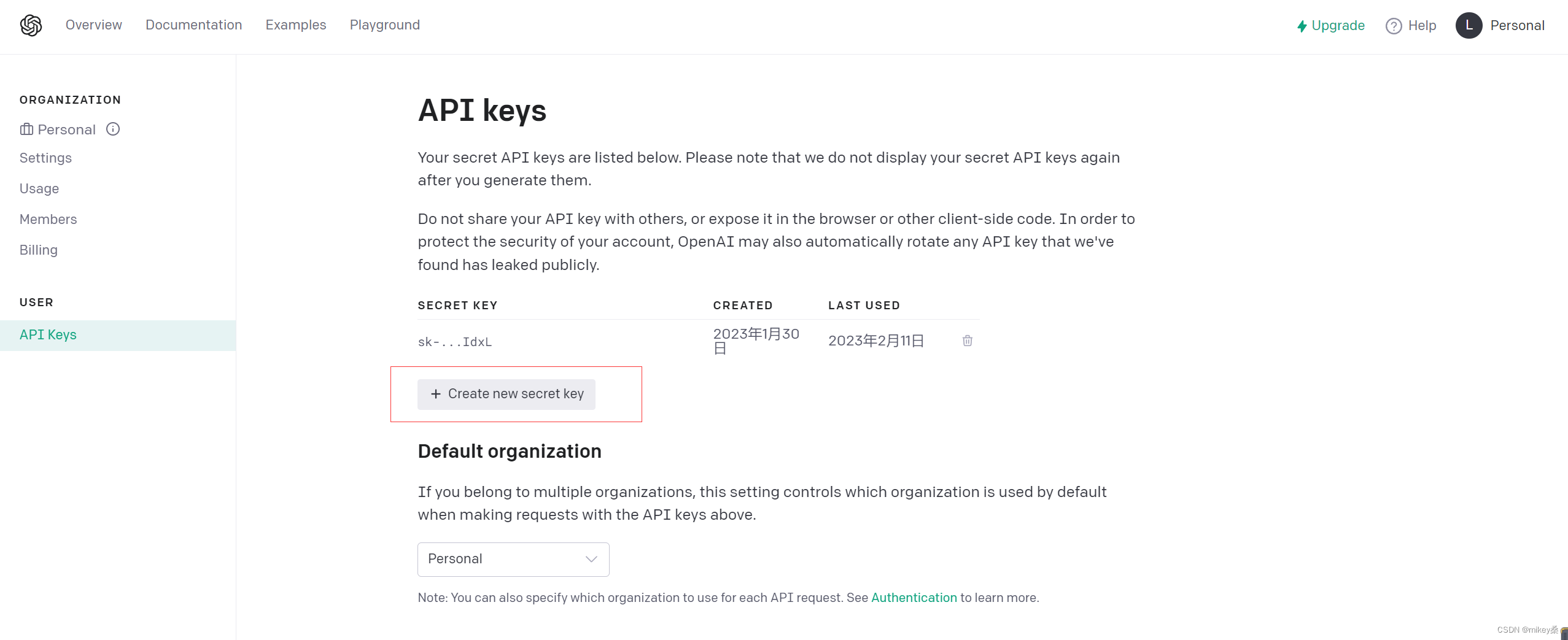
这里的API KEYS妥善保管后面会用到。
2. 配置阶段
2.1 依赖引入
pom.xml中引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.asleepyfish</groupId>
<artifactId>chatgpt</artifactId>
<version>1.0.3</version>
</dependency>
2.2 配置application.yml文件
在application.yml文件中配置chatgpt相关参数
chatgpt:
model: text-davinci-003
token: sk-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
retries: 10
这里的model是选择chatgpt哪个模型,默认填好的是最优的模型了,token就是上面申请的API KEYS,retries指的是当chatgpt第一次请求回答失败时,重新请求的次数(增加该参数的原因是因为大量访问的原因,在某一个时刻,chatgpt服务将处于无法访问的情况)
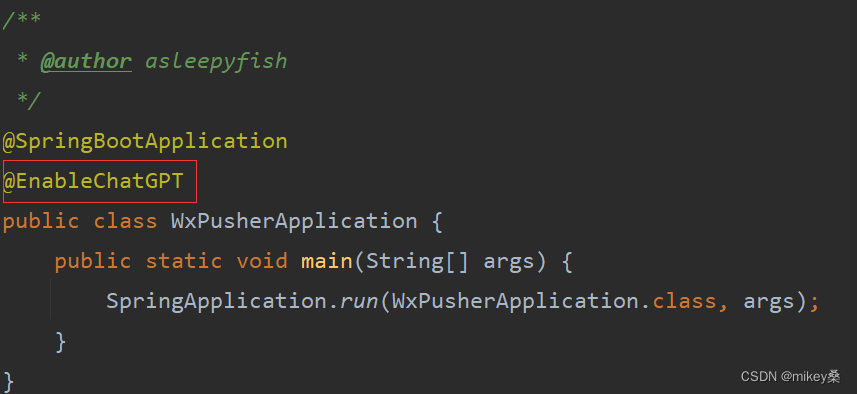
2.3 @EnableChatGPT注解
启动类上加入@EnableChatGPT注解则将ChatGPT服务注入到Spring中。
3. 使用
提供了工具类OpenAiUtils,里面提供了相关方法进行调用。
其中最简单的使用方法是:
OpenAiUtils.createCompletion(prompt);
入参prompt即输入的问题的字符串。
还提供一个通用的静态方法是
public static List<String> createCompletion(CompletionRequest completionRequest) {...}
入参CompletionRequest 里包含模型的一些可调参数。
OpenAiUtils类中还提供了多个可供选择的静态方法,可以自行查看。
上述方法的返回参数是一个list,是因为调整参数返回答案n可以一次性返回多条不同的解答(n为CompletionRequest类中一个参数)。
4. 测试
测试代码:
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void chatGPTTest() {
OpenAiUtils.createCompletion("use c++ write QuickSort").forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
ChatGPT输出结果:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// A utility function to swap two elements
void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
/* This function takes last element as pivot, places
the pivot element at its correct position in sorted
array, and places all smaller (smaller than pivot)
to left of pivot and all greater elements to right
of pivot */
int partition (int arr[], int low, int high)
{
int pivot = arr[high]; // pivot
int i = (low - 1); // Index of smaller element
for (int j = low; j <= high - 1; j++)
{
// If current element is smaller than the pivot
if (arr[j] < pivot)
{
i++; // increment index of smaller element
swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);
}
}
swap(&arr[i + 1], &arr[high]);
return (i + 1);
}
/* The main function that implements QuickSort
arr[] --> Array to be sorted,
low --> Starting index,
high --> Ending index */
void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high)
{
if (low < high)
{
/* pi is partitioning index, arr[p] is now
at right place */
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
// Separately sort elements before
// partition and after partition
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
/* Function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = {10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
quickSort(arr, 0, n - 1);
cout << "Sorted array: " << endl;
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}