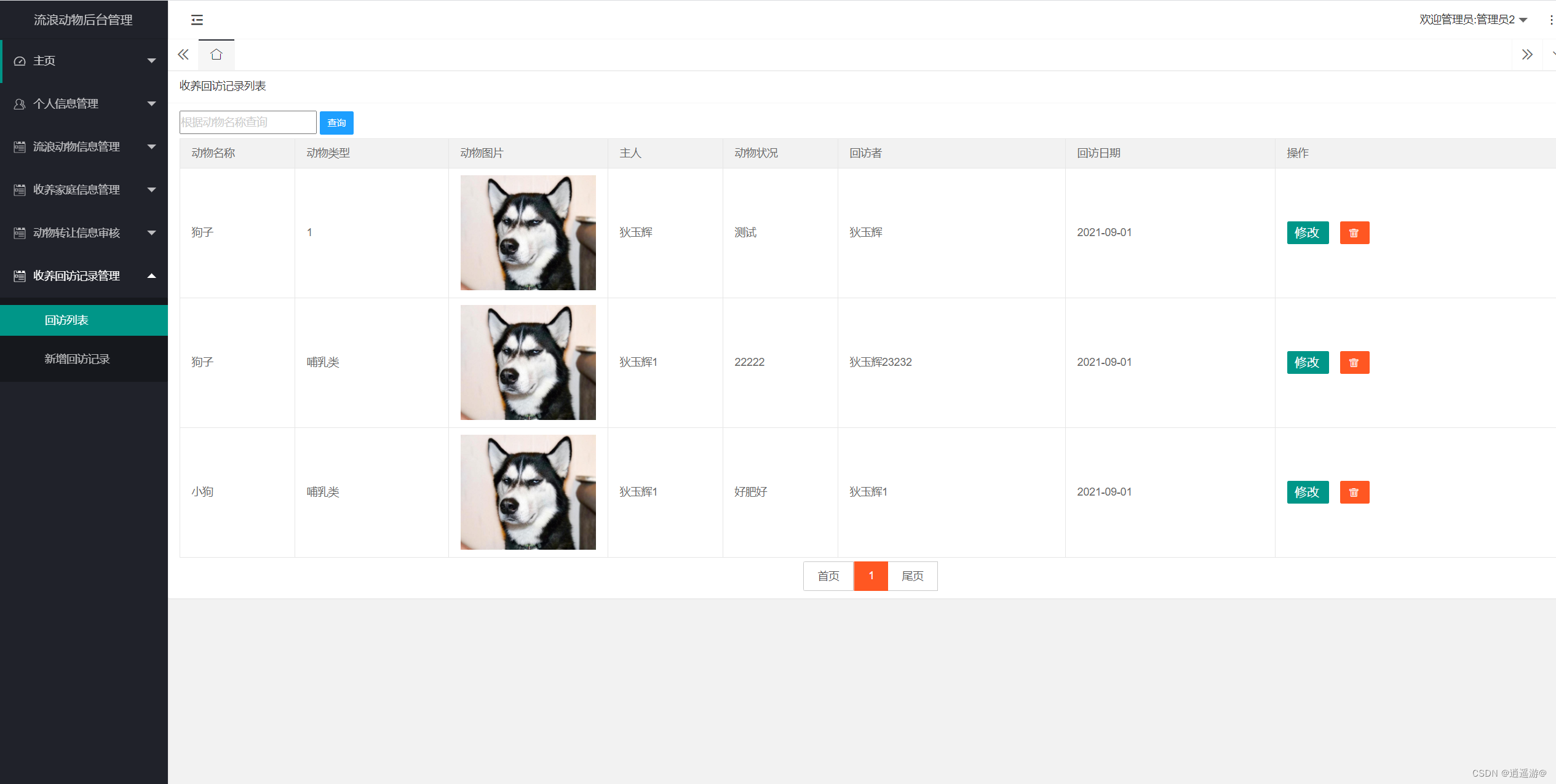
一、问题场景
现在有一只猫tom,姓名为: tom, 年龄为:1,颜色为:白色,请编写程序创建和tom猫属性完全相同的10只猫。
二、传统解决方案
public class Cat {
private String name;
private int age;
private String color;
public Cat(String name, int age, String color) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.color = color;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", color=" + color + "]";
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 传统的方法
Cat sheep = new Cat("tom", 1, "白色");
Cat sheep2 = new Cat(sheep.getName(), sheep.getAge(), sheep.getColor());
Cat sheep3 = new Cat(sheep.getName(), sheep.getAge(), sheep.getColor());
Cat sheep4 = new Cat(sheep.getName(), sheep.getAge(), sheep.getColor());
Cat sheep5 = new Cat(sheep.getName(), sheep.getAge(), sheep.getColor());
//....
System.out.println(sheep);
System.out.println(sheep2);
System.out.println(sheep3);
System.out.println(sheep4);
System.out.println(sheep5);
//...
}
}
三、传统方案分析
传统的方式的优缺点
-
优点是比较好理解,简单易操作。
-
在创建新的对象时,总是需要重新获取原始对象的属性,如果创建的对象比较复杂时,效率较低
-
总是需要重新初始化对象,而不是动态地获得对象运行时的状态, 不够灵活
-
改进的思路分析
思路:Java中Object类是所有类的根类,Object类提供了一个clone()方法,该方法可以将一个Java对象复制一份,但是需要实现clone的Java类必须要实现一个接口Cloneable, 该接口表示该类能够复制且具有复制的能力 => 原型模式
四、原型模式
1、定义
-
原型模式(Prototype模式)是指:用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷 贝这些原型,创建新的对象
-
原型模式是一种创建型设计模式,允许一个对象再创建另外一个可定制的对象, 无需知道如何创建的细节
-
工作原理是:通过将一个原型对象传给那个要发动创建的对象,这个要发动创建的对象通过请求原型对象拷贝它们自己来实施创建,即 对象.clone()
-
形象的理解:孙大圣拔出猴毛, 变出其它孙大圣
2、结构图
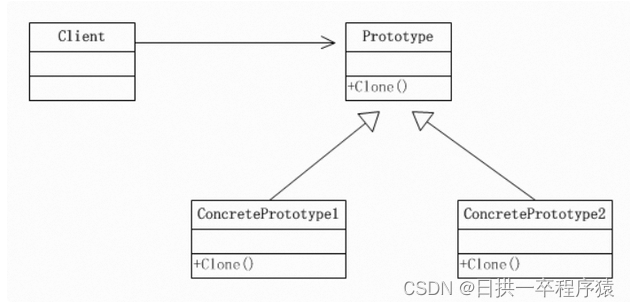
-
Prototype : 原型类,声明一个克隆自己的接口
-
ConcretePrototype: 具体的原型类, 实现一个克隆自己的操作
-
Client: 让一个原型对象克隆自己,从而创建一个新的对象(属性一样)
3、改进方案
public class Cat implements Cloneable {
private String name;
private int age;
private String color;
private String address = "南京猫";
public Cat friend;//是对象,克隆是会如何处理
public Cat(String name, int age, String color) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.color = color;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", color=" + color + ", address=" + address + "]";
}
//克隆该实例,使用默认的clone方法来完成
@Override
protected Object clone() {
Cat cat = null;
try {
cat = (Cat) super.clone();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return cat;
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("原型模式完成对象的创建");
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Cat cat = new Cat("tom", 1, "白色");
cat.friend = new Cat("jack", 2, "黑色");
Cat cat2 = (Cat) cat.clone();
//克隆
Cat cat3 = (Cat)cat.clone();
//克隆
Cat cat4 = (Cat)cat.clone();
//克隆
Cat cat5 = (Cat)cat.clone();
//克隆
System.out.println("cat2 =" + cat2 + "cat2.friend=" + cat2.friend.hashCode());
System.out.println("cat3 =" + cat3 + "cat3.friend=" + cat3.friend.hashCode());
System.out.println("cat4 =" + cat4 + "cat4.friend=" + cat4.friend.hashCode());
System.out.println("cat5 =" + cat5 + "cat5.friend=" + cat5.friend.hashCode());
}
}
4、两种实现
(1)浅拷贝
- 对于数据类型是基本数据类型的成员变量,
浅拷贝会直接进行值传递,也就是将该属性值复制一份给新的对象。
- 对于数据类型是引用数据类型的成员变量,
比如说成员变量是某个数组、某个类 的对象等,那么浅拷贝会进行引用传递,也就是只是将该成员变量的引用值(内 存地址)复制一份给新的对象。
因为实际上两个对象的该成员变量都指向同一个 实例。在这种情况下,在一个对象中修改该成员变量会影响到另一个对象的该成 员变量值
-
前面我们克隆猫就是浅拷贝
-
浅拷贝是使用默认的 clone()方法来实现 cat = (Cat) super.clone();
(2)深拷贝
-
复制对象的所有基本数据类型的成员变量值
-
为所有引用数据类型的成员变量申请存储空间,并复制每个引用数据类型成员变 量所引用的对象,直到该对象可达的所有对象。也就是说,对象进行深拷贝要对整个对象进行拷贝
-
深拷贝实现方式1:重写clone方法来实现深拷贝
-
深拷贝实现方式2:通过对象序列化实现深拷贝(推荐)
5、深拷贝实现
public class DeepProtoType implements Serializable, Cloneable{
public String name; //String 属性
public DeepCloneableTarget deepCloneableTarget;// 引用类型
public DeepProtoType() {
super();
}
//深拷贝 - 方式 1 使用clone 方法
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Object deep = null;
//这里完成对基本数据类型(属性)和String的克隆
deep = super.clone();
//对引用类型的属性,进行单独处理
DeepProtoType deepProtoType = (DeepProtoType)deep;
deepProtoType.deepCloneableTarget = (DeepCloneableTarget)deepCloneableTarget.clone();
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return deepProtoType;
}
//深拷贝 - 方式2 通过对象的序列化实现 (推荐)
public Object deepClone() {
//创建流对象
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
ByteArrayInputStream bis = null;
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
//序列化
bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(this); //当前这个对象以对象流的方式输出
//反序列化
bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
DeepProtoType copyObj = (DeepProtoType)ois.readObject();
return copyObj;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
} finally {
//关闭流
try {
bos.close();
oos.close();
bis.close();
ois.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e2.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
public class DeepCloneableTarget implements Serializable, Cloneable {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String cloneName;
private String cloneClass;
//构造器
public DeepCloneableTarget(String cloneName, String cloneClass) {
this.cloneName = cloneName;
this.cloneClass = cloneClass;
}
//因为该类的属性,都是String , 因此我们这里使用默认的clone完成即可
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
DeepProtoType p = new DeepProtoType();
p.name = "宋江";
p.deepCloneableTarget = new DeepCloneableTarget("大牛", "小牛");
//方式1 完成深拷贝
// DeepProtoType p2 = (DeepProtoType) p.clone();
//
// System.out.println("p.name=" + p.name + "p.deepCloneableTarget=" + p.deepCloneableTarget.hashCode());
// System.out.println("p2.name=" + p.name + "p2.deepCloneableTarget=" + p2.deepCloneableTarget.hashCode());
//方式2 完成深拷贝
DeepProtoType p2 = (DeepProtoType) p.deepClone();
System.out.println("p.name=" + p.name + "p.deepCloneableTarget=" + p.deepCloneableTarget.hashCode());
System.out.println("p2.name=" + p.name + "p2.deepCloneableTarget=" + p2.deepCloneableTarget.hashCode());
}
}
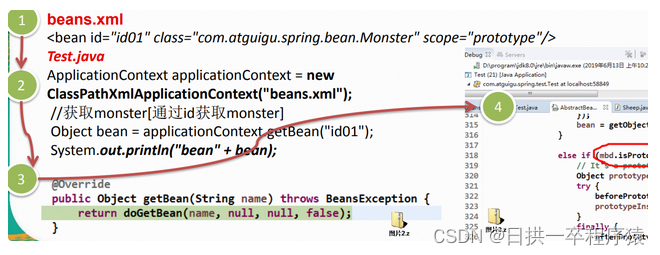
四、原型模式应用
Spring中原型bean的创建,就是原型模式的应用



![学习open62541 --- [75] 生成namespace文件的简便方法](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4152a82e3dcd414a9ed1ebac058e4894.png)