概念与背景
Systemd 是 Linux 系统工具,用来启动守护进程,已成为大多数发行版的标准配置。历史上,Linux 的启动一直采用init进程。在ubuntu18.04以后,都采用systemd启动。
更换主要原因是init进程有两个原因
- 启动时间长。init进程是串行启动,只有前一个进程启动完,才会启动下一个进程。
- 启动脚本复杂。init进程只是执行启动脚本,不管其他事情。脚本需要自己处理各种情况,这往往使得脚本变得很长。
Systemd 就是为了解决这些问题而诞生的。它的设计目标是,为系统的启动和管理提供一套完整的解决方案。
根据 Linux 惯例,字母d是守护进程(daemon)的缩写。 Systemd 这个名字的含义,就是它要守护整个系统。
使用了 Systemd,就不需要再用init了。Systemd 取代了initd,成为系统的第一个进程(PID 等于 1),其他进程都是它的子进程。Systemd 的优点是功能强大,使用方便,缺点是体系庞大,非常复杂。

Systemd搭建自启动服务
Systemd是Ubuntu 18.04默认自带的进程管理服务程序。Systemd 取代了initd,成为系统的第一个进程(PID 等于 1),其他进程都是它的子进程。
Systemd 默认从目录/etc/systemd/system/读取配置文件。但是,里面存放的大部分文件都是符号链接,指向目录/lib/systemd/system/,真正的配置文件存放在/lib/systemd/system/目录。
systemctl enable命令用于在上面两个目录之间,建立符号链接关系.
如果配置文件里面设置了开机启动,systemctl enable命令相当于激活开机启动。
与之对应的,systemctl disable命令用于在两个目录之间,撤销符号链接关系,相当于撤销开机启动。
自启服务搭建
文件复制和软链接
sudo cp -r rc-local.service /lib/systemd/system
sudo cp -r rc.local /etc/
sudo ln -s /lib/systemd/system/rc-local.service /etc/systemd/system/rc-local.service
systemctl命令启动
- 重载所有修改过的配置文件
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
- 重启rc-local服务
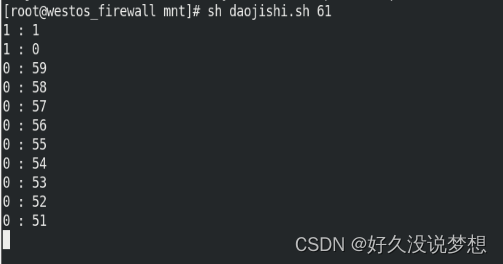
sudo systemctl restart rc-local.service
-
列出rc-local.service配置文件状态
sudo systemctl list-unit-files |grep rc-local.service
rc-local.service enabled-runtime
或
sudo systemctl status rc-local.service
● rc-local.service - /etc/rc.local Compatibility
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/rc-local.service; enabled-runtime; vendor preset: enabled)
Drop-In: /lib/systemd/system/rc-local.service.d
└─debian.conf
Active: active (exited) since Fri 2023-02-10 13:57:58 CST; 3min 44s ago
Docs: man:systemd-rc-local-generator(8)
Process: 14661 ExecStart=/etc/rc.local (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
参考链接
systemd:
http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/03/systemd-tutorial-commands.html
http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/03/systemd-tutorial-part-two.html
rc-local.serice服务文件
# SPDX-License-Identifier: LGPL-2.1+
#
# This file is part of systemd.
#
# systemd is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
# under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
# This unit gets pulled automatically into multi-user.target by
# systemd-rc-local-generator if /etc/rc.local is executable.
[Unit]
Description=/etc/rc.local Compatibility
Documentation=man:systemd-rc-local-generator(8)
ConditionFileIsExecutable=/etc/rc.local
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStart=/etc/rc.local
TimeoutSec=0
RemainAfterExit=yes
GuessMainPID=no
系统管理
Systemd 并不是一个命令,而是一组命令,涉及到系统管理的方方面面。有systemctl、systemd-analyze、hostnamectl、localectl、timedatectl、loginctl多组命令。
systemctl
systemctl是 Systemd 的主命令,用于管理系统。
# 重启系统
$ sudo systemctl reboot
# 关闭系统,切断电源
$ sudo systemctl poweroff
# CPU停止工作
$ sudo systemctl halt
# 暂停系统
$ sudo systemctl suspend
# 让系统进入冬眠状态
$ sudo systemctl hibernate
# 让系统进入交互式休眠状态
$ sudo systemctl hybrid-sleep
# 启动进入救援状态(单用户状态)
$ sudo systemctl rescue
systemd-analyze启动分析
systemd-analyze命令用于查看启动耗时。
# 查看启动耗时
$ systemd-analyze
# 查看每个服务的启动耗时
$ systemd-analyze blame
# 显示瀑布状的启动过程流
$ systemd-analyze critical-chain
# 显示指定服务的启动流
$ systemd-analyze critical-chain atd.service
hostnamectl
hostnamectl命令用于查看当前主机的信息。
# 显示当前主机的信息
$ hostnamectl
# 设置主机名。
$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname 52hz
localectl 本地设置
localectl命令用于查看本地化设置。
# 查看本地化设置
$ localectl
# 设置本地化参数。
$ sudo localectl set-locale LANG=en_GB.utf8
$ sudo localectl set-keymap en_GB
timedatectl
timedatectl命令用于查看当前时区设置。
# 查看当前时区设置
$ timedatectl
# 显示所有可用的时区
$ timedatectl list-timezones
# 设置当前时区
$ sudo timedatectl set-timezone America/New_York
$ sudo timedatectl set-time YYYY-MM-DD
$ sudo timedatectl set-time HH:MM:SS
loginctl查看登陆用户
# 列出当前session
$ loginctl list-sessions
# 列出当前登录用户
$ loginctl list-users
# 列出显示指定用户的信息
$ loginctl show-user ruanyf