ADVERSARIAL EXAMPLE GENERATION
研究推动 ML 模型变得更快、更准、更高效。设计和模型的安全性和鲁棒性经常被忽视,尤其是面对那些想愚弄模型故意对抗时。
本教程将提供您对 ML 模型的安全漏洞的认识,并将深入了解对抗性机器学习这一热门话题。在图像中添加难以察觉的扰动会导致模型性能的显著不同,鉴于这是一个教程,我们将通过图像分类器的示例来探讨这个主题。具体来说,我们将使用第一种也是最流行的攻击方法之一,快速梯度符号攻击( FGSM )来欺骗 MNIST 分类器。
Threat Model (攻击模型)
在论文中,有许多类型的对抗攻击,每种攻击都有不同的目标和攻击者的知识假设。然而,总的来说,首要目标是向输入数据添加最小数量的扰动,以导致期望的错误分类。攻击者的知识有几种假设,其中两种是: white-box (白盒)和 black-box (黑盒);白盒攻击假定攻击者具有对模型的完整知识和访问权限,包括体系结构、输入、输出和权重。黑盒攻击假设攻击者只能访问模型的输入和输出,并且对底层架构或权重一无所知。还有几种类型的目标,包括 misclassification (错误分类)和 source/target misclassification 源/目标错误分类。错误分类的目标意味着对手只希望输出分类错误,而不在乎新的分类是什么。源/目标错误分类意味着对手希望更改最初属于特定源类别的图像,从而将其分类为特定目标类别。
Fast Gradient Sign Attack
FGSM 攻击是白盒攻击,目标是错误分类。
迄今为止最早也是最流行的的对抗攻击是 Fast Gradient Sign Attack, FGSM (Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples),这种攻击非常强大, 也很直观。它旨在利用神经网络的学习方式,即梯度来攻击神经网络。这个想法很简单,而不是通过基于反向传播梯度调整权重来最小化损失,而是基于相同的反向传播梯度来调整输入数据以最大化损失。换句话说,攻击使用输入数据的损失梯度,然后调整输入数据以最大化损失。

从图中可以看出,
x
x
x 是被正确分类为 panda 的原始图像,
y
y
y 是
x
x
x 的正确标签,
θ
\theta
θ 代表的是模型参数,$ J(\theta, x, y)$ 是训练网络的 loss 。攻击反向传播梯度到输入数据计算
∇
x
J
(
θ
,
x
,
y
)
\nabla_x J(\theta, x, y)
∇xJ(θ,x,y) , 然后利用很小的步长 (
ϵ
\epsilon
ϵ 或 0.007 ) 在某个方向上最大化损失(例如:
s
i
g
n
(
∇
x
J
(
θ
,
x
,
y
)
)
sign(\nabla_x J(\theta, x, y))
sign(∇xJ(θ,x,y)) ),最后的扰动图像
x
′
x'
x′ 最后被错误分类为 gibbon, 实际上图像还是 panda 。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from six.moves import urllib
opener = urllib.request.build_opener()
opener.addheaders = [('User-agent', 'Mozilla/5.0')]
urllib.request.install_opener(opener)
Implementation
本节中,我们将讨论教程的输入参数,定义攻击下的模型,以及相关的测试
Inputs
三个输入:
- epsilons: epsilon 列表值,保持 0 在列表中非常重要,代表着原始模型的性能。 epsilon 越大代表着攻击越大。
- pretrained_model: 预训练模型,训练模型的代码在 这里. 也可以直接下载 预训练模型. 因为 google drive 无法下载,所以还可以在 CSDN资源 下载
- use_cuda: 使用 GPU;
Model Under Attack
定义了模型和 DataLoader,初始化模型和加载权重。
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, 3, 1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, 1)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(0.25)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(9216, 128)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(128, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
x = self.dropout1(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.dropout2(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
output = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
return output
epsilons = [0, .05, .1, .15, .2, .25, .3]
pretrained_model = "lenet_mnist_model.pt"
use_cuda = True
# MNIST Test dataset and dataloader declaration
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST('../../../datasets', train=False, download=True, transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
])),
batch_size=1, shuffle=True)
print("CUDA Available: ", torch.cuda.is_available())
device = torch.device('cuda' if (use_cuda and torch.cuda.is_available()) else 'cpu')
# init network
model = Net().to(device)
# load the pretrained model
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(pretrained_model, map_location='cpu'))
# set the model in evaluation mode. In this case this is for the Dropout layers
model.eval()
CUDA Available: True
Net(
(conv1): Conv2d(1, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
(conv2): Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
(dropout1): Dropout(p=0.25, inplace=False)
(dropout2): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(fc1): Linear(in_features=9216, out_features=128, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
FGSM Attack (FGSM 攻击)
我们现在定义一个函数创建一个对抗实例,通过对原始输入进行干扰。 fgsm_attack 函数有3个输入,原始输入图像 x x x,像素方向扰动量 ϵ \epsilon ϵ ,梯度损失,(例如 ∇ x J ( θ , x , y ) \nabla_x J(\mathbf{\theta}, \mathbf{x}, y) ∇xJ(θ,x,y))
创建干扰图像
p e r t u r b e d i m a g e = i m a g e + e p s i l o n ∗ s i g n ( d a t a g r a d ) = x + ϵ ∗ s i g n ( ∇ x J ( θ , x , y ) ) perturbed_image=image+epsilon∗sign(data_grad)=x+ϵ∗sign(∇x J(θ,x,y)) perturbedimage=image+epsilon∗sign(datagrad)=x+ϵ∗sign(∇xJ(θ,x,y))
最后,为了保持原始图像的数据范围,干扰图像被缩放到 [0, 1]
# FGSM attack code
def fgsm_attack(image, epsilon, data_grad):
# collect the element-wise sign of the data gradient
sign_data_grad = data_grad.sign()
# create the perturbed image by adjusting each pixel of the input image
perturbed_image = image + epsilon * sign_data_grad
# adding clipping to maintain [0, 1] range
perturbed_image = torch.clamp(perturbed_image, 0, 1)
# return the perturbed image
return perturbed_image
Testing Function (测试函数)
def test(model, device, test_loader, epsilon):
# accuracy counter
correct = 0
adv_examples = []
# loop over all examples in test set
for data, target in test_loader:
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
# Set requires_grad attribute of tensor. Important for Attack
data.requires_grad = True
#
output = model(data)
init_pred = output.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
# if the initial prediction is wrong, don't botter attacking, just move on
if init_pred.item() != target.item():
continue
# calculate the loss
loss = F.nll_loss(output, target)
# zero all existing grad
model.zero_grad()
# calculate gradients of model in backward loss
loss.backward()
# collect datagrad
data_grad = data.grad.data
# call FGSM attack
perturbed_data = fgsm_attack(data, epsilon, data_grad)
# reclassify the perturbed image
output = model(perturbed_data)
# check for success
final_pred = output.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
#
if final_pred.item() == target.item():
correct += 1
# special case for saving 0 epsilon examples
if (epsilon == 0) and (len(adv_examples) < 5):
adv_ex = perturbed_data.squeeze().detach().cpu().numpy()
adv_examples.append((init_pred.item(), final_pred.item(), adv_ex))
else:
# Save some adv examples for visualization later
if len(adv_examples) < 5:
adv_ex = perturbed_data.squeeze().detach().cpu().numpy()
adv_examples.append( (init_pred.item(), final_pred.item(), adv_ex) )
# Calculate final accuracy for this epsilon
final_acc = correct/float(len(test_loader))
print("Epsilon: {}\tTest Accuracy = {} / {} = {}".format(epsilon, correct,
len(test_loader), final_acc))
# Return the accuracy and an adversarial example
return final_acc, adv_examples
Run Attack (执行攻击)
实现的最后一步是执行攻击,我们针对每个 epsilon 执行全部的 test step,并且保存最终的准确率和一些成功的对抗实例。 ϵ = 0 \epsilon=0 ϵ=0 不执行攻击
accuracies = []
examples = []
# Run test for each epsilon
for eps in epsilons:
acc, ex = test(model, device, test_loader, eps)
accuracies.append(acc)
examples.append(ex)
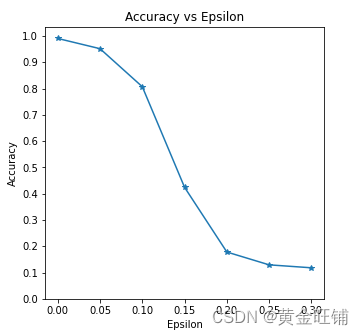
Epsilon: 0 Test Accuracy = 9906 / 10000 = 0.9906
Epsilon: 0.05 Test Accuracy = 9517 / 10000 = 0.9517
Epsilon: 0.1 Test Accuracy = 8070 / 10000 = 0.807
Epsilon: 0.15 Test Accuracy = 4242 / 10000 = 0.4242
Epsilon: 0.2 Test Accuracy = 1780 / 10000 = 0.178
Epsilon: 0.25 Test Accuracy = 1292 / 10000 = 0.1292
Epsilon: 0.3 Test Accuracy = 1180 / 10000 = 0.118
Accuracy vs Epsilon (正确率 VS epsilon)
ϵ \epsilon ϵ 增大时,我们期望正确率下降,因为大的 ϵ \epsilon ϵ 我们在方向上有大的变换可以最大化 loss. 他们的变换不是线性的,一开始下降的慢,中间下降的快,最后下降的慢。
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.plot(epsilons, accuracies, "*-")
plt.yticks(np.arange(0, 1.1, step=0.1))
plt.xticks(np.arange(0, .35, step=0.05))
plt.title("Accuracy vs Epsilon")
plt.xlabel("Epsilon")
plt.ylabel("Accuracy")
plt.show()
Sample Adversarial Examples (对抗实例)
# Plot several examples of adversarial samples at each epsilon
cnt = 0
plt.figure(figsize=(8,10))
for i in range(len(epsilons)):
for j in range(len(examples[i])):
cnt += 1
plt.subplot(len(epsilons),len(examples[0]),cnt)
plt.xticks([], [])
plt.yticks([], [])
if j == 0:
plt.ylabel("Eps: {}".format(epsilons[i]), fontsize=14)
orig,adv,ex = examples[i][j]
plt.title("{} -> {}".format(orig, adv))
plt.imshow(ex, cmap="gray")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

完整代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from six.moves import urllib
opener = urllib.request.build_opener()
opener.addheaders = [('User-agent', 'Mozilla/5.0')]
urllib.request.install_opener(opener)
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, 3, 1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, 1)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(0.25)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(9216, 128)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(128, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
x = self.dropout1(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.dropout2(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
output = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
return output
epsilons = [0, .05, .1, .15, .2, .25, .3]
pretrained_model = "lenet_mnist_model.pt"
use_cuda = True
# MNIST Test dataset and dataloader declaration
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST('../../../datasets', train=False, download=True, transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
])),
batch_size=1, shuffle=True)
print("CUDA Available: ", torch.cuda.is_available())
device = torch.device('cuda' if (use_cuda and torch.cuda.is_available()) else 'cpu')
# init network
model = Net().to(device)
# load the pretrained model
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(pretrained_model, map_location='cpu'))
# set the model in evaluation mode. In this case this is for the Dropout layers
model.eval()
# FGSM attack code
def fgsm_attack(image, epsilon, data_grad):
# collect the element-wise sign of the data gradient
sign_data_grad = data_grad.sign()
# create the perturbed image by adjusting each pixel of the input image
perturbed_image = image + epsilon * sign_data_grad
# adding clipping to maintain [0, 1] range
perturbed_image = torch.clamp(perturbed_image, 0, 1)
# return the perturbed image
return perturbed_image
def test(model, device, test_loader, epsilon):
# accuracy counter
correct = 0
adv_examples = []
# loop over all examples in test set
for data, target in test_loader:
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
# Set requires_grad attribute of tensor. Important for Attack
data.requires_grad = True
#
output = model(data)
init_pred = output.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
# if the initial prediction is wrong, don't botter attacking, just move on
if init_pred.item() != target.item():
continue
# calculate the loss
loss = F.nll_loss(output, target)
# zero all existing grad
model.zero_grad()
# calculate gradients of model in backward loss
loss.backward()
# collect datagrad
data_grad = data.grad.data
# call FGSM attack
perturbed_data = fgsm_attack(data, epsilon, data_grad)
# reclassify the perturbed image
output = model(perturbed_data)
# check for success
final_pred = output.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
#
if final_pred.item() == target.item():
correct += 1
# special case for saving 0 epsilon examples
if (epsilon == 0) and (len(adv_examples) < 5):
adv_ex = perturbed_data.squeeze().detach().cpu().numpy()
adv_examples.append(
(init_pred.item(), final_pred.item(), adv_ex))
else:
# Save some adv examples for visualization later
if len(adv_examples) < 5:
adv_ex = perturbed_data.squeeze().detach().cpu().numpy()
adv_examples.append(
(init_pred.item(), final_pred.item(), adv_ex))
# Calculate final accuracy for this epsilon
final_acc = correct/float(len(test_loader))
print("Epsilon: {}\tTest Accuracy = {} / {} = {}".format(epsilon, correct,
len(test_loader), final_acc))
# Return the accuracy and an adversarial example
return final_acc, adv_examples
accuracies = []
examples = []
# Run test for each epsilon
for eps in epsilons:
acc, ex = test(model, device, test_loader, eps)
accuracies.append(acc)
examples.append(ex)
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.plot(epsilons, accuracies, "*-")
plt.yticks(np.arange(0, 1.1, step=0.1))
plt.xticks(np.arange(0, .35, step=0.05))
plt.title("Accuracy vs Epsilon")
plt.xlabel("Epsilon")
plt.ylabel("Accuracy")
plt.show()
# Plot several examples of adversarial samples at each epsilon
cnt = 0
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 10))
for i in range(len(epsilons)):
for j in range(len(examples[i])):
cnt += 1
plt.subplot(len(epsilons), len(examples[0]), cnt)
plt.xticks([], [])
plt.yticks([], [])
if j == 0:
plt.ylabel("Eps: {}".format(epsilons[i]), fontsize=14)
orig, adv, ex = examples[i][j]
plt.title("{} -> {}".format(orig, adv))
plt.imshow(ex, cmap="gray")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
【参考】
ADVERSARIAL EXAMPLE GENERATION