由于项目的需要提取图像之中的一个接近于竖直的物体,一般的方法是进行图像分割,分割方式使用什么OTSU方式以及hsv方法等等。但是项目中使用的相机是黑白相机,会受到一定的限制。因此想到的是使用线条提取方式。线条提取方式之中最好的方法是使用canny算法,但是这里不能够将接近竖直特征进行提取,因此,此处使用了Prewitt算子进行提取,但是只用这个算法,轮廓提取不出来,就结合了一下canny算子。下面是我的思路,感觉实现过程比较麻烦,但是居然实现了[苦笑]!!!!
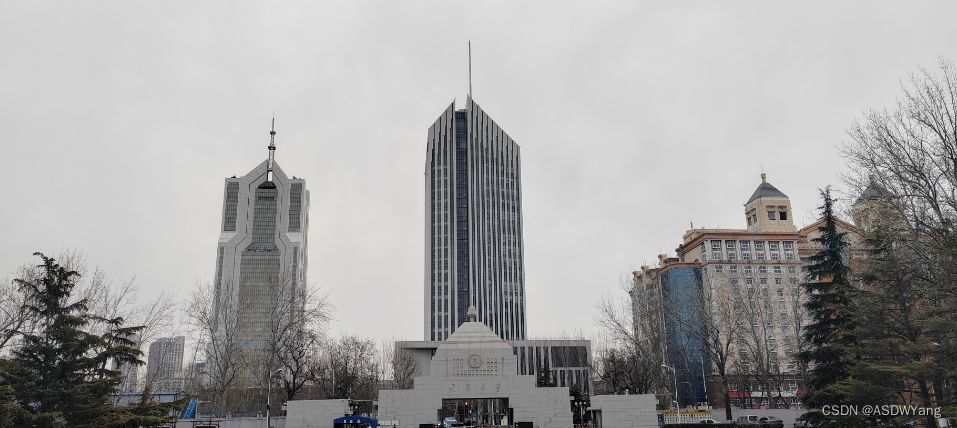
本次测试的案例是使用校门口的一个图片,图中存在很多的干扰,如下图所示

#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void getPrewitt_oper(cv::Mat& getPrewitt_horizontal, cv::Mat& getPrewitt_vertical, cv::Mat& getPrewitt_Diagonal1, cv::Mat& getPrewitt_Diagonal2) {
//水平方向
getPrewitt_horizontal = (cv::Mat_<float>(3, 3) << -1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1);
//垂直方向
getPrewitt_vertical = (cv::Mat_<float>(3, 3) << -1, 0, 1, -1, 0, 1, -1, 0, 1);
//对角135°
getPrewitt_Diagonal1 = (cv::Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 0, 1, 1, -1, 0, 1, -1, -1, 0);
//对角45°
getPrewitt_Diagonal2 = (cv::Mat_<float>(3, 3) << -1, -1, 0, -1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1);
//逆时针反转180°得到卷积核
cv::flip(getPrewitt_horizontal, getPrewitt_horizontal, -1);
cv::flip(getPrewitt_vertical, getPrewitt_vertical, -1);
cv::flip(getPrewitt_Diagonal1, getPrewitt_Diagonal1, -1);
cv::flip(getPrewitt_Diagonal2, getPrewitt_Diagonal2, -1);
}
void edge_Prewitt(cv::Mat& src, cv::Mat& dst1, cv::Mat& dst2, cv::Mat& dst3, cv::Mat& dst4, cv::Mat& dst, int ddepth, double delta = 0, int borderType = cv::BORDER_DEFAULT) {
//获取Prewitt算子
cv::Mat getPrewitt_horizontal;
cv::Mat getPrewitt_vertical;
cv::Mat getPrewitt_Diagonal1;
cv::Mat getPrewitt_Diagonal2;
getPrewitt_oper(getPrewitt_horizontal, getPrewitt_vertical, getPrewitt_Diagonal1, getPrewitt_Diagonal2);
//卷积得到水平方向边缘
cv::filter2D(src, dst1, ddepth, getPrewitt_horizontal, cv::Point(-1, -1), delta, borderType);
//卷积得到4垂直方向边缘
cv::filter2D(src, dst2, ddepth, getPrewitt_vertical, cv::Point(-1, -1), delta, borderType);
//卷积得到45°方向边缘
cv::filter2D(src, dst3, ddepth, getPrewitt_Diagonal1, cv::Point(-1, -1), delta, borderType);
//卷积得到135°方向边缘
cv::filter2D(src, dst4, ddepth, getPrewitt_Diagonal2, cv::Point(-1, -1), delta, borderType);
//边缘强度(近似)
cv::convertScaleAbs(dst1, dst1); //求绝对值并转为无符号8位图
cv::convertScaleAbs(dst2, dst2);
cv::convertScaleAbs(dst3, dst3); //求绝对值并转为无符号8位图
cv::convertScaleAbs(dst4, dst4);
dst = dst1 + dst2;
}
//数组从大到小排序
void reserve(int x[], int n) {
int i, j, temp;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { //一共n个元素,则需要比较n-1次
for (j = 0; j < n - 1 - i; j++) { //每一个元素需要比较的次数
if (x[i] < x[i + j + 1]) {
temp = x[i];
x[i] = x[i + j + 1];
x[i + j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cv::Mat src = cv::imread("楼.jpg");
if (src.empty()) {
return -1;
}
cout << "??" << endl;
if (src.channels() > 1) cv::cvtColor(src, src, CV_RGB2GRAY);
cv::Mat dst, dst1, dst2, dst3, dst4, dst5;
Mat src1 = cv::imread("楼.jpg");
Mat src2 = cv::imread("楼.jpg");
//medianBlur(src, src, 5); //均值滤波
GaussianBlur(src, src, Size(5, 5), 0); //高斯滤波
cout << "??" << endl;
//注意:要采用CV_32F,因为有些地方卷积后为负数,若用8位无符号,则会导致这些地方为0
edge_Prewitt(src, dst1, dst2, dst3, dst4, dst, CV_32F);
cv::namedWindow("垂直边缘", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("垂直边缘", dst2);
cout << "??" << endl;
//获取结构
cv::Mat element1 = cv::getStructuringElement(cv::MORPH_RECT, cv::Size(3, 3));
Mat out1;
//进行形态学开运算操作
morphologyEx(dst2, out1, MORPH_OPEN, element1);//形态学开运算
cv::namedWindow("xingtai", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("xingtai", out1);
//第二次进行形态学操作
edge_Prewitt(dst2, dst1, out1, dst3, dst4, dst, CV_32F);
cv::namedWindow("垂直边缘1", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("垂直边缘1", out1);
cout << "??" << endl;
morphologyEx(out1, out1, MORPH_OPEN, element1);//形态学开运算
cv::namedWindow("xingtai1", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("xingtai1", out1);
//获取结构
cv::Mat element2 = cv::getStructuringElement(cv::MORPH_ELLIPSE, cv::Size(10, 10));
Mat out2;
//进行形态学闭运算操作
morphologyEx(out1, out2, MORPH_CLOSE, element2);//形态学开运算
cv::namedWindow("xingtai2", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("xingtai2", out2);
imwrite("xingtai2.jpg", out2);
/*
//膨胀运算,将细小缝隙填补上,非必要
Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(0, Size(3, 3));
dilate(out2, dst2, kernel);
cv::namedWindow("膨胀", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("膨胀", dst2);
*/
cv::threshold(out2, dst2, 5, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
cv::namedWindow("二值化", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("二值化", dst2);
cv::threshold(dst2, dst2, 5, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY_INV);
cv::namedWindow("反二值化", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("反二值化", dst2);
//进行形态学闭运算操作
morphologyEx(dst2, out2, MORPH_CLOSE, element2);//形态学开运算
cv::namedWindow("xingtai3", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("xingtai3", out2);
imwrite("xingtai3.jpg", out2);
/*
cv::threshold(dst2, dst2, 5, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
cv::namedWindow("反二值化", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("反二值化", dst2);
imwrite("反二值化.jpg", dst2);
*/
/*
//膨胀运算,将细小缝隙填补上,非必要
Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(0, Size(5, 5));
dilate(out2, out2, kernel);
cv::namedWindow("膨胀1", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("膨胀1", out2);*/
Canny(out2, dst2, 5, 10);
cv::namedWindow("Canny", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("Canny", dst2);
imwrite("Canny.jpg", dst2);
vector<Vec4i> lines;
HoughLinesP(dst2, lines, 1, CV_PI / 180, 50, 200, 30);
int Length[100] = {0};//存放直线长度
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++)
{
Vec4i I = lines[i];
double x1 = I[0];
double y1 = I[1];
double x2 = I[2];
double y2 = I[3];
//筛选满足条件的点
if (abs(x1 - x2) + abs(y1 - y2) > 50)
{
Length[i] = sqrt( (x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
//将满足条件的点画出
line(src1, Point2d(x1, y1), Point2d(x2, y2), Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2);
cout << " " << "(" << x1 << "," << y1 << ")" << " " << "(" << x2 << "," << y2 << ")" << endl;
//line(canny, Point2d(x1, y1), Point2d(x2, y2), Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2);
}
}
Mat imgShow;
imgShow = src1;
resize(imgShow, imgShow, Size(imgShow.cols / 4, imgShow.rows / 4));
imshow("imgShow", imgShow);
imwrite("shuchu.png", src1);
reserve(Length, 100);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
cout << "长度"<<Length[i] << endl; //输出排序后的数组元素
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++)
{
Vec4i I = lines[i];
double x1 = I[0];
double y1 = I[1];
double x2 = I[2];
double y2 = I[3];
cout << "sdjk" << endl;
cout << int(sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2))) << endl;
//筛选满足条件的点
if ((int(sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2))) == Length[0] ) || (int(sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2))) == Length[1]))
{
//将满足条件的点画出
line(src2, Point2d(x1, y1), Point2d(x2, y2), Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2);
cout << "djfkljsa " << "(" << x1 << "," << y1 << ")" << " " << "(" << x2 << "," << y2 << ")" << endl;
//line(canny, Point2d(x1, y1), Point2d(x2, y2), Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2);
}
}
imgShow = src2;
resize(imgShow, imgShow, Size(imgShow.cols / 4, imgShow.rows / 4));
imshow("imgShow2", imgShow);
imwrite("shuchu2.png", src2);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}调试过程:本次在进行调试过程之中进行了两次垂直检测迭代,进一步去排除水平线的干扰.使用形态学操作去除图片之中的空洞等等.
第一次进行垂直检测,注意这个地方只能够用特定的算子进行垂直检测,别的算子没有这个效果.
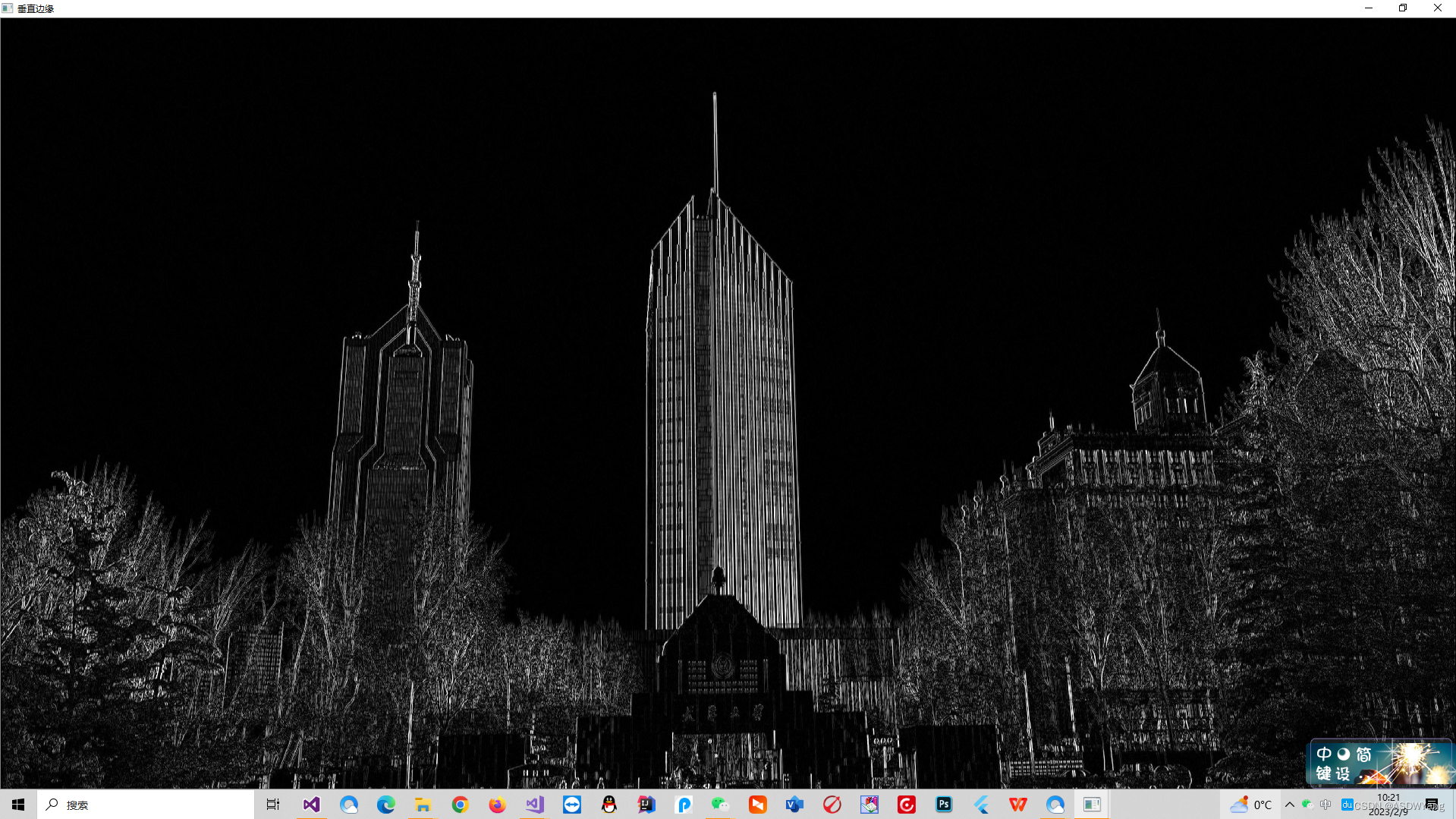
为了减少图片之中白色空洞的干扰,使用开操作.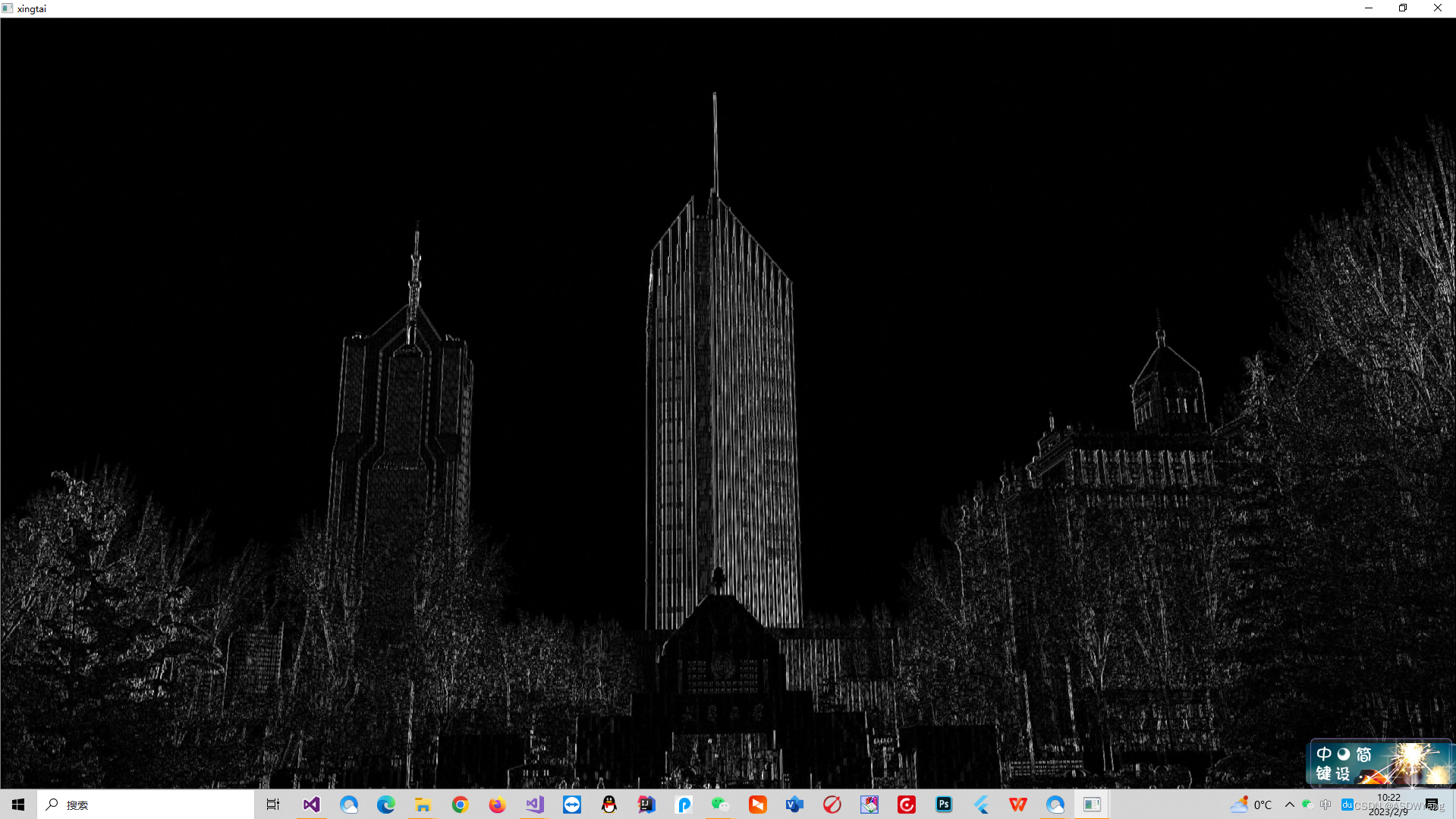
重复上述操作,进一步排除水平线的干扰.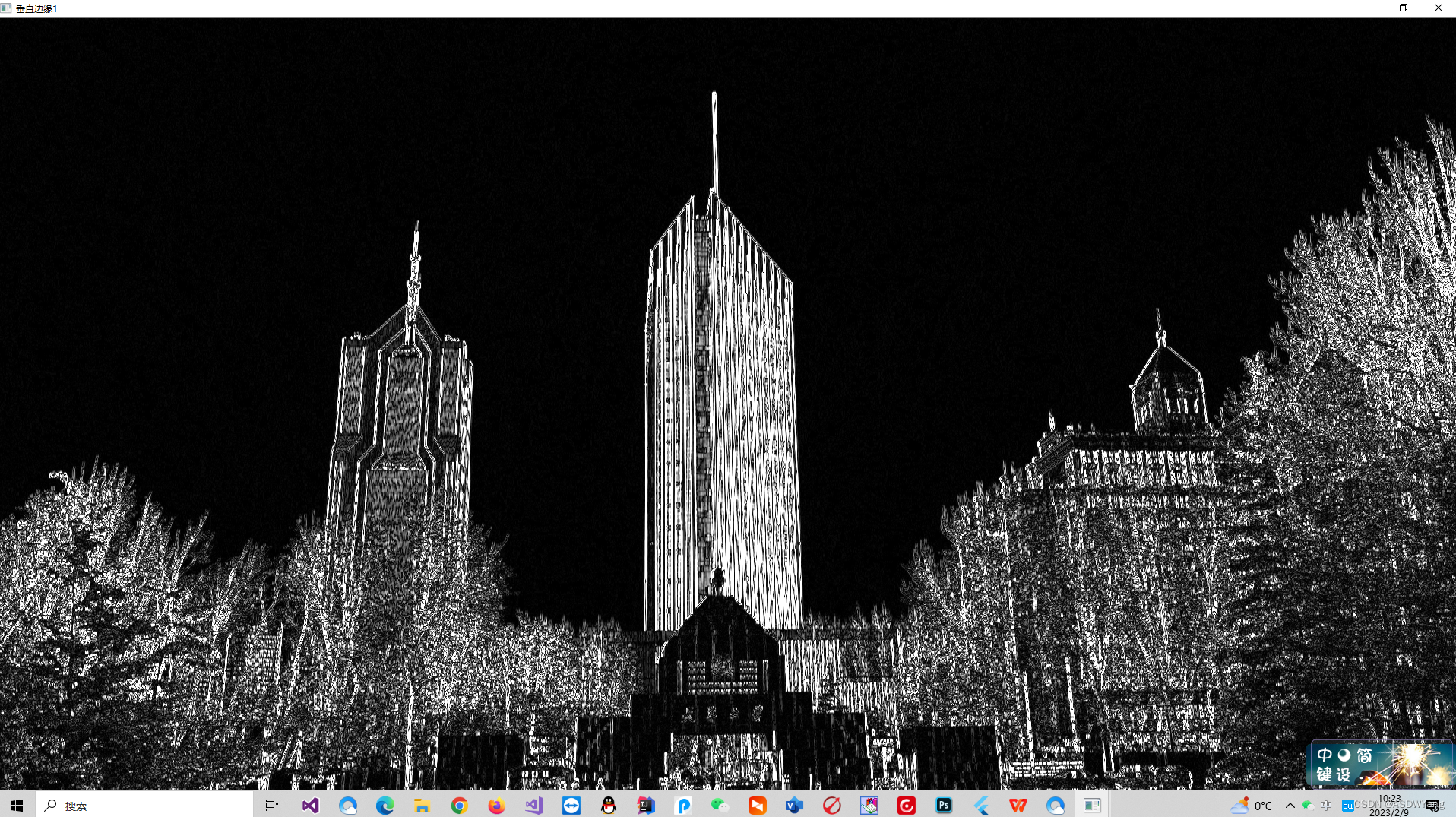
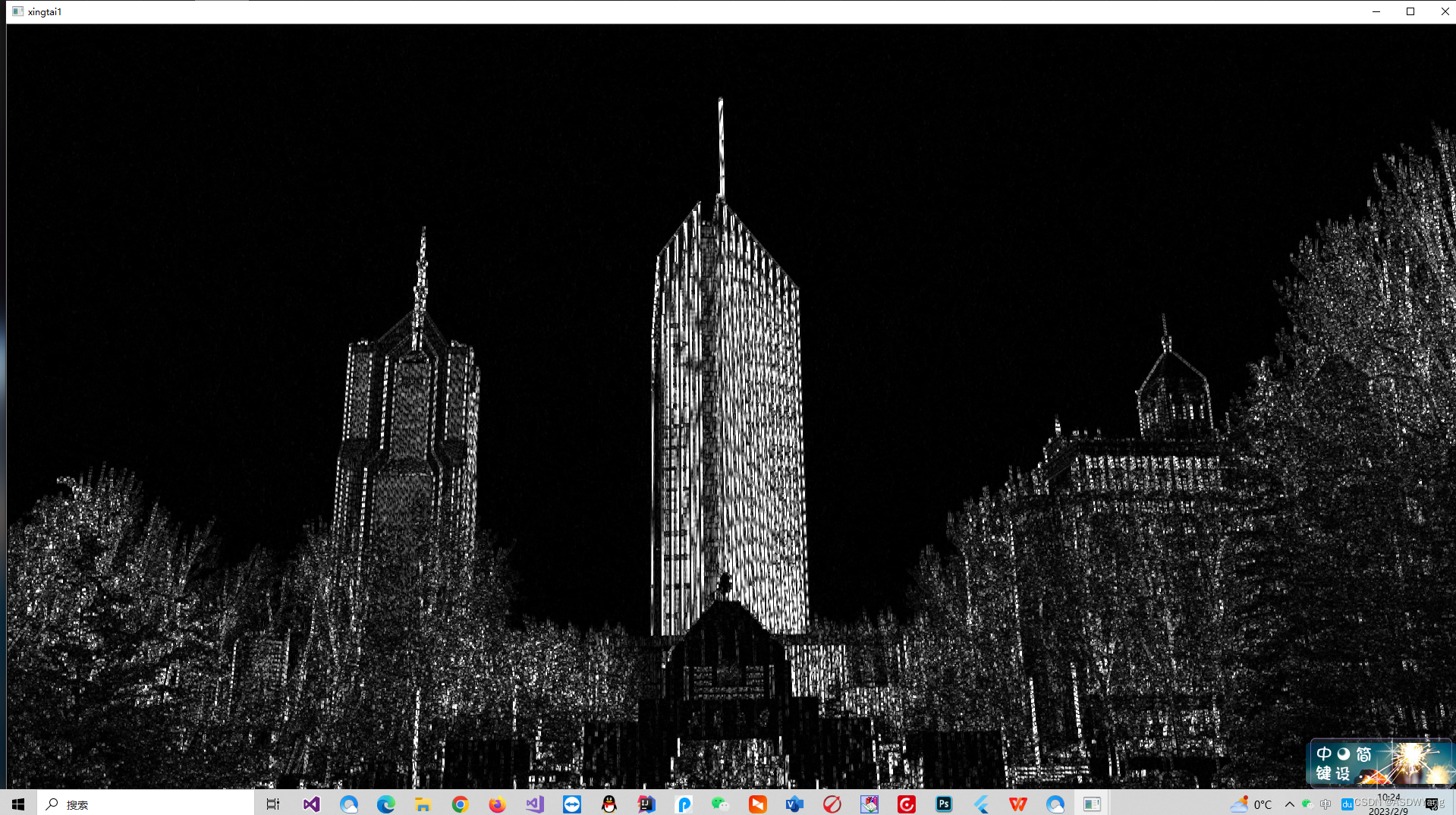
接下来是进行闭操作,将图中的白色线条尽可能连在一起,上图之中的楼左侧的线有一些断开了.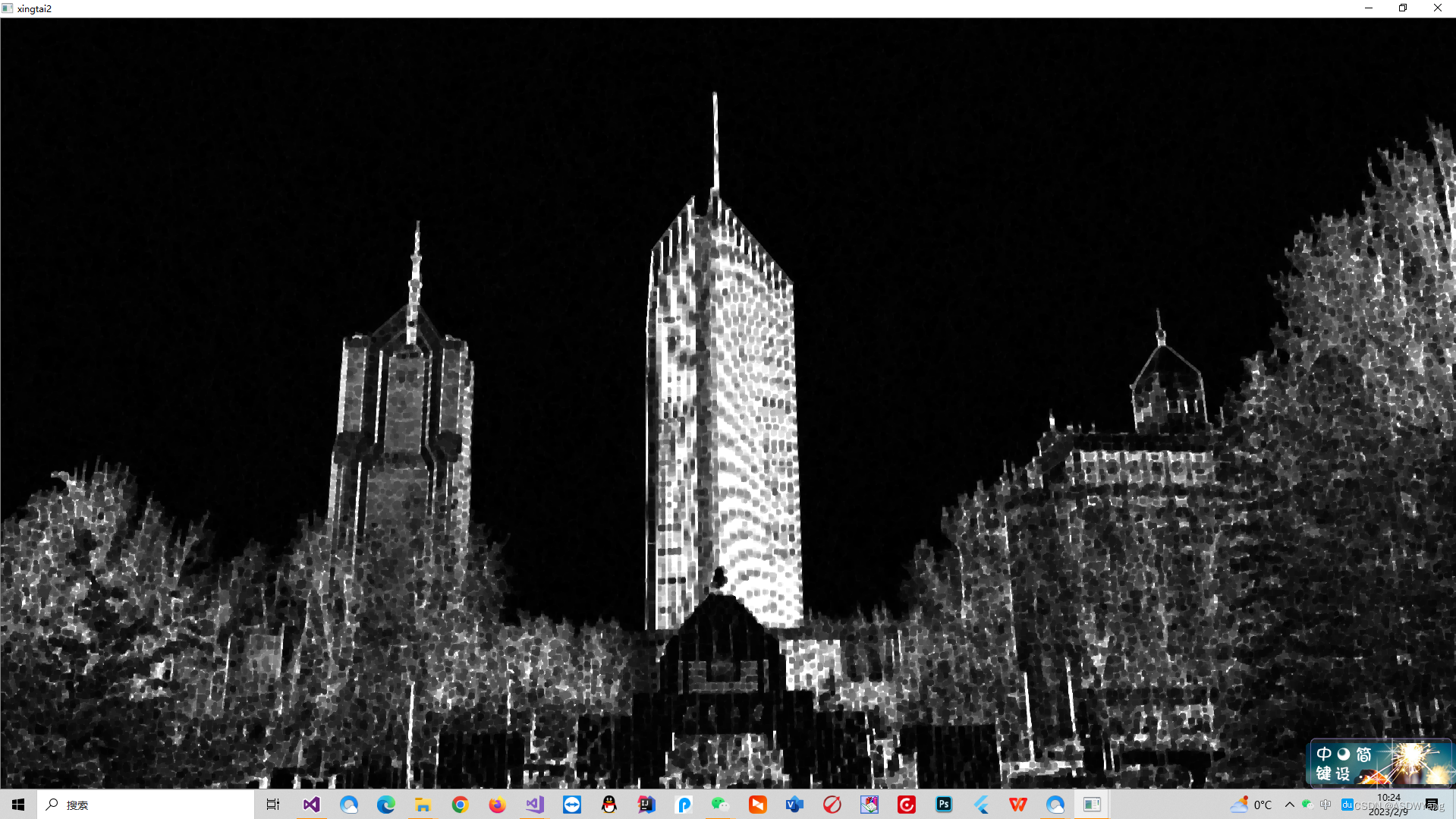
闭操作的缺陷是会产生小白点点.如下二值化过程

再进行一次反二值化,因为我不会用别的算子结合霍夫直线检测检测出来直线,只能转回去进行操作.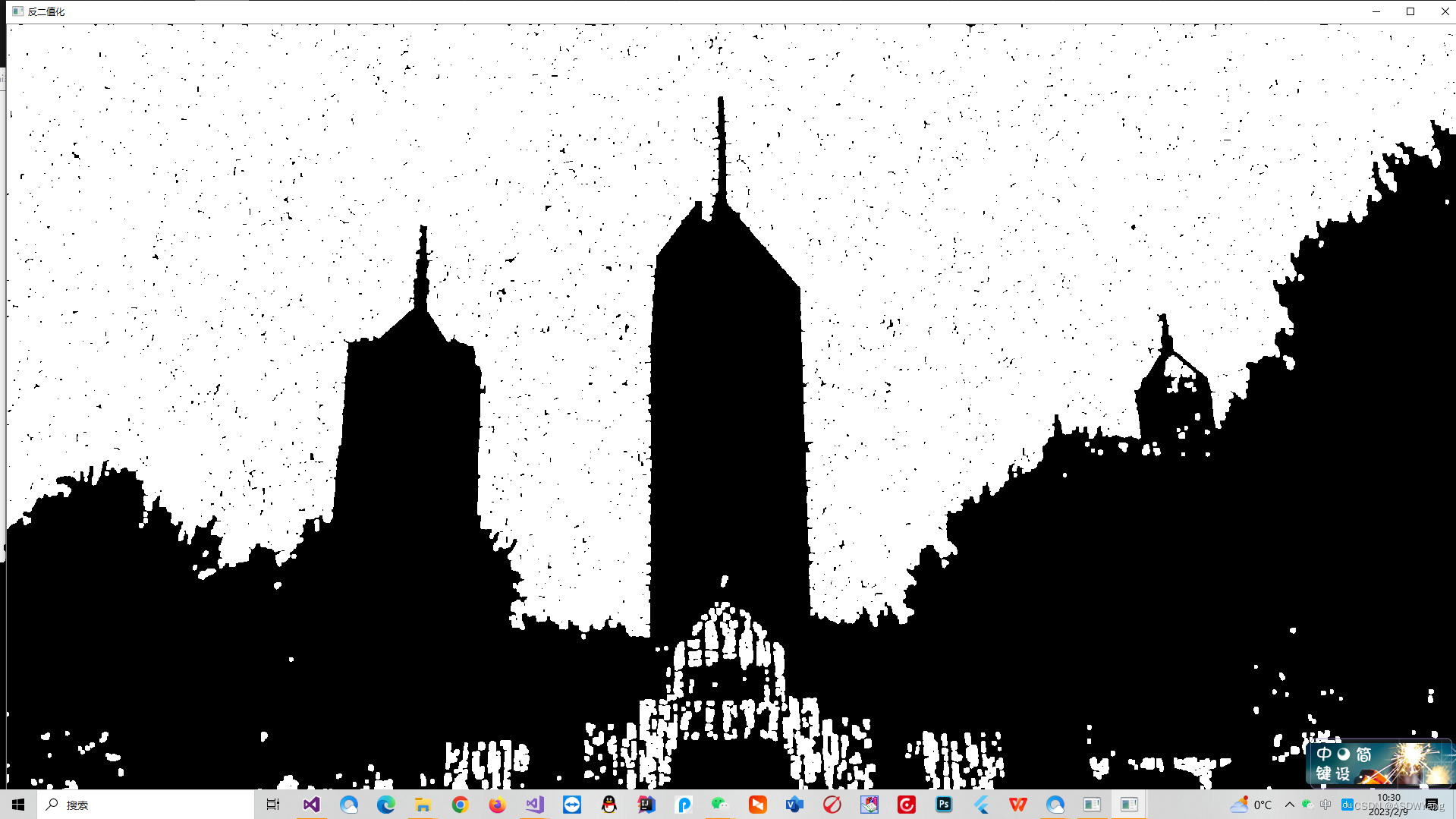
形态学操作,去除白点
canny一下检测出来轮廓
显示全部直线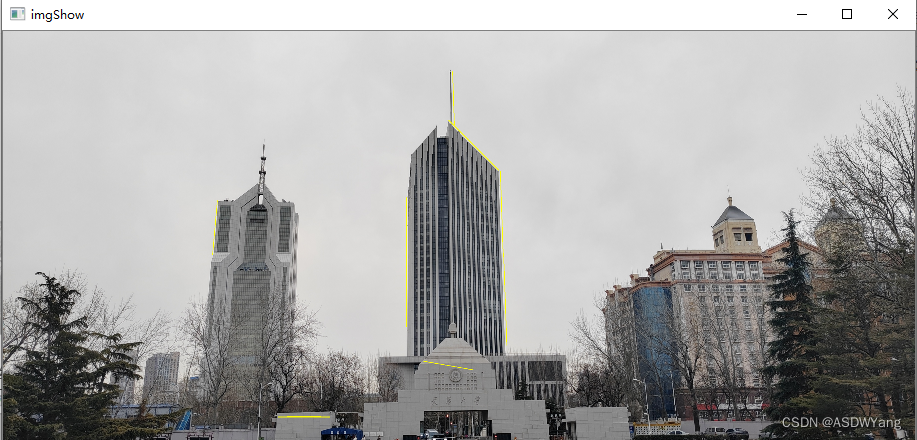
直线提取,我的方式是提取最长的两段直线。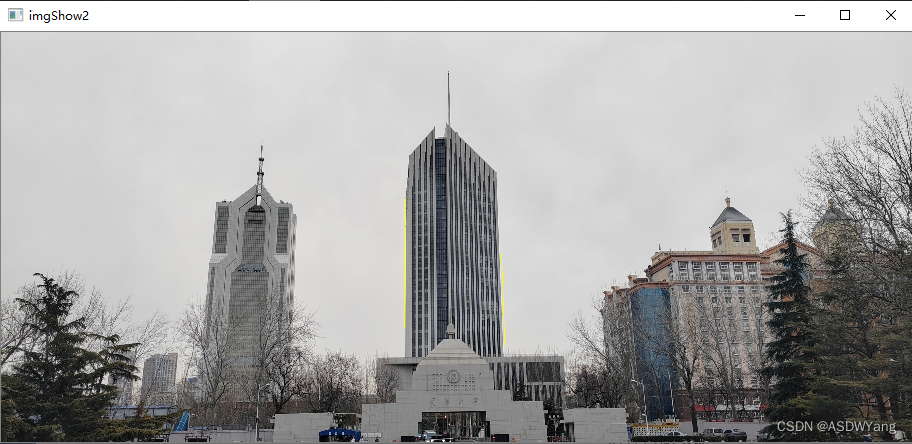
在上述操作完成之后,得到了物体的粗定位直线。
但是上面的算法还是存在相应的问题,换了一个别的图像可能就检测的不准。发现问题就是出在了二值化的过程。
为了修正上方的算法的失败,使用提取外部轮廓的方式进行求取,将代码改了改。
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void getPrewitt_oper(cv::Mat& getPrewitt_horizontal, cv::Mat& getPrewitt_vertical, cv::Mat& getPrewitt_Diagonal1, cv::Mat& getPrewitt_Diagonal2) {
//水平方向
getPrewitt_horizontal = (cv::Mat_<float>(3, 3) << -1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1);
//垂直方向
getPrewitt_vertical = (cv::Mat_<float>(3, 3) << -1, 0, 1, -1, 0, 1, -1, 0, 1);
//对角135°
getPrewitt_Diagonal1 = (cv::Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 0, 1, 1, -1, 0, 1, -1, -1, 0);
//对角45°
getPrewitt_Diagonal2 = (cv::Mat_<float>(3, 3) << -1, -1, 0, -1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1);
//逆时针反转180°得到卷积核
cv::flip(getPrewitt_horizontal, getPrewitt_horizontal, -1);
cv::flip(getPrewitt_vertical, getPrewitt_vertical, -1);
cv::flip(getPrewitt_Diagonal1, getPrewitt_Diagonal1, -1);
cv::flip(getPrewitt_Diagonal2, getPrewitt_Diagonal2, -1);
}
void edge_Prewitt(cv::Mat& src, cv::Mat& dst1, cv::Mat& dst2, cv::Mat& dst3, cv::Mat& dst4, cv::Mat& dst, int ddepth, double delta = 0, int borderType = cv::BORDER_DEFAULT) {
//获取Prewitt算子
cv::Mat getPrewitt_horizontal;
cv::Mat getPrewitt_vertical;
cv::Mat getPrewitt_Diagonal1;
cv::Mat getPrewitt_Diagonal2;
getPrewitt_oper(getPrewitt_horizontal, getPrewitt_vertical, getPrewitt_Diagonal1, getPrewitt_Diagonal2);
//卷积得到水平方向边缘
cv::filter2D(src, dst1, ddepth, getPrewitt_horizontal, cv::Point(-1, -1), delta, borderType);
//卷积得到4垂直方向边缘
cv::filter2D(src, dst2, ddepth, getPrewitt_vertical, cv::Point(-1, -1), delta, borderType);
//卷积得到45°方向边缘
cv::filter2D(src, dst3, ddepth, getPrewitt_Diagonal1, cv::Point(-1, -1), delta, borderType);
//卷积得到135°方向边缘
cv::filter2D(src, dst4, ddepth, getPrewitt_Diagonal2, cv::Point(-1, -1), delta, borderType);
//边缘强度(近似)
cv::convertScaleAbs(dst1, dst1); //求绝对值并转为无符号8位图
cv::convertScaleAbs(dst2, dst2);
cv::convertScaleAbs(dst3, dst3); //求绝对值并转为无符号8位图
cv::convertScaleAbs(dst4, dst4);
dst = dst1 + dst2;
}
//数组从大到小排序
void reserve(int x[], int n) {
int i, j, temp;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { //一共n个元素,则需要比较n-1次
for (j = 0; j < n - 1 - i; j++) { //每一个元素需要比较的次数
if (x[i] < x[i + j + 1]) {
temp = x[i];
x[i] = x[i + j + 1];
x[i + j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cv::Mat src = cv::imread("楼.jpg");
if (src.empty()) {
return -1;
}
cout << "??" << endl;
if (src.channels() > 1) cv::cvtColor(src, src, CV_RGB2GRAY);
cv::Mat dst, dst1, dst2, dst3, dst4, dst5;
Mat src1 = cv::imread("楼.jpg");
Mat src2 = cv::imread("楼.jpg");
//medianBlur(src, src, 5); //均值滤波
GaussianBlur(src, src, Size(5, 5), 0); //高斯滤波
cout << "??" << endl;
//注意:要采用CV_32F,因为有些地方卷积后为负数,若用8位无符号,则会导致这些地方为0
edge_Prewitt(src, dst1, dst2, dst3, dst4, dst, CV_32F);
cv::namedWindow("垂直边缘", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("垂直边缘", dst2);
cout << "??" << endl;
/*
Mat shdjk;
cv::threshold(dst2, shdjk, 25, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
cv::namedWindow("二值化1212", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("二值化1212", shdjk);
*/
//获取结构
cv::Mat element1 = cv::getStructuringElement(cv::MORPH_RECT, cv::Size(3, 3));
Mat out1;
//进行形态学开运算操作
morphologyEx(dst2, out1, MORPH_OPEN, element1);//形态学开运算
cv::namedWindow("xingtai", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("xingtai", out1);
Mat out2;
//第二次进行形态学操作
edge_Prewitt(out1, dst1, out1, dst3, dst4, dst, CV_32F);
cv::namedWindow("垂直边缘1", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("垂直边缘1", out1);
cout << "??" << endl;
/*
morphologyEx(out1, out1, MORPH_OPEN, element1);//形态学开运算
cv::namedWindow("xingtai1", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("xingtai1", out1);
//获取结构
cv::Mat element2 = cv::getStructuringElement(cv::MORPH_ELLIPSE, cv::Size(10, 10));
//进行形态学闭运算操作
morphologyEx(out1, out2, MORPH_CLOSE, element2);//形态学闭合运算
cv::namedWindow("xingtai2", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("xingtai2", out2);
imwrite("xingtai2.jpg", out2);
waitKey(0);
*/
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>> contours;
std::vector<cv::Vec4i> hierarchy;
findContours(out1, contours, CV_RETR_EXTERNAL, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
double maxArea = 0;
int index = 0;
vector<cv::Point> maxContour;
for (size_t i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++)
{
double area = cv::contourArea(contours[i]);
if (area > maxArea)
{
maxArea = area;
maxContour = contours[i];
index = i;
}
}
drawContours(src1, contours, index, Scalar(255)); // 参数
cv::namedWindow("test", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("test", src1);
waitKey(0);
/*
Mat shdjk;
cv::threshold(out1, shdjk, 10, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
cv::namedWindow("二值化1212", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("二值化1212", shdjk);
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>> contours;
std::vector<cv::Vec4i> hierarchy;
cv::findContours(shdjk, contours, hierarchy, cv::RETR_EXTERNAL, cv::CHAIN_APPROX_NONE); //只找最外层轮廓
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>> approxCurves(contours.size());
for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); ++i) { //绘制逼近后的轮廓
double epsilon = 0.1 * cv::arcLength(contours[i], true);
cv::approxPolyDP(contours[i], approxCurves[i], epsilon, true);
cv::drawContours(src1, approxCurves, i, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
}
cv::namedWindow("success", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("success", src1);
cv::waitKey();
*/
//
/*
Mat dhfjua;
cv::threshold(out2, dhfjua, 15, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
cv::namedWindow("二值化000", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("二值化000", dhfjua);
*/
/*
//膨胀运算,将细小缝隙填补上,非必要
Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(0, Size(3, 3));
dilate(out2, dst2, kernel);
cv::namedWindow("膨胀", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("膨胀", dst2);
*/
/*0
cv::threshold(out2, dst2, 5, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
cv::namedWindow("二值化", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("二值化", dst2);
cv::threshold(dst2, dst2, 5, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY_INV);
cv::namedWindow("反二值化", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("反二值化", dst2);
*/
/*
Mat out3;
//进行形态学闭运算操作
morphologyEx(dst2, out3, MORPH_CLOSE, element2);//形态学开运算
cv::namedWindow("xingtai3", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("xingtai3", out3);
imwrite("xingtai3.jpg", out3);
*/
waitKey(0);
vector<Vec4i> lines;
HoughLinesP(src1, lines, 1, CV_PI / 180, 100, 400, 30);
int Length[1000] = { 0 };//存放直线长度
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++)
{
Vec4i I = lines[i];
double x1 = I[0];
double y1 = I[1];
double x2 = I[2];
double y2 = I[3];
//筛选满足条件的点
if (abs(x1 - x2) + abs(y1 - y2) > 50)
{
Length[i] = sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
//将满足条件的点画出
line(src1, Point2d(x1, y1), Point2d(x2, y2), Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2);
cout << " " << "(" << x1 << "," << y1 << ")" << " " << "(" << x2 << "," << y2 << ")" << endl;
//line(canny, Point2d(x1, y1), Point2d(x2, y2), Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2);
}
}
Mat imgShow;
imgShow = src1;
resize(imgShow, imgShow, Size(imgShow.cols / 4, imgShow.rows / 4));
imshow("imgShow", imgShow);
imwrite("shuchu.png", src1);
reserve(Length, 1000);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
cout << "长度" << Length[i] << endl; //输出排序后的数组元素
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++)
{
Vec4i I = lines[i];
double x1 = I[0];
double y1 = I[1];
double x2 = I[2];
double y2 = I[3];
cout << "sdjk" << endl;
cout << int(sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2))) << endl;
//筛选满足条件的点
if ((int(sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2))) == Length[0]) || (int(sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2))) == Length[1]))
{
//将满足条件的点画出
line(src2, Point2d(x1, y1), Point2d(x2, y2), Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2);
cout << "djfkljsa " << "(" << x1 << "," << y1 << ")" << " " << "(" << x2 << "," << y2 << ")" << endl;
//line(canny, Point2d(x1, y1), Point2d(x2, y2), Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2);
}
}
imgShow = src2;
resize(imgShow, imgShow, Size(imgShow.cols / 4, imgShow.rows / 4));
imshow("imgShow2", imgShow);
imwrite("shuchu2.png", src2);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}效果还是不好,问题就是出在了相应的一个二值化的过程,因此,想到使用区域增长算法改进
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
//------------------------------【两步法新改进版】----------------------------------------------
// 对二值图像进行连通区域标记,从1开始标号
void Two_PassNew(const Mat &bwImg, Mat &labImg)
{
assert(bwImg.type() == CV_8UC1);
labImg.create(bwImg.size(), CV_32SC1); //bwImg.convertTo( labImg, CV_32SC1 );
labImg = Scalar(0);
labImg.setTo(Scalar(1), bwImg);
assert(labImg.isContinuous());
const int Rows = bwImg.rows - 1, Cols = bwImg.cols - 1;
int label = 1;
vector<int> labelSet;
labelSet.push_back(0);
labelSet.push_back(1);
//the first pass
int *data_prev = (int*)labImg.data; //0-th row : int* data_prev = labImg.ptr<int>(i-1);
int *data_cur = (int*)(labImg.data + labImg.step); //1-st row : int* data_cur = labImg.ptr<int>(i);
for (int i = 1; i < Rows; i++)
{
data_cur++;
data_prev++;
for (int j = 1; j < Cols; j++, data_cur++, data_prev++)
{
if (*data_cur != 1)
continue;
int left = *(data_cur - 1);
int up = *data_prev;
int neighborLabels[2];
int cnt = 0;
if (left > 1)
neighborLabels[cnt++] = left;
if (up > 1)
neighborLabels[cnt++] = up;
if (!cnt)
{
labelSet.push_back(++label);
labelSet[label] = label;
*data_cur = label;
continue;
}
int smallestLabel = neighborLabels[0];
if (cnt == 2 && neighborLabels[1] < smallestLabel)
smallestLabel = neighborLabels[1];
*data_cur = smallestLabel;
// 保存最小等价表
for (int k = 0; k < cnt; k++)
{
int tempLabel = neighborLabels[k];
int& oldSmallestLabel = labelSet[tempLabel]; //这里的&不是取地址符号,而是引用符号
if (oldSmallestLabel > smallestLabel)
{
labelSet[oldSmallestLabel] = smallestLabel;
oldSmallestLabel = smallestLabel;
}
else if (oldSmallestLabel < smallestLabel)
labelSet[smallestLabel] = oldSmallestLabel;
}
}
data_cur++;
data_prev++;
}
//更新等价队列表,将最小标号给重复区域
for (size_t i = 2; i < labelSet.size(); i++)
{
int curLabel = labelSet[i];
int prelabel = labelSet[curLabel];
while (prelabel != curLabel)
{
curLabel = prelabel;
prelabel = labelSet[prelabel];
}
labelSet[i] = curLabel;
}
//second pass
data_cur = (int*)labImg.data;
for (int i = 0; i < Rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < bwImg.cols - 1; j++, data_cur++)
*data_cur = labelSet[*data_cur];
data_cur++;
}
}
//-------------------------------【老版两步法】-------------------------------------------
void Two_PassOld(const cv::Mat& _binImg, cv::Mat& _lableImg)
{
//connected component analysis (4-component)
//use two-pass algorithm
//1. first pass: label each foreground pixel with a label
//2. second pass: visit each labeled pixel and merge neighbor label
//
//foreground pixel: _binImg(x,y) = 1
//background pixel: _binImg(x,y) = 0
if (_binImg.empty() || _binImg.type() != CV_8UC1)
{
return;
}
// 1. first pass
_lableImg.release();
_binImg.convertTo(_lableImg, CV_32SC1);
int label = 1; // start by 2
std::vector<int> labelSet;
labelSet.push_back(0); //background: 0
labelSet.push_back(1); //foreground: 1
int rows = _binImg.rows - 1;
int cols = _binImg.cols - 1;
for (int i = 1; i < rows; i++)
{
int* data_preRow = _lableImg.ptr<int>(i - 1);
int* data_curRow = _lableImg.ptr<int>(i);
for (int j = 1; j < cols; j++)
{
if (data_curRow[j] == 1)
{
std::vector<int> neighborLabels;
neighborLabels.reserve(2); //reserve(n) 预分配n个元素的存储空间
int leftPixel = data_curRow[j - 1];
int upPixel = data_preRow[j];
if (leftPixel > 1)
{
neighborLabels.push_back(leftPixel);
}
if (upPixel > 1)
{
neighborLabels.push_back(upPixel);
}
if (neighborLabels.empty())
{
labelSet.push_back(++label); //assign to a new label
data_curRow[j] = label;
labelSet[label] = label;
}
else
{
std::sort(neighborLabels.begin(), neighborLabels.end());
int smallestLabel = neighborLabels[0];
data_curRow[j] = smallestLabel;
//save equivalence
for (size_t k = 1; k < neighborLabels.size(); k++)
{
int tempLabel = neighborLabels[k];
int& oldSmallestLabel = labelSet[tempLabel];
if (oldSmallestLabel > smallestLabel)
{
labelSet[oldSmallestLabel] = smallestLabel;
oldSmallestLabel = smallestLabel;
}
else if (oldSmallestLabel < smallestLabel)
{
labelSet[smallestLabel] = oldSmallestLabel;
}
}
}
}
}
}
//update equivalent labels
//assigned with the smallest label in each equivalent label set
for (size_t i = 2; i < labelSet.size(); i++)
{
int curLabel = labelSet[i];
int prelabel = labelSet[curLabel];
while (prelabel != curLabel)
{
curLabel = prelabel;
prelabel = labelSet[prelabel];
}
labelSet[i] = curLabel;
}
//2. second pass
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
int *data = _lableImg.ptr<int>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
int& pixelLabel = data[j];
pixelLabel = labelSet[pixelLabel];
}
}
}
//---------------------------------【种子填充法老版】-------------------------------
void SeedFillOld(const cv::Mat& binImg, cv::Mat& lableImg) //种子填充法
{
// 4邻接方法
if (binImg.empty() ||
binImg.type() != CV_8UC1)
{
return;
}
lableImg.release();
binImg.convertTo(lableImg, CV_32SC1);
int label = 1;
int rows = binImg.rows - 1;
int cols = binImg.cols - 1;
for (int i = 1; i < rows - 1; i++)
{
int* data = lableImg.ptr<int>(i);
for (int j = 1; j < cols - 1; j++)
{
if (data[j] == 1)
{
std::stack<std::pair<int, int>> neighborPixels;
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(i, j)); // 像素位置: <i,j>
++label; // 没有重复的团,开始新的标签
while (!neighborPixels.empty())
{
std::pair<int, int> curPixel = neighborPixels.top(); //如果与上一行中一个团有重合区域,则将上一行的那个团的标号赋给它
int curX = curPixel.first;
int curY = curPixel.second;
lableImg.at<int>(curX, curY) = label;
neighborPixels.pop();
if (lableImg.at<int>(curX, curY - 1) == 1)
{//左边
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curX, curY - 1));
}
if (lableImg.at<int>(curX, curY + 1) == 1)
{// 右边
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curX, curY + 1));
}
if (lableImg.at<int>(curX - 1, curY) == 1)
{// 上边
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curX - 1, curY));
}
if (lableImg.at<int>(curX + 1, curY) == 1)
{// 下边
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curX + 1, curY));
}
}
}
}
}
}
//-------------------------------------------【种子填充法新版】---------------------------
void SeedFillNew(const cv::Mat& _binImg, cv::Mat& _lableImg)
{
// connected component analysis(4-component)
// use seed filling algorithm
// 1. begin with a forgeground pixel and push its forground neighbors into a stack;
// 2. pop the pop pixel on the stack and label it with the same label until the stack is empty
//
// forground pixel: _binImg(x,y)=1
// background pixel: _binImg(x,y) = 0
if (_binImg.empty() ||
_binImg.type() != CV_8UC1)
{
return;
}
_lableImg.release();
_binImg.convertTo(_lableImg, CV_32SC1);
int label = 0; //start by 1
int rows = _binImg.rows;
int cols = _binImg.cols;
Mat mask(rows, cols, CV_8UC1);
mask.setTo(0);
int *lableptr;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
int* data = _lableImg.ptr<int>(i);
uchar *masKptr = mask.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
if (data[j] == 255 && mask.at<uchar>(i, j) != 1)
{
mask.at<uchar>(i, j) = 1;
std::stack<std::pair<int, int>> neighborPixels;
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(i, j)); // pixel position: <i,j>
++label; //begin with a new label
while (!neighborPixels.empty())
{
//get the top pixel on the stack and label it with the same label
std::pair<int, int> curPixel = neighborPixels.top();
int curY = curPixel.first;
int curX = curPixel.second;
_lableImg.at<int>(curY, curX) = label;
//pop the top pixel
neighborPixels.pop();
//push the 4-neighbors(foreground pixels)
if (curX - 1 >= 0)
{
if (_lableImg.at<int>(curY, curX - 1) == 255 && mask.at<uchar>(curY, curX - 1) != 1) //leftpixel
{
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curY, curX - 1));
mask.at<uchar>(curY, curX - 1) = 1;
}
}
if (curX + 1 <= cols - 1)
{
if (_lableImg.at<int>(curY, curX + 1) == 255 && mask.at<uchar>(curY, curX + 1) != 1)
// right pixel
{
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curY, curX + 1));
mask.at<uchar>(curY, curX + 1) = 1;
}
}
if (curY - 1 >= 0)
{
if (_lableImg.at<int>(curY - 1, curX) == 255 && mask.at<uchar>(curY - 1, curX) != 1)
// up pixel
{
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curY - 1, curX));
mask.at<uchar>(curY - 1, curX) = 1;
}
}
if (curY + 1 <= rows - 1)
{
if (_lableImg.at<int>(curY + 1, curX) == 255 && mask.at<uchar>(curY + 1, curX) != 1)
//down pixel
{
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int, int>(curY + 1, curX));
mask.at<uchar>(curY + 1, curX) = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
//---------------------------------【颜色标记程序】-----------------------------------
//彩色显示
cv::Scalar GetRandomColor()
{
uchar r = 255 * (rand() / (1.0 + RAND_MAX));
uchar g = 255 * (rand() / (1.0 + RAND_MAX));
uchar b = 255 * (rand() / (1.0 + RAND_MAX));
return cv::Scalar(b, g, r);
}
void LabelColor(const cv::Mat& labelImg, cv::Mat& colorLabelImg)
{
int num = 0;
if (labelImg.empty() ||
labelImg.type() != CV_32SC1)
{
return;
}
std::map<int, cv::Scalar> colors;
int rows = labelImg.rows;
int cols = labelImg.cols;
colorLabelImg.release();
colorLabelImg.create(rows, cols, CV_8UC3);
colorLabelImg = cv::Scalar::all(0);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
const int* data_src = (int*)labelImg.ptr<int>(i);
uchar* data_dst = colorLabelImg.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
int pixelValue = data_src[j];
if (pixelValue > 1)
{
if (colors.count(pixelValue) <= 0)
{
colors[pixelValue] = GetRandomColor();
num++;
}
cv::Scalar color = colors[pixelValue];
*data_dst++ = color[0];
*data_dst++ = color[1];
*data_dst++ = color[2];
}
else
{
data_dst++;
data_dst++;
data_dst++;
}
}
}
printf("color num : %d \n", num);
}
//------------------------------------------【测试主程序】-------------------------------------
int main()
{
cv::Mat binImage = cv::imread("sda.jpg", 0);
//cv::threshold(binImage, binImage, 50, 1, CV_THRESH_BINARY);
cv::Mat labelImg;
double time;
time = getTickCount();
SeedFillNew(binImage, labelImg);
time = 1000 * ((double)getTickCount() - time) / getTickFrequency();
cout << std::fixed << time << "ms" << endl;
//彩色显示
/*
cv::Mat colorLabelImg;
LabelColor(labelImg, colorLabelImg);
cv::imshow("colorImg", colorLabelImg);
*/
//灰度显示
cv::Mat grayImg;
labelImg *= 10;
labelImg.convertTo(grayImg, CV_8UC1);
cv::imshow("labelImg", grayImg);
double minval, maxval;
minMaxLoc(labelImg, &minval, &maxval);
cout << "minval" << minval << endl;
cout << "maxval" << maxval << endl;
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
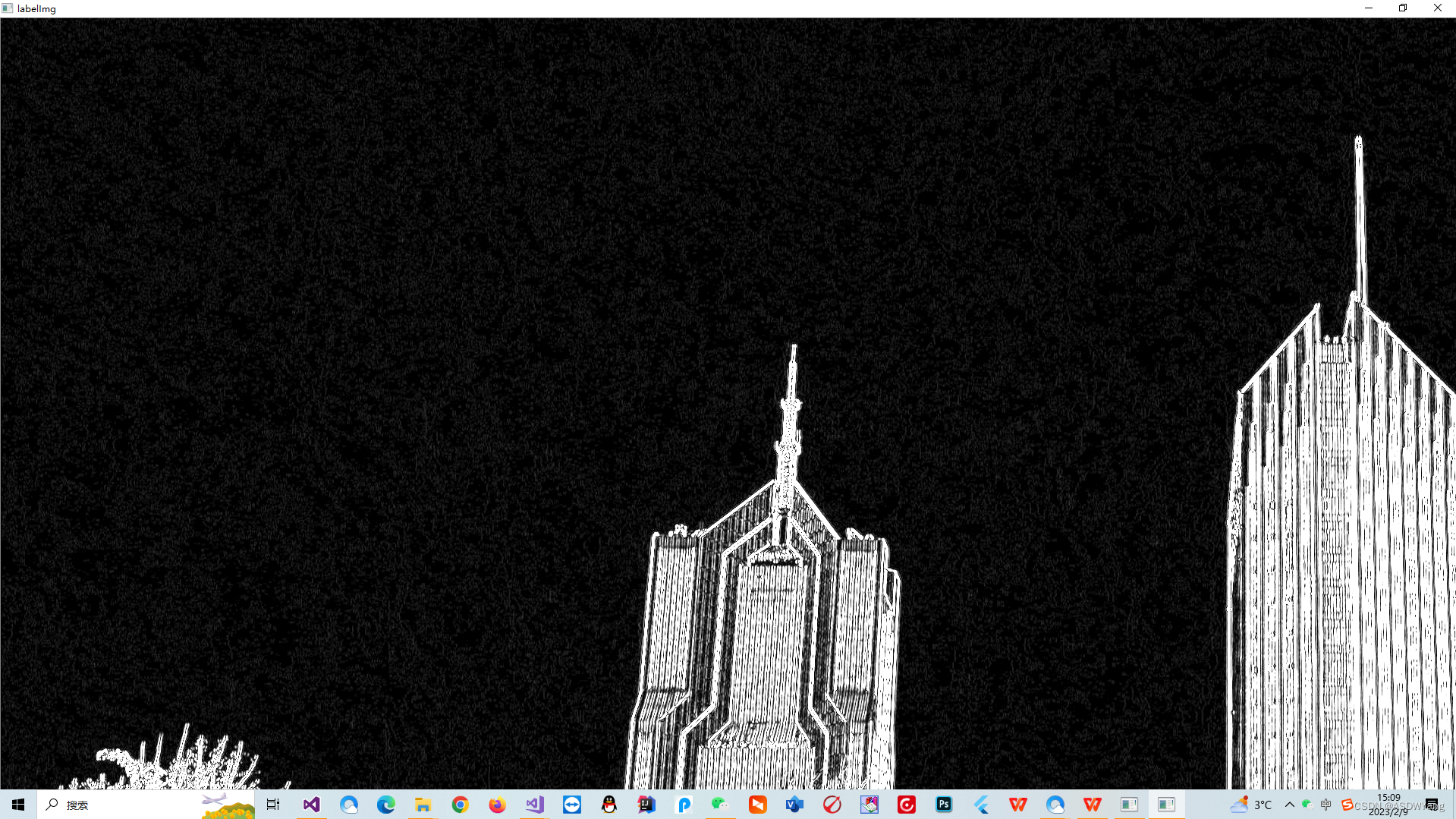
终于知道是啥原因了,我在进行Prewitt算子对边缘进行粗定位检测过后,没有进行去噪处理,一定要把图像转换为二值图像,就方便多了。并且还要记住,霍夫检测的直线像素是255白线才可以,经过长时间的试错终于解决了。输入原图像如下所示,我这里使用的去噪对比了四种,但是下面这种是最好的。Opencv 非局部降噪_51CTO博客_opencv降噪Opencv 非局部降噪,opencv自带的非局部降噪算法:CV_EXPORTS_WvoidfastNlMeansDenoising(InputArraysrc,OutputArraydst,floath=3,inttemplateWindowSize=7,intsearchWindowSize=21);h是过滤强度,templateWindowSize是分块大小,searchWindowSize是搜索区域大小。应用实例intmain(){MatI..https://blog.51cto.com/u_15458280/4843576

#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
//数组从大到小排序
void reserve(int x[], int n) {
int i, j, temp;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { //一共n个元素,则需要比较n-1次
for (j = 0; j < n - 1 - i; j++) { //每一个元素需要比较的次数
if (x[i] < x[i + j + 1]) {
temp = x[i];
x[i] = x[i + j + 1];
x[i + j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
void add_salt_pepper_noise(Mat &image) {
RNG rng(12345);
int h = image.rows;
int w = image.cols;
int nums = 10000;
for (int i = 0; i < nums; i++) {
int x = rng.uniform(0, w);
int y = rng.uniform(0, h);
if (i % 2 == 1) {
image.at<Vec3b>(y, x) = Vec3b(255, 255, 255);
}
else {
image.at<Vec3b>(y, x) = Vec3b(0, 0, 0);
}
}
imshow("salt pepper", image);
}
void gaussian_noise(Mat &image) {
Mat noise = Mat::zeros(image.size(), image.type());
randn(noise, (15, 15, 15), (30, 30, 30));
Mat dst;
add(image, noise, dst);
imshow("gaussian noise", dst);
dst.copyTo(image);
}
Mat convertTo3Channels(const Mat& binImg)
{
Mat three_channel = Mat::zeros(binImg.rows, binImg.cols, CV_8UC3);
vector<Mat> channels;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
channels.push_back(binImg);
}
merge(channels, three_channel);
return three_channel;
}
int main(int argc, char*argv[])
{
//加载图像
Mat img, gray_image, dst;
img = imread("垂直边缘.jpg");
Mat img1 = imread("垂直边缘.jpg");
//判断图像是否导入成功
if (img.empty())
{
cout << "加载失败" << endl;
return -1;
}
//显示图像
namedWindow("original image", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("original image", img);
//转换灰度图像
cvtColor(img, gray_image, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
//获取灰度图像宽度和高度
int width = gray_image.cols;
int height = gray_image.rows;
//遍历像素值(单通道)
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < width; col++)
{
int gray = gray_image.at<uchar>(row, col);
gray_image.at<uchar>(row, col) = 255 - gray; //图像取反
};
};
namedWindow("inv_gray_image", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("inv_gray_image", gray_image);
Mat sh;
fastNlMeansDenoising(gray_image, sh, 21, 7, 21);
namedWindow("inv_gray_image1", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("inv_gray_image1", sh);
waitKey(50);
//Mat s;
//获取灰度图像宽度和高度
width = sh.cols;
height = sh.rows;
//遍历像素值(单通道)
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < width; col++)
{
int gray = sh.at<uchar>(row, col);
sh.at<uchar>(row, col) = 255 - gray; //图像取反
};
};
namedWindow("inv_gray_image2", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("inv_gray_image2", sh);
cv::threshold(sh, sh, 50, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
cv::namedWindow("二值化", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("二值化", sh);
vector<Vec4i> lines;
HoughLinesP(sh, lines, 1, CV_PI / 180, 50,100, 5);
int Length[100] = { 0 };//存放直线长度
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++)
{
Vec4i I = lines[i];
double x1 = I[0];
double y1 = I[1];
double x2 = I[2];
double y2 = I[3];
//筛选满足条件的点
if (abs(x1 - x2) + abs(y1 - y2) > 50)
{
Length[i] = sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
//将满足条件的点画出
line(img, Point2d(x1, y1), Point2d(x2, y2), Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2);
cout << " " << "(" << x1 << "," << y1 << ")" << " " << "(" << x2 << "," << y2 << ")" << endl;
//line(canny, Point2d(x1, y1), Point2d(x2, y2), Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2);
}
}
Mat imgShow;
imgShow = img;
resize(imgShow, imgShow, Size(imgShow.cols / 4, imgShow.rows / 4));
imshow("imgShow", imgShow);
imwrite("shuchu.png", imgShow);
reserve(Length, 100);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
cout << "长度" << Length[i] << endl; //输出排序后的数组元素
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++)
{
Vec4i I = lines[i];
double x1 = I[0];
double y1 = I[1];
double x2 = I[2];
double y2 = I[3];
cout << "sdjk" << endl;
cout << int(sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2))) << endl;
//筛选满足条件的点
if ((int(sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2))) == Length[0]) || (int(sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2))) == Length[1]))
{
//将满足条件的点画出
line(img1, Point2d(x1, y1), Point2d(x2, y2), Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2);
cout << "djfkljsa " << "(" << x1 << "," << y1 << ")" << " " << "(" << x2 << "," << y2 << ")" << endl;
//line(canny, Point2d(x1, y1), Point2d(x2, y2), Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2);
}
}
imgShow = img1;
resize(imgShow, imgShow, Size(imgShow.cols / 4, imgShow.rows / 4));
imshow("imgShow2", imgShow);
imwrite("shuchu2.png", imgShow);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
};
结果图如下所示:
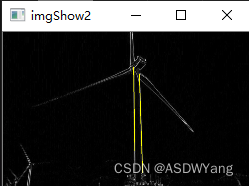
终于弄出来了,去干饭。