文章目录
- 1. AOP 简介
- 2. AOP 入门案例
- 3. AOP 工作流程(略)
- 4. AOP 切入点表达式
- 4.1 语法格式
- 4.2 通配符
- 4.3 书写技巧
- 5. AOP 通知类型
- 5.1 前置通知、后置通知
- 5.2 环绕通知(重点)
- 5.3 返回后通知(了解)
- 5.4 抛出异常后通知(了解)
- 6. 案例:业务层接口执行效率
- 7. AOP 通知获取数据
- 7.1 获取参数
- 7.2 获取返回值
- 7.3 获取异常(了解)
- 8. 案例:百度网盘密码数据兼容处理
1. AOP 简介
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming):面向切面编程,是一种编程范式,指导开发者如何组织程序结构。
作用:在不惊动原始设计的基础上为其进行功能增强。如果有相同的功能需要在很多地方加的话,可以选择 AOP。
Spring 理念:无入侵式/无侵入式
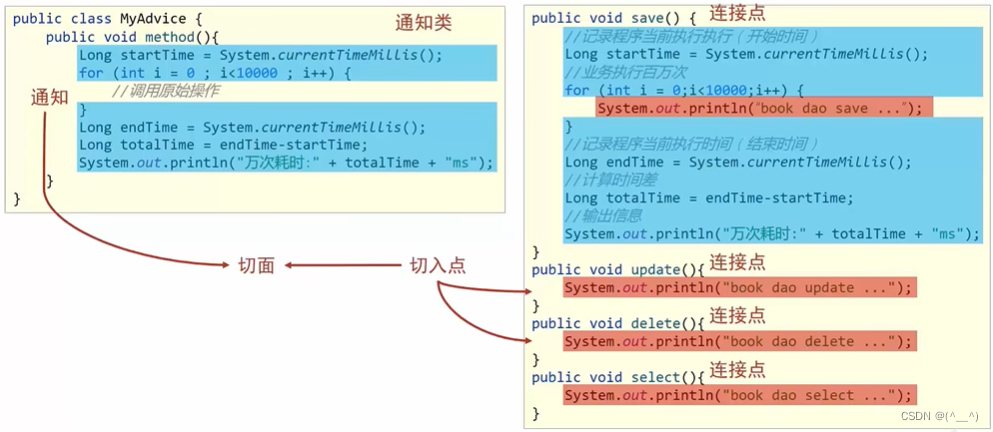
找到程序中共性的部分,抽出来,写一个通知类;
在通知类中定义一个方法,这个方法叫通知,方法里面是共性的功能;
并不是所有方法都要执行这些通知,要把执行这些通知的方法找出来,定义成切入点;
有了切入点和通知,把二者的关系进行绑定,就得到切面。
连接点(JoinPoint):原始方法,如 save()、update()、delete() 方法。
切入点(Pointcut):匹配连接点的式子,用于描述要追加功能的方法。一个切入点可以描述一个或多个方法。
通知(Advice):共性的功能。
通知类:定义通知的类。
切面(Aspect):描述通知与切入点的对应关系。
2. AOP 入门案例
任务:在接口执行前输出当前系统时间
开发模式:XML or 注解
思路分析:
- 导入坐标(pom.xml)
- 制作连接点方法(原始操作,Dao接口与实现类)
- 制作共性功能(通知类与通知)
- 定义切入点
- 绑定切入点与通知关系(切面)
(1) 导入依赖
导入context 时,自动导入了 AOP 的包:
除此之外,还需要导入:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>
(2) 定义接口和实现类
public interface BookDao {
void save();
void update();
}
@Service
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("book dao save...");
}
@Override
public void update() {
System.out.println("book dao update...");
}
}
(3) 通知类:制作通知,定义切入点,绑定切入点与的通知关系
@Component//得到受spring控制的bean
@Aspect//设置当前类为AOP切面类
public class MyAdvice {
//定义切入点:哪些方法需要添加共性功能(通知)
@Pointcut("execution(void com.itheima.dao.BookDao.update())")
private void pt(){}
//绑定切入点与通知关系,通知在切入点前面执行
@Before("pt()")
public void method(){//共性功能(通知)
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
(4) 开启 Spring 对 AOP 注解驱动支持
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy//启动了Myadvice中的@Aspect注解
public class SpringConfig {
}
(5) 测试
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
BookDao bookDao = ctx.getBean(BookDao.class);
bookDao.save();
bookDao.update();
}
}
输出结果:
1675523916075
book dao save...
1675523916080
book dao update...
3. AOP 工作流程(略)
4. AOP 切入点表达式
4.1 语法格式
切入点:要进行增强的方法
切入点表达式:要进行增强的方法的描述方式

描述方式一:执行 BookDao 接口中的无参 update 方法
execution(void com.itheima.dao.BookDao.update())
描述方式二:执行 BookDaoImpl 类中的无参 update 方法
execution(void com.itheima.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl.update())
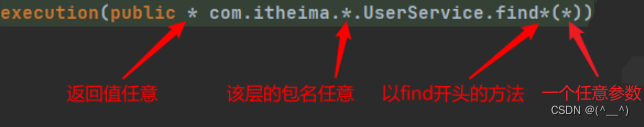
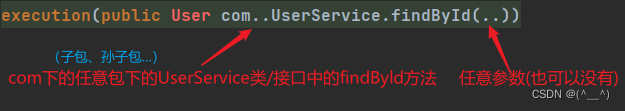
切入点表达式标准格式:动作关键字([访问修饰符] 返回值 包名.类/接口名.方法名(参数) [异常名])
- execution:动作关键字,描述切入点的行为动作,例如 execution 表示执行到指定切入点。
- public:访问修饰符,可以是 public、private 等,可以省略(开发时方法一般都是 public 的,所以一般省略)。
- User:返回值,写返回值类型 com.itheima.service:包名,多级包使用点连接。
- UserService:类 / 接口名称。
- findById:方法名。
- int:参数,直接写参数的类型,多个类型用逗号隔开。
- 异常名:方法定义中抛出指定异常,可以省略。
切入点表达式就是要找到需要增强的方法,所以它就是对一个具体方法的描述,但是方法的定义会有很多,所以如果每一个方法对应一个切入点表达式就会很麻烦,有没有更简单的方式呢?
就需要用到下面所学习的通配符。
4.2 通配符
* :单个独立的任意符号,可以独立出现,也可以作为前缀或者后缀的匹配符出现。
..:多个连续的任意符号,可以独立出现,常用于简化包名与参数的书写。
+:专用于匹配子类类型
4.3 书写技巧
- 所有代码按照标准规范开发,否则以下技巧全部失效
- 描述切入点通常描述接口,而不描述实现类,如果描述到实现类,就出现紧耦合了
- 访问控制修饰符针对接口开发均采用 public 描述(可省略访问控制修饰符描述)
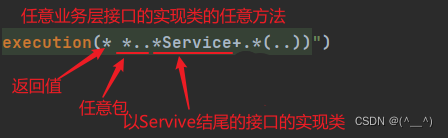
- 返回值类型对于增删改类使用精准类型加速匹配,对于查询类使用
*通配快速描述(查询结果返回有多种情况) - 包名书写尽量不使用
..匹配,效率过低,常用*做单个包描述匹配,或精准匹配 - 接口名 / 类名书写名称与模块相关的采用
*匹配,例如 UserService 书写成*Service - 方法名书写以动词进行精准匹配,名词采用
*匹配,例如 getById 书写成getBy*,selectAll 书写成 selectAll - 参数规则较为复杂,根据业务方法灵活调整
- 通常不使用异常作为匹配规则
5. AOP 通知类型
AOP 通知描述了抽取的共性功能,根据共性功能抽取的位置不同,最终运行代码时要将其加到合理的位置。
5.1 前置通知、后置通知
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(void com.itheima.dao.BookDao.update())")
private void pt(){
}
@Before("pt()")//前置通知
public void before() {
System.out.println("before advice ...");
}
@After("pt()")//后置通知
public void after() {
System.out.println("after advice ...");
}
}
输出结果:
before advice...
book dao update...
after advice...
5.2 环绕通知(重点)
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(void com.itheima.dao.BookDao.update())")
private void pt(){
}
@Around("pt()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{
//要抛出异常,原始操作中如果出现错误,不管
System.out.println("around before advice ...");
//表示对原始操作的调用
pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("around after advice ...");
}
}
输出结果:
around before advice...
book dao update...
around after advice...
【注意事项】原始方法有返回值的处理
修改 MyAdvice,对 BookDao 中的 select 方法添加环绕通知。
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(int com.itheima.dao.BookDao.select())")
private void pt2(){
}
@Around("pt2()")
public void aroundSelect(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("around before advice ...");
//表示对原始操作的调用
//如果没有这句,原始操作不会执行
pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("around after advice ...");
}
}
在 App 类中调用 select 方法
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
BookDao bookDao = ctx.getBean(BookDao.class);
int num = bookDao.select();
System.out.println(num);
}
}
运行后会报错,错误内容为:

错误大概的意思是:空的返回(Null)不匹配原始方法(select方法)的 int 返回。原因是 aroundSelect 方法将 select 方法的返回值拦截了。
所以使用环绕通知时,要根据原始方法的返回值来设置环绕通知的返回值,具体解决方案为:
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(int com.itheima.dao.BookDao.select())")
private void pt2(){
}
@Around("pt2()")
public Object aroundSelect(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("around before advice ...");
//表示对原始操作的调用,并接收返回值
//如果没有这句,原始操作不会执行
Object ret = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("around after advice ...");
return ret;
}
}
为什么返回的是 Object 而不是 int:Object 类型更通用。
在环绕通知中可以对原始方法返回值进行修改,如上面代码可改为:
Integer ret = (Integer) pjp.proceed();
...
return ret+100;
环绕通知小结:
- 环绕通知必须依赖形参 ProceedingJoinPoint 才能实现对原始方法的调用,进而实现原始方法调用前后同时添加通知。
- 通知中如果未使用 ProceedingJoinPoint 对原始方法进行调用将跳过原始方法的执行。
- 对原始方法的调用可以不接收返回值,通知方法设置成void 即可(不推荐,一般也用 Object 类型接收);如果接收返回值,最好设定为 Object 类型。
- 由于无法预知原始方法运行后是否会抛出异常,因此环绕通知方法必须要处理 Throwable 异常。
5.3 返回后通知(了解)
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(int com.itheima.dao.BookDao.select())")
private void pt2(){
}
@AfterReturning("pt2()")
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("afterReturning advice ...");
}
}
输出结果:
book dao select...
afterReturning advice...
100
返回后通知是需要在原始方法 select 正常执行后才会被执行,如果 select() 方法执行过程中出现异常,则返回后通知不会执行。后置通知不管原始方法有没有抛出异常都会执行。
5.4 抛出异常后通知(了解)
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(int com.itheima.dao.BookDao.select())")
private void pt2(){
}
@AfterThrowing("pt2()")
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("afterThrowing advice ...");
}
}
异常后通知是需要原始方法抛出异常,可以在 select() 方法中添加一行代码 int i = 1/0 即可。如果没有抛异常,异常后通知将不会被执行。

6. 案例:业务层接口执行效率
需求:显示任意业务层接口的执行效率(执行时长)
分析:
业务功能:业务层接口执行前后分别记录时间,求差值得到执行效率。
通知类型:前后均可以增强的类型——环绕通知。
在 Spring 的主配置文件 SpringConfig 类中添加注解
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
创建AOP的通知类
@Component
@Aspect
public class ProjectAdvice {
//匹配业务层的所有方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.*Service.*(..))")
private void servicePt(){}
//@Around("ProjectAdvice.servicePt()") 可以简写为下面的方式
@Around("servicePt()")
public void runSpeed(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
//原始方法中若有错误,不做处理,直接抛异常
pjp.proceed();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("业务层接口万次执行时间: "+(end-start)+"ms");
// 没有可返回的东西,就不返回了
// 若原始方法返回值为对象,此处不返回没什么问题,相当于返回null
}
}
测试
//spring整合junit的专用类运行器
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Autowired
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void testFindById() {
accountService.findById(1);
}
@Test
public void testFindAll(){
accountService.findAll();
}
//其他的测试方法同理
}
输出结果:
业务层接口万次执行时间: 4080ms
业务层接口万次执行时间: 3366ms
目前程序所面临的问题是,多个方法一起执行测试的时候,控制台都打印的是:业务层接口万次执行时间:xxxms,没办法区分是哪个接口的哪个方法执行的具体时间,具体如何优化?
@Component
@Aspect
public class ProjectAdvice {
//匹配业务层的所有方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.*Service.*(..))")
private void servicePt() {
}
//@Around("ProjectAdvice.servicePt()") 可以简写为下面的方式
@Around("servicePt()")
public void runSpeed(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
//获取执行签名信息
Signature signature = pjp.getSignature();
//通过签名获取执行操作名称(接口名)
String className = signature.getDeclaringTypeName();
//通过签名获取执行操作名称(方法名)
String methodName = signature.getName();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
//原始方法中若有错误,不做处理,直接抛异常
pjp.proceed();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("万次执行:"+ className+"."+methodName+"---->" +
(end-start) + "ms");
// 没有可返回的东西,就不返回了
// 若原始方法返回值为对象,此处不返回没什么问题,相当于返回null
}
}
输出结果:
万次执行:com.itheima.service.AccountService.findAll---->3949ms
万次执行:com.itheima.service.AccountService.findById---->3137ms
补充说明:
- 当前测试的接口执行效率仅仅是一个理论值,并不是一次完整的执行过程。
- 这块只是通过该案例把AOP的使用进行了学习,具体的实际值是有很多因素共同决定的。
7. AOP 通知获取数据
目前写 AOP 仅仅是在原始方法前后追加一些操作,接下来要说说 AOP 中数据相关的内容。
我们将从获取参数、获取返回值和获取异常三个方面来研究切入点的相关信息。
7.1 获取参数
(1) 前置通知获取原始方法的参数
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
//原始方法
@Override
public String findName(int id, String name) {
System.out.println("id: "+id+" name: "+name);
return "itcast";
}
}
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.dao.BookDao.findName(..))")
private void pt(){}
@Before("pt()")
public void before(JoinPoint jp) {
//获取原始方法的参数,以数组形式返回
Object[] args = jp.getArgs();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(args));
System.out.println("before advice ..." );
}
}
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//加载配置类
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
//按类型获取bean
BookDao bookDao = ctx.getBean(BookDao.class);
//执行方法
String name = bookDao.findName(100, "itheima");
System.out.println(name);
}
}
输出结果:
[100, itheima]
before advice ...
id: 100name: itheima
itcast
(2) 后置通知获取原始方法的参数
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.dao.BookDao.findName(..))")
private void pt(){}
@After("pt()")
public void after(JoinPoint jp) {
//获取原始方法的参数,以数组形式返回
Object[] args = jp.getArgs();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(args));
System.out.println("after advice ..." );
}
}
输出结果:
id: 100 name: itheima
[100, itheima]
after advice ...
itcast
(3) 环绕通知获取原始方法的参数
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.dao.BookDao.findName(..))")
private void pt(){}
@Around("pt()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(args));
// args[0]=666;
Object ret = pjp.proceed(args);
return ret;
}
}
输出结果:
[100, itheima]
id: 100 name: itheima
itcast
pjp.proceed()方法有两个构造方法,分别是:
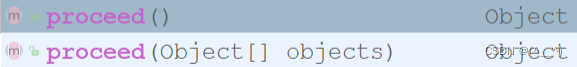
调用无参的 proceed,会在原始方法有参数时自动传入参数;调用无参的 proceed 需要手动传参。所以调用两个方法都可以完成功能。
但需要修改原始方法的参数时,就只能用有参方法,如下:
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.dao.BookDao.findName(..))")
private void pt(){}
@Around("pt()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(args));
args[0]=666;
Object ret = pjp.proceed(args);
return ret;
}
}
输出结果:
[100, itheima]
id: 666 name: itheima
itcast
有了这个特性,就可以在环绕通知中对原始方法的参数进行拦截过滤,避免由于参数问题导致程序无法正确运行,保证了代码的健壮性。
(4) 返回后通知获取原始方法的参数
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.dao.BookDao.findName(..))")
private void pt(){}
@AfterReturning("pt()")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint jp) {
//获取原始方法的参数,以数组形式返回
Object[] args = jp.getArgs();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(args));
System.out.println("afterReturning advice...");
}
}
(5) 抛出异常后通知获取原始方法的参数
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.dao.BookDao.findName(..))")
private void pt(){}
@AfterThrowing("pt()")
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint jp) {
//获取原始方法的参数,以数组形式返回
Object[] args = jp.getArgs();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(args));
System.out.println("afterThrowing advice...");
}
}
7.2 获取返回值
只有环绕通知和返回后通知可以获取返回值,环绕通知获取返回值的方法前面已经讲过,不再赘述。
下面只看返回后通知获取返回值的方法。
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
//原始方法
@Override
public String findName(int id, String name) {
System.out.println("id: "+id+" name: "+name);
return "itcast";
}
}
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.dao.BookDao.findName(..))")
private void pt(){}
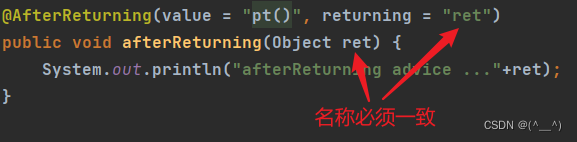
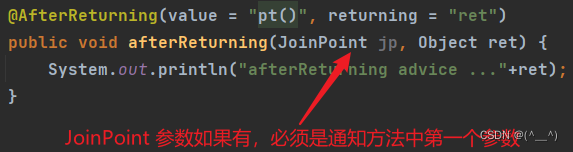
@AfterReturning(value = "pt()", returning = "ret")
public void afterReturning(Object ret) {
System.out.println("afterReturning advice ..."+ret);
}
}
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//加载配置类
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
//按类型获取bean
BookDao bookDao = ctx.getBean(BookDao.class);
//执行方法
String name = bookDao.findName(100, "itheima");
System.out.println(name);
}
}
输出结果:
id: 100 name: itheima
afterReturning advice ...itcast
itcast
注意:
(1) 参数名的问题
(2) afterReturning 方法参数类型的问题
参数类型可以写成 String,但是为了能匹配更多的参数类型,建议写成 Object 类型。
(3) afterReturning 方法的参数顺序问题
7.3 获取异常(了解)
获取抛出的异常,只有抛出异常后 AfterThrowing 和环绕 Around 这两个通知类型可以做到。
抛出异常后 AfterThrowing:
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.dao.BookDao.findName(..))")
private void pt(){}
@Around("pt()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(args));
args[0]=666;
Object ret = null;
try {
ret = pjp.proceed(args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
return ret;
}
}
环绕 Around:
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.dao.BookDao.findName(..))")
private void pt(){}
@AfterThrowing(value = "pt()", throwing = "t")
public void afterThrowing(Throwable t) {
System.out.println("afterThrowing advice..."+t);
}
}
如何让原始方法抛出异常,方式有很多:
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
//原始方法
@Override
public String findName(int id, String name) {
System.out.println("id: "+id+" name: "+name);
if (true) {//让语法通过
throw new NullPointerException();
}
return "itcast";
}
}
8. 案例:百度网盘密码数据兼容处理
需求:对百度网盘分享链接输入密码时尾部多输入的空格做兼容处理。
- 从别人发给我们的内容中复制提取码的时候,有时候会多复制到一些空格,直接粘贴到百度的提取码输入框
- 但是百度那边记录的提取码是没有空格的
- 这时如果直接对比,就会引发提取码不一致,导致无法访问百度盘上的内容
- 所以多输入一个空格可能会导致项目的功能无法正常使用。
此时,可以将用户输入的提取码先去掉空格再操作。
只需要在业务方法执行前,对所有的输入参数进行格式处理——trim()
以后涉及到需要去除前后空格的业务可能会有很多,这个去空格的代码是每个业务都写吗?当然不是,可以考虑使用 AOP 来统一处理。
@Repository
public class ResourceDaoImpl implements ResourceDao {
@Override
public boolean readResources(String url, String password) {
//模拟校验:只比较字符串是否相等(是否去掉了前后空格),实际还涉及加密问题
return password.equals("root");
}
}
@Service
public class ResourceServiceImpl implements ResourceService {
@Autowired
private ResourceDao resourceDao;
@Override
public boolean openURL(String url, String password) {
return resourceDao.readResources(url, password);
}
}
@Configuration//该类是配置类
@ComponentScan("com.itheima")//扫描这个包下的类,找bean
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class SpringConfig {
}
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(boolean com.itheima.service.ResourceService.openURL(*,*))")
private void pt(){}
@Around("pt()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
//如果某个参数是字符串
if (args[i].getClass().equals(String.class)){
args[i]=args[i].toString().trim();
}
}
Object ret = pjp.proceed(args);
return ret;
}
}
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//加载配置类
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
//按类型获取bean
ResourceService resourceService = ctx.getBean(ResourceService.class);
//执行方法
boolean flag = resourceService.openURL("http://pan.baidu.com/haha", "root ");
System.out.println(flag);
}
}
输出结果:
true