本篇主要是在初级数据结构中介绍的二叉树的提升,了解二叉搜索树的特性。
文章目录
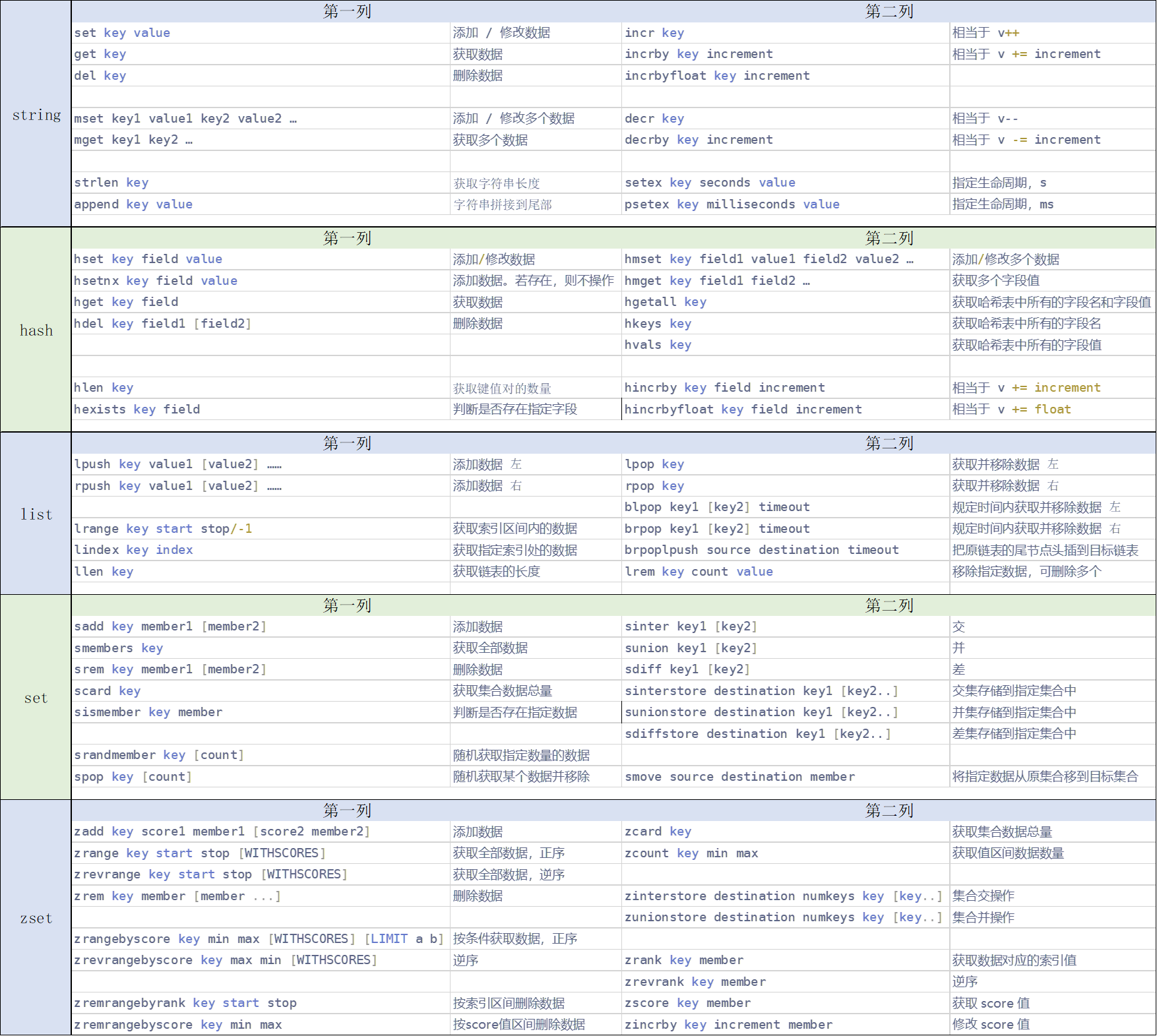
- 一、二叉搜索树的概念
- 二、二叉搜索树操作
- 1、二叉搜索树的查找
- 2、二叉搜索树的插入
- 3、二叉搜索树的删除
- 三、二叉搜索树的实现
- 四、二叉搜索树的应用
- 五、关于二叉树进阶面试题
一、二叉搜索树概念
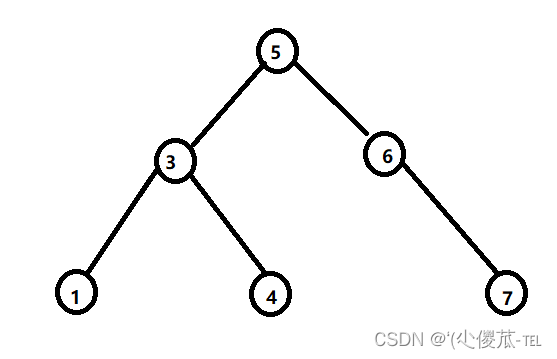
概念:二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下特征:
一、它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有的节点的值都小于根节点的值
二、它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有的节点的值都大于根节点的值
三、它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
如果所示:
二、二叉搜索树的操作
1.二叉搜索树的查找
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
cur = cur->_right;
else if(cur->_key>key)
cur = cur->_left;
else
return true;
}
return false;
}2.二叉树的插入
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
//如果此时根结点不存在需要创建根结点
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
//插入新结点的时候需要将父类的节点进行连接
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->key < key)
parent->_right = cur;
else
parent->_left = cur;
return true;
}3.二叉树的删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
//开始删除
//左为空
//右为空
//左右都不为空
//这里需要考虑根节点的情况
if (cur->left == nullptr)
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
parent->left = cur->_right;
else
parent->_right = cur->right;
}
}
delete cur;
cur = nullptr;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (_root == cur)
_root = cur->_left;
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
parent->_left = cur->_left;
else
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
delete cur;
cur = nullptr;
}
else
{
//找到右子树最小节点进行替换
Node* minParent = cur;
Node* min = cur->_right;
while (min->_left)
{
minParent = min;
min = min->_left;
}
swap(cur->_key, min->_key);
if (minParent->_left == min)
minParent->_left = min->_right;
else
minParent->_right = min->_right;
delete min;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
}三、二叉搜索树的实现
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
{}
};
//class BinarySearchTree
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key < key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
// 开始删除
// 1、左为空
// 2、右为空
// 3、左右都不为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
cur = nullptr;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (_root == cur)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
cur = nullptr;
}
else
{
// 找到右子树最小节点进行替换
Node* minParent = cur;
Node* min = cur->_right;
while (min->_left)
{
minParent = min;
min = min->_left;
}
swap(cur->_key, min->_key);
if (minParent->_left == min)
minParent->_left = min->_right;
else
minParent->_right = min->_right;
delete min;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
/
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
~BSTree()
{
_Destory(_root);
}
/*BSTree()
{}*/
// C++的用法:强制编译器生成默认的构造
BSTree() = default;
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{
_root = _Copy(t._root);
}
// t2 = t1
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
private:
Node* _Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* copyRoot = new Node(root->_key);
copyRoot->_left = _Copy(root->_left);
copyRoot->_right = _Copy(root->_right);
return copyRoot;
}
void _Destory(Node*& root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_Destory(root->_left);
_Destory(root->_right);
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
else
{
Node* del = root;
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else
{
// 找右树的最左节点替换删除
Node* min = root->_right;
while (min->_left)
{
min = min->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, min->_key);
//return EraseR(key); 错的
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key < key)
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
else
return false;
}
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
else
return true;
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};四、二叉搜索树的应用
1.K模型:K模型即只有key作为关键码,结构中只需要存储Key即可,关键码即为需要搜索到
的值。
2.KV模型:每一个关键码key,都有与之对应的值Value,即<Key, Value>的键值对。
五、关于二叉树进阶面试题

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
string tree2str(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr)
return string();
string str;
str+=to_string(root->val);
//如果左子树不为空或者左右子树都不为空,左边需要加括号
if(root->left||root->right)
{
str+='(';
str+=tree2str(root->left);
str+=')';
}
//右边如果不为空,右边需要加括号
if(root->right)
{
str+='(';
str+=tree2str(root->right);
str+=')';
}
return str;
}
}; 
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
//如果此时二叉树为空,则返回vector<vector<int>>的匿名对象
if(root==nullptr)
return vector<vector<int>>();
//利用队列先进先出的特性进行判断
queue<TreeNode*> q;
//利用二维数组来保存当前没一层的节点
vector<vector<int>> vv;
int levelSize=1;//每一行的节点数
q.push(root);//将此时的根节点如队
while(!q.empty())//如果队列不为空就继续
{
vector<int> v;
for(int i=0;i<levelSize;i++)
{
TreeNode*front=q.front();//将队列的第一个数据保存然后出队
q.pop();
v.push_back(front->val);
if(front->left)
q.push(front->left);
if(front->right)
q.push(front->right);
}
levelSize=q.size();//将此时队列中的个数求出来
vv.push_back(v);
}
return vv;
}
}; 
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
//如果此时二叉树为空,则返回vector<vector<int>>的匿名对象
if(root==nullptr)
return vector<vector<int>>();
//利用队列先进先出的特性进行判断
queue<TreeNode*> q;
//利用二维数组来保存当前没一层的节点
vector<vector<int>> vv;
int levelSize=1;//每一行的节点数
q.push(root);//将此时的根节点如队
while(!q.empty())//如果队列不为空就继续
{
vector<int> v;
for(int i=0;i<levelSize;i++)
{
TreeNode*front=q.front();//将队列的第一个数据保存然后出队
q.pop();
v.push_back(front->val);
if(front->left)
q.push(front->left);
if(front->right)
q.push(front->right);
}
levelSize=q.size();//将此时队列中的个数求出来
vv.push_back(v);
}
reverse(vv.begin(),vv.end());
return vv;
}
};

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool Find(TreeNode*root,TreeNode*x,stack<TreeNode*>&path)
{
if(root==nullptr) return false;
path.push(root);
if(root==x) return true;
//如果没有找到从左子树开始找,如果没找到去右子树中找,如果都没有找到此时需要将所有的当前节点需要进行出栈的操作
if(Find(root->left,x,path)) return true;
if(Find(root->right,x,path)) return true;
path.pop();
return false;
}
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root==nullptr) return nullptr;
//利用DFS来保存每一次搜索的路径
stack<TreeNode*> pPath,qPath;
Find(root,p,pPath);
Find(root,q,qPath);
//根据求两个链表公共节点的策略来求出二叉树中两个节点的最近的公共祖先的问题
while(pPath.size()!=qPath.size())
{
if(pPath.size()>qPath.size()) pPath.pop();
else qPath.pop();
}
while(pPath.top()!=qPath.top())
{
pPath.pop();
qPath.pop();
}
return pPath.top();
}
}; 
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
void InOrderConvert(TreeNode*cur,TreeNode*&prev)
{
if(cur==nullptr) return;
//先找出左子树
InOrderConvert(cur->left,prev);
cur->left=prev;
if(prev)
prev->right=cur;
prev=cur;
InOrderConvert(cur->right,prev);
}
TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) {
TreeNode*prev=nullptr;
InOrderConvert(pRootOfTree,prev);
while(pRootOfTree&&pRootOfTree->left)
pRootOfTree=pRootOfTree->left;
return pRootOfTree;
}
};

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
//利用前序来创建树,中序来分割区间
TreeNode*buildTreeHelper(vector<int>&preorder,vector<int>&inorder,int& prei,int inbegin,int inend)//这里previ需要利用引用,因为下一次递归prei会发生改变
{
if(inbegin>inend) return nullptr;
TreeNode*root=new TreeNode(preorder[prei++]);
//将中序的区间进行划分
int ini=inbegin;
while(ini<=inend)
{
if(inorder[ini]==root->val) break;
else ++ini;
}
//利用分治法的思想继续分割左右区间
root->left=buildTreeHelper(preorder,inorder,prei,inbegin,ini-1);
root->right=buildTreeHelper(preorder,inorder,prei,ini+1,inend);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int i=0;
return buildTreeHelper(preorder,inorder,i,0,inorder.size()-1);
}
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
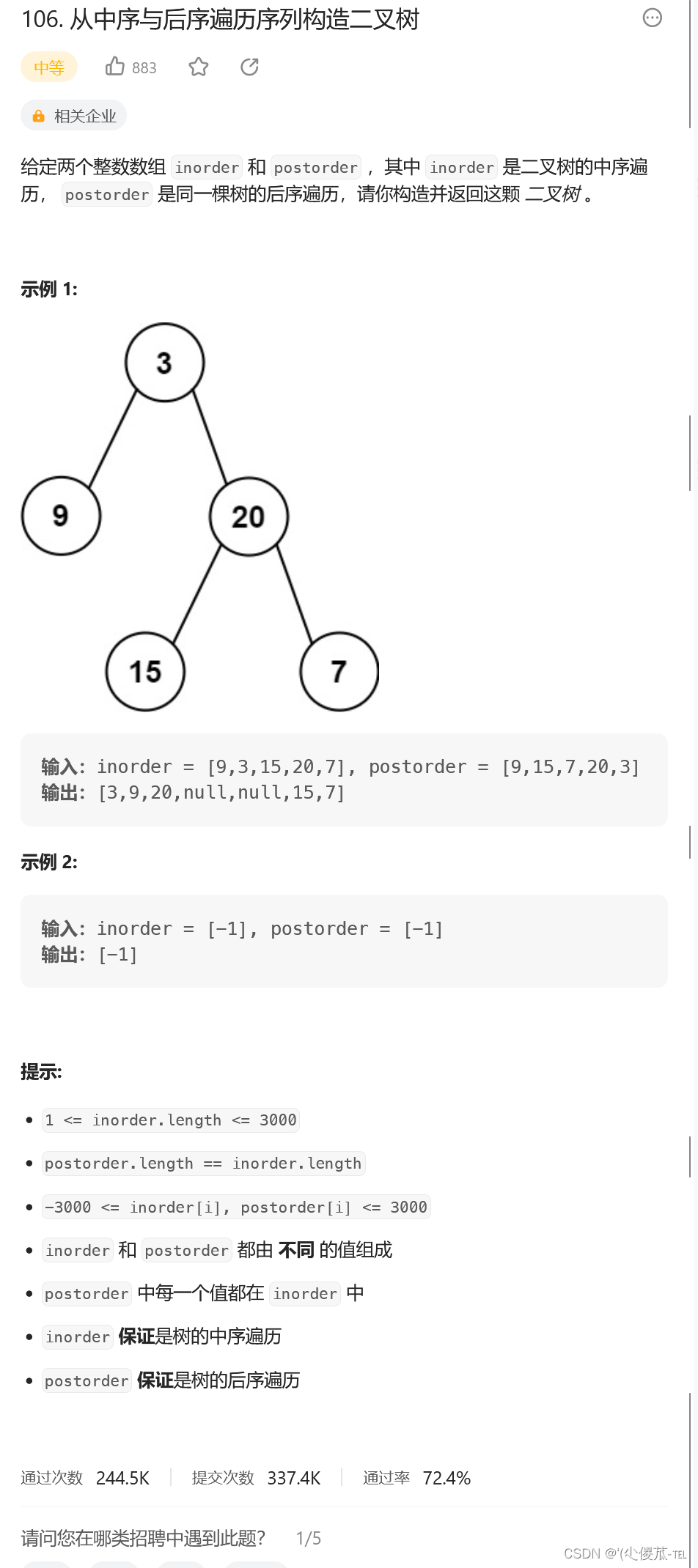
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr)
return vector<int>();
vector<int> v;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode*cur=root;
while(cur||!st.empty())
{
//左路节点入栈
while(cur)
{
v.push_back(cur->val);
st.push(cur);
cur=cur->left;
}
//右路节点的右子树
TreeNode*top=st.top();
st.pop();
cur=top->right;
}
return v;
}
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return vector<int>();
TreeNode*cur=root;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> v;
while(cur||!st.empty())
{
while(cur)
{
st.push(cur);
cur=cur->left;
}
TreeNode*top=st.top();
v.push_back(top->val);
st.pop();
cur=top->right;
}
return v;
}
}; 
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return vector<int>();
TreeNode*cur=root;
TreeNode*prev=nullptr;
vector<int> v;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
//一个节点不为空的情况下:
//右子树没有访问,访问右子树
//右子树已经访问过了,访问根节点
while(cur||!st.empty())
{
//左路节点入栈
while(cur)
{
st.push(cur);
cur=cur->left;
}
TreeNode*top=st.top();
//右路节点
//如果右为空或者没有访问过
if(top->right==nullptr||top->right==prev)
{
v.push_back(top->val);
prev=top;
st.pop();
}
else
{
cur=top->right;
}
}
return v;
}
};



![[附源码]计算机毕业设计JAVA剧本杀门店管理系统-](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a00e7614a4714c0789a2a81917ee3d07.png)