枫の个人主页
你不能改变过去,但你可以改变未来
算法/C++/数据结构/C
Hello,这里是小枫。C语言与数据结构和算法初阶两个板块都更新完毕,我们继续来学习C++的内容呀。C++是接近底层有比较经典的语言,因此学习起来注定枯燥无味,西游记大家都看过吧~,我希望能带着大家一起跨过九九八十一难,降伏各类难题,学会C++,我会尽我所能,以通俗易懂、幽默风趣的方式带给大家形象生动的知识,也希望大家遇到困难不退缩,遇到难题不放弃,学习师徒四人的精神!!!故此得名【C++游记】
话不多说,让我们一起进入今天的学习吧~~~
目录
1>>标准库的String
1.1>>auto和范围for小知识
1.2>>string常用接口(组件)这里都可以查找到
容量接口
访问和遍历
string类对象的修改操作
非成员函数但会用到
2>>string的模拟实现
3>>Boos战——string重要接口的模拟实现
1.String.h
2.String.cpp
3.wctest.cpp
4>>结语
1>>标准库的String
1.1>>auto和范围for小知识
师傅别怕,赠与“武器”一把 i
auto基本知识:
它声明引用类型时,必须在auto后加上&。
声明多个变量时,这些变量必须是相同的类型。
auto不能作为函数参数,可以作为返回值。
不能用于声明数组。
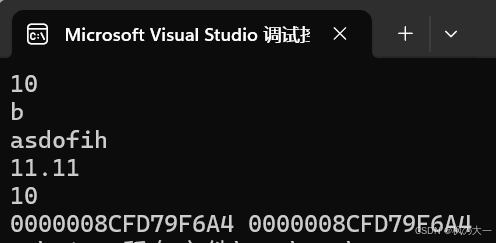
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
auto a = 10;
auto b = 'b';
auto c = "asdofih";
auto d = 11.11;
auto& e = a;
cout << a << endl;
cout << b << endl;
cout << c << endl;
cout << d << endl;
cout << e << endl;
printf("%p %p", &a, &e);
return 0;
}
范围for:
对比C语言的for循环,C++使用更好用的范围for代替, 格式为:“for(auto 范围内用于迭代的变量 : 被迭代的范围)”,自动迭代、取数据、结束,这就是自动范围for。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
for (auto& e : arr) {//若要更改里面的数值,那么就要用引用才能修改到数组本身
e += 2;
}
for (auto e : arr) {
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
string str("hello world");
for (auto ch : str) {
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
1.2>>string常用接口(组件)这里都可以查找到
师傅后面都会介绍,不必担心
| String函数名称 | 功能说明 |
| string() | 构造空的string类对象,即空字符串 |
| string(const char* s) | 用C-string(常量字符串)来构造string类对象 |
| string(size_t n,char c) | string类对象中包含n个字符c |
| string(const string&s) | 拷贝构造函数 |
void Test1() {
string s1;//构造空的string类对象
string s2("hello feng");//用常量字符串构造string类对象
string s3(s2);//用s2拷贝构造s3
}容量接口
若定义为string s,以下表size为例,就是s.size();
| size | 返回字符串有效字符长度,使用范围比length广 |
| length | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| capacity | 返回总空间大小 |
| empty | 检测字符串释放为空串,空返回true,非空返回false |
| clear | 清空有效字符 |
| reserve | 为字符串预留空间 |
| resize | 将有效字符个数设置为n个,多余用c填充 |
补充说明:size和length的区别只有在引入迭代器才能体现出来,一般都用size,length有使用限制。
clear只清空,不改大小
resize(size_t n,char c)用变量c的字符填充多余空间,resize(size_t)则是用0来填充。
reserve预留空间,小于string的空间大小时不作改动。
访问和遍历
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
| operator[] | 返回pos位置的字符,const string类对象调用 |
| begin+end | begin获取一个字符的迭代器+end获取最后一个字符下一个位置的迭代器 |
| rbegin+rend | rbegin获取最后一个字符的迭代器+rend获取一个字符的迭代器 |
| 范围for | C++11的遍历方式 |
string类对象的修改操作
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
| push_back | 在字符串后尾插字符c(单个) |
| append | 在字符串后追加一个字符串(多个) |
| operator+= | 在字符串后追加一个字符串(多个) |
| c_str | 返回C格式字符串 |
| find+npos | 从字符串pos位置往后查找字符c,返回它的位置 |
| rfind | 从字符串pos位置往前查找字符c,返回它的位置 |
| substr | 在str中从pos位置开始,截取n个字符,将其返回 |
非成员函数但会用到
| 函数 | 功能说明 |
| operator+ | 深拷贝,效率低 |
| operator>> | 输入运算符重载 |
| operator<< | 输出运算符重载 |
| getline | 获取一行字符串 |
| relational operators | 大小比较 |
2>>string的模拟实现
错误示范:
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
class MyString {
public:
MyString(const char* str = "") {
if (str == nullptr) {
perror("flase");
return;
}
_str = new char[strlen(str) + 1];//加1放\0
strcpy(_str, str);
}
~MyString() {
if (_str) {
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
}
private:
char* _str;
};
void Test2() {
string s1("hello feng");
string s2(s1);
}
int main() {
/*Test1();*/
Test2();
return 0;
}上述过程会报错,因为没有写拷贝构造,s2会调用s1的默认构造,而在类和对象章节中我们知道默认构造都是浅拷贝,这里是一个字符数组,因此要调用深拷贝。
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
class MyString {
public:
MyString(const char* str = "") {//构造
if (str == nullptr) {
perror("flase");
return;
}
_str = new char[strlen(str) + 1];//加1放\0
strcpy(_str, str);
}
MyString(const MyString& s)//拷贝构造
:_str(nullptr)
{
MyString tmp(s._str);
swap(tmp._str, _str);
}
~MyString() {//析构
if (_str) {
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
}
private:
char* _str;
};
void Test2() {
string s1("hello feng");
string s2(s1);
}
int main() {
/*Test1();*/
Test2();
return 0;
}3>>Boos战——string重要接口的模拟实现
这里直接附上上个文件源码,大部分已经注释完毕,请大家伙享用,感兴趣可以复制过去测试,不过还是自己敲一遍比较好。
1.String.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
namespace wc
{
class string
{
public:
typedef char* iterator;//手动自造迭代器,名字与库中相同,但在wc的命名空间里
typedef const char* const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _str;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _str + _size;
}
void swap(string& s);//交换,直接套用标准库里的swap
string(size_t n, char ch);//设置相同字符多少个为一个字符串
string(const char* str = "");//构造函数
string(const string& s);//拷贝构造函数
~string();//析构函数
void clear()//清除
{
_str[0] = '\0';
_size = 0;
}
string& operator=(string s);//string& operator=(const string& s);
const char* c_str() const//常数直接返回自己地址,比较快因此调用内联
{
return _str;
}
void reserve(size_t n);//保存,为字符串预留空间
void push_back(char ch);//类似于尾插
void append(const char* str);//尾插一个字符串
string& operator+=(char ch);//类似于尾插
string& operator+=(const char* str);//尾插一个字符串
void insert(size_t pos, size_t n, char ch);//在pos位置插入n个ch字符
void insert(size_t pos, const char* str);//在pos位置插入一个字符串
void erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);//在pos位置删除len个字符
size_t find(char ch, size_t pos = 0);
size_t find(const char* str, size_t pos = 0);
size_t size() const
{
return _size;
}
size_t capacity() const
{
return _size;
}
char& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
const char& operator[](size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
string substr(size_t pos, size_t len = npos);//从pos位置开始取len个作为子串返回
bool operator==(const string& s) const;
bool operator!=(const string& s) const;
bool operator<(const string& s) const;
bool operator<=(const string& s) const;
bool operator>(const string& s) const;
bool operator>=(const string& s) const;
private:
char* _str = nullptr;//定义字符串数组_str
size_t _size = 0;//有效个数
size_t _capacity = 0;//总容量
const static size_t npos;//设置默认结束值
};
// cout<<s1
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s);
// cin>>s1
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s);
istream& getline(istream& is, string& s, char delim = '\n');
void test_string1();
void test_string2();
void test_string3();
void test_string4();
void test_string5();
void test_string6();
void test_string7();
}2.String.cpp
//#include<iostream>
//using namespace std;
//int main() {
// auto a = 10;
// auto b = 'b';
// auto c = "asdofih";
// auto d = 11.11;
// auto& e = a;
// cout << a << endl;
// cout << b << endl;
// cout << c << endl;
// cout << d << endl;
// cout << e << endl;
// printf("%p %p", &a, &e);
// return 0;
//}
//#include<iostream>
//using namespace std;
//int main() {
// int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
// for (auto& e : arr) {//若要更改里面的数值,那么就要用引用才能修改到数组本身
// e += 2;
// }
// for (auto e : arr) {
// cout << e << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// string str("hello world");
// for (auto ch : str) {
// cout << ch << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// return 0;
//}
//void Test1() {
// string s1;//构造空的string类对象
// string s2("hello feng");//用常量字符串构造string类对象
// string s3(s2);//用s2拷贝构造s3
//}
//#include<iostream>
//#include<assert.h>
//using namespace std;
//class MyString {
//public:
// MyString(const char* str = "") {//构造
// if (str == nullptr) {
// perror("flase");
// return;
// }
// _str = new char[strlen(str) + 1];//加1放\0
// strcpy(_str, str);
// }
// MyString(const MyString& s)//拷贝构造
// :_str(nullptr)
// {
// MyString tmp(s._str);
// swap(tmp._str, _str);
// }
// ~MyString() {//析构
// if (_str) {
// delete[] _str;
// _str = nullptr;
// }
// }
//private:
// char* _str;
//};
//void Test2() {
// string s1("hello feng");
// string s2(s1);
//}
//
//int main() {
// /*Test1();*/
// Test2();
// return 0;
//}
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"string.h"
namespace wc
{
const size_t string::npos = -1;
void string::swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
string::string(size_t n, char ch)
:_str(new char[n + 1])
, _size(n)
,_capacity(n)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
_str[i] = ch;
}
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
string::string(const char* str)//声明中写过默认值,这里就不能再写了
:_size(strlen(str))
{
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_size + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);//复制还没复制\0
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
string::string(const string& s)
{
string tmp(s._str);
swap(tmp);
}
string::~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}
string& string::operator=(string s)
{
swap(s);
return *this;
}
void string::reserve(size_t n) {//预留空间
if (n > _capacity) {//大于就扩容
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];
strcpy(tmp, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}
void string::push_back(char ch) {
if (_size + 1 > _capacity) {//大于就扩容
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2);//预留空间刚写就能用
}
_str[_size] = ch;
_size++;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
void string::append(const char* str) {
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity) {
reserve(_size + len);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
_size += len;
}
string& string::operator+=(char ch)
{
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
string& string::operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
void string::insert(size_t pos, size_t n, char ch)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
assert(n > 0);
if (_size + n > _capacity)
{
// 扩容
size_t newCapacity = 2 * _capacity;
if (_size + n > 2 * _capacity)
{
newCapacity = _size + n;
}
reserve(newCapacity);
}
size_t end = _size + n;
while (end > pos + n - 1) {
_str[end] = _str[end - n];
end--;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
_str[pos + i] = ch;
}
_size += n;
}
void string::insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
size_t n = strlen(str);
insert(pos, n, 'x');//覆盖一下
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
_str[pos + i] = str[i];
}
}
void string::erase(size_t pos, size_t len) {
if (len > _size - pos) {//多删了
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else {
size_t end = pos + len;
while (end <= _size) {//\0也拷贝
_str[end - len] = _str[end];
end++;
}
_size -= len;
}
}
size_t string::find(char ch, size_t pos)
{
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++)
{
if (_str[i] == ch)
{
return i;
}
}
return npos;
}
size_t string::find(const char* str, size_t pos)
{
const char* p = strstr(_str + pos, str);
if (p == nullptr)
{
return npos;
}
else
{
return p - _str;
}
}
string string::substr(size_t pos, size_t len)
{
if (len > _size - pos)//若超出,就等于剩下长度
len = _size - pos;
string tmp;
tmp.reserve(len);
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++) {
tmp += _str[pos + i];//直接加等,简单易懂
}
return tmp;
}
bool string::operator==(const string& s) const
{
return strcmp(_str, s._str) == 0;
}
bool string::operator!=(const string& s) const
{
return !(*this == s);
}
bool string::operator<(const string& s) const
{
return strcmp(_str, s._str) < 0;
}
bool string::operator<=(const string& s) const
{
return *this < s || *this == s;
}
bool string::operator>(const string& s) const
{
return !(*this <= s);
}
bool string::operator>=(const string& s) const
{
return !(*this < s);
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s)
{
for (size_t i=0;i<s.size();i++)
{
out << s[i];
}
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
// 输入短串,不会浪费空间
// 输入长串,避免不断扩容
const size_t N = 1024;
char buff[N];
int i = 0;
char ch = in.get();
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')//遇到空格和\n停止
{
buff[i++] = ch;
if (i == N - 1)
{
buff[i] = '\0';//最后一个复制为0然后加上
s += buff;
i = 0;
}
//也可以直接写s+=ch,不过占用内存高
ch = in.get();
}
if (i > 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return in;
}
istream& getline(istream& in, string& s, char delim)
{
s.clear();
const size_t N = 1024;
char buff[N];
int i = 0;
char ch = in.get();
while (ch != delim)
{
buff[i++] = ch;
if (i == N - 1)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
i = 0;
}
ch = in.get();
}
if (i > 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return in;
}
void test_string1()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string s2;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s1 += ' ';
s1 += '+';
s1 += "hello ";
s1 += "hello feng1111111111111111111111111";
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string2()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.insert(11, 3, 'x');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.insert(6, 3, 'x');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.insert(0, 3, 'x');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string s2("hello world");
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s2.insert(11, "yyy");
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s2.insert(6, "yyy");
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s2.insert(0, "yyy");
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string3()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.erase(6, 2);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.erase(6, 20);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.erase(3);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string s2("hello helleoo");
cout << s2.find('e') << endl;
cout << s2.find("helle") << endl;
}
void test_string4()
{
string s1("hello world");
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
s1[i]++;
cout << s1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : s1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
const string s2("hello world");
for (auto e : s2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_string5()
{
string s1("hello world");
string sub1 = s1.substr(6, 3);
cout << sub1.c_str() << endl;
string sub2 = s1.substr(6, 300);
cout << sub2.c_str() << endl;
string sub3 = s1.substr(6);
cout << sub3.c_str() << endl;
string s2("hello fengxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx");
s1 = s2;
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s1 = s1;
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string6()
{
/*string s1("hello world");
string s2("hello bit");
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
string s3;
cin >> s3;
cout << s3 << endl;*/
string s1, s2;
cin >> s1 >> s2;
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
string s3;
//getline(cin, s3);
getline(cin, s3, '!');
cout << s3 << endl;
}
void test_string7()
{
string s1("1111111111111");
string s2(s1);
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
string s3("222222222222222222222222222");
s1 = s3;
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
//s1.swap(s2);
//swap(s1, s2);
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
}
}
3.wctest.cpp
#include"string.h"
int main()
{
//wc::test_string1();
//wc::test_string3();
wc::test_string5();
return 0;
}4>>结语
今日C++到这里就结束啦,如果觉得文章还不错的话,可以三连支持一下。感兴趣的宝子们欢迎持续订阅小枫,小枫在这里谢谢宝子们啦~小枫の主页还有更多生动有趣的文章,欢迎宝子们去点评鸭~C++的学习很陡,时而巨难时而巨简单,希望宝子们和小枫一起坚持下去~你们的三连就是小枫的动力,感谢支持~