1.行业背景
纯血鸿蒙,即鸿蒙Next版已于2014年1月正式发版,鸿蒙生态设备数量已经突破10亿台,已经有超过15000+个应用和元服务上架。鸿蒙生态不只是移动设备这么简单,他打造的是一个1+8+n的全场景战略,真正做到了“万物互联”。最近较火的“云端一体化”计划,开发者只需要同一种开发语言写一套代码,不用关心云端部署、不用关心负载均衡、CPU、内存等性能瓶颈,将运维工作交给华为团队,且接口调用按调用次数收费,达到了“无运维、零浪费”的效果。
2.预研背景
近期公司有预研纯血鸿蒙应用层调用C/C++代码的需求,借此机会深入了解、学习鸿蒙生态。
本文会以一个《高仿Mac计算器》应用开发为案例,讲解鸿蒙应用的开发流程,重点讲解c++开发模块,主要讲述开发、编译、引用流程,而不是深入c/c++语法细节。
3.目标
鸿蒙开发作为一个全新的生态、要零基础看本文可能有点吃力,不过笔者尽量以通俗语言来描述,另外由于篇幅限制,本文不再从零讲解鸿蒙整体开发流程、ArtTS语法细节,重点讲解Napi开发流程。
学习本文后能达到的效果:
1.可以从0开发一个c/c++模块,并编译生成so包
2.借助DevEco Studio可将三方so包集成至项目里
4.Napi概述
4.1.简介
Node-API是用于封装JavaScript能力为Native插件的API,独立于底层JavaScript,并作为Node.js的一部分。
4.2.支持的能力
Node-API可以去除底层的JavaScript引擎的差异,提供一套稳定的接口。
HarmonyOS的Node-API组件对Node-API的接口进行了重新实现,底层对接了ArkJS等引擎。当前支持Node-API标准库中的部分接口。
4.3.交互及场景分析
| 交互方式 | 适用场景 | 本文是否包含 |
| ArtTS直接调用C/C++ | native和ArtTS源码在一块,均从零混合开发 | 是 |
| C/C++调用ArtTS | 通常用于防逆向、加大逆向难度 | 否 |
| ArtTS调用so包间接调用C/C++ | 将C/C++编译为so包作为类似STL,可供甲方调用 | 是 |
| C/C++Native层调用so包 | 用户C/C++有二次开发封装的场景,例如基于so包二次封装 | 否 |
4.4.当前支持的Node-API标准库接口
5.开发环境
5.1.开发工具
5.1.1.DevEco Studio版本
Build Version: 5.0.3.900, built on October 8, 2024
5.1.2.SDK版本
HarmonyOS NEXT Beta1 SDK, based on OpenHarmony SDK Ohos_sdk_public 5.0.0.71 (API Version 12 Release)
5.1.3.项目模型
选择stage模型
拓展:
HarmonyOS先后提供了两种应用模型
- FA(Feature Ability)模型:HarmonyOS早期版本开始支持的模型,已经不再主推。
- Stage模型:HarmonyOS 3.1版本开始新增的模型,是目前主推且会长期演进的模型。
5.1.4.技术栈
5.1.4.1.界面搭建
基于声明式UI-ArtUI
演变过程:JavaScript =>TypeScript => ArtTs =>ArtUI
感兴趣的小伙伴可以基于演变历史补充下营养
5.1.4.2.算法逻辑
四则运算基于c/c++语法
5.1.4.3.NDK胶水语言
NAPI作为ArtTs相互调用C/C++的粘合剂,本质上也是C/C++实现的,需要深入学习了解其api
5.1.4.4.编译工具链
CMake编译工具,C/C++代码通过CMake编译工具编译成动态链接库so文件,使用index.d.ts文件对外提供接口,ArkTS引入so文件后调用其中的接口。
6.效果图
6.1.MacOS原版计算器效果
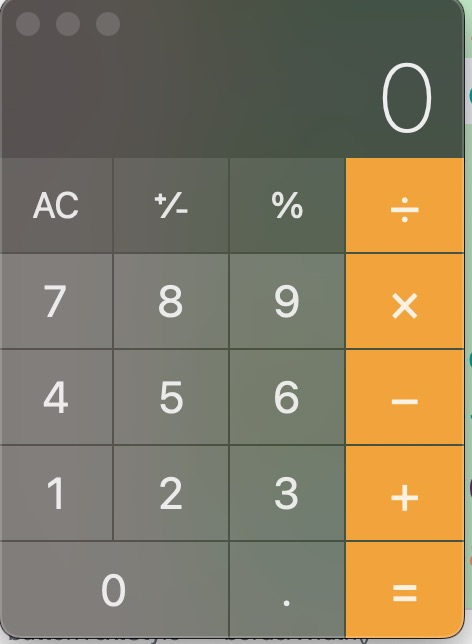
6.2.高仿MacOS计算器效果图
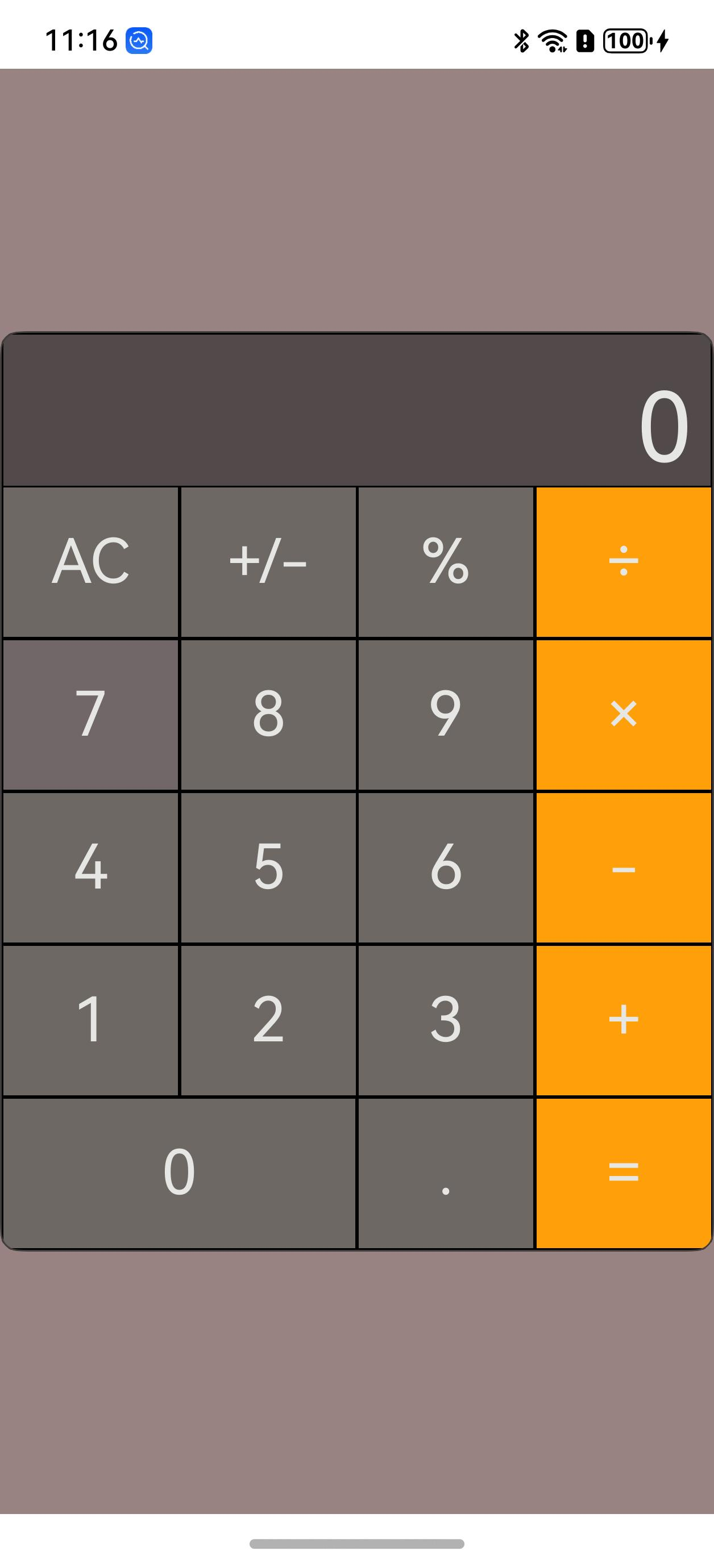
6.3.Gif动图展示

7.项目结构
项目结构交复杂,本文只简明扼要的列举用到的地方,所谓“用”有两方面的意思,要么基于之前的配置进行修改,一般为配置文件;要么创建新文件,一般为开发代码文件。
7.1.so包module
|─CDemo // 项目根目录
├──app/src/main // 代码区
│ │
│ ├──cpp // C/C++代码区
│ │ ├──CMakeLists.txt // CMake编译配置文件
│ │ ├──napi_init.cpp // napi代码
│ │ ├──utils
│ │ │ └──calculator.h // C++头文件,用于函数、变量定义
│ │ │ └──calculator.cpp // C++文件,用户逻辑实现
│ │ └──types // ArtTS层
│ │ └──libapp // ArtTS层识别的接口存放文件夹
│ │ ├──index.d.ts // ArtTS层识别的接口文件
│ │ └──oh-package.json5 // 接口注册配置文件
│ ├──ets // ArtTS代码区
│ │ ├──entryability // 能力包
│ │ ├──EntryAbility.ets // 程序入口类
│ │ ├──pages // 界面包
│ │ └──Index.ets // 主界面
│ ├──resources // 资源文件目录
│ └──module.json5 // 模块级配置文件
└──app/build-profile.json5 // 项目构建文件7.2.宿主module
|─Calculator // 项目根目录
├app // 代码区
├──libs // 本地三方库
│ └──arm64-v8a // arm64-v8a包
│ └──────libapp.so // arm64-v8a架构so能力包
│ └──x86_64 // x86_64包
│ └──────libapp.so // x86_64架构so能力包
├──src/main // 代码区
│ └──ets // ArtTS代码区
│ ├──entryability // 能力包
│ │ └──EntryAbility.ets // 程序入口类
│ └──pages // 界面包
│ └──Index.ets // 主界面
└──────────────────resources // 资源文件目录
└──────────────────module.json5 // 模块级配置文件8.so包module开发步骤
8.1.C/C++代码算法逻辑编写
文件放到app/src/main/cpp目录下:
/**
* 加法运算
*/
double add(double param1, double param2);
/**
* 减法运算
*/
double sub(double param1, double param2);
/**
* 乘法运算
*/
double mul(double param1, double param2);
/**
* 除法运算
*/
double div(double param1, double param2);
/**
* 取反运算
*/
double oppo(double param);#include "calculator.h"
double add(double param1, double param2) {
return param1 + param2;
}
double sub(double param1, double param2) {
return param1 - param2;
}
double mul(double param1, double param2) {
return param1 * param2;
}
double div(double param1, double param2) {
if (param2 == 0) {
return 0;
}
return param1 / param2;
}
double oppo(double param) {
return -param;
}8.2.CMake文件编写
这个文件是创建Native项目的时候自动生成的,我们一般情况下仅仅需要改动两个地方:
#add_library
#target_link_libraries
# CMAKE 的最小版本号
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5.0)
# 项目名
project(Calculator)
# 设置编译参数
set(NATIVERENDER_ROOT_PATH ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR})
if(DEFINED PACKAGE_FIND_FILE)
include(${PACKAGE_FIND_FILE})
endif()
# 指定目标include目录路径
include_directories(${NATIVERENDER_ROOT_PATH}
${NATIVERENDER_ROOT_PATH}/include)
# 指定C/C++源码目录路径,此路径是相对于CmakeLists.txt的路径,同时注意有多个源文件要用空格或换行符隔开
add_library(app SHARED
napi_init.cpp
utils/calculator.h
utils/calculator.cpp)
# 指定C/C++生成的动态链接的库名字
target_link_libraries(app PUBLIC libace_napi.z.so)8.3.Napi代码编写
// 引入Napi模块
#include "napi/native_api.h"
// 引入自定义头文件
#include "./utils/calculator.h"
/**
* 获取 ArtTs层 function(double a,double b)签名函数的参数
* @param env ArtTS层环境
* @param info ArtTS层方法信息
* @param param0 参数1地址
* @param param1 参数2地址
*/
static void getTwoDoubleParams(napi_env env, napi_callback_info info, double *param0, double *param1) {
size_t argc = 2;
napi_value args[2] = {nullptr};
napi_get_cb_info(env, info, &argc, args, nullptr, nullptr);
napi_valuetype valuetype0;
napi_typeof(env, args[0], &valuetype0);
napi_valuetype valuetype1;
napi_typeof(env, args[1], &valuetype1);
double value0;
napi_get_value_double(env, args[0], &value0);
*param0 = value0;
double value1;
napi_get_value_double(env, args[1], &value1);
*param1 = value1;
}
/**
* 加法运算翻译
*
* @param env
* @param info
* @return
*/
static napi_value Add(napi_env env, napi_callback_info info) {
double value0 = 0, value1 = 0;
getTwoDoubleParams(env, info, &value0, &value1);
napi_value sum;
napi_create_double(env, add(value0, value1), &sum);
return sum;
}
/**
* 减法运算翻译
*
* @param env
* @param info
* @return
*/
static napi_value NAPI_Global_sub(napi_env env, napi_callback_info info) {
double value0 = 0, value1 = 0;
getTwoDoubleParams(env, info, &value0, &value1);
napi_value sum;
napi_create_double(env, sub(value0, value1), &sum);
return sum;
}
/**
* 乘法运算翻译
*
* @param env
* @param info
* @return
*/
static napi_value NAPI_Global_mul(napi_env env, napi_callback_info info) {
double value0 = 0, value1 = 0;
getTwoDoubleParams(env, info, &value0, &value1);
napi_value sum;
napi_create_double(env, mul(value0, value1), &sum);
return sum;
}
/**
* 除法运算翻译
*
* @param env
* @param info
* @return
*/
static napi_value NAPI_Global_div(napi_env env, napi_callback_info info) {
double value0 = 0, value1 = 0;
getTwoDoubleParams(env, info, &value0, &value1);
napi_value sum;
napi_create_double(env, div(value0, value1), &sum);
return sum;
}
/**
* 取反运算翻译
*
* @param env
* @param info
* @return
*/
static napi_value NAPI_Global_oppo(napi_env env, napi_callback_info info) {
size_t argc = 1;
napi_value args[1] = {nullptr};
napi_get_cb_info(env, info, &argc, args, nullptr, nullptr);
napi_valuetype valuetype0;
napi_typeof(env, args[0], &valuetype0);
double value0;
napi_get_value_double(env, args[0], &value0);
napi_value sum;
napi_create_double(env, oppo(value0), &sum);
return sum;
}
/**
* 初始化函数,用于设置模块导出的内容
*
* @param env
* @param exports
* @return
*/
EXTERN_C_START // 宏定义,用于在 C++ 代码中标记需要以 C 语言方式编译的代码块。比extern "C"更灵活
static napi_value Init(napi_env env, napi_value exports) {
// 定义要导出的属性/方法
napi_property_descriptor desc[] = {
{"add", nullptr, Add, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, napi_default, nullptr},
{"sub", nullptr, NAPI_Global_sub, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, napi_default, nullptr},
{"mul", nullptr, NAPI_Global_mul, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, napi_default, nullptr},
{"div", nullptr, NAPI_Global_div, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, napi_default, nullptr},
{"oppo", nullptr, NAPI_Global_oppo, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, napi_default, nullptr}};
// 将属性添加到导出对象中
napi_define_properties(env, exports, sizeof(desc) / sizeof(desc[0]), desc);
return exports;
}
EXTERN_C_END
/**
* 定义模块结构体
*/
static napi_module demoModule = {
.nm_version = 1, // 模块版本号
.nm_flags = 0, // 模块标志,默认为0
.nm_filename = nullptr, // 模块文件名,通常不需要
.nm_register_func = Init, // 注册函数,指向上面的Init函数
.nm_modname = "app", // 模块名称,这将是JS中引入模块时使用的名称
.nm_priv = ((void *)0), // 私有数据,这里未使用
.reserved = { 0 } // 保留字段,用于未来扩展
};
// 告诉编译器:"这部分代码要用 C 的方式来处理,不要用 C++ 的方式"
extern "C" __attribute__((constructor)) void RegisterAppModule(void) { napi_module_register(&demoModule); }
备注napi_property_descriptor结构体说明:
typedef struct napi_property_descriptor {
const char* utf8name; // 属性名称(UTF8字符串)
napi_value name; // 属性名称(napi_value类型)
napi_callback method; // 方法回调
napi_callback getter; // getter回调
napi_callback setter; // setter回调
napi_value value; // 静态属性值
napi_property_attributes attributes; // 属性特性
void* data; // 用户数据
} napi_property_descriptor;代码层面流程是这样的:
- 冷启动时系统首先会自动执行#RegisterModule函数
- #RegisterModule函数将结构体demoModule注册到 Node-API系统
- 结构体demoModule初始化时会调用 Init函数
- Init 函数设置模块的导出内容
- 这样以后ArtTS就可以调用Native方法了
8.4.暴露给ArtTS接口编写
export const add: (a: number, b: number) => number;
export const sub: (a: number, b: number) => number;
export const mul: (a: number, b: number) => number;
export const div: (a: number, b: number) => number;
export const oppo: (a: number) => number8.5.配置oh-package.json5
{
// so包名称
"name": "libapp.so",
//Index.d.ts文件路径
"types": "./Index.d.ts",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "Please describe the basic information."
}8.6.配置build-profile.json5
默认产出的so包仅为arm64-v8a架构,如果要支持其他架构需要配置build-profile.json5文件
{
"apiType": "stageMode",
"buildOption": {
"externalNativeOptions": {
"abiFilters": ["arm64-v8a", "x86_64"],
...8.7.导出so包
代码及配置文件编写完成,执行Build->Build Hap(s)/App(s)->Build Hap(s)
build完成后对应的so包会在此目录下:
|─CDemo // 项目根目录
├app/build/default/intermediates/libs/default // 代码区 // 本地三方库
│ └──arm64-v8a // arm64-v8a包
│ └──────libapp.so // arm64-v8a架构so能力包
│ └──x86_64 // x86_64包
│ └──────libapp.so // x86_64架构so能力包8.8.编写C/C++模块标准接口文档
此步是为了方便二次开发者开发。
9.宿主开发步骤
相比于繁琐的so包开发,宿主即引用方开发起来较简单,它的工作主要在计算器界面搭建
9.1.引入so包
将libapp.so包导入到如下目录
|─Calculator // 项目根目录
├app // 代码区
├──libs // 本地三方库
│ └──arm64-v8a // arm64-v8a包
│ └──────libapp.so // arm64-v8a架构so能力包
│ └──x86_64 // x86_64包
│ └──────libapp.so // x86_64架构so能力包在对应的ets文件中直接导包并调用api即可
import napi from 'libapp.so';
napi.add(1,2);
...值得注意的是:
- import napi from 'libapp.so';当前代码会飘红,编译器无法识别so包,但是实际上不影响编译打包运行
- libapp.so包里的函数不会提示,如果让甲方调用建议输出标准接口文档
9.2.界面搭建及交互调用
基于ArtUI的声明式UI开发,这里只列举核心代码:
import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit';
import napi from 'libapp.so';
const INPUT_MAX: number = 10
const RESULT_MAX: number = 12
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State result: string = '0'
array: string[] = []
build() {
Column() {
Grid() {
GridItem() {
Text(this.result + '')
.screenTextStyle()
}.columnStart(0).columnEnd(3)
GridItem() {
Button('AC', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
})
.buttonTextStyle()
.onClick(() => {
this.result = '0'
this.array = []
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('+/-', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
})
.buttonTextStyle()
.onClick(() => {
try {
if (this.array.length == 0) {
return
}
this.result = napi.oppo(this.getNumber(this.result)).toString()
console.info("message is" + this.getNumber(this.result))
if (this.array.length > 0 &&
(this.array[this.array.length-1].match(/^\d+$/) || this.array[this.array.length-1].match(/^-\d+$/))) {
this.array[this.array.length-1] = this.result
}
} catch (e) {
console.error("类型转换错误!")
}
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('%', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
})
.buttonTextStyle()
.onClick(() => {
this.array.push(this.result.toString())
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('÷', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
})
.buttonTextStyle('#ffff9f0a')
.onClick(() => {
if (this.array.length == 0) {
return
}
if (this.isSignal(this.array[this.array.length-1])) {
this.array.pop()
}
this.array.push('÷')
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('7', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
})
.buttonTextStyle()
.backgroundColor('#ff716768')
.onClick(() => {
this.processNumber(7)
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('8', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
})
.buttonTextStyle()
.onClick(() => {
this.processNumber(8)
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('9', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
})
.buttonTextStyle()
.onClick(() => {
this.processNumber(9)
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('×', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
})
.buttonTextStyle('#ffff9f0a')
.onClick(() => {
if (this.array.length == 0) {
return
}
if (this.isSignal(this.array[this.array.length-1])) {
this.array.pop()
}
this.array.push('×')
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('4', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
})
.buttonTextStyle()
.onClick(() => {
this.processNumber(4)
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('5', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
})
.buttonTextStyle()
.onClick(() => {
this.processNumber(5)
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('6', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
})
.buttonTextStyle()
.onClick(() => {
this.processNumber(6)
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('-', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
})
.buttonTextStyle('#ffff9f0a')
.onClick(() => {
if (this.array.length == 0) {
return
}
if (this.isSignal(this.array[this.array.length-1])) {
this.array.pop()
}
this.array.push('-')
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('1', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
})
.buttonTextStyle()
.onClick(() => {
this.processNumber(1)
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('2', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
})
.buttonTextStyle()
.onClick(() => {
this.processNumber(2)
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('3', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
})
.buttonTextStyle()
.onClick(() => {
this.processNumber(3)
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('+', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
}).buttonTextStyle('#ffff9f0a')
.onClick(() => {
if (this.array.length == 0) {
return
}
if (this.isSignal(this.array[this.array.length-1])) {
this.array.pop()
}
this.array.push('+')
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('0', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
}).buttonTextStyle()
.onClick(() => {
this.processNumber(0)
})
}.columnStart(0).columnEnd(1)
GridItem() {
Button('.', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
}).buttonTextStyle()
.onClick(() => {
if (!this.isSignal(this.array[this.array.length-1])) {
if (!this.array[this.array.length-1].endsWith('.')) {
this.result = this.result + '.'
this.array[this.array.length-1] = this.result
}
}
})
}
GridItem() {
Button('=', {
type: ButtonType.Normal
}).buttonTextStyle('#ffff9f0a')
.onClick(() => {
this.processResult()
})
}
}
.gridStyle()
.rowsTemplate('1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr')
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr')
}.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor('#ff988282')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
isSignal(str: string): boolean {
return str == '+' || str == '-' || str == '×' || str == '÷'
}
processResult() {
if (this.array.length != 3) {
return
}
let value = this.array[1]
if (value == '+') {
this.result = napi.add(this.getNumber(this.array[0]), this.getNumber(this.array[2])).toString()
}
if (value == '-') {
this.result = napi.sub(this.getNumber(this.array[0]), this.getNumber(this.array[2])).toString()
}
if (value == '×') {
this.result = napi.mul(this.getNumber(this.array[0]), this.getNumber(this.array[2])).toString()
}
if (value == '÷') {
this.result = napi.div(this.getNumber(this.array[0]), this.getNumber(this.array[2])).toString()
}
if (this.result.length > RESULT_MAX) {
this.array = ['0']
return
}
this.array = [this.result]
}
getNumber(str: string): number {
if (str.endsWith('.')) {
return Number(str.replace('.', ''))
}
return Number(str)
}
processNumber(n: number) {
if (this.array.length > 0) {
if (this.array[this.array.length-1].toString().length >= INPUT_MAX) {
return
}
if (this.array[this.array.length-1].toString().includes('.')) {
this.result = this.result + n
this.array[this.array.length-1] = this.result
} else if (!this.isSignal(this.array[this.array.length-1])) {
this.result = (this.getNumber(this.result) * 10 + n).toString()
this.array[this.array.length-1] = this.result
} else {
this.result = n.toString()
this.array.push(this.result.toString())
}
} else {
this.result = n.toString()
this.array.push(this.result.toString())
}
}
}
@Extend(Text)
function screenTextStyle() {
.backgroundColor('#ff51494a')
.textAlign(TextAlign.End)
.height('100%')
.width('100%')
.fontColor("#ffe6e6e5")
.padding(10)
.borderWidth(1)
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Normal)
}
@Extend(Button)
function buttonTextStyle(color: string = '#ff6e6865') {
.backgroundColor(color)
.height('100%')
.width('100%')
.fontColor("#ffe6e6e5")
.padding(10)
.borderWidth(1)
.fontSize(32)
}
@Extend(Grid)
function gridStyle() {
.width('100%')
.height(480)
.borderWidth(1)
.borderColor('#ff423e3d')
.borderRadius(10)
}至此,ArtTS调用C/C++开发已完成。
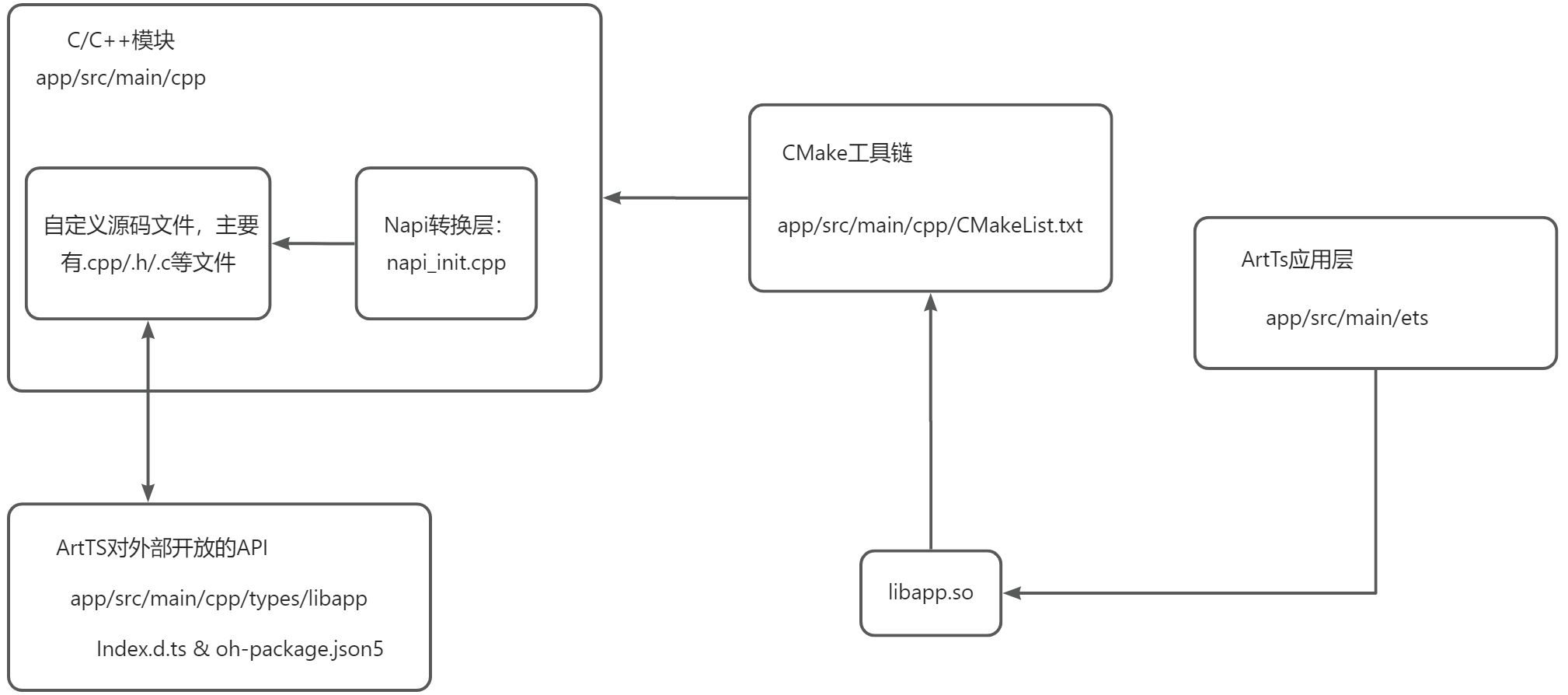
10.应用架构
此图特意备注了文件路径,可结合章节7.1的目录结构看,方便理解,在架构层面梳理了C/C++模块、Napi、CMake工具链、ArtTs应用层之间的关系。
注意:
- 对C库的支持请参考《Native层支持说明》章节1
- 对C++库的支持请参考《Native层支持说明》章节2
- 对Napi标准库的支持请参考《Native层支持说明》章节3