目录
- 一、maven依赖
- 二、Schema 定义
- 三、代码集成
- 3.1 创建模型类
- 3.2 创建服务类
- 3.3 创建控制器类
- 四、单元测试
- 五、实际 HTTP 请求测试
- 5.1 查询单个 Person
- 5.2 查询所有 People
- 5.3 添加 Person
- 六、其他
- 6.1 开启graphiql
- 6.2 开启schema查看端点
一、maven依赖
首先,在 pom.xml 文件中添加以下依赖:
<!-- Spring GraphQL -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-graphql</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring GraphQL Test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.graphql</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-graphql-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Unless already present in the compile scope -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
二、Schema 定义
在 src/main/resources/graphql 目录下创建 person.graphqls 文件,定义 GraphQL Schema:
type Query {
person(id: ID!): Person
people: [Person]
}
type Mutation {
addPerson(input: PersonInput!): Person
}
type Person {
id: ID!
name: String!
age: Int
dept: Dept
}
type Dept {
id: ID!
code: String!
name: String!
}
input PersonInput {
name: String!
age: Int
deptId: String
}
三、代码集成
3.1 创建模型类
Person 、Dept和 PersonInput 模型类:
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Person {
private String id;
private String name;
private int age;
private Dept dept;
}
@Data
public class Dept {
private String id;
private String code;
private String name;
}
@Data
public class PersonInput {
private String name;
private int age;
private String deptId;
}
3.2 创建服务类
PersonService 服务类:
注:如下服务类可根据需求调整,本实现仅作为示例作用,实际开发时可通过数据库存储、调用其他服务等来生成相应的底层数据。
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.UUID;
@Service
public class PersonService {
private List<Person> people = new ArrayList<>();
public Person getPersonById(String id) {
return people.stream().filter(person -> person.getId().equals(id)).findFirst().orElse(null);
}
public Dept getDeptByPersonId(String id) {
Dept dept = new Dept();
dept.setId("dept_001");
dept.setCode("001");
dept.setName("dept001");
return dept;
}
public List<Person> getAllPeople() {
return people;
}
public Person addPerson(PersonInput input) {
Person person = new Person();
person.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
person.setName(input.getName());
person.setAge(input.getAge());
people.add(person);
return person;
}
}
3.3 创建控制器类
PersonController 控制器类:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.graphql.data.method.annotation.Argument;
import org.springframework.graphql.data.method.annotation.MutationMapping;
import org.springframework.graphql.data.method.annotation.QueryMapping;
import org.springframework.graphql.data.method.annotation.SchemaMapping;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
public class PersonController {
@Autowired
private PersonService personService;
@QueryMapping
public Person person(@Argument String id) {
return personService.getPersonById(id);
}
@SchemaMapping
public Dept dept(Person person) {
return personService.getDeptByPersonId(person.getId());
}
@QueryMapping
public List<Person> people() {
return personService.getAllPeople();
}
@MutationMapping
public Person addPerson(@Argument PersonInput input) {
return personService.addPerson(input);
}
}
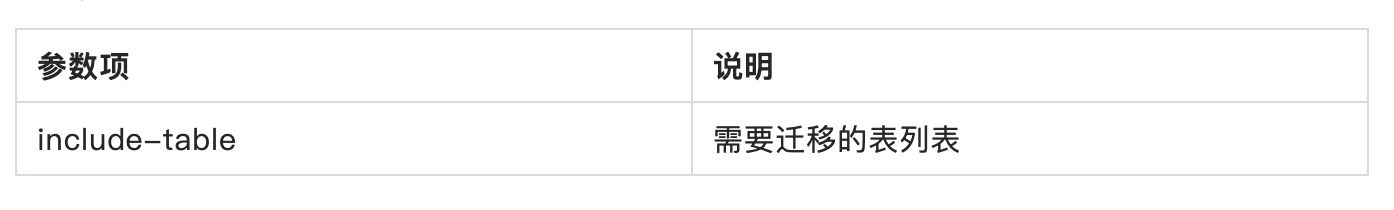
关于映射注解的说明可参见下表:
| 注解 | 用途 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
@QueryMapping | 映射 GraphQL 查询操作 | 将 GraphQL 查询请求映射到控制器中的方法 |
@MutationMapping | 映射 GraphQL 变更操作 | 将 GraphQL 变更请求(如创建、更新、删除操作)映射到控制器中的方法 |
@SchemaMapping | 映射 GraphQL 模式中的字段 | 将 GraphQL 模式中的字段映射到控制器中的方法,通常用于嵌套对象的解析 |
重点解释下@SchemaMapping注解,该注解将 GraphQL 模式中的字段映射到控制器中的方法,通常用于嵌套对象的解析,包括属性如下:
- typeName:指定 GraphQL 类型的名称。默认情况下,Spring 会根据 方法参数类型 自动推断。
- field:指定 GraphQL 字段的名称。默认情况下,Spring 会根据 方法名称 自动推断。
示例代码
# schema.graphqls
type Person {
id: ID!
name: String!
age: Int
dept: Dept
}
type Dept {
id: ID!
code: String!
name: String!
}
@SchemaMapping(typeName = "Person", field = "dept")
public Dept dept(Person person) {
return personService.getDeptByPersonId(person.getId());
}
- typeName:在上面的示例中,
typeName被设置为"Person",表示这个方法是处理Person类型 。 - field:
field被设置为"dept",表示这个方法是处理Person类型中的dept字段。 - 如上 typeName 和 field 属性可以省略,若省略则根据 方法参数类型 推断
typeName为Person,根据 方法名 推断field为dept。
而@QueryMapping和@MutationMapping可以看作是特殊的@SchemaMapping,具体对应关系如下表:
| 注解 | 说明 | 适用范围 |
|---|---|---|
@SchemaMapping | 需要自定义typeName和field属性 | 均适用,通常用于type类型(对象类型)中的field映射 |
@QueryMapping | typeName固定为Query,仅需自定义field属性 | 适用于type Query { ... } 中方法映射 |
@MutationMapping | typeName固定为Mutation,仅需自定义field属性 | 适用type Mutation { ... } 中方法映射 |
四、单元测试
PersonControllerTest 单元测试类:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.graphql.GraphQlTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockBean;
import org.springframework.graphql.test.tester.GraphQlTester;
import java.util.Arrays;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertNotNull;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
@GraphQlTest({PersonController.class})
public class PersonControllerTest {
@MockBean
private PersonService personService;
@Autowired
private GraphQlTester graphQlTester;
@Test
public void testPersonQuery_withQueryStr() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setId("1");
person.setName("John Doe");
person.setAge(30);
when(personService.getPersonById("1")).thenReturn(person);
//document对应查询文本
graphQlTester.document("{ person(id: \"1\") { id name age } }")
.execute()
.path("person")
.entity(Person.class)
.satisfies(p -> {
assertEquals("1", p.getId());
assertEquals("John Doe", p.getName());
assertEquals(30, p.getAge());
});
}
@Test
public void testPersonQuerySimple() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setId("1");
person.setName("John Doe");
person.setAge(30);
when(personService.getPersonById("1")).thenReturn(person);
//documentName对应查询文本文件名(位于src/text/resources/graphql-test下)
graphQlTester.documentName("person_simple")
.execute()
.path("person")
.entity(Person.class)
.satisfies(p -> {
assertEquals("1", p.getId());
assertEquals("John Doe", p.getName());
assertEquals(30, p.getAge());
});
}
@Test
public void testPersonQueryComplex() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setId("1");
person.setName("John Doe");
person.setAge(30);
Dept dept = new Dept();
dept.setId("dept_001");
dept.setCode("001");
dept.setName("dept001");
when(personService.getPersonById("1")).thenReturn(person);
when(personService.getDeptByPersonId("1")).thenReturn(dept);
graphQlTester.documentName("person_complex")
.execute()
.path("person")
.entity(Person.class)
.satisfies(p -> {
assertEquals("1", p.getId());
assertEquals("John Doe", p.getName());
assertEquals(30, p.getAge());
Dept dept1 = p.getDept();
assertNotNull(dept1);
assertEquals("dept_001", dept1.getId());
assertEquals("001", dept1.getCode());
assertEquals("dept001", dept1.getName());
});
}
@Test
public void testPeopleQuery() {
Person person1 = new Person();
person1.setId("1");
person1.setName("John Doe");
person1.setAge(30);
Person person2 = new Person();
person2.setId("2");
person2.setName("Jane Doe");
person2.setAge(25);
when(personService.getAllPeople()).thenReturn(Arrays.asList(person1, person2));
graphQlTester.documentName("people")
.execute()
.path("people")
.entityList(Person.class)
.satisfies(people -> {
assertEquals(2, people.size());
assertEquals("1", people.get(0).getId());
assertEquals("John Doe", people.get(0).getName());
assertEquals(30, people.get(0).getAge());
assertEquals("2", people.get(1).getId());
assertEquals("Jane Doe", people.get(1).getName());
assertEquals(25, people.get(1).getAge());
});
}
@Test
public void testAddPersonMutation() {
PersonInput input = new PersonInput();
input.setName("John Doe");
input.setAge(30);
Person person = new Person();
person.setId("1");
person.setName("John Doe");
person.setAge(30);
when(personService.addPerson(input)).thenReturn(person);
graphQlTester.documentName("addPerson")
.execute()
.path("addPerson")
.entity(Person.class)
.satisfies(p -> {
assertEquals("1", p.getId());
assertEquals("John Doe", p.getName());
assertEquals(30, p.getAge());
});
}
}
如上测试类中注意区分graphQLTester.document和graphQLTester.documentName,其中document方法的参数为query字符串,而documentName对应query文件名(不包括文件类型,如people.graphql即对应people),文件内容即为具体的query字符串,dcoumentName参数中指定的文件位于src/test/resources/graphql-test目录下,如下图:

具体的query文件内容如下:
person_simple.graphql
{
person(id: "1") {
id
name
age
}
}
person_complex.graphql
{
person(id: "1") {
id
name
age
dept {
id
code
name
}
}
}
people.graphql
{
people {
id
name
age
}
}
addPerson.graphql
mutation {
addPerson(input: { name: "John Doe", age: 30 }) {
id
name
age
}
}
五、实际 HTTP 请求测试
可以使用 Apifox、Postman 或 cURL 来测试 GraphQL API。
5.1 查询单个 Person
注:
/graphql查询请求的method为 POST,
查询参数以JSON请求体进行传输,
且注意 双引号需要进行转义。

具体请求参数:
{
"query": "{ person(id: \"48afdb68-0dcb-457b-ba55-bb2750e35b82\") { id name age dept { id code name } } }"
}
亦可替换为(添加query前缀,后续query方法同):
{
"query": "query { person(id: \"48afdb68-0dcb-457b-ba55-bb2750e35b82\") { id name age dept { id code name } } }"
}
5.2 查询所有 People

具体请求参数:
{
"query": "{ people { id name age } }"
}
5.3 添加 Person

具体请求参数:
{
"query": "mutation { addPerson(input: { name: \"Alice\", age: 28 }) { id name age dept { id code name } } }"
}
六、其他
6.1 开启graphiql
在application.yaml配置文件中开启graphiql相关配置:
spring:
graphql:
# 启用graphiql
graphiql:
enabled: true
path: /graphiql
之后即可访问该/graphiql端点进行graphql调试:

6.2 开启schema查看端点
在application.yaml配置文件中开启schema查看端点相关配置:
spring:
graphql:
# schema相关配置
schema:
# 启用接口/graphql/schema - 查询schema定义
printer:
enabled: true
之后即可访问该/graphql/schema端点查看schema定义:

参考:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/reference/web/spring-graphql.html
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/reference/testing/spring-boot-applications.html#testing.spring-boot-applications.spring-graphql-tests
https://docs.spring.io/spring-graphql/reference/controllers.html
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-graphql/tree/1.0.x/samples/webmvc-http