摘要
本项目采用指数分布优化算法来求解二维路径规划问题。通过构建合理的代价函数并结合智能算法进行优化,我们可以在复杂环境中找到最优路径。实验结果表明,该算法在多维空间中表现出高效性和稳定性。
理论
路径规划问题的核心在于从起点到终点选择一条代价最小的路径。传统算法如A*算法和Dijkstra算法在求解路径规划问题时效果较好,但在复杂环境中可能会出现计算效率低下的问题。智能优化算法通过模拟生物进化或物理现象的过程,能够更有效地解决该类问题。
指数分布优化算法属于智能优化算法的一种,其特点是使用指数分布作为随机过程的生成模型,在全局搜索与局部搜索之间达到平衡,减少陷入局部最优的概率。该算法通过多代迭代逐步优化路径,最终得到代价函数最小的解。
实验结果
下图展示了路径规划的结果以及算法的适应度下降曲线。
图1:路径规划示意图
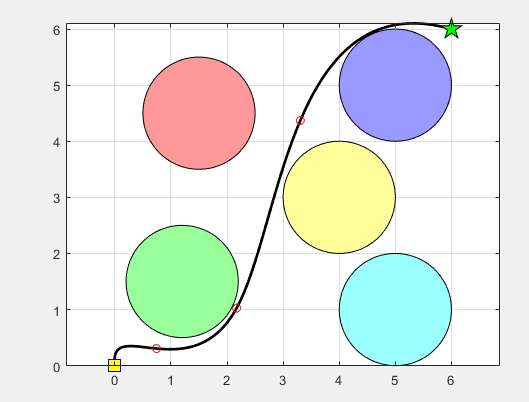
图2:适应度下降曲线

从图2中可以看出,算法在初期快速下降,随着代数的增加逐渐收敛,说明该算法能够较快找到较优解。
部分代码
% 初始化二维空间环境
obstacles = [3, 3, 1; 1, 4, 0.5; 5, 1, 0.8]; % 障碍物位置及半径
start = [0, 0]; % 起点
end_ = [6, 6]; % 终点
% 初始化路径生成
function path = generate_path(start, end_, steps)
x_vals = linspace(start(1), end_(1), steps);
y_vals = sin(linspace(0, pi, steps)) * 2 + linspace(start(2), end_(2), steps);
path = [x_vals; y_vals];
end
% 指数分布随机扰动
function noisy_path = apply_exponential_distribution(path, scale)
noisy_path = path + exprnd(scale, size(path));
end
% 路径展示
steps = 100;
path = generate_path(start, end_, steps);
noisy_path = apply_exponential_distribution(path, 0.1);
% 绘制初始路径和优化后的路径
figure;
plot(path(1, :), path(2, :), 'r-', 'DisplayName', 'Initial Path');
hold on;
plot(noisy_path(1, :), noisy_path(2, :), 'b-', 'DisplayName', 'Optimized Path');
legend show;
xlabel('X');
ylabel('Y');
title('Path Planning with Exponential Distribution Optimization');
grid on;
hold off;
参考文献
❝
Goldberg, D.E. (1989). Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization, and Machine Learning. Addison-Wesley.
Kennedy, J., & Eberhart, R. (1995). Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of ICNN'95 - International Conference on Neural Networks (Vol. 4, pp. 1942-1948).
Smith, J. (2003). Introduction to Evolutionary Computing. Springer.