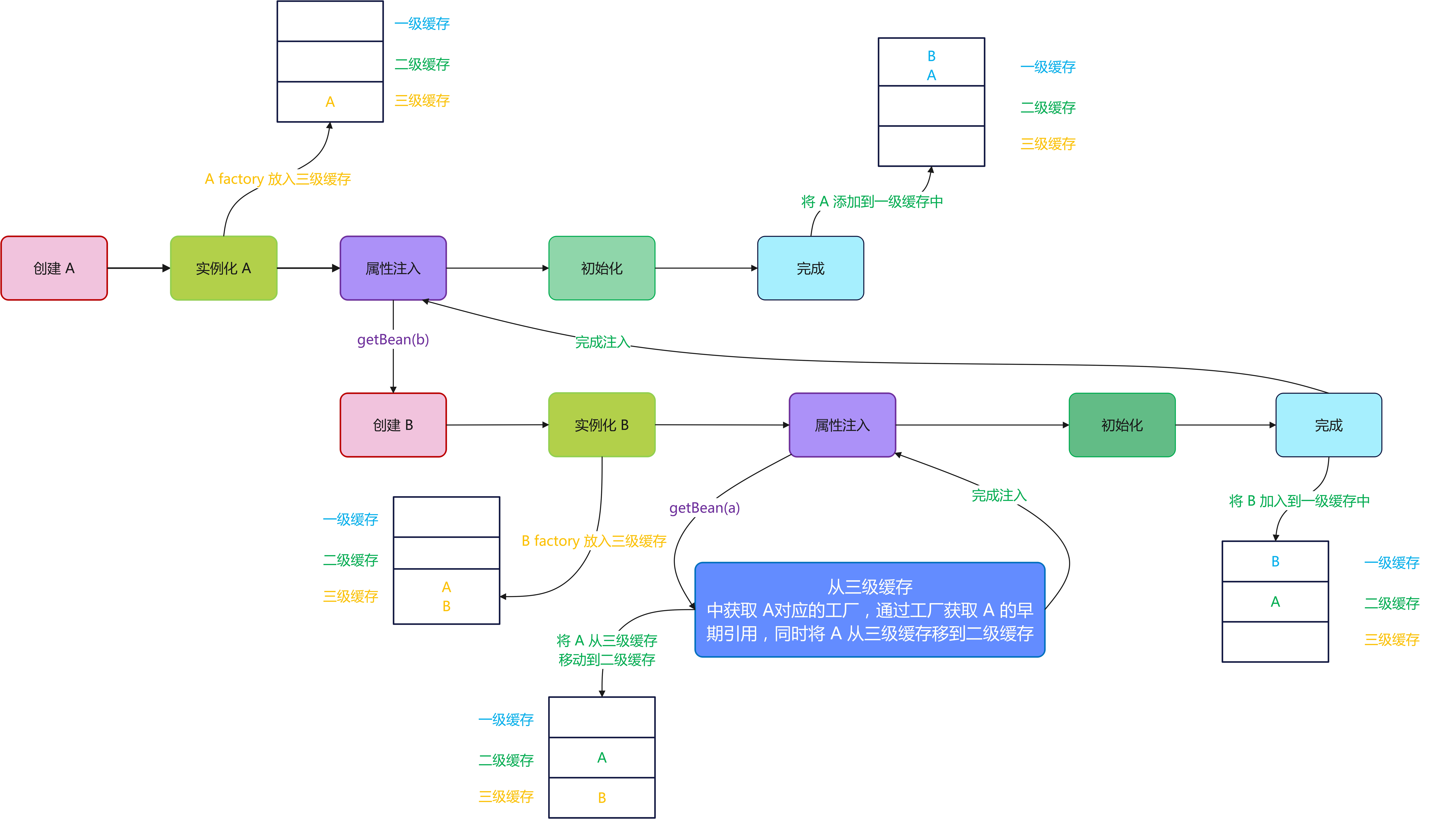
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/feriman/article/details/113725937
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_73366745/article/details/137113791?spm=1001.2014.3001.5506
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/g1sRR6tJ8qHhFzl-vrG5fw
A*算法
import sys
import time
from typing import List
import random
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
"""
Point类是数学坐标系的一个抽象的点,和Node类不是一回事
"""
class Point:
def __init__(self, x, y) -> None:
self.x = x
self.y = y
# 重载“==”运算符,(x1,y1)==(x2,y2),当且仅当x1=x2,y1=y2
def __eq__(self, other) -> bool:
return self.x == other.x and self.y == other.y
class Node:
def __init__(self, point: Point, endpoint: Point, g: float): # 初始化中间节点的参数
self.point = point
self.endpoint = endpoint
self.father = None
self.g = g
# h取曼哈顿距离,c=|x2-x1|+|y2-y1|
self.h = (abs(endpoint.x - point.x) + abs(endpoint.y - point.y)) * 10
self.f = self.g + self.h
def get_near(self, ud, rl): # 获取相邻节点
near_point = Point(self.point.x + rl, self.point.y + ud)
near_node = Node(near_point, self.endpoint, self.g + (10 if ud == 0 or rl == 0 else 14))
return near_node
class AStar:
def __init__(self, start: Point, end: Point, map_data): # 初始化A*算法的参数
self.path = [start, end]
self.closed_list = []
self.open_list = []
self.start = start
self.end = end
self.obstacle_map = map_data
# 从open_list里面找到一个代价最小的节点
def select_current(self) -> Node:
min_f = sys.maxsize
node_temp = None
for node in self.open_list:
if node.f < min_f:
min_f = node.f
node_temp = node
return node_temp
def is_in_open_list(self, node: Node) -> bool: # 判断节点是否在待检测队列中
return any([open_node.point == node.point for open_node in self.open_list])
def is_in_closed_list(self, node: Node) -> bool: # 判断节点是否在已检测队列中
return any([closed_node.point == node.point for closed_node in self.closed_list])
def is_obstacle(self, node: Node) -> bool:
""" 验证机器人的当前位置是否合理 """
# 检查当前位置是否在环境内
if node.point.x < 0 or node.point.x > len(self.obstacle_map) - 1:
return True
if node.point.y < 0 or node.point.y > len(self.obstacle_map) - 1:
return True
# 检查当前位置是否处于障碍物中
if self.obstacle_map[node.point.x][node.point.y] != 0:
return True
return False
def explore_neighbors(self, current_node: Node) -> bool:
up = (0, 1) # 上
down = (0, -1) # 下
right = (1, 0) # 右
left = (-1, 0) # 左
top_right = (1, 1) # 右上
top_left = (-1, 1) # 左上
Bottom_right = (1, -1) # 右下
Bottom_left = (-1, -1) # 左下
directions = [up, down, right, left, top_right, top_left, Bottom_right, Bottom_left]
for direction in directions:
ud, rl = direction
# current_neighbor是当前节点的邻点
current_neighbor = current_node.get_near(ud, rl)
# 如果检测到的节点是终点,就没必要接着往下探索了,直接退出循环,结束这个函数
if current_neighbor.point == self.end:
return True
# 判断一下邻点是不是已经检测或者是障碍物,如果是,就跳过这个邻点
if self.is_in_closed_list(current_neighbor) or self.is_obstacle(current_neighbor):
continue
if self.is_in_open_list(current_neighbor):
previous_current_neighbor = next(
open_node for open_node in self.open_list if open_node.point == current_neighbor.point)
if current_neighbor.f < previous_current_neighbor.f:
# 更新父节点
previous_current_neighbor.father = current_node
# 更新g值
previous_current_neighbor.g = current_neighbor.g
else:
# 对应状态3,直接入队
current_neighbor.father = current_node
self.open_list.append(current_neighbor)
return False
def find_path(self):
start_node = Node(point=self.start, endpoint=self.end, g=0)
self.open_list.append(start_node)
while True:
# 从open_list里面取出一个代价值最小节点
current_node = self.select_current()
if current_node is None:
return []
# 取出来后,从open_list里面删除,添加到closed_list里面
self.open_list.remove(current_node)
self.closed_list.append(current_node)
# 当current_node是终点时,explore_neighbors函数会返回一个True
if current_node.point == self.end or self.explore_neighbors(current_node):
while current_node.father is not None:
self.path.insert(1, current_node.point)
# 这里其实就是相当于遍历一个链表
current_node = current_node.father
return self.path
if __name__ == "__main__":
start_point = Point(0, 0)
end_point = Point(38, 3)
# 设置环境地图
neighbors = [
[0, 1], # 上
[0, -1], # 下
[-1, 0], # 左
[1, 0], # 右
[1, 1], # 右上
[1, -1], # 右下
[-1, -1], # 左下
[-1, 1] # 左上
]
map_data = [[0] * 41 for i in range(41)]
for i in range(20):
map_data[5][i] = 1
map_data[30][i] = 2
map_data[i][25] = 1
for node in [[20, 20], [30, 35], [10, 33]]:
map_data[node[0]][node[1]] = 3
for neighbor in neighbors:
map_data[node[0] + neighbor[0]][node[1] + neighbor[1]] = 3
# 运行A*算法
start_time = time.time()
a_star = AStar(start_point, end_point, map_data)
path = a_star.find_path()
end_time = time.time()
print("程序运行时间:", end_time - start_time, "秒", f"路径长度为{len(path) - 1}")
for i in range(41):
for j in range(41):
if map_data[i][j] != 0:
plt.plot(i, j, '.k')
plt.plot(start_point.x, start_point.y, 'og')
plt.plot(end_point.x, end_point.y, 'or')
# plt.grid('True')
plt.axis('equal')
rx = [path[i].x for i in range(len(path))]
ry = [path[i].y for i in range(len(path))]
plt.plot(rx, ry, '-r')
plt.show()
蚁群算法
import random
import math
class Ant:
def __init__(self, numAnts, numCities, maxIterations):
self.numAnts = numAnts
self.numCities = numCities
self.maxIterations = maxIterations
self.evaporationRate = 0.5
self.alpha = 1.0
self.beta = 2.0
self.pheromones = []
def run(self, distances):
random.seed()
self.initialize_pheromones()
for iter in range(self.maxIterations):
antPaths = []
for ant in range(self.numAnts):
path = self.generate_ant_path(distances)
antPaths.append(path)
self.update_pheromones(path)
self.evaporate_pheromones()
bestPath = antPaths[0]
# print(f"Iteration {iter + 1}: Best Path -> {' -> '.join(map(str, bestPath))}")
return bestPath
def initialize_pheromones(self):
global pheromones
pheromones = [[1.0] * self.numCities for _ in range(self.numCities)]
def generate_ant_path(self, distances):
startCity = 0
path = [startCity]
while len(path) < self.numCities:
currentCity = path[-1]
nextCity = self.choose_next_city(currentCity, path, distances)
path.append(nextCity)
return path
def choose_next_city(self, currentCity, path, distances):
availableCities = [city for city in range(self.numCities) if city not in path]
probabilities = []
totalProbability = 0.0
for nextCity in availableCities:
pheromone = math.pow(pheromones[currentCity][nextCity], self.alpha)
distance = 1.0 / distances[currentCity][nextCity]
probability = pheromone * distance
probabilities.append(probability)
totalProbability += probability
probabilities = [probability / totalProbability for probability in probabilities]
randomValue = random.random()
cumulativeProbability = 0.0
for i, probability in enumerate(probabilities):
cumulativeProbability += probability
if randomValue <= cumulativeProbability:
return availableCities[i]
return availableCities[-1]
def update_pheromones(self, path):
pheromoneDeposit = 1.0
for i in range(len(path) - 1):
currentCity = path[i]
nextCity = path[i + 1]
pheromones[currentCity][nextCity] += pheromoneDeposit
pheromones[nextCity][currentCity] += pheromoneDeposit
def evaporate_pheromones(self):
for i in range(self.numCities):
for j in range(self.numCities):
pheromones[i][j] *= (1.0 - self.evaporationRate)
if __name__ == '__main__':
distances = \
[[0, 2, 5, 7],
[2, 0, 6, 3],
[5, 6, 0, 8],
[7, 3, 8, 0]]
ant = Ant(5, 4, 100)
best_path = ant.run(distances)
print(best_path)
寻找多目标点最优路径
方式一 不适用蚁群算法
import time
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from A_star.A_Star import AStar, Point
def test_multi_node_path():
start_point = Point(0, 0)
end_point = Point(38, 3)
# 设置环境地图
neighbors = [
[0, 1], # 上
[0, -1], # 下
[-1, 0], # 左
[1, 0], # 右
[1, 1], # 右上
[1, -1], # 右下
[-1, -1], # 左下
[-1, 1] # 左上
]
map_data = [[0] * 41 for i in range(41)]
for i in range(20):
map_data[5][i] = 1
map_data[30][i] = 1
map_data[i][25] = 1
for node in [[20, 20], [30, 35], [10, 33]]:
map_data[node[0]][node[1]] = 1
for neighbor in neighbors:
map_data[node[0] + neighbor[0]][node[1] + neighbor[1]] = 1
import random
y_stones = [[random.randint(0, 40), random.randint(0, 40)] for i in range(3)]
q_stones = [[random.randint(0, 40), random.randint(0, 40)] for i in range(3)]
r_stones = [[random.randint(0, 40), random.randint(0, 40)] for i in range(3)]
for i in range(3):
map_data[y_stones[i][0]][y_stones[i][1]] = 3
for i in range(3):
map_data[q_stones[i][0]][q_stones[i][1]] = 4
for i in range(3):
map_data[r_stones[i][0]][r_stones[i][1]] = 5
start_time = time.time()
dis = float("inf")
path = None
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
for k in range(3):
ystone = Point(y_stones[i][0], y_stones[i][1])
qstone = Point(q_stones[j][0], q_stones[j][1])
rstone = Point(r_stones[k][0], r_stones[k][1])
# 计算距离
import itertools
stone_com = list(itertools.permutations([ystone, qstone, rstone], 3))
for com in stone_com:
p1 = AStar(start_point, com[0], map_data).find_path()
p2 = AStar(com[0], com[1], map_data).find_path()
p3 = AStar(com[1], com[2], map_data).find_path()
# p4 = AStar(com[2], end_point, map_data).find_path()
# if len(p1) > 0 and len(p2) > 0 and len(p3) > 0 and len(p4) > 0:
# tmp_dis = len(p1) + len(p2) + len(p3) + len(p4)
# if tmp_dis < dis:
# node_list = com
# dis = tmp_dis
# path = p1 + p2 + p3 + p4
if len(p1) > 0 and len(p2) > 0 and len(p3) > 0:
tmp_dis = len(p1) + len(p2) + len(p3)
if tmp_dis < dis:
node_list = com
dis = tmp_dis
path = p1 + p2 + p3
end_time = time.time()
print("程序运行时间:", end_time - start_time, "秒", f"路径长度为{len(path) - 1}")
for i in range(41):
for j in range(41):
if map_data[i][j] == 1:
plt.plot(i, j, '.k')
if map_data[i][j] == 3:
plt.plot(i, j, '.g')
if map_data[i][j] == 4:
plt.plot(i, j, '.r')
if map_data[i][j] == 5:
plt.plot(i, j, '.b')
plt.plot(start_point.x, start_point.y, 'og')
plt.plot(end_point.x, end_point.y, 'or')
# plt.grid('True')
plt.axis('equal')
rx = [path[i].x for i in range(len(path))]
ry = [path[i].y for i in range(len(path))]
plt.plot(rx, ry, '-r')
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_multi_node_path()
方式二 使用蚁群算法
import time
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from A_star.A_Star import AStar, Point
def test_multi_node_path():
start_point = Point(0, 0)
end_point = Point(38, 3)
# 设置环境地图
neighbors = [
[0, 1], # 上
[0, -1], # 下
[-1, 0], # 左
[1, 0], # 右
[1, 1], # 右上
[1, -1], # 右下
[-1, -1], # 左下
[-1, 1] # 左上
]
map_data = [[0] * 41 for i in range(41)]
for i in range(20):
map_data[5][i] = 1
map_data[30][i] = 1
map_data[i][25] = 1
for node in [[20, 20], [30, 35], [10, 33]]:
map_data[node[0]][node[1]] = 1
for neighbor in neighbors:
map_data[node[0] + neighbor[0]][node[1] + neighbor[1]] = 1
import random
y_stones = [[random.randint(0, 40), random.randint(0, 40)] for i in range(3)]
q_stones = [[random.randint(0, 40), random.randint(0, 40)] for i in range(3)]
r_stones = [[random.randint(0, 40), random.randint(0, 40)] for i in range(3)]
for i in range(3):
map_data[y_stones[i][0]][y_stones[i][1]] = 3
for i in range(3):
map_data[q_stones[i][0]][q_stones[i][1]] = 4
for i in range(3):
map_data[r_stones[i][0]][r_stones[i][1]] = 5
start_time = time.time()
dis = float("inf")
path = None
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
for k in range(3):
ystone = Point(y_stones[i][0], y_stones[i][1])
qstone = Point(q_stones[j][0], q_stones[j][1])
rstone = Point(r_stones[k][0], r_stones[k][1])
# 计算距离
nodes = [start_point, ystone, qstone, rstone]
distances = [[0] * 4 for i in range(4)]
paths = {}
for x in range(4):
for y in range(x + 1, 4, 1):
p = AStar(nodes[x], nodes[y], map_data).find_path()
p_len = len(p)
distances[x][y] = p_len
distances[y][x] = p_len
paths[(x, y)] = p
paths[(y, x)] = p
from ant import Ant
ant = Ant(5, 4, 50)
best_path = ant.run(distances)
tmp_dis = distances[best_path[0]][best_path[1]] + distances[best_path[1]][best_path[2]] +\
distances[best_path[2]][best_path[3]]
if tmp_dis < dis:
dis = tmp_dis
path = paths[(best_path[0], best_path[1])] + paths[(best_path[1],best_path[2])] +\
paths[(best_path[2], best_path[3])]
# print(best_path)
end_time = time.time()
print("程序运行时间:", end_time - start_time, "秒", f"路径长度为{len(path) - 1}")
for i in range(41):
for j in range(41):
if map_data[i][j] == 1:
plt.plot(i, j, '.k')
if map_data[i][j] == 3:
plt.plot(i, j, '.g')
if map_data[i][j] == 4:
plt.plot(i, j, '.r')
if map_data[i][j] == 5:
plt.plot(i, j, '.b')
plt.plot(start_point.x, start_point.y, 'og')
plt.plot(end_point.x, end_point.y, 'or')
# plt.grid('True')
plt.axis('equal')
rx = [path[i].x for i in range(len(path))]
ry = [path[i].y for i in range(len(path))]
plt.plot(rx, ry, '-r')
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_multi_node_path()