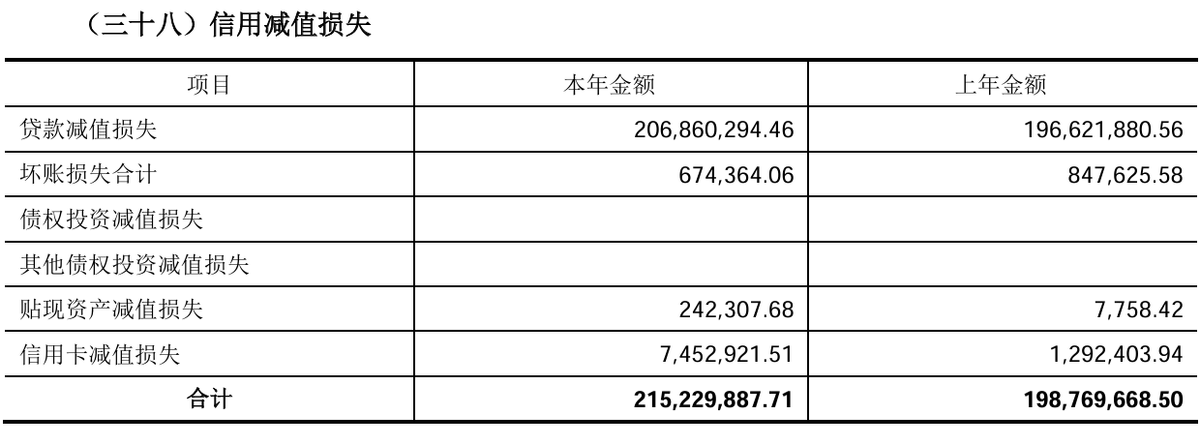
#!/bin/bash
#使用date精确延时的函数,参数是毫秒
function precise_sleep_ms() {
local duration_ms=$1
# 将毫秒转换为秒
local duration_sec=$(echo "scale=9; $duration_ms / 1000" | bc)
duration_sec=$(printf "%.3f" "$duration_sec")
# 计算结束时间点
local end_time=$(echo "$(date +%s.%N) + $duration_sec" | bc)
while [[ $(date +%s.%N) < $end_time ]]; do
sleep 0.000001 # 使用更短暂的sleep减少CPU占用
done
}
#使用date来获取到毫秒级别
function get_millisecond() {
date +%Y-%m-%d' '%H:%M:%S.%N | cut -b 1-23
}
#延时length毫秒
function mt_sleep_ms() {
local length=$1
#延时$length毫秒
if ! date +%N | grep -q '[0-9]\{9\}'; then
#有些系统上的date命令可能不支持%N(纳秒),则使用不精确的sleep函数
echo "Error: Your system's 'date' command does not support nanoseconds, use sleep cmd."
sleep $length/1000
else
precise_sleep_ms $length
fi
}
echo "test 5ms"
get_millisecond
mt_sleep_ms 5
get_millisecond
echo -e "\n"
echo "test 10ms"
get_millisecond
mt_sleep_ms 10
get_millisecond
echo -e "\n"
echo "test 100ms"
get_millisecond
mt_sleep_ms 100
get_millisecond
echo -e "\n"
echo "test 1000ms"
get_millisecond
mt_sleep_ms 1000
get_millisecond
echo -e "\n"
echo "test 5000ms"
get_millisecond
mt_sleep_ms 5000
get_millisecond
echo -e "\n"
echo "test 10000ms"
get_millisecond
mt_sleep_ms 10000
get_millisecond运行结果如下,可以看出,5ms和10ms都不是特别准确,100ms完后准确点