题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum/
视频题解: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1xyiueHEb4/
LeetCode 39. 组合总和
题目描述
给你一个无重复元素的整数数组candidates和一个目标整数target,找出candidates中可以使数字和为目标数target的所有不同组合,并以列表形式返回。你可以按任意顺序返回这些组合。
candidates中的同一个数字可以无限制重复被选取。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
对于给定的输入,保证和为target的不同组合数少于150个。
举个例子:
输入: candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7
输出: [[2,2,3],[7]]
解释:
2和3可以形成一组候选,2 + 2 + 3 = 7。注意2可以使用多次。
7也是一个候选,7 = 7。
仅有这两种组合。
视频题解
组合总和
思路来源
思路来源
知识回顾
回溯是一种通过将原问题分解为子问题来求解复杂问题的算法思想。它通常用于求解组合问题、排列问题等。回溯的核心思想是通过自上而下递归的方式枚举所有可能的解,直到找到符合条件的解为止。回溯算法通常使用递归函数来实现,每次递归时都会对当前状态进行判断,如果符合条件则继续递归,否则回溯到上一层状态。
思路解析
本题是组合问题需要枚举所有可能的解,可以用回溯法来解,回溯的关键在于划分子问题和确定回溯条件。
下图是target = 7, candidates = [2, 3, 7],自上而下枚举所有可能解的过程,叶子节点为0,说明找到一个符合条件的解,其解就是由根节点到叶子节点之间树枝上的数组成。比如[2, 2, 3],[2, 3, 2],[3, 2, 2],[7]都是符合条件的解。
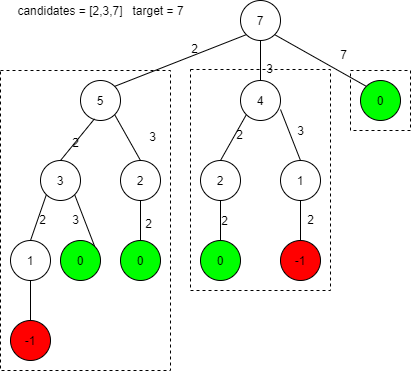
从上面的例子可以看出对于target = 7的情况可以划分为求target = 5,target = 4,target = 0三个子问题,这样就明确了子问题的划分: 对于target = n,我们可以划分成target = n - candidates[0],...,target = n - candidates[m-1],m个子问题,其中m为candidates的长度。
接下来就是确定回溯条件,很明显本题的回溯条件是叶子节点为0或为负数。
到这里回溯的两个关键问题都已经明确了,细心的同学应该已经看到对于上面的例子推导出了重复的解,[2, 2, 3],[2, 3, 2],[3, 2, 2]这三个解是重复的,这个时候就需要剪枝来剪掉重复的解。要如何剪枝呢,其实只需要在推导值为n - candidates[i]节点的子节点时,令target = n - candidates[i] - candidates[j],i <= j < m就可以将重复的解给剪掉。
有些同学对剪枝这部分有点疑惑,还是用上面的例子,target = 7,零钱的集合为candidates=[2, 3, 7]。我们可以选择三个2、两个2、一个2、零个2,四种情况。我们把所有包含2的情况一次性选完,然后再从除去2以后的集合[3, 7]去做选择。这样就避免了重复解,如果还是有疑惑可以在纸上画一画,可以更直观的去理解。
C++代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> temp;
help(candidates, target, 0, res, temp);
return res;
}
void help(vector<int>& candidates, int target, int start, vector<vector<int>>& res, vector<int>& temp) {
//回溯条件
if (target == 0) {
//找到符合条件的解,保存起来
res.push_back(temp);
//开始回溯
return;
}
//回溯条件
if (target < 0) {
//开始回溯
return;
}
int candidates_len = candidates.size();
//i=start是剪枝操作,如果i=0会存在重复解。
for (int i = start; i < candidates_len; ++i) {
if (target - candidates[i] >= 0) {
temp.push_back(candidates[i]);
//子问题
help(candidates, target - candidates[i], i, res, temp);
//回到上一个状态
temp.pop_back();
}
}
}
};
java代码
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
help(candidates, target, 0, res, temp);
return res;
}
private void help(int[] candidates, int target, int start, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> temp) {
// 回溯条件
if (target == 0) {
// 找到符合条件的解,保存起来
res.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
// 开始回溯
return;
}
// 回溯条件
if (target < 0) {
// 开始回溯
return;
}
int candidates_len = candidates.length;
// i=start是剪枝操作,如果i=0会存在重复解。
for (int i = start; i < candidates_len; ++i) {
if (target - candidates[i] >= 0) {
temp.add(candidates[i]);
// 子问题
help(candidates, target - candidates[i], i, res, temp);
// 回到上一个状态
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}
python代码
class Solution:
def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
temp = []
self.help(candidates, target, 0, res, temp)
return res
def help(self, candidates, target, start, res, temp):
# 回溯条件
if target == 0:
# 找到符合条件的解,保存起来
res.append(list(temp))
# 开始回溯
return
# 回溯条件
if target < 0:
# 开始回溯
return
candidates_len = len(candidates)
# i=start是剪枝操作,如果i=0会存在重复解。
for i in range(start, candidates_len):
if target - candidates[i] >= 0:
temp.append(candidates[i])
# 子问题
self.help(candidates, target - candidates[i], i, res, temp)
# 回到上一个状态
temp.pop()
复杂度分析
时间复杂度: 时间复杂度为整个推导树节点的个数,最大为 1 + m + m2 + … + mk-1,其中m为candidates的长度,k为树的高度。
空间复杂度: 空间复杂度跟解的个数有关,为所有解的元素个数之和。
![[ACP云计算]易错题(原题)](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/743516ea1bf846dcaa0d25a52239004c.png)