任务
实现
根据作业文档里的伪代码,可以对着写出代码。需要注意的一点是,如果纯按照这里的伪代码来写,最后的结果光源的位置是纯黑的,需要再加一段判断射线是否击中光源的代码。
Vector3f Scene::castRay(const Ray &ray, int depth) const
{
Vector3f L_dir;
Vector3f L_indir;
// 视线
Intersection obj_inter = intersect(ray);
if (!obj_inter.happened)
return L_dir;
// 打到光源,直接返回光源的光照。
if (obj_inter.m->hasEmission())
return obj_inter.m->getEmission();
Vector3f p = obj_inter.coords; // 交点坐标
Material *m = obj_inter.m; // 交点材质
Vector3f N = obj_inter.normal.normalized(); // 交点法线
Vector3f wo = ray.direction; // 射线方向
// 有交点,对光源采样
Intersection light_inter;
float pdf_L;
sampleLight(light_inter, pdf_L); // 得到光源位置和对光源采样的pdf
Vector3f x = light_inter.coords;
Vector3f ws = (x - p).normalized(); // 物体到光源
Vector3f emit = light_inter.emit;
Vector3f NN = light_inter.normal.normalized();
float d = (x - p).norm();
// 判断光源和物体之间是否被其他物体遮挡
Ray Obj2Light(p, ws);
float d2 = intersect(Obj2Light).distance;
// 根据距离判断是否遮挡
if (d2 - d > -0.001)
{
Vector3f eval = m->eval(wo, ws, N);
float cos_theta = dotProduct(N, ws);
float cos_theta_x = dotProduct(NN, -ws);
L_dir = emit * eval * cos_theta * cos_theta_x / std::pow(d, 2) / pdf_L;
}
// 计算间接光照
float P_RR = get_random_float();
if (P_RR < RussianRoulette)
{
Vector3f wi = m->sample(wo, N).normalized();
Ray r(p, wi);
Intersection inter = intersect(r);
// 判断计算间接光照时是否打到了光源
if (inter.happened && !inter.m->hasEmission())
{
Vector3f eval = m->eval(wo, wi, N);
float pdf_O = m->pdf(wo, wi, N); // 1/2PI
float cos_theta = dotProduct(wi, N);
L_indir = castRay(r, depth + 1) * eval * cos_theta / pdf_O / RussianRoulette;
}
}
return L_dir + L_indir;
}结果
spp = 256

提高
多线程
这里直接简单的采用c++自带的thread来实现多线程
int thread_num = 24;
std::thread renders[thread_num];
int rate = 0;
std::cout << "SPP: " << spp << "\n";
auto render_row = [&](uint32_t start_height,uint32_t end_height){
for (uint32_t j = start_height; j < end_height; ++j) {
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < scene.width; ++i) {
// generate primary ray direction
float x = (2 * (i + 0.5) / (float)scene.width - 1) *
imageAspectRatio * scale;
float y = (1 - 2 * (j + 0.5) / (float)scene.height) * scale;
Vector3f dir = normalize(Vector3f(-x, y, 1));
for (int k = 0; k < spp; k++){
framebuffer[j * scene.width + i] += scene.castRay(Ray(eye_pos, dir), 0) / spp;
}
}
rate++;
UpdateProgress(rate / (float)scene.height);
}
};
for(int k =0;k<thread_num;k++){
uint32_t start = k * scene.height / thread_num;
uint32_t end = (k == thread_num - 1) ? scene.height : (k+1)*scene.height / thread_num;
renders[k] = std::thread(render_row,start,end);
}
for(int k=0;k<thread_num;k++){
renders[k].join();
}以长方体和正方体的场景为例,设置spp为1,不采用多线程时,消耗了14秒的时间,当采用多线程时(这里采用24线程),所消耗的时间仅为3秒。


微平面模型
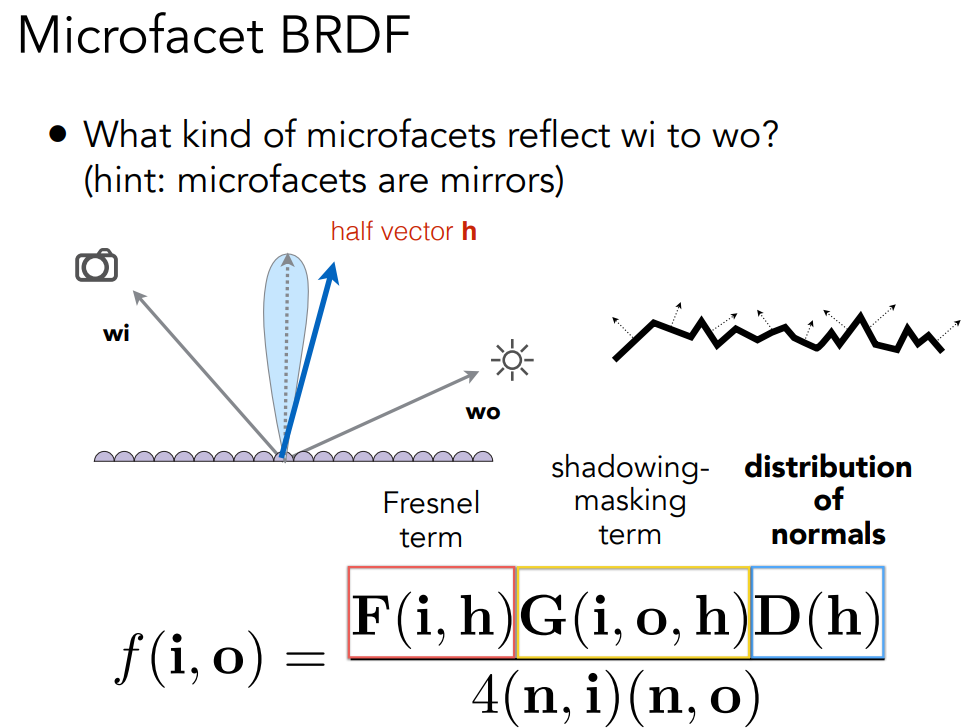
微平面(microfacet)理论假设物体表面由不同法向量的微小平面组成。
它引入了三个函数:D、G、F
-
D:是法线分布函数,它解释了在观看者角度反射光的微平面的比例。法线分布函数描述了在这个表面周围的法线分布情况,当输入向量h时,如果微平面中有35%与向量h取向一致,则法线分布函数就会返回0.35
-
G:是几何衰减函数,它解释了微平面彼此之间的阴影和遮挡。
-
F:是菲涅尔函数,它解释了菲涅耳效应,该效应使得与表面成较高的入射角的光线会以更高的镜面反射率进行反射。
昨天晚上看完教程后手写推了一下该BRDF,微平面理论cook-torrance BRDF的推导
菲涅尔函数的精确计算与近似,这里直接采用了作业框架自带的函数来求精确的菲涅尔函数的值。


几何衰减函数

法线分布函数,这里采用了各向同性的GGX法线分布函数

代码实现
菲涅尔函数(直接使用作业框架自带的菲涅尔函数)
void fresnel(const Vector3f &I, const Vector3f &N, const float &ior, float &kr) const
{
float cosi = clamp(-1, 1, dotProduct(I, N));
float etai = 1, etat = ior;
if (cosi > 0) { std::swap(etai, etat); }
// Compute sini using Snell's law
float sint = etai / etat * sqrtf(std::max(0.f, 1 - cosi * cosi));
// Total internal reflection
if (sint >= 1) {
kr = 1;
}
else {
float cost = sqrtf(std::max(0.f, 1 - sint * sint));
cosi = fabsf(cosi);
float Rs = ((etat * cosi) - (etai * cost)) / ((etat * cosi) + (etai * cost));
float Rp = ((etai * cosi) - (etat * cost)) / ((etai * cosi) + (etat * cost));
kr = (Rs * Rs + Rp * Rp) / 2;
}
// As a consequence of the conservation of energy, transmittance is given by:
// kt = 1 - kr;
}几何函数,将公式独立成GeometrySchlickGGX,然后在GeometrySmith中调用两次,这样能求得入射光和出射光各自的遮蔽情况。
float GeometrySchlickGGX(float NdotV, float k)
{
float nom = NdotV;
float denom = NdotV * (1.0 - k) + k;
return nom / denom;
}
float GeometrySmith(Vector3f N, Vector3f V, Vector3f L, float roughness)
{
float r = (roughness + 1.0);
float k = (r * r) / 8.0;
float NdotV = std::max(dotProduct(N, V), 0.0f);
float NdotL = std::max(dotProduct(N, L), 0.0f);
float ggx2 = GeometrySchlickGGX(NdotV, k);
float ggx1 = GeometrySchlickGGX(NdotL, k);
return ggx1 * ggx2;
}法线分布函数
float DistributionGGX(Vector3f N, Vector3f H, float roughness)
{
float a = roughness * roughness;
float a2 = a * a;
float NdotH = std::max(dotProduct(N, H), 0.0f);
float NdotH2 = NdotH * NdotH;
float nom = a2;
float denom = (NdotH2 * (a2 - 1.0) + 1.0);
denom = M_PI * denom * denom;
return nom / std::max(denom, 0.0000001f);
}对材质的sample,pdf和eval方法都作相应的更改,以及添加一个新的材质项MIRCO
enum MaterialType { DIFFUSE , MIRCO};Vector3f Material::sample(const Vector3f &wi, const Vector3f &N){
switch(m_type){
case DIFFUSE:
{
// uniform sample on the hemisphere
float x_1 = get_random_float(), x_2 = get_random_float();
float z = std::fabs(1.0f - 2.0f * x_1);
float r = std::sqrt(1.0f - z * z), phi = 2 * M_PI * x_2;
Vector3f localRay(r*std::cos(phi), r*std::sin(phi), z);
return toWorld(localRay, N);
break;
}
case MIRCO:
{
float x_1 = get_random_float(), x_2 = get_random_float();
float z = std::fabs(1.0f - 2.0f * x_1);
float r = std::sqrt(1.0f - z * z), phi = 2 * M_PI * x_2;
Vector3f localRay(r*std::cos(phi), r*std::sin(phi), z);
return toWorld(localRay, N);
break;
}
}
}float Material::pdf(const Vector3f &wi, const Vector3f &wo, const Vector3f &N){
switch(m_type){
case DIFFUSE:
{
// uniform sample probability 1 / (2 * PI)
if (dotProduct(wo, N) > 0.0f)
return 0.5f / M_PI;
else
return 0.0f;
break;
}
case MIRCO:
{
if (dotProduct(wo, N) > 0.0f)
return 0.5f / M_PI;
else
return 0.0f;
break;
}
}
}Vector3f Material::eval(const Vector3f &wi, const Vector3f &wo, const Vector3f &N)
{
switch (m_type)
{
case DIFFUSE:
{
// calculate the contribution of diffuse model
float cosalpha = dotProduct(N, wo);
if (cosalpha > 0.0f)
{
Vector3f diffuse = Kd / M_PI;
return diffuse;
}
else
return Vector3f(0.0f);
break;
}
case MIRCO:
{
float cosalpha = dotProduct(N, wo);
if (cosalpha > 0.0f)
{
Vector3f V = -wi;
Vector3f L = wo;
Vector3f H = normalize(V + L);
float D = DistributionGGX(N, H, roughness);
float G = GeometrySmith(N, V, L, roughness);
float F;
fresnel(wi, N, ior, F);
Vector3f nominator = D * G * F;
float denominator = 4 * std::max(dotProduct(N, V), 0.0f) * std::max(dotProduct(N, L), 0.0f);
Vector3f specular = nominator / std::max(denominator, 0.001f);
// 根据能量守恒,反射以外的能量被吸收发生漫反射
float ks_ = F;
float kd_ = 1.0f - ks_;
Vector3f diffuse = 1.0f / M_PI;
return Ks * specular + kd_ * Kd * diffuse;
}
else
return Vector3f(0.0f);
break;
}
}
}在main里面创建材质
Material* mirco = new Material(MIRCO,Vector3f(0.0f));
mirco->Kd = Vector3f(0.6);
mirco->Ks = Vector3f(0.7);
mirco->ior = 30;
mirco->roughness = 0.9;引入兔子模型
直接引入兔子模型会发生错误,因为兔子过小,参考论坛和他人的博客,需要对初始化模型的函数进行小小的修改。
MeshTriangle(const std::string& filename, Material *mt = new Material(),
Vector3f Trans = Vector3f(0.0,0.0,0.0), Vector3f Scale = Vector3f(1.0,1.0,1.0))
{
objl::Loader loader;
loader.LoadFile(filename);
area = 0;
m = mt;
assert(loader.LoadedMeshes.size() == 1);
auto mesh = loader.LoadedMeshes[0];
Vector3f min_vert = Vector3f{std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity(),
std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity(),
std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity()};
Vector3f max_vert = Vector3f{-std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity(),
-std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity(),
-std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity()};
for (int i = 0; i < mesh.Vertices.size(); i += 3) {
std::array<Vector3f, 3> face_vertices;
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
auto vert = Vector3f(mesh.Vertices[i + j].Position.X,
mesh.Vertices[i + j].Position.Y,
mesh.Vertices[i + j].Position.Z);
vert = Scale*vert+Trans;
face_vertices[j] = vert;
min_vert = Vector3f(std::min(min_vert.x, vert.x),
std::min(min_vert.y, vert.y),
std::min(min_vert.z, vert.z));
max_vert = Vector3f(std::max(max_vert.x, vert.x),
std::max(max_vert.y, vert.y),
std::max(max_vert.z, vert.z));
}
triangles.emplace_back(face_vertices[0], face_vertices[1],
face_vertices[2], mt);
}
bounding_box = Bounds3(min_vert, max_vert);
std::vector<Object*> ptrs;
for (auto& tri : triangles){
ptrs.push_back(&tri);
area += tri.area;
}
bvh = new BVHAccel(ptrs);
}在main里使用兔子模型,并赋予自定义的材质
MeshTriangle bunny("../models/bunny/bunny.obj",mirco,Vector3f(200,0,350),Vector3f(2000,2000,2000));
scene.Add(&bunny);
结果
以下是修改粗糙度roughness后产生的两种不同的结果
spp = 8 spp =8
kd = 0.6 kd = 0.6
ks = 0.7 ks = 0.7
roughness = 0.1 roughness = 0.9
ior = 30 ior = 30


另外的将sample和pdf更改成镜面反射采样后的结果