算法介绍
本篇推文将介绍一种新的智能优化算法,牛顿-拉夫逊优化算法(Newton-Raphson-based optimizer, NBRO),该成果由学者Sowmya等人于2024年2月发表于期刊《Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence》。文末提供了原文作者的完整代码github代码。

NRBO算法通过模拟自然界中资源的分配和利用来优化问题,其核心思想为:通过使用向量集定义解空间,采用Natural Resource Strategy(NRSR)以及Trap Avoidance Operator(TAO)等算子来搜索解空间。由于原文中公式计算较多,本文只对关键原理进行简单介绍,感兴趣读者可以自行下载原文学习。文末同样提供原文下载链接。
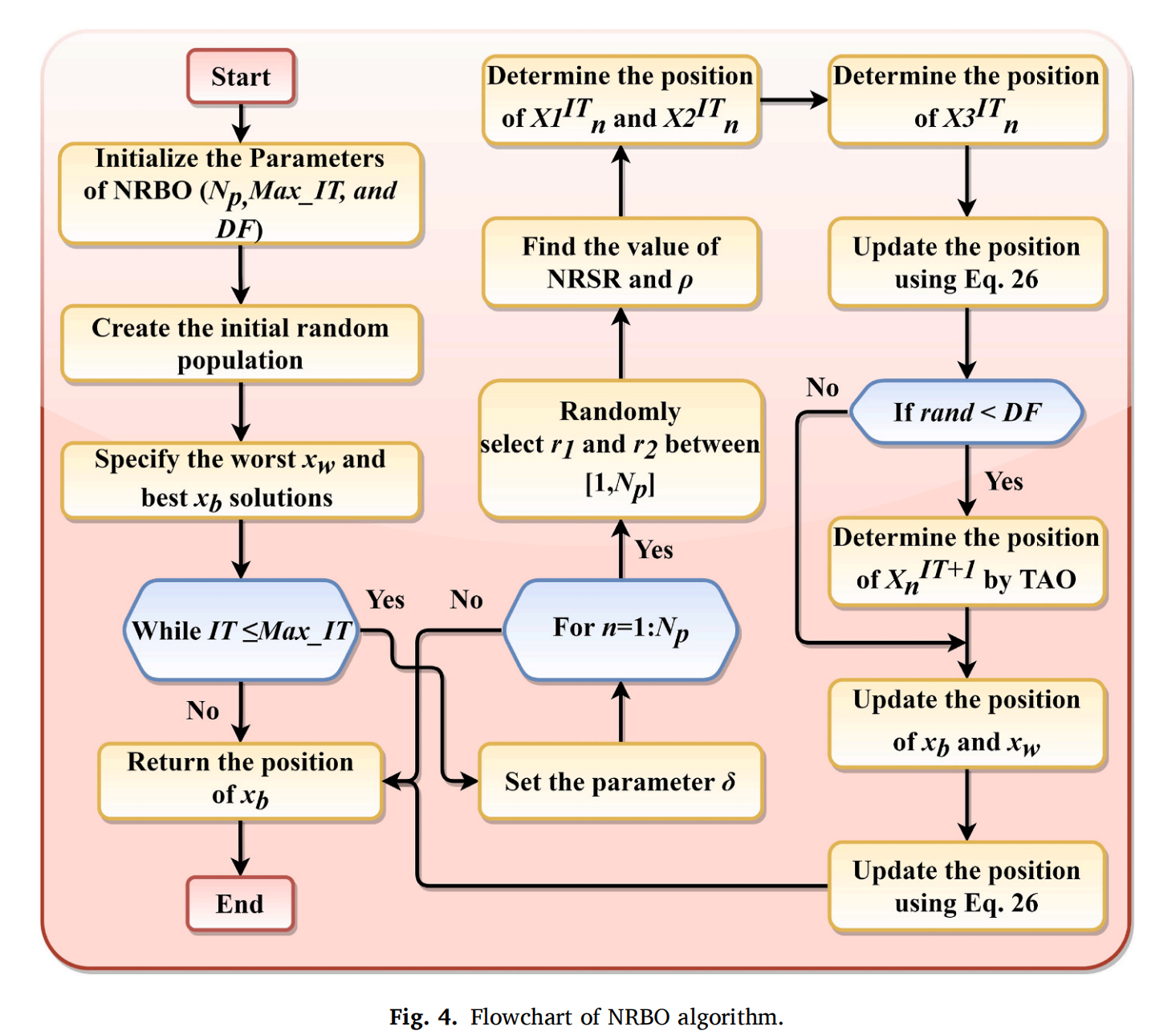
算法流程
算法伪代码流程如下:
种群初始化
初始化阶段,算法随机产生初始种群,生成规则如下:
x j n = l b + r a n d × ( u b − l b ) , n = 1 , 2 , ⋯ , N p , j = 1 , 2 , ⋯ , d i m x_j^n=lb + rand\times(ub-lb), n=1,2,\cdots,N_p, j=1,2,\cdots,dim xjn=lb+rand×(ub−lb),n=1,2,⋯,Np,j=1,2,⋯,dim
式中, x j n x_j^n xjn表示种群中第 n n n个个体在第 j j j个维度的位置, r a n d rand rand表示(0,1)之间的随机数,lb和ub分别表示变量的上下界。
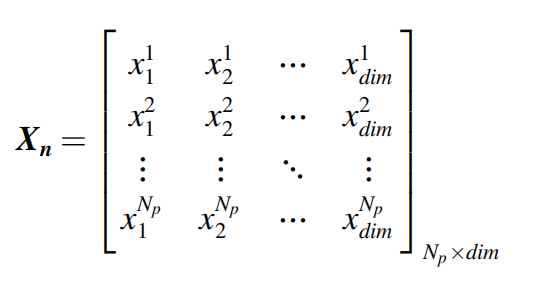
所有维度的种群矩阵表示如下:
NRSR搜索规则
NBRO算法的核心策略为NRSR搜索规则,NRSR搜索策略用于指导算法的种群搜索过程,以便于探索解空间。NRSR算法的解搜索过程如下:
-
算法倾向于保留并进一步探索那些表现出较高适应度的解。具体而言,算法将 x n − Δ x x_n-Δx xn−Δx的位置替换为 X b X_b Xb的位置,其中 X b X_b Xb表示其邻域内具有比 x n x_n xn更好的位置。
-
算法同时保留部分劣解,有助于算法避免陷入局部最优解,同时促进种群的多样性。具体而言,算法将 x n + Δ x x_n+Δx xn+Δx的位置替换为 X w X_w Xw的位置,其中 X w X_w Xw表示其邻域内具有比 x n x_n xn更差的位置。
其中, x n x_n xn代表当前位置, Δ x = r a n d ( 1 , d i m ) × a b s ( X b − X n I T ) Δx=rand(1, dim)\times abs(X_b - X_n^{IT}) Δx=rand(1,dim)×abs(Xb−XnIT)表示扰动量。
搜索过程中,算法通过下式更新解的位置:

NRSR的计算式如下:
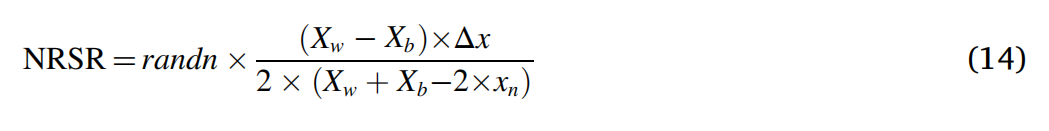
搜索过程代码如下:

Trap Avoidance Operator策略
NBRO算法采用Trap Avoidance Operator来避免算法陷入局部最优。解更新规则如下式:
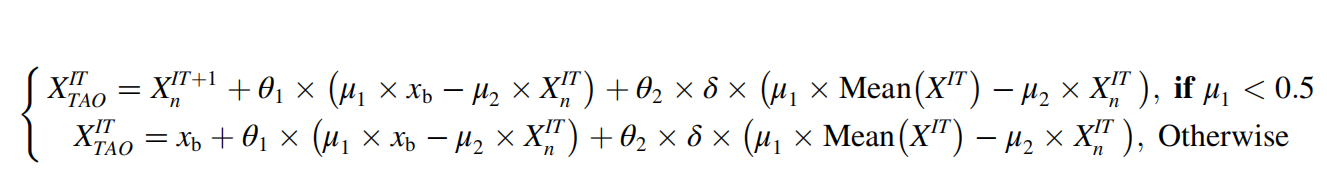
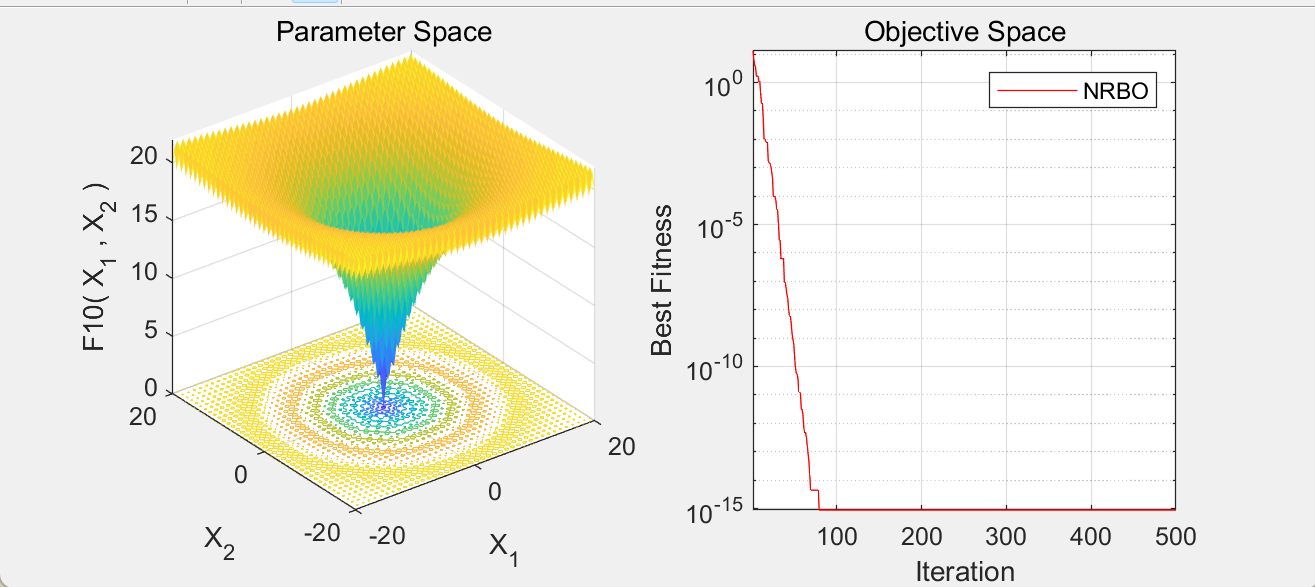
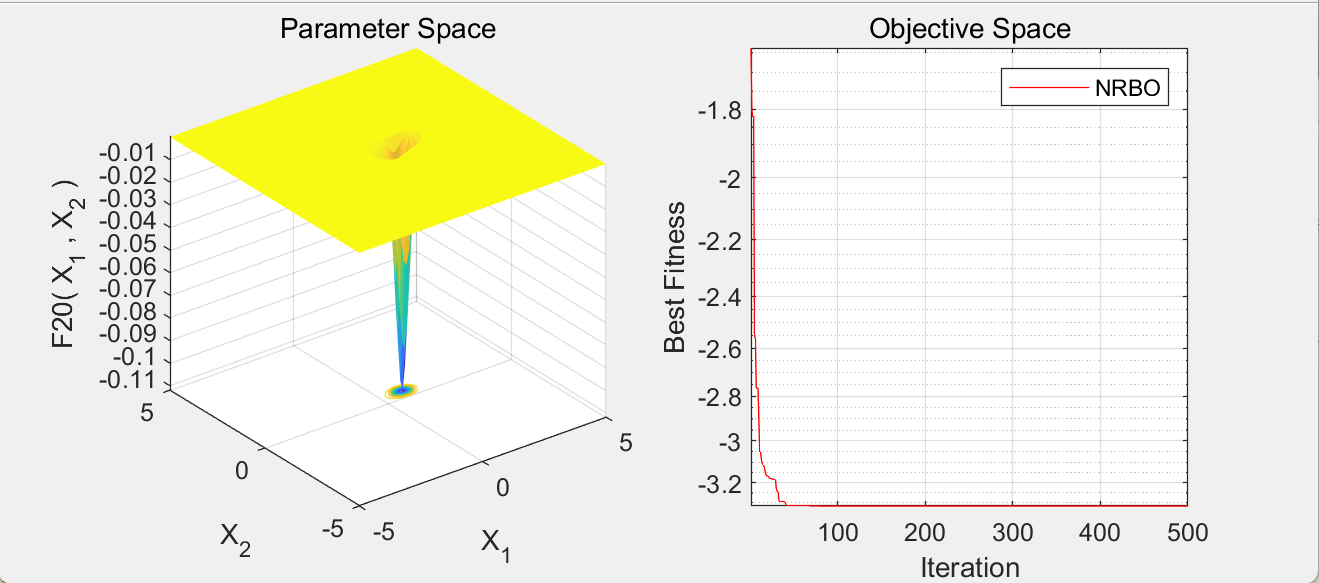
运行结果
参考文献
Sowmya R, Premkumar M, Jangir P. Newton-Raphson-based optimizer: A new population-based metaheuristic algorithm for continuous optimization problems[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2024, 128: 107532.
部分代码
% Newton-Raphson Search Rule Function
function NRSR = SearchRule(Best_Pos, Worst_Pos, Position, rho, Flag)
% Inputs:
% Best_Pos, Worst_Pos - Best and worst positions in the population
% Position - Current position
% rho - Step size
% Flag - Indicator for search rule application
dim = size(Position, 2); % Number of dimensions
DelX = rand(1, dim) .* abs(Best_Pos - Position); % Delta X for search rule
% Initial Newton-Raphson step
NRSR = randn * ((Best_Pos - Worst_Pos) .* DelX) ./ (2 * (Best_Pos + Worst_Pos - 2 * Position));
% Adjust position based on flag
if Flag == 1
Xa = Position - NRSR + rho;
else
Xa = Best_Pos - NRSR + rho;
end
% Further refine the Newton-Raphson step
r1 = rand; r2 = rand;
yp = r1 * (mean(Xa + Position) + r1 * DelX);
yq = r2 * (mean(Xa + Position) - r2 * DelX);
NRSR = randn * ((yp - yq) .* DelX) ./ (2 * (yp + yq - 2 * Position));
end
function [Best_Score, Best_Pos, CG_curve] = NRBO(N, MaxIt, LB, UB, dim, fobj)
% Input arguments:
% N - Number of particles in the population
% MaxIt - Maximum number of iterations
% LB - Lower bound of the search space
% UB - Upper bound of the search space
% dim - Dimensionality of the search space
% fobj - Objective function to minimize/maximize
% Deciding Factor for Trap Avoidance Operator
DF = 0.6;
% Initialize the bounds for each dimension
LB = ones(1, dim) * LB;
UB = ones(1, dim) * UB;
% Initialization of the population
Position = initialization(N, dim, UB, LB);
Fitness = zeros(N, 1); % Vector to store individual costs
% Calculate the initial fitness for each particle
for i = 1:N
Fitness(i) = fobj(Position(i,:));
end
% Determine the best and worst fitness in the initial population
[~, Ind] = sort(Fitness);
Best_Score = Fitness(Ind(1));
Best_Pos = Position(Ind(1),:);
Worst_Cost = Fitness(Ind(end));
Worst_Pos = Position(Ind(end),:);
% Initialize convergence curve
CG_curve = zeros(1, MaxIt);
% Main optimization loop
for it = 1:MaxIt
% Dynamic parameter delta, decreases over iterations
delta = (1 - ((2 * it) / MaxIt)) .^ 5;
% Loop over all particles in the population
for i = 1:N
% Randomly select two different indices for differential evolution
P1 = randperm(N, 2);
a1 = P1(1); a2 = P1(2);
% Calculate the step size rho
rho = rand * (Best_Pos - Position(i,:)) + rand * (Position(a1,:) - Position(a2,:));
% Apply Newton-Raphson Search Rule
Flag = 1;
NRSR = SearchRule(Best_Pos, Worst_Pos, Position(i,:), rho, Flag);
X1 = Position(i,:) - NRSR + rho;
X2 = Best_Pos - NRSR + rho;
% Update position of particle
Xupdate = zeros(1, dim);
for j = 1:dim
X3 = Position(i,j) - delta * (X2(j) - X1(j));
a1 = rand; a2 = rand;
Xupdate(j) = a1 * (a1 * X1(j) + (1 - a2) * X2(j)) + (1 - a2) * X3;
end
% Trap Avoidance Operator to prevent local optima
if rand < DF
theta1 = -1 + 2 * rand(); theta2 = -0.5 + rand();
beta = rand < 0.5;
u1 = beta * 3 * rand + (1 - beta); u2 = beta * rand + (1 - beta);
if u1 < 0.5
X_TAO = Xupdate + theta1 * (u1 * Best_Pos - u2 * Position(i,:)) + theta2 * delta * (u1 * mean(Position) - u2 * Position(i,:));
else
X_TAO = Best_Pos + theta1 * (u1 * Best_Pos - u2 * Position(i,:)) + theta2 * delta * (u1 * mean(Position) - u2 * Position(i,:));
end
Xnew = X_TAO;
else
Xnew = Xupdate;
end
% Enforce boundary conditions
Xnew = min(max(Xnew, LB), UB);
% Evaluate new solution
Xnew_Cost = fobj(Xnew);
% Update the best and worst positions
if Xnew_Cost < Fitness(i)
Position(i,:) = Xnew;
Fitness(i) = Xnew_Cost;
% Update the global best solution
if Fitness(i) < Best_Score
Best_Pos = Position(i,:);
Best_Score = Fitness(i);
end
end
% Update the global worst solution
if Fitness(i) > Worst_Cost
Worst_Pos = Position(i,:);
Worst_Cost = Fitness(i);
end
end
% Update convergence curve
CG_curve(it) = Best_Score;
% Display iteration information
disp(['Iteration ' num2str(it) ': Best Fitness = ' num2str(CG_curve(it))]);
end
end
原文及作者算法代码下载链接如下:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1dZvgcG3qkjKkU9dVLXWZ-A?pwd=bzzs 提取码: bzzs
若有运筹优化建模及算法定制需求,欢迎联系我们私聊沟通