接上篇
五、Random
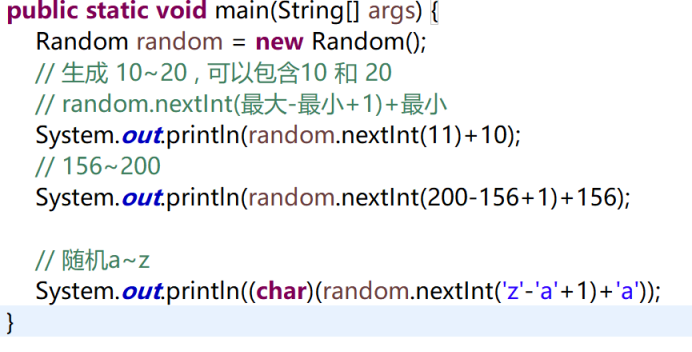
5.1 使用

5.2 练习
六、包装类
6.1 是什么
包装类:封装了基本类的一些操作,更加方便使用
为了对象的完整性,更重要的是配合泛型一起使用
byte Byte
short Short
int Integer
long Long
float Float
double Double
boolean Boolean
char Character
八种包装类,都在Java.lang包下,使用不需要导包,并且都覆写equals和toString等方法
6.2 使用

6.3 Integer
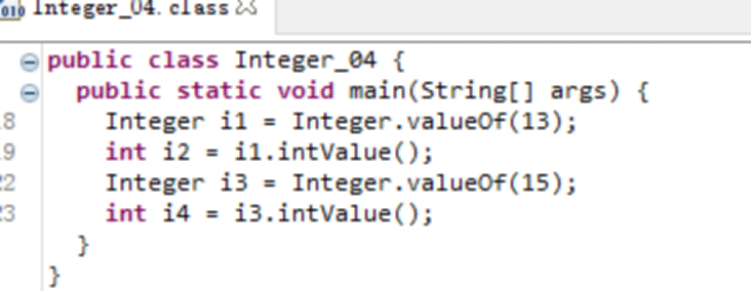
6.3.1 基本使用

6.3.2 常用方法

6.3.3 自动装箱和拆箱
1.5 新特性
自动装箱:装箱就是把基本类型转换位引用类型
自动拆箱:拆箱就是把引用类型转换为基本类型
在编译时,是对自动装箱和拆箱进行处理,自动帮助我们补齐相关方法调用

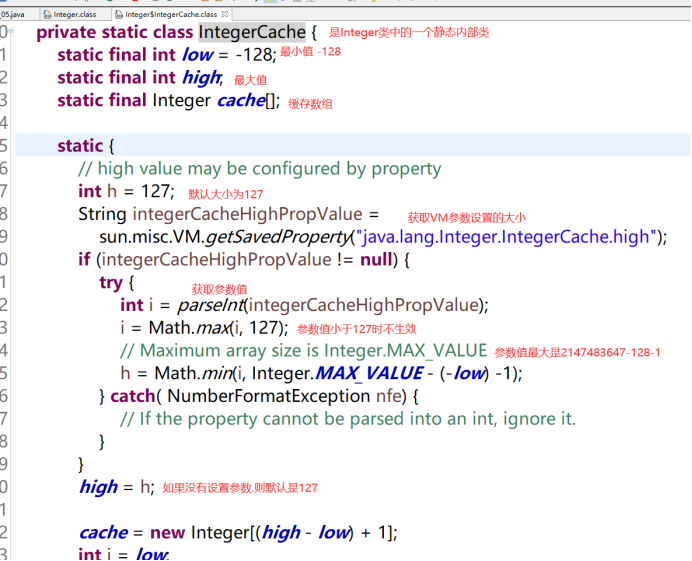
6.3.4 深入自动装箱-整形常量池
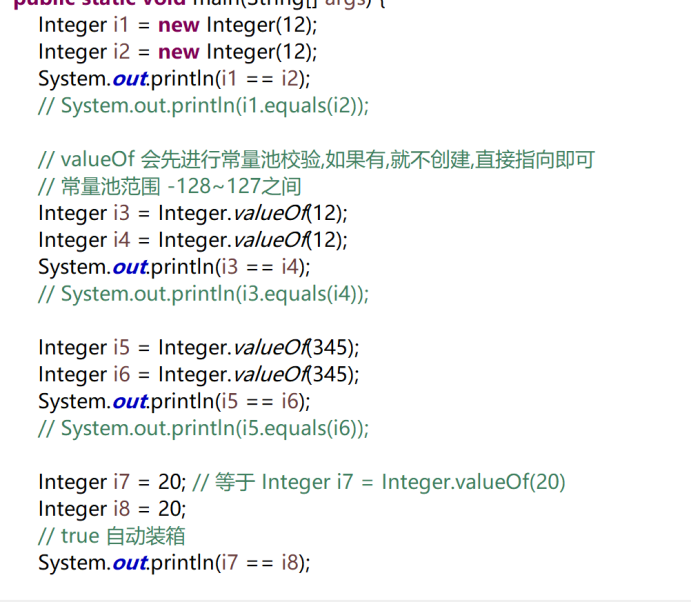
valueof方法会先进行常量池检查,没有就在堆内存创建,有就不创建了,直接保存现有的引用
默认的容量大小为-128~127共256个,会先把256个对象提前创建好,并进行存储
只要值在这个范围内,都直接保存创建好的引用即可
可以通过-XX.AutobBoxCacheMax=size,来进行设置常量池缓存大小,最小也是127


七、Calendar

八、Math
8.1 使用
// abs 绝对值
System.out.println(Math.abs(-1.5));
// ceil 向上取整
System.out.println(Math.ceil(5.00000001));
// floor 向下取整
System.out.println(Math.floor(5.99999));
// max 取两数最大值
System.out.println(Math.max(5.6, 8.2));
System.out.println(Math.min(5.6, 8.2));
// sqrt 平方根
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(9));
// cbrt 立方根
System.out.println(Math.cbrt(8));
// random 随机数, 随机获取一个 大于等于0 且 小于1 的值
// 本质就是random中的nextDouble
System.out.println(Math.random());
// 中间值 : 10~20
// Math.random()*(最大-最小+1)+最小
System.out.println(Math.floor(Math.random() * (20 - 10 + 1) + 10));
// 四舍五入
System.out.println(Math.round(4.4));
// 负数 .5 不进位
System.out.println(Math.round(-4.5));
// 四舍六入五留双, 大于.5 都入 , 小于.5 都舍, .5 取偶数
System.out.println(Math.rint(10.5));
// 5的3次方
System.out.println(Math.pow(5, 3));
8.2 练习
//随机生成a~z
九、Number
9.1 DecimalFormat
9.2 BigDecimal
的3次方
System.out.println(Math.pow(5, 3));
## 8.2 练习
//随机生成a~z
# 九、Number
## 9.1 DecimalFormat
## 9.2 BigDecimal