0. 概要
本文将介绍一个用于监控一组进程CPU使用率的Shell脚本,,当检测到某进程的CPU使用率超出阈值时,使用 perf 工具抓取该进程的详细信息。
本shell脚本为了能在普通嵌入式系统上运行做了妥协和优化。
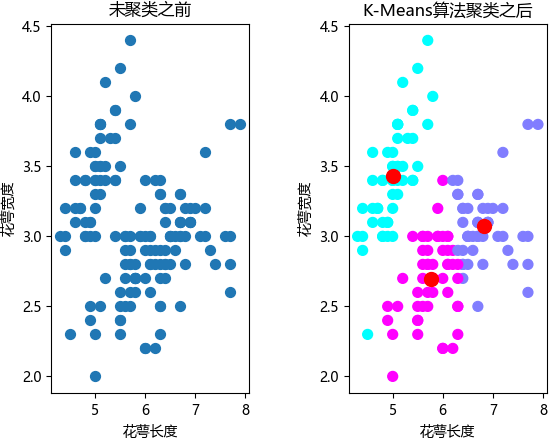
1. shell脚本流程的简要图示:

2. perf介绍
perf 是 Linux 内核提供的一个强大性能分析工具,能够用于分析和调优系统性能。它支持多种事件类型,如CPU时钟、缓存命中/未命中、中断等。
在本脚本中,当某个进程的CPU使用率超过设定阈值(例如80%)时,会使用以下命令抓取该进程的详细性能数据:
perf record -F 99 -e cpu-clock -p $pid -g -o "perf-$process_name.data" -- sleep $perf_sleep_time
-F 99:以每秒99次的频率进行采样。-e cpu-clock:采样的事件类型为CPU时钟周期。-p $pid:指定要采样的进程ID。-g:记录调用栈信息,帮助分析性能瓶颈。-o "perf-$process_name.data":将采样数据输出到指定文件中。-- sleep $perf_sleep_time:持续采样时间为10秒。
通过抓取高CPU使用率进程的详细性能数据,我们可以深入分析性能瓶颈,找出导致高CPU使用的原因,从而进行针对性的优化。
更多介绍请查看:
使用perf(火焰图)查看热点函数和系统调用最大延迟函数
如何使用perf 统计cpu和内存?
3. shell脚本详解
-
日志文件配置:
# Log file location LOGFILE="process_monitor.log" # Redirect standard input, output, and error to log file exec 1>>"$LOGFILE" exec 2>>"$LOGFILE"这部分代码配置日志文件,并将标准输入、输出和错误重定向到日志文件中。
-
后台运行检测:
# Check if the script is already running if [ "$1" != "background" ]; then "$0" background & exit 0 fi这段代码用于检测脚本是否已经在后台运行,如果没有,则重新以后台模式启动自己。
-
初始化上次报告时间文件:
# Initialize last report time file last_report_time_file="last_report_time" touch "$last_report_time_file"初始化用于存储上次报告时间的文件。
-
获取CPU总时间的函数:
# Function to get the total CPU usage from /proc/stat get_total_cpu_time() { awk '/^cpu / {print $2 + $3 + $4 + $5 + $6 + $7 + $8}' /proc/stat }从
/proc/stat文件中获取CPU总时间。 -
获取进程CPU时间的函数:
# Function to get the process CPU usage from /proc/[pid]/stat get_process_cpu_time() { pid=$1 awk '{print $14 + $15 + $16 + $17}' /proc/$pid/stat }从
/proc/[pid]/stat文件中获取指定进程的CPU时间。 -
计算进程CPU使用率的函数:
# Function to calculate CPU usage of a process calculate_cpu_usage() { pid=$1 prev_process_time=$(get_process_cpu_time "$pid") prev_total_time=$(get_total_cpu_time) sleep 1 process_time=$(get_process_cpu_time "$pid") total_time=$(get_total_cpu_time) process_delta=$((process_time - prev_process_time)) total_delta=$((total_time - prev_total_time)) cpu_usage=$((100 * process_delta / total_delta)) echo $cpu_usage }计算指定进程的CPU使用率。
-
加载上次报告时间的函数:
# Function to load the last report time for a PID load_last_report_time() { pid=$1 grep "^$pid=" "$last_report_time_file" | cut -d'=' -f2 }从文件中加载上次报告时间。
-
保存上次报告时间的函数:
# Function to save the last report time for a PID save_last_report_time() { pid=$1 time=$2 sed -i "/^$pid=/d" "$last_report_time_file" echo "$pid=$time" >> "$last_report_time_file" }将上次报告时间保存到文件中。
-
进程监控列表:
# List of process names to monitor process_names="top systemd"定义需要监控的进程名称列表。
-
监控循环:
while true; do
current_time=$(date +%s)
for process_name in $process_names; do
if [ -n "$DEBUG_ON" ]; then
echo "Checking process: $process_name"
fi
# Find all matching process PIDs
pids=$(ps aux | grep "$process_name" | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}')
for pid in $pids; do
# Calculate CPU usage
cpu_usage=$(calculate_cpu_usage "$pid")
# Check if CPU usage exceeds $max_cpu_usage%
if [ "$cpu_usage" -gt $max_cpu_usage ]; then
echo "High CPU usage detected for process '$process_name' (PID: $pid): $cpu_usage%"
# Load the last report time for this PID
last_time=$(load_last_report_time "$pid")
last_time=${last_time:-0}
time_diff=$((current_time - last_time))
# Check if the last report time is more than 60 seconds ago
if [ "$time_diff" -ge 60 ]; then
echo "time_diff: $time_diff, perf record -F 99 -e cpu-clock -p $pid -g -o perf-$process_name.data -- sleep $perf_sleep_time"
ps -p "$pid" -o pid,ppid,cmd,%mem,%cpu >> "$LOGFILE"
perf record -F 99 -e cpu-clock -p $pid -g -o "perf-$process_name.data" -- sleep $perf_sleep_time
# Save the last report time for this PID
save_last_report_time "$pid" "$current_time"
# sleep for 1 second
sleep 1
fi
else
if [ -n "$DEBUG_ON" ]; then
echo "CPU usage for process '$process_name' (PID: $pid): $cpu_usage%"
fi
fi
done
done
done
这是主要的监控循环,定期检查指定进程的CPU使用率,并在超过阈值时使用 perf 抓取详细信息。
4. 完整脚本实现
以下是优化后的Shell脚本,适用于普通嵌入式系统:
#!/bin/sh
# This script monitors the CPU usage of a list of processes
DEBUG_ON=1
# Log file location
LOGFILE="process_monitor.log"
# Redirect standard input, output, and error to log file
exec 1>>"$LOGFILE"
exec 2>>"$LOGFILE"
# Check if the script is already running
if [ "$1" != "background" ]; then
"$0" background &
exit 0
fi
# Initialize last report time file
last_report_time_file="last_report_time"
touch "$last_report_time_file"
# Function to get the total CPU usage from /proc/stat
get_total_cpu_time() {
awk '/^cpu / {print $2 + $3 + $4 + $5 + $6 + $7 + $8}' /proc/stat
}
# Function to get the process CPU usage from /proc/[pid]/stat
get_process_cpu_time() {
pid=$1
awk '{print $14 + $15 + $16 + $17}' /proc/$pid/stat
}
# Function to calculate CPU usage of a process
calculate_cpu_usage() {
pid=$1
prev_process_time=$(get_process_cpu_time "$pid")
prev_total_time=$(get_total_cpu_time)
sleep 1
process_time=$(get_process_cpu_time "$pid")
total_time=$(get_total_cpu_time)
process_delta=$((process_time - prev_process_time))
total_delta=$((total_time - prev_total_time))
cpu_usage=$((100 * process_delta / total_delta))
echo $cpu_usage
}
# Function to load the last report time for a PID
load_last_report_time() {
pid=$1
grep "^$pid=" "$last_report_time_file" | cut -d'=' -f2
}
# Function to save the last report time for a PID
save_last_report_time() {
pid=$1
time=$2
sed -i "/^$pid=/d" "$last_report_time_file"
echo "$pid=$time" >> "$last_report_time_file"
}
# List of process names to monitor
process_names="top systemd"
echo "Monitoring CPU usage for processes: $process_names"
# Perf sleep time
perf_sleep_time=10
max_cpu_usage=80
# Monitoring loop
while true; do
current_time=$(date +%s)
for process_name in $process_names; do
if [ -n "$DEBUG_ON" ]; then
echo "Checking process: $process_name"
fi
# Find all matching process PIDs
# pids=$(ps | grep "$process_name" | grep -v grep | awk '{print $1}')
pids=$(ps aux | grep "$process_name" | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}')
for pid in $pids; do
# Calculate CPU usage
cpu_usage=$(calculate_cpu_usage "$pid")
# Check if CPU usage exceeds $max_cpu_usage%
if [ "$cpu_usage" -gt $max_cpu_usage ]; then
echo "High CPU usage detected for process '$process_name' (PID: $pid): $cpu_usage%"
# Load the last report time for this PID
last_time=$(load_last_report_time "$pid")
last_time=${last_time:-0}
time_diff=$((current_time - last_time))
# Check if the last report time is more than 60 seconds ago
if [ "$time_diff" -ge 60 ]; then
echo "time_diff: $time_diff, perf record -F 99 -e cpu-clock -p $pid -g -o perf-$process_name.data -- sleep $perf_sleep_time"
ps -p "$pid" -o pid,ppid,cmd,%mem,%cpu >> "$LOGFILE"
perf record -F 99 -e cpu-clock -p $pid -g -o "perf-$process_name.data" -- sleep $perf_sleep_time
# Save the last report time for this PID
save_last_report_time "$pid" "$current_time"
# sleep for 1 second
sleep 1
fi
else
if [ -n "$DEBUG_ON" ]; then
echo "CPU usage for process '$process_name' (PID: $pid): $cpu_usage%"
fi
fi
done
done
done
通过这种方式,我们可以有效地监控嵌入式系统中高CPU使用率的进程,并通过 perf 工具获取详细的性能数据,帮助我们进行性能调优和问题排查。















![[译] How things get done on the Go Team](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/0d7023e7d624fee39f5751eb6512c0fb.png)