Title
题目
Early Indicators of the Impact of Using AI in Mammography Screening for Breast Cancer
使用人工智能在乳腺癌筛查中的早期影响指标
01
文献速递介绍
基于人群的乳腺癌筛查通过使用乳房X线摄影成功地降低了乳腺癌的死亡率,但这给乳腺放射科医生带来了巨大的工作负担。乳腺放射科医生需要阅读大量的乳房X线片,其中大多数没有显示可疑病变或需要召回的迹象。为了提高癌症检测率和减少误报召回,一些筛查项目采用双重阅读,这进一步加重了阅读工作负担。此外,召回女性进行进一步的诊断测试也增加了放射科医生的临床工作负担。这种工作负担的增加因乳腺专科放射科医生的普遍短缺而更加严重。
近年来,回顾性研究表明,在筛查中使用人工智能(AI)系统可能有助于缓解放射科医生的工作负担,同时保持筛查性能。一项研究建议,对于由AI系统认为可能正常的筛查,使用单次阅读而不是双重阅读,可以减少放射科医生的工作负担,同时保持筛查敏感性、提高特异性并减少误报召回。鉴于这些最新证据以及放射科医生工作负担的增加,AI系统作为支持工具来根据乳腺癌的概率对筛查进行分层,可能是有用的,这也激发了在基于人群的乳腺癌筛查中探索其应用的动机。
此外,让放射科医生在AI辅助决策支持和AI提供的病变标记下阅读乳房X线片,可能会提高筛查敏感性。在筛查分层和决策支持中同时使用AI,不仅有可能保持筛查性能,还可能改进筛查表现。
Background
背景
Retrospective studies have suggested that using artificial intelligence (AI) may decrease the workload of radiologists while preserving mammography screening performance.
回顾性研究表明,使用人工智能(AI)可能在保持乳腺癌筛查性能的同时,减少放射科医生的工作量。
Method
方法
This retrospective study included 50–69-year-old women who underwent biennial mammography screening in the Capital Region of Denmark. Before AI system implementation (October 1, 2020, to November 17, 2021), all screenings involved double reading. For screenings conducted after AI system implementation (November 18, 2021, to October 17, 2022), likely normal screenings (AI examination score ≤5 before May 3, 2022, or ≤7 on or after May 3, 2022) were single read by one of 19 senior fulltime breast radiologists. The remaining screenings were read by two radiologists with AI-assisted decision support. Biopsy and surgical outcomes were retrieved between October 1, 2020, and April 15, 2023, ensuring at least 180 days of follow-up. Screening metrics were compared using the χ2 test. Reading workload reduction was measured as saved screening reads.
这项回顾性研究包括了在丹麦首都地区接受两年一次乳腺癌筛查的50-69岁女性。在AI系统实施前(2020年10月1日至2021年11月17日),所有筛查均采用双读法。AI系统实施后(2021年11月18日至2022年10月17日),可能正常的筛查(2022年5月3日之前AI检查评分≤5,或2022年5月3日之后评分≤7)由19位全职资深乳腺放射科医生之一单独阅读。其余筛查由两名放射科医生通过AI辅助决策支持阅读。活检和手术结果在2020年10月1日至2023年4月15日之间进行检索,确保至少180天的随访期。筛查指标使用χ2检验进行比较,阅读工作量减少通过节省的筛查阅读次数来衡量。
Conclusion
结论
In a population-based mammography screening program, using AI reduced the overall workload of breast radiologists while improving screening performance.
在基于人群的乳腺癌筛查项目中,使用人工智能(AI)减少了乳腺放射科医生的整体工作量,同时提高了筛查性能。
Results
结果
In total, 60751 and 58246 women were screened before and after AI system implementation, respectively (median age, 58 years [IQR, 54–64 years] for both cohorts), with a median screening interval before AI of 845 days (IQR, 820–878 days) and with AI of 993 days (IQR, 968–1013 days; P < .001). After AI system implementation, the recall rate decreased by 20.5% (3.09% before AI [1875 of 60751] vs 2.46% with AI [1430 of 58246]; P < .001), the cancer detection rate increased (0.70% [423 of 60751] vs 0.82% [480 of 58246]; P = .01), the false-positive rate decreased (2.39% [1452 of 60751] vs 1.63% [950 of 58246]; P < .001), the positive predictive value increased (22.6% [423 of 1875] vs 33.6% [480 of 1430]; P < .001), the rate of small cancers (≤1 cm) increased (36.6% [127 of 347] vs 44.9% [164 of 365]; P = .02), the rate of node-negative cancers was unchanged (76.7% [253 of 330] vs 77.8% [273 of 351]; P = .73), and the rate of invasive cancers decreased (84.9% [359 of 423] vs 79.6% [382 of 480]; P = .04). The reading workload was reduced by 33.5% (38977 of 116492 reads).
共计60751名女性在AI系统实施前接受了筛查,58246名女性在AI系统实施后接受了筛查(两组的中位年龄均为58岁[IQR,54–64岁]),AI实施前的中位筛查间隔为845天(IQR,820–878天),AI实施后的中位筛查间隔为993天(IQR,968–1013天;P < .001)。AI系统实施后,召回率下降了20.5%(AI前为3.09%[60751中的1875],AI后为2.46%[58246中的1430];P < .001),癌症检出率上升(0.70%[60751中的423] vs 0.82%[58246中的480];P = .01),假阳性率下降(2.39%[60751中的1452] vs 1.63%[58246中的950];P < .001),阳性预测值增加(22.6%[1875中的423] vs 33.6%[1430中的480];P < .001),小癌症(≤1 cm)率增加(36.6%[347中的127] vs 44.9%[365中的164];P = .02),无淋巴结转移的癌症率保持不变(76.7%[330中的253] vs 77.8%[351中的273];P = .73),浸润性癌症率下降(84.9%[423中的359] vs 79.6%[480中的382];P = .04)。阅读工作量减少了33.5%(116492次阅读中的38977次)。
Figure
图
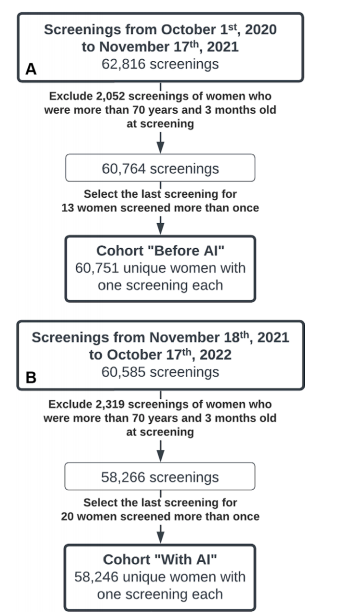
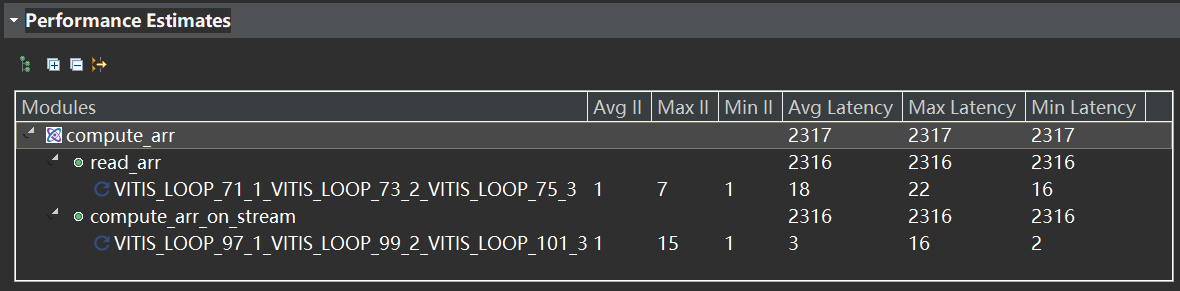
Figure 1: Flow diagram of the inclusion and exclusion process for the cohort of women screened (A) before the implementation of an artificial intelligence (AI) system and (B) after the AI system was implemented for mammography screening
图1:筛查女性队列的纳入和排除过程的流程图 (A) 在人工智能(AI)系统实施前的筛查 (B) 在实施AI系统后的乳腺癌筛查
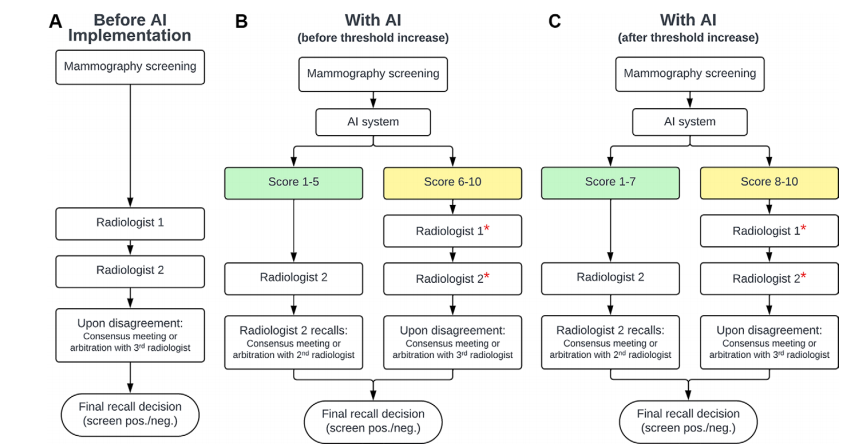
Figure 2: Flow diagram depicts mammography reading protocols (A) before an artificial intelligence (AI) system was implemented in screening and (B, C) after the AI system was implemented with (B) the original (before May 3, 2022) or (C) a higher (on or after May 3, 2022) AI examination score threshold for selecting screenings for single reading. Green boxes indicate likely normal screenings selected for single reading; yellow boxes indicate screenings selected for AI-assisted double reading, in which case radiologists (*) had access to decision support in the form of highlighted lesions provided by the AI system. neg. = negative, pos. = positive.
图2:流程图描述了乳腺癌筛查的阅读协议 (A) 在人工智能(AI)系统实施前的情况和 (B, C) 在AI系统实施后的情况,其中 (B) 为原始的筛查评分阈值(2022年5月3日之前),(C) 为更高的筛查评分阈值(2022年5月3日之后)选择单次阅读的筛查。绿色框表示可能正常的筛查,选定为单次阅读;黄色框表示选定为AI辅助双重阅读的筛查,在这种情况下,放射科医生可以使用AI系统提供的高亮病灶形式的决策支持。neg. = 阴性,pos. = 阳性。
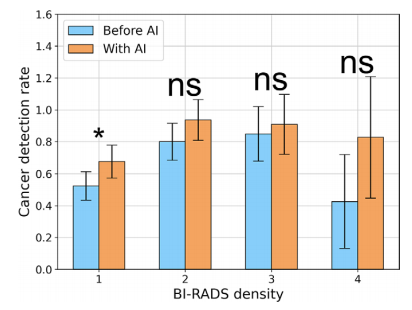
Figure 3: Cancer detection rates across Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) density categories, as assigned by the second senior radiologist. Error bars indicate 95% CIs. = P < .05. AI = artificial intelligence, ns = not significant.
图3:不同乳腺影像报告和数据系统(BI-RADS)密度类别下的癌症检出率,由第二位资深放射科医生评定。误差条表示95%的置信区间。表示 P < .05。AI = 人工智能,ns = 无统计显著性。
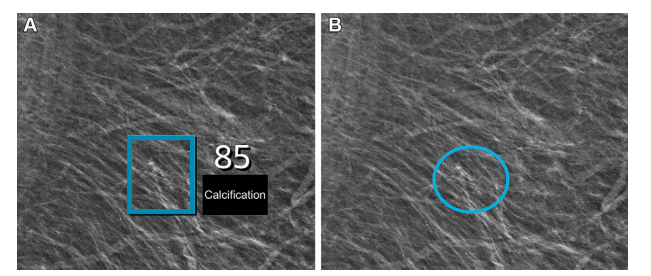
Figure 4: Left mediolateral oblique full-field digital mammographic view in a 67-year-old woman with a Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System density of 1 who underwent screening with the artificial intelligence (AI) system. (A) Image shows AI-provided marking (square). The screening received a high AI examination score of 10, based on this area with arterial calcifications being given a score of 85 out of 100 by the AI system. (B) Same image as in A, but with findings by the radiologists. Because of the high AI examination score, the screening was double read by two radiologists, who determined that the arterial calcifications (circle) did not yield suspicions for breast cancer. The woman was not recalled for diagnostic assessment.
图4:一名67岁女性的左侧内外斜位全视野数字乳腺X线片,其乳腺影像报告和数据系统密度为1,该女性在人工智能(AI)系统下接受筛查。(A) 图像显示了AI提供的标记(方框)。由于该区域动脉钙化,AI系统给出了85分(满分100)的评分,筛查得到了10分的高AI检查评分。(B) 与(A)相同的图像,但显示了放射科医生的发现。由于高AI检查评分,该筛查由两名放射科医生进行了双重阅读,他们确定动脉钙化(圆圈)未引起对乳腺癌的怀疑。该女性未被召回进行诊断评估。
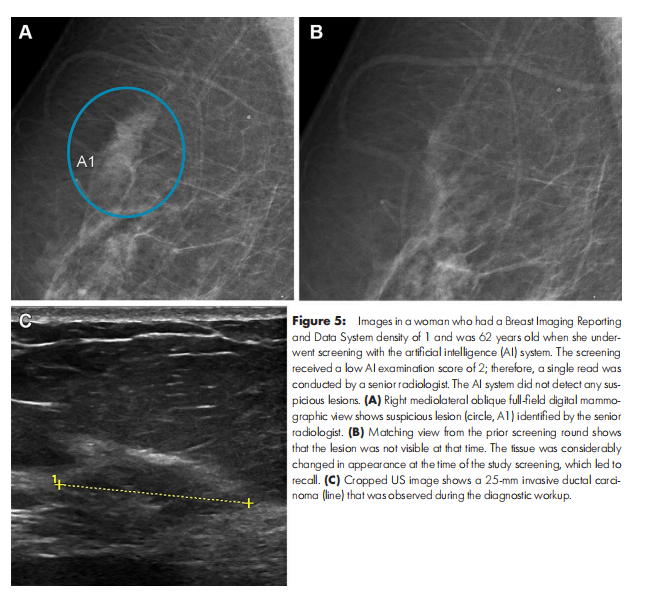
Figure 5: Images in a woman who had a Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System density of 1 and was 62 years old when she underwent screening with the artificial intelligence (AI) system. The screening received a low AI examination score of 2; therefore, a single read was conducted by a senior radiologist. The AI system did not detect any suspicious lesions. (A) Right mediolateral oblique full-field digital mammographic view shows suspicious lesion (circle, A1) identified by the senior radiologist. (B) Matching view from the prior screening round shows that the lesion was not visible at that time. The tissue was considerably changed in appearance at the time of the study screening, which led to recall. (C) Cropped US image shows a 25-mm invasive ductal carcinoma (line) that was observed during the diagnostic workup.
图5:图像显示了一名乳腺影像报告和数据系统密度为1的62岁女性,她在人工智能(AI)系统下接受筛查。筛查得到了2分的低AI检查评分,因此由一名资深放射科医生进行单独阅读。AI系统未检测到任何可疑病变。(A) 右侧内外斜位全视野数字乳腺X线片显示了由资深放射科医生识别的可疑病变(圆圈,A1)。(B) 之前筛查轮次的匹配视图显示当时未发现该病变。在本次研究筛查时,组织外观发生了显著变化,导致该患者被召回。(C) 裁剪后的超声图像显示了诊断过程中观察到的25毫米的侵袭性导管癌(线)。
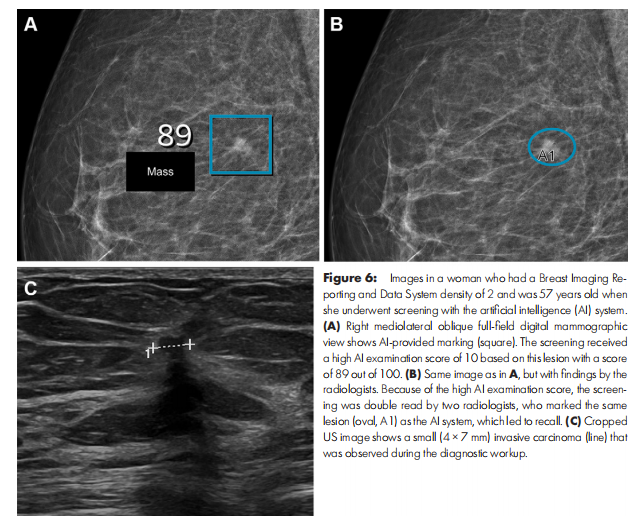
Figure 6: Images in a woman who had a Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System density of 2 and was 57 years old when she underwent screening with the artificial intelligence (AI) system. (A) Right mediolateral oblique full-field digital mammographic view shows AI-provided marking (square). The screening received a high AI examination score of 10 based on this lesion with a score of 89 out of 100. (B) Same image as in A, but with findings by the radiologists. Because of the high AI examination score, the screening was double read by two radiologists, who marked the same lesion (oval, A1) as the AI system, which led to recall. (C) Cropped US image shows a small (4 × 7 mm) invasive carcinoma (line) that was observed during the diagnostic workup
图6:图像显示了一名乳腺影像报告和数据系统密度为2的57岁女性,她在人工智能(AI)系统下接受筛查。(A) 右侧内外斜位全视野数字乳腺X线片显示了AI提供的标记(方框)。由于该病变评分为89分(满分100),筛查得到了10分的高AI检查评分。(B) 与(A)相同的图像,但显示了放射科医生的发现。由于高AI检查评分,该筛查由两名放射科医生进行了双重阅读,他们标记了与AI系统相同的病变(椭圆形,A1),导致该患者被召回。(C) 裁剪后的超声图像显示了诊断过程中观察到的小型侵袭性癌(4×7毫米,线)。
Table
表
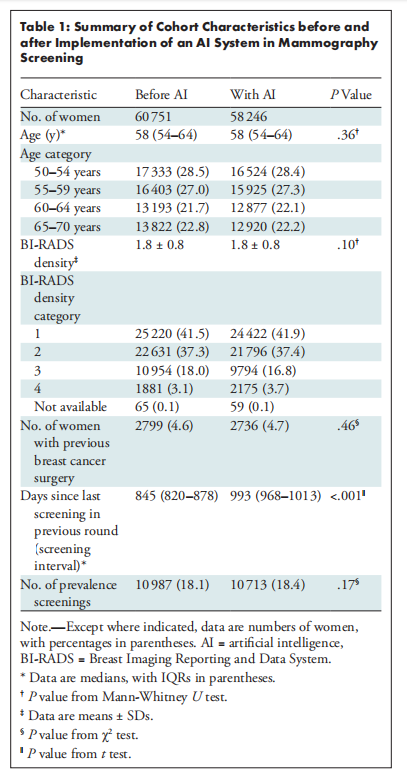
Table 1: Summary of Cohort Characteristics before and after Implementation of an AI System in Mammography Screening
表1:乳腺癌筛查中AI系统实施前后队列特征总结
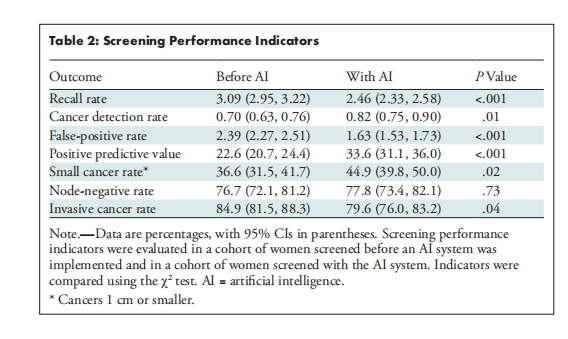
Table 2: Screening Performance Indicators
表2:筛查性能指标
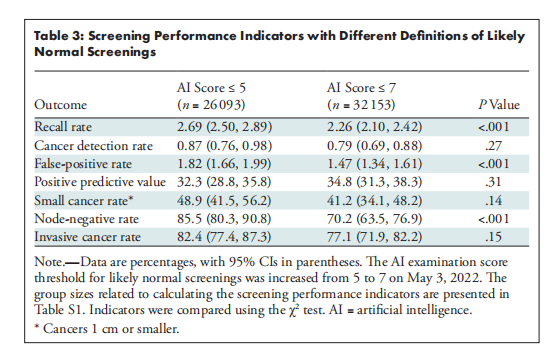
Table 3: Screening Performance Indicators with Different Definitions of Likely Normal Screenings
表3:不同定义的可能正常筛查的筛查性能指标
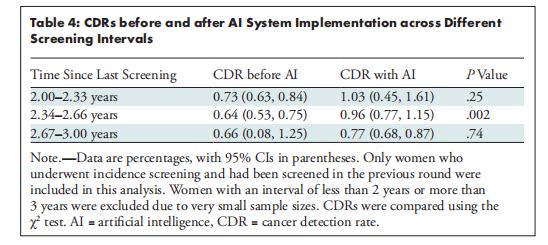
Table 4: CDRs before and after AI System Implementation across Different Screening Intervals
表4:不同筛查间隔下AI系统实施前后的癌症检出率(CDRs)