一、前言
在应用系统中提交是一个极为常见的功能,倘若不加管控,极易由于用户的误操作或网络延迟致使同一请求被发送多次,从而生成重复的数据记录。针对用户的误操作,前端通常会实现按钮的 loading 状态,以阻止用户进行多次点击。然而,对于网络波动造成的请求重发问题,仅依靠前端是难以解决的。因此,后端也应当施行相应的防止重复提交逻辑,保证在网络波动的情形下不会接收并处理同一请求多次。
二、防止重复提交该怎么设计?
1、哪一类接口需要防止重复提交?
并非所有接口都需要防止重复提交,通常以下几类接口有添加防止重复提交的需求:
- 用户输入类接口:像搜索框输入、表单输入等。用户输入操作通常会频繁触发接口请求,但每次触发不一定非得立即发送请求,可以等待用户完成输入一段时间后再进行发送。
- 按钮点击类接口:例如提交表单、保存设置等。用户可能频繁点击按钮,但每次点击并非必须立刻发送请求,可待用户停止点击一段时间后再发送。
2、如何判断接口是重复的?
那么怎样来判定两次接口调用是重复的呢?
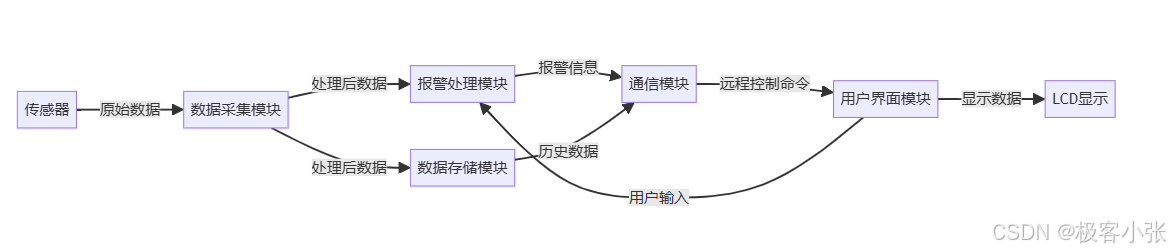
首先,我们需要为这两次接口调用设定一个时间间隔,超过这个时间间隔的必然不是重复提交;
其次,对两次请求提交的参数进行比对,不必涵盖全部参数,选取具有较强标识性的参数就行。
此外,还要将请求接口的用户标识纳入考虑范畴,若用户标识相同,能进一步辅助判断是否为重复提交;
最后,如果想要实现更优的效果,还可以增加一个请求地址的对比,如果请求不是来自接口也需要防重也可使用类名+方法名进行对比。
根据上面的思路防重逻辑的流程图如下:

三、分布式部署下防止重复提交该如何实现?
1、引入依赖
考虑到多机器部署和分布式的场景,我们需要一个分布式组件来存储和获取key,这里我们选择了Redisson。所以使用需要导入以下依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId>
<version>1.8.14.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.15.2</version>
</dependency>2、定义防重注解
首先我们先定义一个注解RepeatSubmit,注解包含以下几个参数 :
waitTime: 等待时间,默认0秒
expireTime: 锁过期时间,默认10秒
completeRelease: 执行完成后是否释放锁,默认是
timeUnit: 超时时间单位,默认毫秒
errorMsg: 报错信息,默认 "点击太快了,请慢一点!"
注解定义的代码如下:
/**
* @author fhey
* @date 2022-01-23 14:42:23
* @description: TODO
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface RepeatSubmit {
/**
* 等待时间,默认0秒
*/
int waitTime() default 0;
/**
* 锁过期时间,默认10秒
*/
int expireTime() default 1000;
/**
* 执行完成后是否释放锁,默认是
*/
boolean completeRelease() default true;
/**
* 超时时间单位,默认毫秒
*/
TimeUnit timeUnit() default TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS;
/**
* 报错信息
*/
String errorMsg() default "点击太快了,请慢一点!";
}3、建立aop环绕通知
接着建立一个Spring AOP的环绕通知类RepeatSubmitAspect,代码如下:
/**
* @author fhey
* @date 2022-02-02 19:30:34
* @description: 防止重复提交
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class RepeatSubmitAspect {
public static final String KEYPREX = "fhey:noRpeat:";
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
/**
* 进行接口防重复操作处理
*
* @param joinPoint
* @return
*/
@Around("@annotation(com.fhey.common.annotation.RepeatSubmit)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.info("RepeatSubmitAspect in");
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
RepeatSubmit annotation = method.getAnnotation(RepeatSubmit.class);
if (annotation == null) {
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
//获取request
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) Objects.requireNonNull(RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes())).getRequest();
String lockKey = getLockKey(request, joinPoint);
log.info("repeat lockKey:" + lockKey);
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockKey);
Object result = null;
// 默认10秒自动解锁
try {
if (!lock.tryLock(annotation.waitTime(), annotation.expireTime(), annotation.timeUnit())) {
throw new BusinessException(annotation.errorMsg());
}
result = joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("repeat 加锁异常,请求参数:{}", request, e);
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("repeat 加锁异常,请求参数:{}", request, e);
throw e;
} finally {
if (annotation.completeRelease() && lock.isLocked() && lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) {
lock.unlock();
}
}
return result;
}
}4、保证请求唯一key如何生成?
上面的环绕通知里有一个获取请求唯一key的getLockKey方法,那么这个方法应该怎么实现呢?
这里我通过拼接各种与请求相关的信息,如用户唯一标识 、请求路径(或者类名+方法名)参数等来生成key。因为拼接的字符可能过长所以我使用摘要算法生成最终key。实现的代码如下:
/**
* 获取锁名
* @param request 请求
* @param joinPoint 切点
* @return redisKey
*/
private String getLockKey(HttpServletRequest request, ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
//拿到userId
String userId = StringUtils.isBlank(request.getHeader("userId")) ? StringUtils.EMPTY : request.getHeader("userId");
if(StringUtils.isBlank(userId)){
sb.append("userId:").append(userId);
}
String path = request.getRequestURI().toString();
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(path)){
sb.append("path:").append(path);
} else{
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) signature;
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
Class<?> targetClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
String className = targetClass.getName();
String methodName = method.getName();
sb.append("class:").append(className);
sb.append("method:").append(methodName);
}
String args = JSON.toJSONString(joinPoint.getArgs());
sb.append("args:").append(args);
String sbStr = sb.toString();
String lockKey = KEYPREX + DigestUtils.md5Hex(sbStr);
return lockKey;
}5、验证注解
写一个在Controller里写一个测试的接口,代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@PostMapping(value = "/testRepeatSubmit",produces = { "application/json;charset=UTF-8" })
@RepeatSubmit
public String testRepeatSubmit() throws IOException {
return "点击太快了,请慢一点!";
}
}接下来使用Postman进行进行请求验证。
第一次请求,返回成功。

第二次请求在 2 秒内发出,返回重复提交的提示。

四、总结
这种防止重复提交的机制,通过 Redis 锁和切面技术的结合,有效地保障了系统的稳定性和数据的一致性。例如,在一个订单提交的场景中,如果没有这样的防止重复提交机制,用户可能会因为误操作或网络延迟等原因多次提交订单,导致数据混乱和业务逻辑错误。而有了这个机制,就能很好地避免这类问题的发生。