Unity DOTS中的world
- 注册销毁逻辑
- 自定义创建逻辑
- 创建world
- 创建system group
- 插入player loop
- Reference
DOTS中,world是一组entity的集合。entity的ID在其自身的世界中是唯一的。每个world都拥有一个EntityManager,可以用它来创建、销毁和修改world中的entity。一个world还拥有一组system,这些system通常只访问同一个world中的entity。此外,一个world中具有相同component类型的entity集合会被一起存储在一个archetype中,archetype决定了component在内存中的组织方式。
默认情况下,Unity会自动创建两个world,一个是editor world,一个是default world,分别用于编辑器环境与运行时环境。Unity定义了3个宏,用于禁用这两个world的自动创建:
#UNITY_DISABLE_AUTOMATIC_SYSTEM_BOOTSTRAP_RUNTIME_WORLD: 禁止defualt world自动创建#UNITY_DISABLE_AUTOMATIC_SYSTEM_BOOTSTRAP_EDITOR_WORLD: 禁止editor world自动创建#UNITY_DISABLE_AUTOMATIC_SYSTEM_BOOTSTRAP: 禁止editor world与default world自动创建
那么,我们先来看看editor world自动创建的时机。通过上述几个宏,可以顺藤摸瓜找到相应的代码:
/// <summary>
/// Can be called when in edit mode in the editor to initialize a the default world.
/// </summary>
public static void DefaultLazyEditModeInitialize()
{
#if UNITY_EDITOR
if (World.DefaultGameObjectInjectionWorld == null)
{
// * OnDisable (Serialize monobehaviours in temporary backup)
// * unload domain
// * load new domain
// * OnEnable (Deserialize monobehaviours in temporary backup)
// * mark entered playmode / load scene
// * OnDisable / OnDestroy
// * OnEnable (Loading object from scene...)
if (UnityEditor.EditorApplication.isPlayingOrWillChangePlaymode)
{
// We are just gonna ignore this enter playmode reload.
// Can't see a situation where it would be useful to create something inbetween.
// But we really need to solve this at the root. The execution order is kind if crazy.
}
else
{
#if !UNITY_DISABLE_AUTOMATIC_SYSTEM_BOOTSTRAP_EDITOR_WORLD
Initialize("Editor World", true);
#endif
}
}
#endif
}
而DefaultLazyEditModeInitialize的有效引用只有两处,一是在SubScene的OnEnable,二是在SubSceneInspector的OnInspectorGUI,换言之只有当场景中存在SubScene时,editor world才会被创建。我们可以实际验证一下,首先创建一个空场景,然后观察Systems Window,发现空空如也:
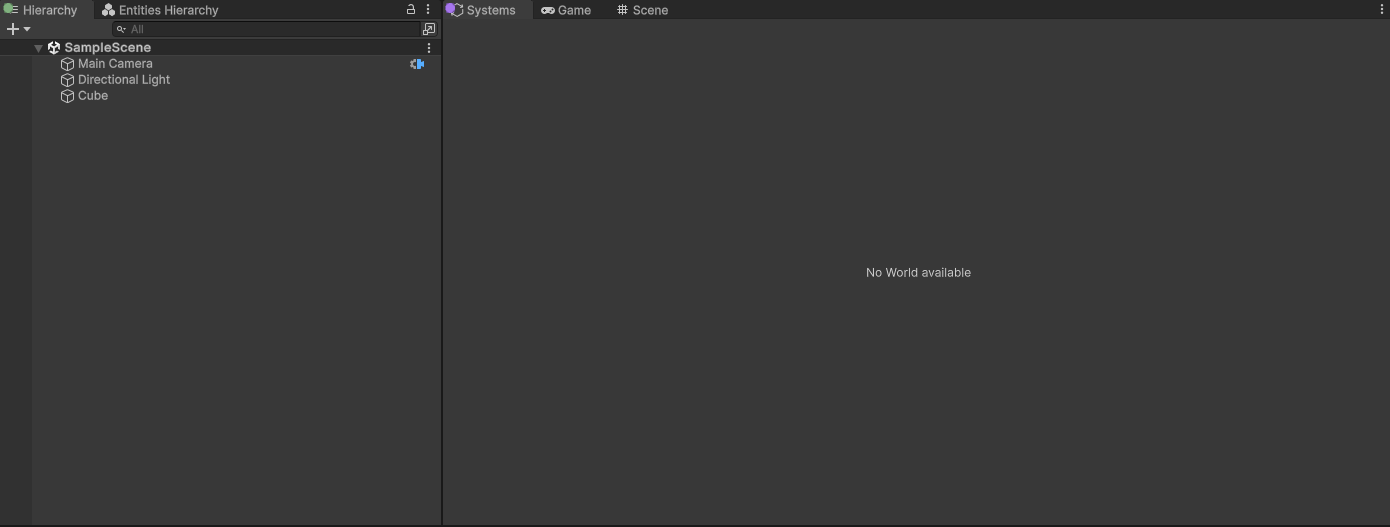
但如果此时,创建一个SubScene,就不一样了:
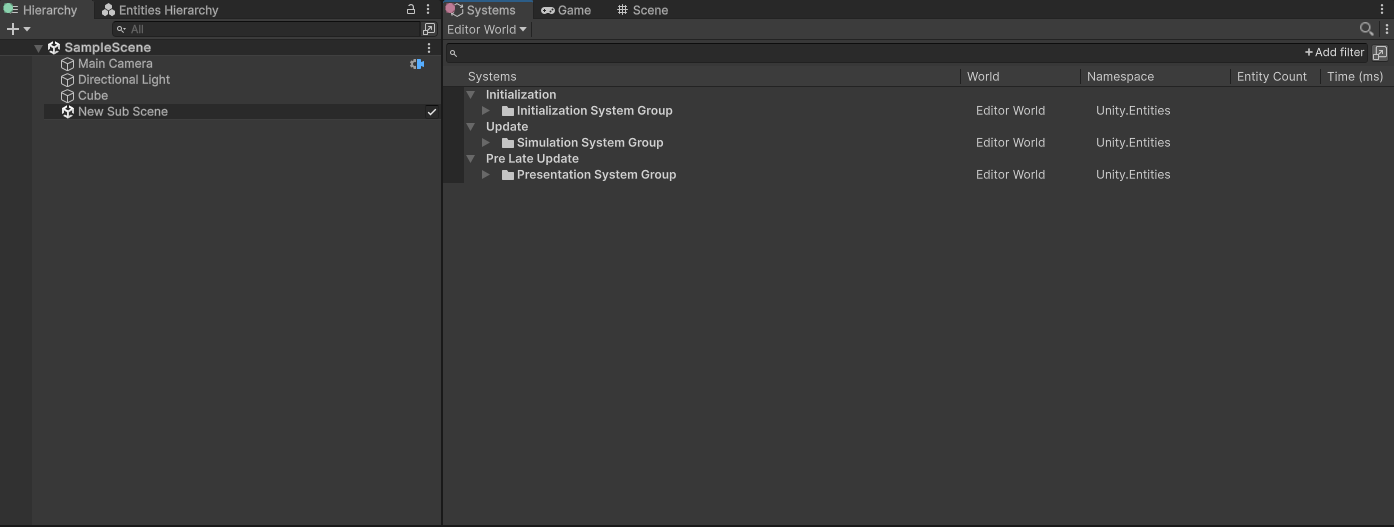
再看看default world创建的时机:
#if !UNITY_DISABLE_AUTOMATIC_SYSTEM_BOOTSTRAP_RUNTIME_WORLD
static class AutomaticWorldBootstrap
{
[RuntimeInitializeOnLoadMethod(RuntimeInitializeLoadType.BeforeSceneLoad)]
static void Initialize()
{
DefaultWorldInitialization.Initialize("Default World", false);
}
}
#endif
带有RuntimeInitializeLoadType.BeforeSceneLoad属性的函数会在第一个场景加载时触发,因此,在runtime下,default world一定会被创建。
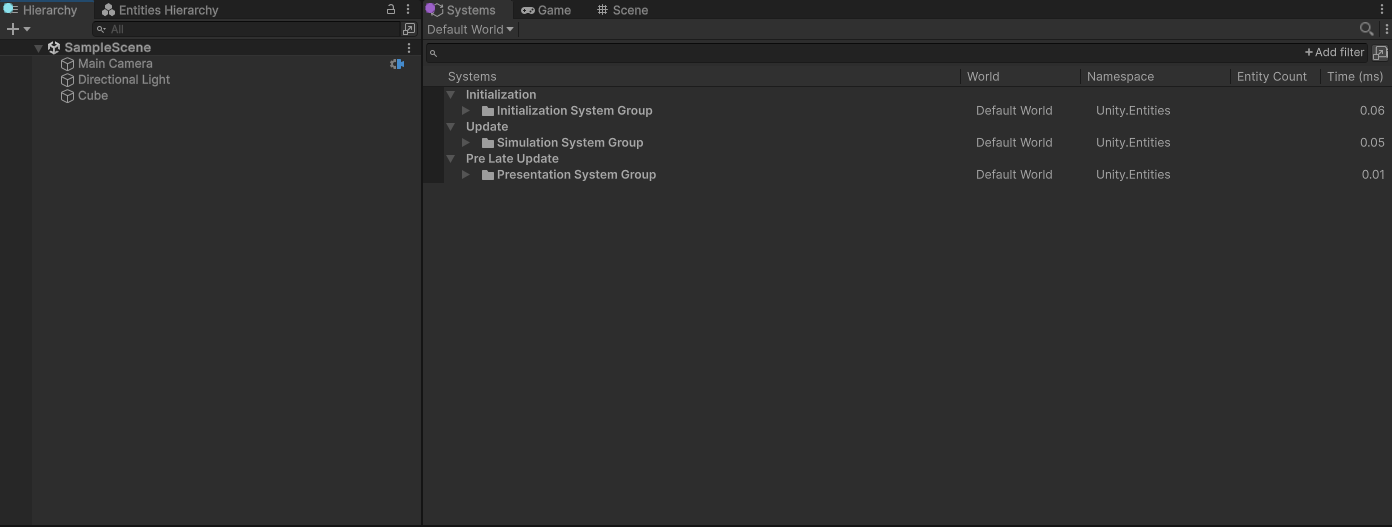
可以看到,两个world创建调用的其实是同一个函数DefaultWorldInitialization.Initialize,只是参数不同。
/// <summary>
/// Initializes the default world or runs ICustomBootstrap if one is available.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="defaultWorldName">The name of the world that will be created. Unless there is a custom bootstrap.</param>
/// <param name="editorWorld">Editor worlds by default only include systems with [WorldSystemFilter(WorldSystemFilterFlags.Editor)]. If editorWorld is true, ICustomBootstrap will not be used.</param>
/// <returns>The initialized <see cref="World"/> object.</returns>
public static World Initialize(string defaultWorldName, bool editorWorld = false)
{
using var marker = new ProfilerMarker("Create World & Systems").Auto();
RegisterUnloadOrPlayModeChangeShutdown();
#if ENABLE_PROFILER
EntitiesProfiler.Initialize();
#endif
#if (UNITY_EDITOR || DEVELOPMENT_BUILD) && !DISABLE_ENTITIES_JOURNALING
EntitiesJournaling.Initialize();
#endif
if (!editorWorld)
{
var bootStrap = CreateBootStrap();
if (bootStrap != null && bootStrap.Initialize(defaultWorldName))
{
Assert.IsTrue(World.DefaultGameObjectInjectionWorld != null,
$"ICustomBootstrap.Initialize() implementation failed to set " +
$"World.DefaultGameObjectInjectionWorld, despite returning true " +
$"(indicating the World has been properly initialized)");
return World.DefaultGameObjectInjectionWorld;
}
}
var world = new World(defaultWorldName, editorWorld ? WorldFlags.Editor : WorldFlags.Game);
World.DefaultGameObjectInjectionWorld = world;
AddSystemToRootLevelSystemGroupsInternal(world, GetAllSystemTypeIndices(WorldSystemFilterFlags.Default, editorWorld));
ScriptBehaviourUpdateOrder.AppendWorldToCurrentPlayerLoop(world);
DefaultWorldInitialized?.Invoke(world);
return world;
}
我们来仔细研究一下world的创建流程。它大致分为以下若干步骤:
- 注册world的销毁逻辑;
- 判断是否有用户自定义的创建逻辑,如果有直接调用并返回;
- 如果没有,调用world自带的构造函数创建world;
- 创建world的system group,把属于world的尚未创建的system添加到相对应的group中;
- 把system group中的sytem,根据不同的执行顺序插入到player loop中;
- 初始化完毕,触发
DefaultWorldInitialized回调,并返回world。
注册销毁逻辑
注册销毁逻辑这里Unity处理得其实比较粗糙,首先world什么时候应当被销毁?Unity在函数注释中给出了三种情形:
a. 从editor mode切换到play mode,此时editor world需要销毁;
b. 从play mode切换到editor mode,此时default world需要销毁;
c. 卸载当前AppDomain时(例如修改了scripts触发domain reloading),此时editor/default world都需要销毁。
/// <summary>
/// Ensures the current World destruction on shutdown or when entering/exiting Play Mode or Domain Reload.
/// 1) When switching to Play Mode Editor World (if created) has to be destroyed:
/// - after the current scene objects are destroyed and OnDisable/Destroy are called,
/// - before game scene is loaded and Awake/OnEnable are called.
/// 2) When switching to Edit Mode Game World has to be destroyed:
/// - after the current scene objects are destroyed and OnDisable/Destroy are called,
/// - before backup scene is loaded and Awake/OnEnable are called.
/// 3) When Unloading Domain (as well as Editor/Player exit) Editor or Game World has to be destroyed:
/// - after OnDisable/OnBeforeSerialize are called,
/// - before AppDomain.DomainUnload.
/// Point 1) is covered by RuntimeInitializeOnLoadMethod attribute.
/// For points 2) and 3) there are no entry point in the Unity API and they have to be handled by a proxy MonoBehaviour
/// which in OnDisable can drive the World cleanup for both Exit Play Mode and Domain Unload.
/// </summary>
static void RegisterUnloadOrPlayModeChangeShutdown()
{
if (s_UnloadOrPlayModeChangeShutdownRegistered)
return;
var go = new GameObject { hideFlags = HideFlags.HideInHierarchy };
if (Application.isPlaying)
UnityEngine.Object.DontDestroyOnLoad(go);
else
go.hideFlags = HideFlags.HideAndDontSave;
go.AddComponent<DefaultWorldInitializationProxy>().IsActive = true;
RuntimeApplication.RegisterFrameUpdateToCurrentPlayerLoop();
s_UnloadOrPlayModeChangeShutdownRegistered = true;
}
情形a使用RuntimeInitializeLoadType.SubsystemRegistration属性即可解决,而b和c没有合适的回调时机,只能借助创建一个MonoBehaviour,通过其onDisable方法来曲线救国。
自定义创建逻辑
如果不是editor world,unity允许用户自定义创建world,负责创建的类需要继承自ICustomBootstrap接口,并实现Initialize方法。该方法返回值类型为bool,如果为true则会跳过default world的初始化。
创建world
World的构造函数接受两个参数,一个是name,一个是flag。World类中包含一个非托管struct的WorldUnmanaged对象,构造函数的主要工作就是在初始化这一非托管对象,而WorldUnmanaged类里又包含一个WorldUnmanagedImpl非托管struct的对象,工作重心又转移到了它的初始化身上。它的初始化分为两步,一是构建WorldUnmanagedImpl对象,二是初始化EntityManager:
UnsafeUtility.AsRef<WorldUnmanagedImpl>(m_Impl) = new WorldUnmanagedImpl(world,
NextSequenceNumber.Data++,
flags,
worldAllocatorHelper,
world.Name);
/*
* if we init the entitymanager inside the WorldUnmanagedImpl ctor, m_Impl will not be set, and so when the
* EM asks for the sequence number, it will ask for GetImpl().SequenceNumber and get uninitialized data.
* so, init it here instead.
*/
m_Impl->m_EntityManager.Initialize(world);
创建system group
一个system group可以包含若干sytem,也可以包含其他的system group。一个sytem group会按照一定顺序在主线程上调用子sytem/sytem group的更新逻辑。Unity默认会创建3个system group:
var initializationSystemGroup = world.GetOrCreateSystemManaged<InitializationSystemGroup>();
var simulationSystemGroup = world.GetOrCreateSystemManaged<SimulationSystemGroup>();
var presentationSystemGroup = world.GetOrCreateSystemManaged<PresentationSystemGroup>();
创建完毕后,Unity接着开始创建所有符合条件的system,再根据system的UpdateInGroup属性,判断system属于上述哪个system group:
// Add systems to their groups, based on the [UpdateInGroup] attribute.
for (int i=0; i<systemTypesOrig.Length; i++)
{
SystemHandle system = allSystemHandlesToAdd[i];
// Skip the built-in root-level system groups
if (rootGroups.IsRootGroup(systemTypesOrig[i]))
{
continue;
}
var updateInGroupAttributes = TypeManager.GetSystemAttributes(systemTypesOrig[i],
TypeManager.SystemAttributeKind.UpdateInGroup);
if (updateInGroupAttributes.Length == 0)
{
defaultGroup.AddSystemToUpdateList(system);
}
foreach (var attr in updateInGroupAttributes)
{
var group = FindGroup(world, systemTypesOrig[i], attr);
if (group != null)
{
group.AddSystemToUpdateList(system);
}
}
}
如果system没有UpdateInGroup属性,那么就会放到默认的group里,这里就是SimulationSystemGroup;如果有,就根据属性中的参数类型,找到相应的system group。我们可以新增一个system加以验证:
using Unity.Entities;
using UnityEngine;
[UpdateInGroup(typeof(InitializationSystemGroup))]
public partial struct FirstSystem : ISystem
{
public void OnCreate(ref SystemState state) { Debug.Log("========FirstSystem==========="); }
public void OnDestroy(ref SystemState state) { }
public void OnUpdate(ref SystemState state) { }
}
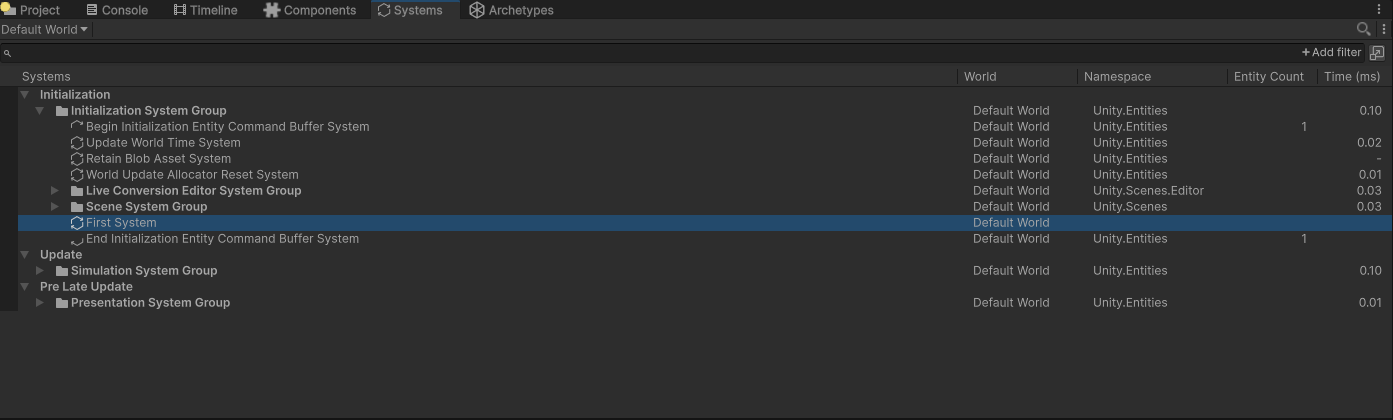
可以看到,我们创建的FirstSystem,被归到InitializationSystemGroup里了。将system分完类之后,还需要对system进行排序,因为有的system可能设置了OrderFirst/OrderLast参数,或是拥有UpdateBefore/UpdateAfter的属性。
插入player loop
最后,需要把3个顶层的system group插入到Unity的player loop中,让Unity在自身生命周期的不同阶段驱动system的update。
/// <summary>
/// Add this World's three default top-level system groups to a PlayerLoopSystem object.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>
/// This function performs the following modifications to the provided PlayerLoopSystem:
/// - If an instance of InitializationSystemGroup exists in this World, it is appended to the
/// Initialization player loop phase.
/// - If an instance of SimulationSystemGroup exists in this World, it is appended to the
/// Update player loop phase.
/// - If an instance of PresentationSystemGroup exists in this World, it is appended to the
/// PreLateUpdate player loop phase.
/// If instances of any or all of these system groups don't exist in this World, then no entry is added to the player
/// loop for that system group.
///
/// This function does not change the currently active player loop. If this behavior is desired, it's necessary
/// to call PlayerLoop.SetPlayerLoop(playerLoop) after the systems have been removed.
/// </remarks>
/// <param name="world">The three top-level system groups from this World will be added to the provided player loop.</param>
/// <param name="playerLoop">Existing player loop to modify (e.g. (e.g. PlayerLoop.GetCurrentPlayerLoop())</param>
public static void AppendWorldToPlayerLoop(World world, ref PlayerLoopSystem playerLoop)
{
if (world == null)
return;
var initGroup = world.GetExistingSystemManaged<InitializationSystemGroup>();
if (initGroup != null)
AppendSystemToPlayerLoop(initGroup, ref playerLoop, typeof(Initialization));
var simGroup = world.GetExistingSystemManaged<SimulationSystemGroup>();
if (simGroup != null)
AppendSystemToPlayerLoop(simGroup, ref playerLoop, typeof(Update));
var presGroup = world.GetExistingSystemManaged<PresentationSystemGroup>();
if (presGroup != null)
AppendSystemToPlayerLoop(presGroup, ref playerLoop, typeof(PreLateUpdate));
}
这里,Initialization,Update和PreLateUpdate是Unity引擎update过程中的不同阶段。具体add的逻辑很简单,就是递归查找符合type的player loop,然后插入到update list的末尾。在player loop内部的时序里,Initialization在Update之前,而Update又在PreLateUpdate之前。
static bool AppendToPlayerLoopList(Type updateType, PlayerLoopSystem.UpdateFunction updateFunction, ref PlayerLoopSystem playerLoop, Type playerLoopSystemType)
{
if (updateType == null || updateFunction == null || playerLoopSystemType == null)
return false;
if (playerLoop.type == playerLoopSystemType)
{
var oldListLength = playerLoop.subSystemList != null ? playerLoop.subSystemList.Length : 0;
var newSubsystemList = new PlayerLoopSystem[oldListLength + 1];
for (var i = 0; i < oldListLength; ++i)
newSubsystemList[i] = playerLoop.subSystemList[i];
newSubsystemList[oldListLength] = new PlayerLoopSystem
{
type = updateType,
updateDelegate = updateFunction
};
playerLoop.subSystemList = newSubsystemList;
return true;
}
if (playerLoop.subSystemList != null)
{
for (var i = 0; i < playerLoop.subSystemList.Length; ++i)
{
if (AppendToPlayerLoopList(updateType, updateFunction, ref playerLoop.subSystemList[i], playerLoopSystemType))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
Reference
[1] World concepts
[2] RuntimeInitializeOnLoadMethodAttribute
[3] Details of disabling Domain and Scene Reload
[4] Interface ICustomBootstrap
[5] System groups







![[css3] 如何设置边框颜色渐变](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/56689110c39643f5a1e2196094a96303.png)








