1. 前言
本篇文章为 Python 对金融的投资组合优化的示例。投资组合优化是从一组可用的投资组合中选择最佳投资组合的过程,目的是最大限度地提高回报和降低风险。
投资组合优化是从一组可用的投资组合中选择最佳投资组合的过程,目的是最大限度地提高回报和降低风险。
本案例研究涵盖了我们在前几课中介绍的许多 Python 编程基础知识,例如获取真实世界的市场财务数据、使用 pandas 执行数据分析以及使用 Matplotlib、Seaborn 和 Plotly Express 可视化投资组合数据。
2. 导入库和数据集
在本课中,您将学习如何导入库(例如用于数值分析的 NumPy),并学习如何导入和使用 datetime。此外,您还将学习如何导入数据以执行库提供的一些操作。
在开始之前,我们需要定义以下术语:
-
打开:股票市场开盘时证券首次交易的价格。
-
高:给定股票在常规交易时段内交易的最高价格。
-
低:给定股票在常规交易时段内交易的最低价格。
-
关闭:给定股票在常规交易时段交易的最后价格。
-
卷:开盘和收盘之间的交易股票数量。
-
调整关闭:考虑股票分割和股息后调整后的股票收盘价。
另请注意,纽约证券交易所 (NYSE) 于美国东部时间上午 9:30 开市,上海证券交易所 (SSE) 于中国标准时间上午 9:30 开市。
# Import key librares and modules
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Import datetime module that comes pre-installed in Python
# datetime offers classes that work with date & time information
import datetime as dt
# Use Pandas to read stock data (the csv file is included in the course package)
stock_df = pd.read_csv('Amazon.csv')
stock_df.head(15)
# Count the number of missing values in "stock_df" Pandas DataFrame
stock_df.isnull().sum()
# Obtain information about the Pandas DataFrame such as data types, memory utilization..etc
stock_df.info()
3. 计算每日回报率
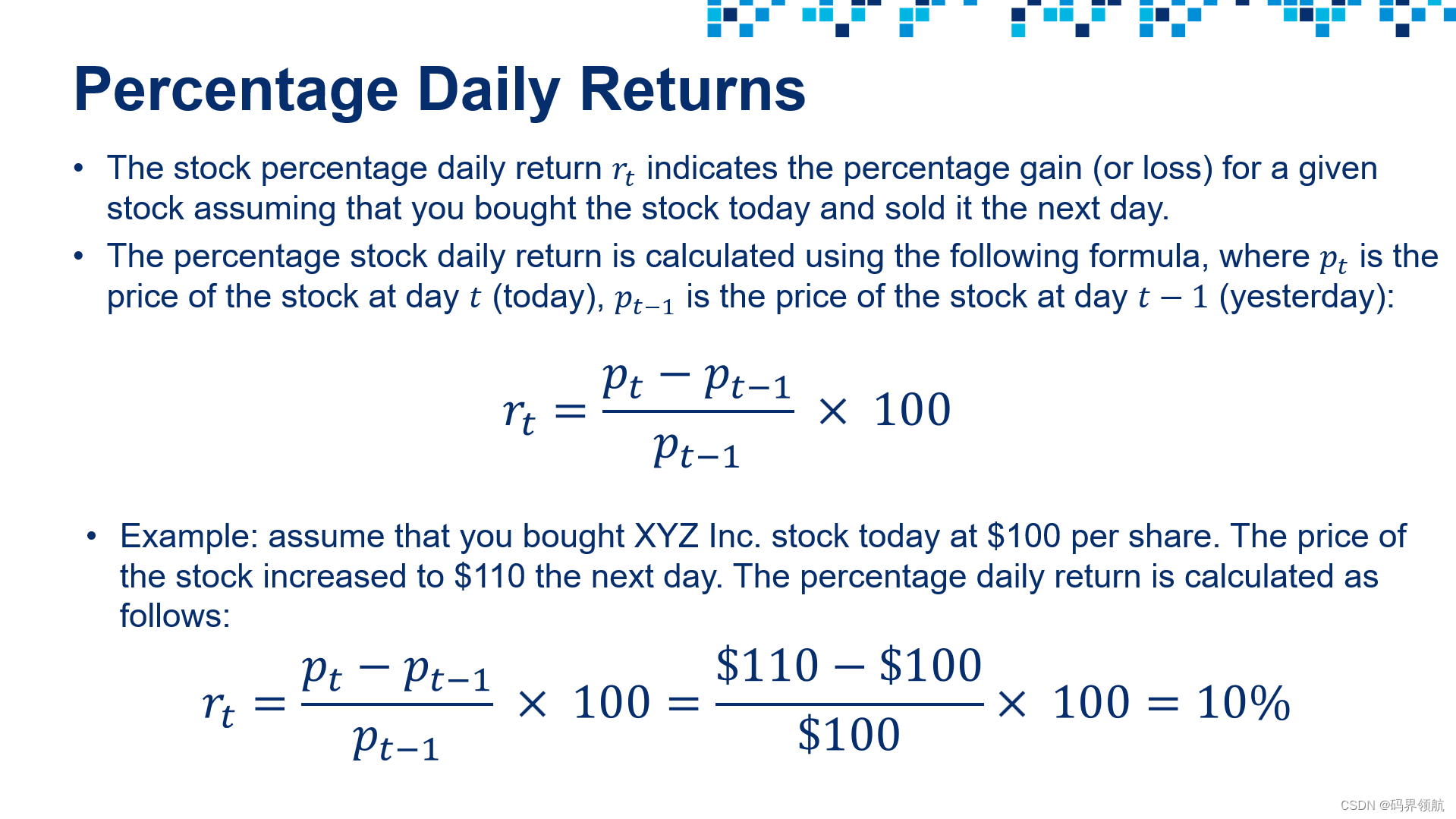
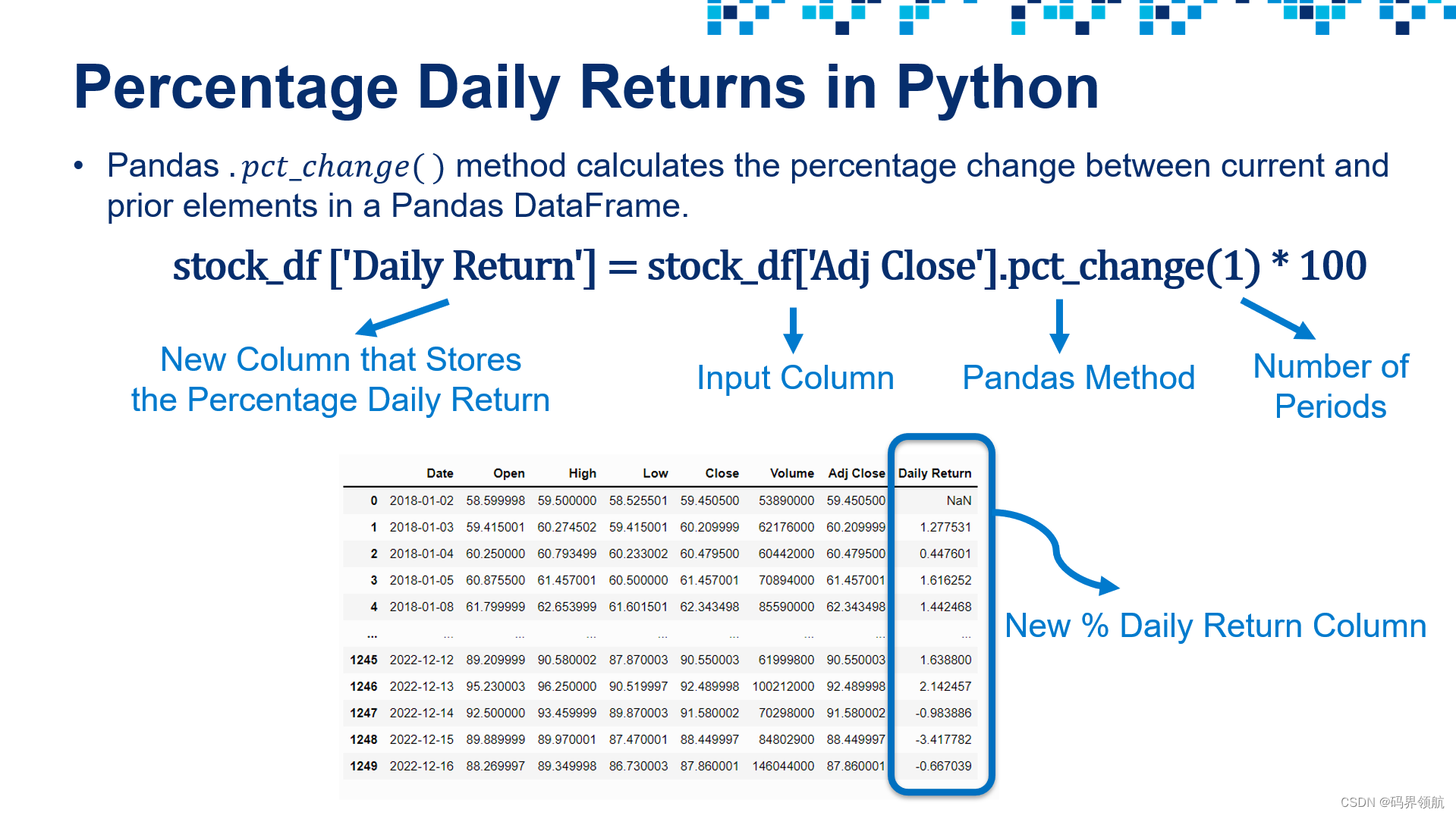
# Calculate the percentage daily return
stock_df['Daily Return'] = stock_df['Adj Close'].pct_change(1) * 100
stock_df
输出:

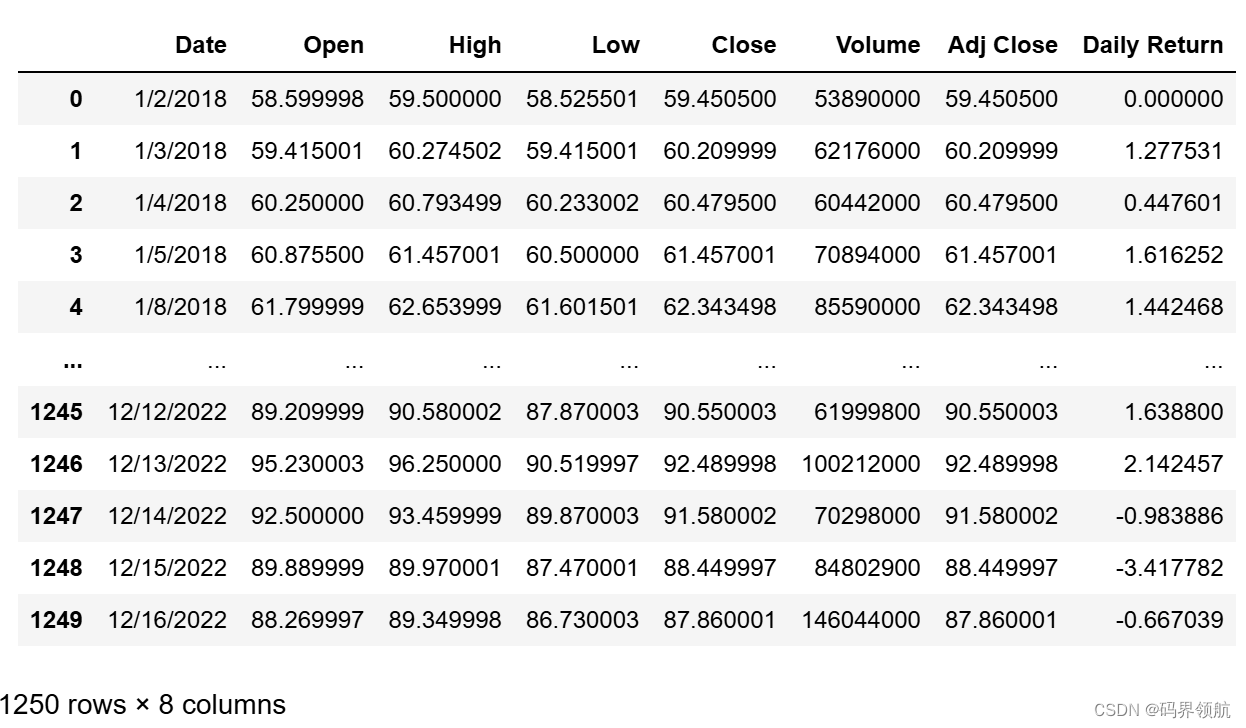
# Let's replace the first row with zeros instead of NaN
stock_df['Daily Return'].replace(np.nan, 0, inplace = True)
stock_df
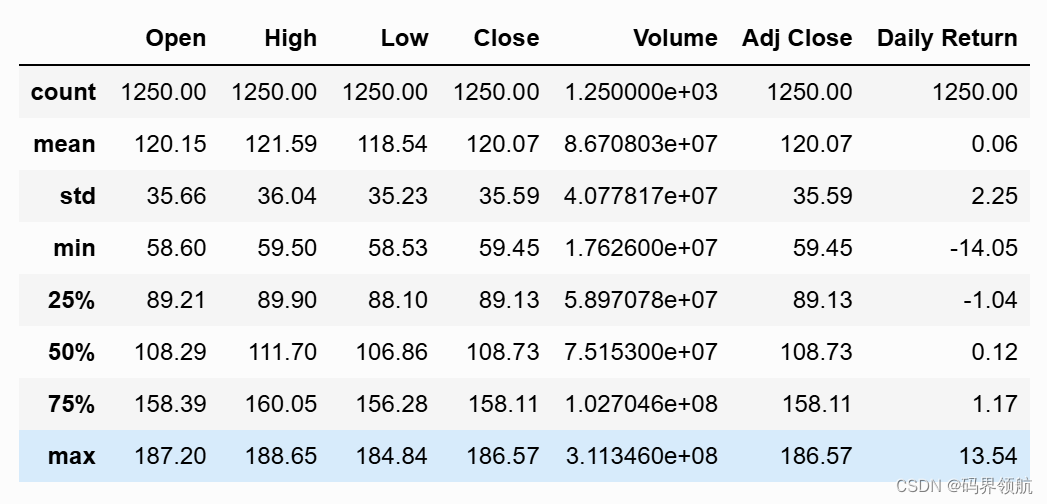
# Use the describe() method to obtain a statistical summary about the data
# Over the specified time period, the average adjusted close price for Amazon stock was $120.07
# The maximum adjusted close price was $186.57
# The maximum volume of shares traded on one day were 311,346,000
stock_df.describe().round(2)
4. 为单只股票进行数据可视化:第一部分

Matplotlib 官方文档: https://matplotlib.org/
Seaborn 官方文档: https://seaborn.pydata.org/
Plotly 官方文档: https://plotly.com/python/
# Matplotlib is a comprehensive data visualization library in Python
# Seaborn is a visualization library that sits on top of matplotlib and offers enhanced features
# plotly.express module contains functions that can create interactive figures using a few lines of code
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
!pip install seaborn
import seaborn as sns
import plotly.express as px
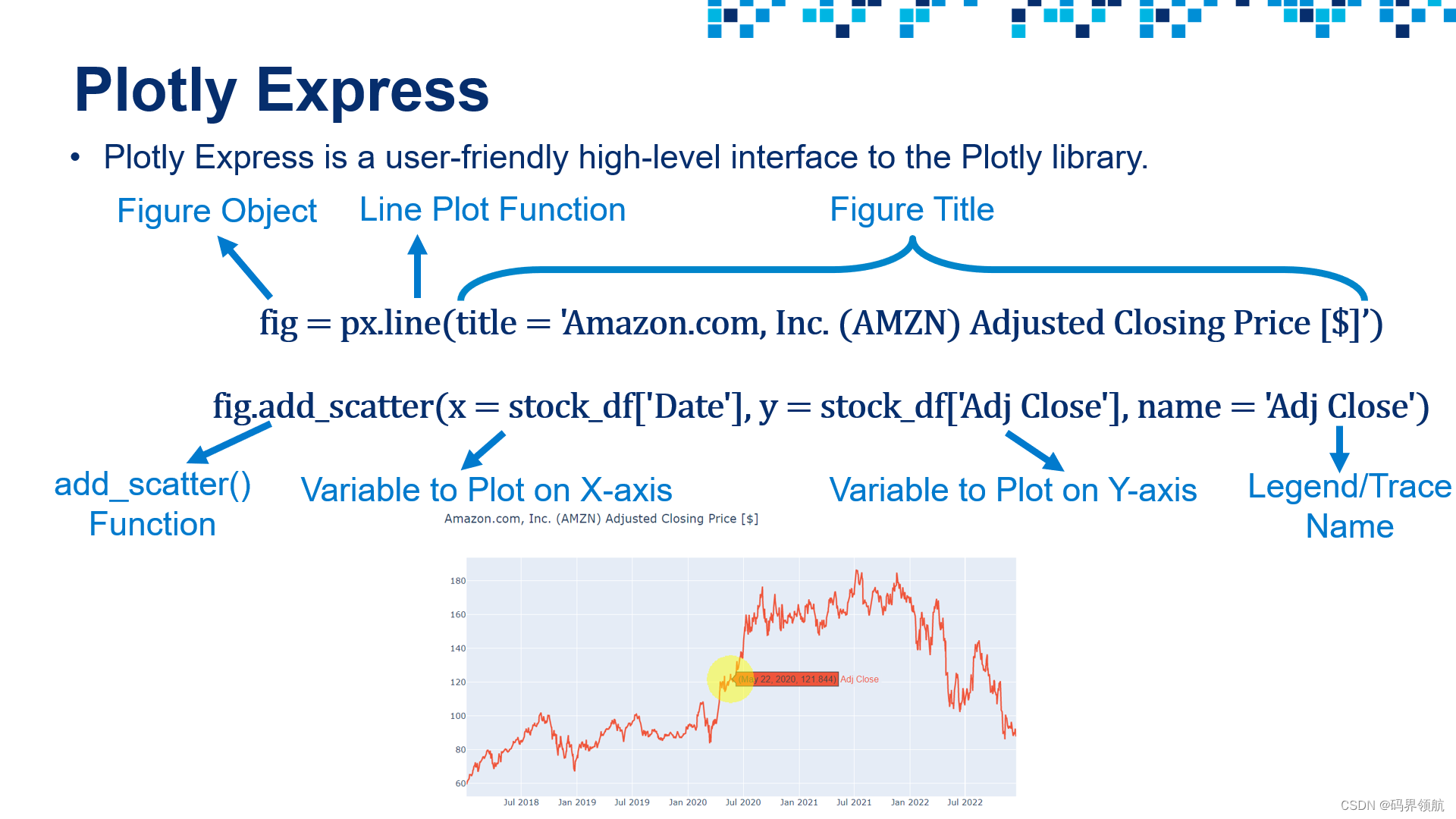
# Plot a Line Plot Using Plotly Express
fig = px.line(title = 'Amazon.com, Inc. (AMZN) Adjusted Closing Price [$]')
fig.add_scatter(x = stock_df['Date'], y = stock_df['Adj Close'], name = 'Adj Close')
stock_df
# Define a function that performs interactive data visualization using Plotly Express
def plot_financial_data(df, title):
fig = px.line(title = title)
# For loop that plots all stock prices in the pandas dataframe df
# Note that index starts with 1 because we want to skip the date column
for i in df.columns[1:]:
fig.add_scatter(x = df['Date'], y = df[i], name = i)
fig.update_traces(line_width = 5)
fig.update_layout({'plot_bgcolor': "white"})
fig.show()
# Plot High, Low, Open, Close and Adj Close
plot_financial_data(stock_df.drop(['Volume', 'Daily Return'], axis = 1), 'Amazon.com, Inc. (AMZN) Stock Price [$]')
# Plot trading volume
plot_financial_data(stock_df.iloc[:,[0,5]], 'Amazon.com, Inc. (AMZN) Trading Volume')
# Plot % Daily Returns
plot_financial_data(stock_df.iloc[:,[0,7]], 'Amazon.com, Inc. (AMZN) Percentage Daily Return [%]')
5. 为单只股票进行数据可视化:第二部分
# Define a function that classifies the returns based on the magnitude
# Feel free to change these numbers
def percentage_return_classifier(percentage_return):
if percentage_return > -0.3 and percentage_return <= 0.3:
return 'Insignificant Change'
elif percentage_return > 0.3 and percentage_return <= 3:
return 'Positive Change'
elif percentage_return > -3 and percentage_return <= -0.3:
return 'Negative Change'
elif percentage_return > 3 and percentage_return <= 7:
return 'Large Positive Change'
elif percentage_return > -7 and percentage_return <= -3:
return 'Large Negative Change'
elif percentage_return > 7:
return 'Bull Run'
elif percentage_return <= -7:
return 'Bear Sell Off'
# Apply the function to the "Daily Return" Column and place the result in "Trend" column
stock_df['Trend'] = stock_df['Daily Return'].apply(percentage_return_classifier)
stock_df
# Count distinct values in the Trend column
trend_summary = stock_df['Trend'].value_counts()
trend_summary
# Plot a pie chart using Matplotlib Library
plt.figure(figsize = (8, 8))
trend_summary.plot(kind = 'pie', y = 'Trend');
# Plot a pie chart using Matplotlib Library
plt.figure(figsize = (8, 8))
trend_summary.plot(kind = 'pie', y = 'Trend');
6. 为单只股票进行数据可视化:第三部分
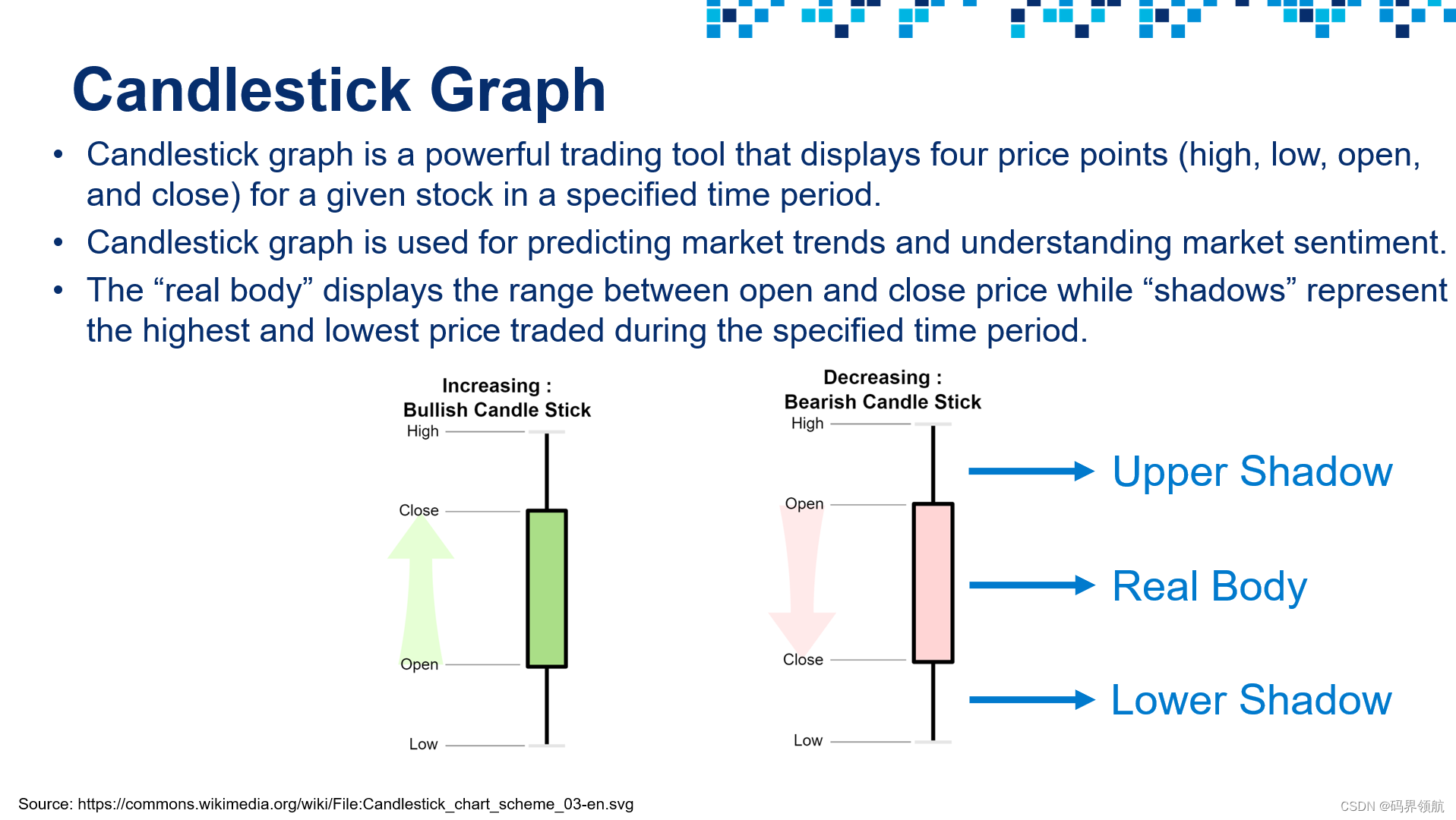
# Let's plot a candlestick graph using Cufflinks library
# Cufflinks is a powerful Python library that connects Pandas and Plotly for generating plots using few lines of code
# Cufflinks allows for interactive data visualization
! pip install cufflinks
import cufflinks as cf
cf.go_offline() # Enabling offline mode for interactive data visualization locally
stock_df
# Set the date to be the index for the Pandas DataFrame
# This is critical to show the date on the x-axis when using cufflinks
stock_df.set_index(['Date'], inplace = True)
stock_df
# Plot Candlestick figure using Cufflinks QuantFig module
figure = cf.QuantFig(stock_df, title = 'Amazon.com, Inc. (AMZN) Candlestick Chart', name = 'AMZN')
figure.add_sma(periods =[14, 21], column = 'Close', color = ['magenta', 'green'])
figure.iplot(theme = 'white', up_color = 'green', down_color = 'red')
7. 为多只股票进行数据可视化
# Let's read multiple stocks data contained in "stock_prices.csv" attached in the course package
# The Appendix includes details on how to obtain this data using yfinance and Pandas Datareader
# Note that yfinance and Pandas Datareader might experience outage in some geographical regions
# We will focus our analysis on U.S. stocks, similar analysis could be performed on Asian, European or African stocks
# AMZN: Amazon Inc. - Multinational tech company focusing on e-commerce, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence
# JPM: JPMorgan Chase and Co. - Multinational investment bank and financial services holding company
# META: Meta Platforms, formerly named Facebook Inc. - META owns Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp
# PG: Procter and Gamble (P&G) - Multinational consumer goods corporation
# GOOG: Google (Alphabet Inc.) - Multinational company that focuses on search engine tech, e-commerce, Cloud and AI
# CAT: Caterpillar - World's largest construction-equipment manufacturer
# PFE: Pfizer Inc. - Multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation
# EXC: Exelon - An American Fortune 100 energy company
# DE: Deere & Company (John Deere) - Manufactures agricultural machinery and heavy equipment
# JNJ: Johnson & Johnson - A multinational corporation that develops medical devices and pharmaceuticals
close_price_df = pd.read_csv('stock_prices.csv')
close_price_df
# The objective of this code cell is to calculate the percentage daily return
# We will perform this calculation on all stocks except for the first column which is "Date"
daily_returns_df = close_price_df.iloc[:, 1:].pct_change() * 100
daily_returns_df.replace(np.nan, 0, inplace = True)
daily_returns_df
# Insert the date column at the start of the Pandas DataFrame (@ index = 0)
daily_returns_df.insert(0, "Date", close_price_df['Date'])
daily_returns_df
# Plot closing prices using plotly Express. Note that we used the same pre-defined function "plot_financial_data"
plot_financial_data(close_price_df, 'Adjusted Closing Prices [$]')
# Plot the stocks daily returns
plot_financial_data(daily_returns_df, 'Percentage Daily Returns [%]')
# Plot histograms for stocks daily returns using plotly express
# Compare META to JNJ daily returns histograms
fig = px.histogram(daily_returns_df.drop(columns = ['Date']))
fig.update_layout({'plot_bgcolor': "white"})
# Plot a heatmap showing the correlations between daily returns
# Strong positive correlations between Catterpillar and John Deere - both into heavy equipment and machinery
# META and Google - both into Tech and Cloud Computing
plt.figure(figsize = (10, 8))
sns.heatmap(daily_returns_df.drop(columns = ['Date']).corr(), annot = True);
# Plot the Pairplot between stocks daily returns
sns.pairplot(daily_returns_df);
# Function to scale stock prices based on their initial starting price
# The objective of this function is to set all prices to start at a value of 1
def price_scaling(raw_prices_df):
scaled_prices_df = raw_prices_df.copy()
for i in raw_prices_df.columns[1:]:
scaled_prices_df[i] = raw_prices_df[i]/raw_prices_df[i][0]
return scaled_prices_df
price_scaling(close_price_df)
8. 定义一个生成随机投资组合权重的函数
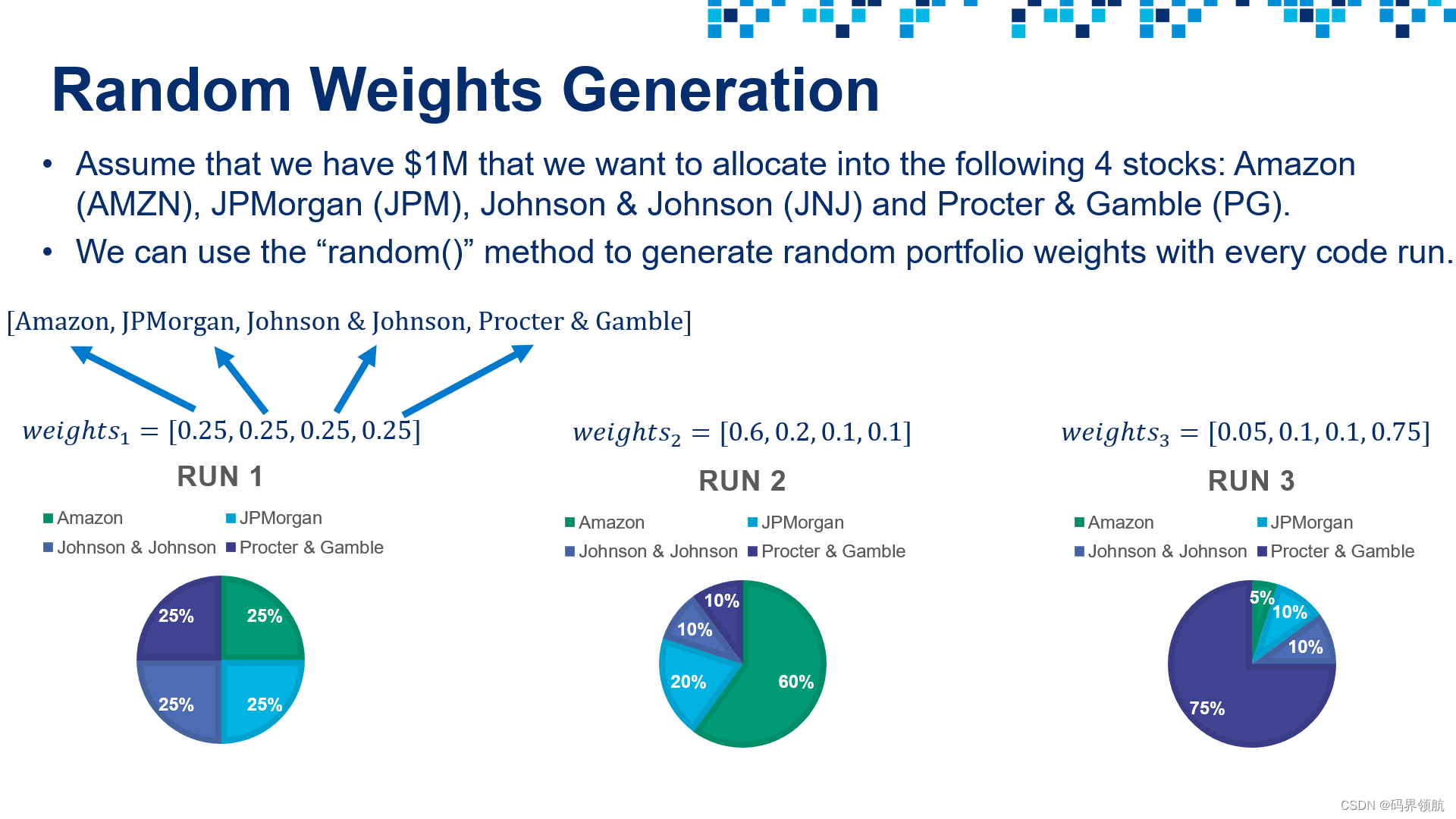
# Let's create an array that holds random portfolio weights
# Note that portfolio weights must add up to 1
import random
def generate_portfolio_weights(n):
weights = []
for i in range(n):
weights.append(random.random())
# let's make the sum of all weights add up to 1
weights = weights/np.sum(weights)
return weights
# Call the function (Run this cell multiple times to generate different outputs)
weights = generate_portfolio_weights(4)
print(weights)
9. 进行资产配置并计算投资组合的日价值/回报率
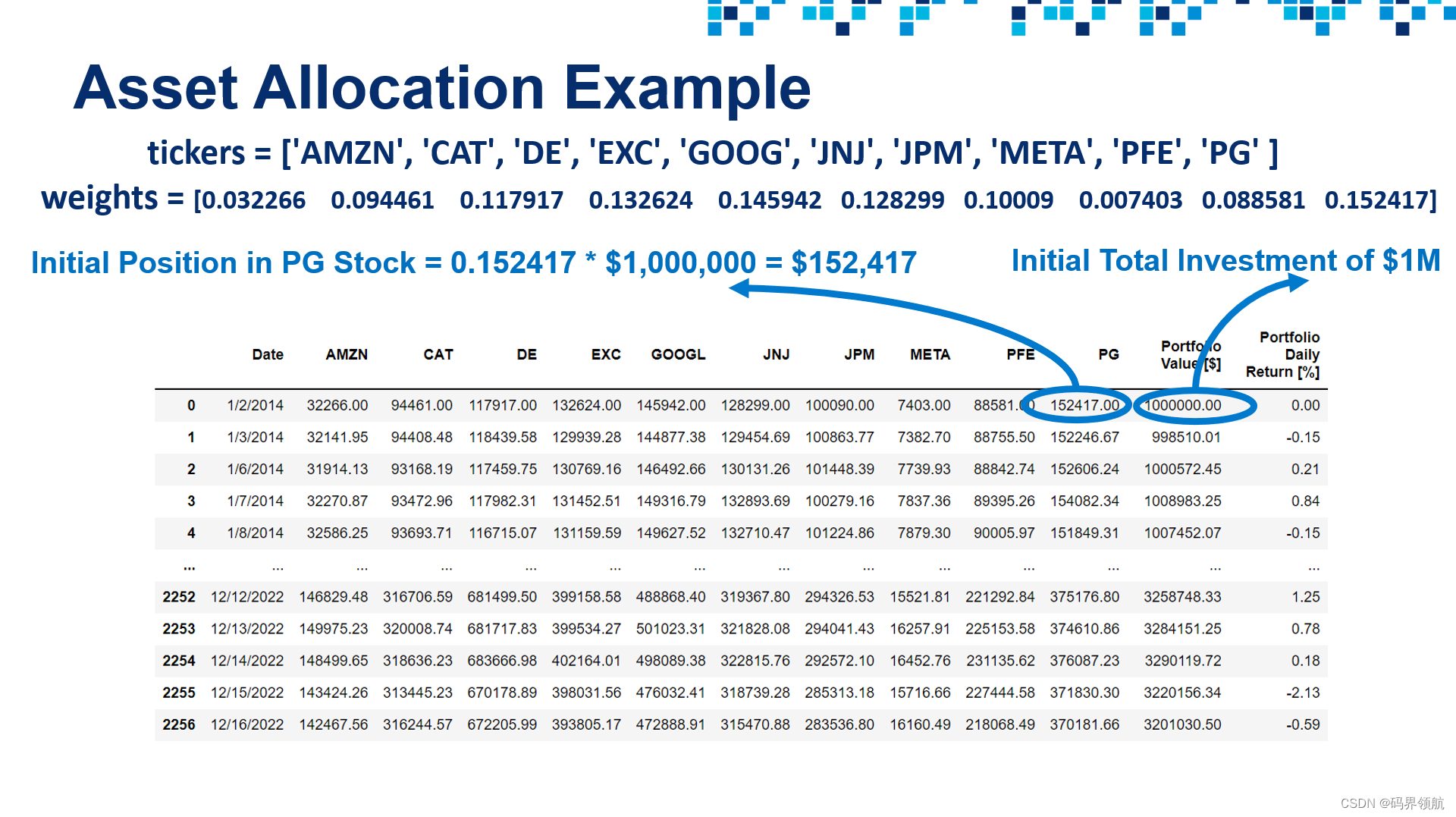


# Let's define the "weights" list similar to the slides
weights = [0.032266, 0.094461, 0.117917, 0.132624, 0.145942, 0.128299, 0.10009, 0.007403, 0.088581, 0.152417]
weights
# Let's display "close_price_df" Pandas DataFrame
close_price_df
# Scale stock prices using the "price_scaling" function that we defined earlier (make all stock values start at 1)
portfolio_df = close_price_df.copy()
scaled_df = price_scaling(portfolio_df)
scaled_df
# Use enumerate() method to obtain the stock names along with a counter "i" (0, 1, 2, 3,..etc.)
# This counter "i" will be used as an index to access elements in the "weights" list
initial_investment = 1000000
for i, stock in enumerate(scaled_df.columns[1:]):
portfolio_df[stock] = weights[i] * scaled_df[stock] * initial_investment
portfolio_df.round(1)
# Assume that we have $1,000,000 that we would like to invest in one or more of the selected stocks
# Let's create a function that receives the following arguments:
# (1) Stocks closing prices
# (2) Random weights
# (3) Initial investment amount
# The function will return a DataFrame that contains the following:
# (1) Daily value (position) of each individual stock over the specified time period
# (2) Total daily value of the portfolio
# (3) Percentage daily return
def asset_allocation(df, weights, initial_investment):
portfolio_df = df.copy()
# Scale stock prices using the "price_scaling" function that we defined earlier (Make them all start at 1)
scaled_df = price_scaling(df)
for i, stock in enumerate(scaled_df.columns[1:]):
portfolio_df[stock] = scaled_df[stock] * weights[i] * initial_investment
# Sum up all values and place the result in a new column titled "portfolio value [$]"
# Note that we excluded the date column from this calculation
portfolio_df['Portfolio Value [$]'] = portfolio_df[portfolio_df != 'Date'].sum(axis = 1, numeric_only = True)
# Calculate the portfolio percentage daily return and replace NaNs with zeros
portfolio_df['Portfolio Daily Return [%]'] = portfolio_df['Portfolio Value [$]'].pct_change(1) * 100
portfolio_df.replace(np.nan, 0, inplace = True)
return portfolio_df
# Now let's put this code in a function and generate random weights
# Let's obtain the number of stocks under consideration (note that we ignored the "Date" column)
n = len(close_price_df.columns)-1
# Let's generate random weights
print('Number of stocks under consideration = {}'.format(n))
weights = generate_portfolio_weights(n).round(6)
print('Portfolio weights = {}'.format(weights))
# Let's test out the "asset_allocation" function
portfolio_df = asset_allocation(close_price_df, weights, 1000000)
portfolio_df.round(2)
# Plot the portfolio percentage daily return
plot_financial_data(portfolio_df[['Date', 'Portfolio Daily Return [%]']], 'Portfolio Percentage Daily Return [%]')
# Plot each stock position in our portfolio over time
# This graph shows how our initial investment in each individual stock grows over time
plot_financial_data(portfolio_df.drop(['Portfolio Value [$]', 'Portfolio Daily Return [%]'], axis = 1), 'Portfolio positions [$]')
# Plot the total daily value of the portfolio (sum of all positions)
plot_financial_data(portfolio_df[['Date', 'Portfolio Value [$]']], 'Total Portfolio Value [$]')
10. 定义“模拟”函数,该函数执行资产配置并计算关键的投资组合指标



# Let's define the simulation engine function
# The function receives:
# (1) portfolio weights
# (2) initial investment amount
# The function performs asset allocation and calculates portfolio statistical metrics including Sharpe ratio
# The function returns:
# (1) Expected portfolio return
# (2) Expected volatility
# (3) Sharpe ratio
# (4) Return on investment
# (5) Final portfolio value in dollars
def simulation_engine(weights, initial_investment):
# Perform asset allocation using the random weights (sent as arguments to the function)
portfolio_df = asset_allocation(close_price_df, weights, initial_investment)
# Calculate the return on the investment
# Return on investment is calculated using the last final value of the portfolio compared to its initial value
return_on_investment = ((portfolio_df['Portfolio Value [$]'][-1:] -
portfolio_df['Portfolio Value [$]'][0])/
portfolio_df['Portfolio Value [$]'][0]) * 100
# Daily change of every stock in the portfolio (Note that we dropped the date, portfolio daily worth and daily % returns)
portfolio_daily_return_df = portfolio_df.drop(columns = ['Date', 'Portfolio Value [$]', 'Portfolio Daily Return [%]'])
portfolio_daily_return_df = portfolio_daily_return_df.pct_change(1)
# Portfolio Expected Return formula
expected_portfolio_return = np.sum(weights * portfolio_daily_return_df.mean() ) * 252
# Portfolio volatility (risk) formula
# The risk of an asset is measured using the standard deviation which indicates the dispertion away from the mean
# The risk of a portfolio is not a simple sum of the risks of the individual assets within the portfolio
# Portfolio risk must consider correlations between assets within the portfolio which is indicated by the covariance
# The covariance determines the relationship between the movements of two random variables
# When two stocks move together, they have a positive covariance when they move inversely, the have a negative covariance
covariance = portfolio_daily_return_df.cov() * 252
expected_volatility = np.sqrt(np.dot(weights.T, np.dot(covariance, weights)))
# Check out the chart for the 10-years U.S. treasury at https://ycharts.com/indicators/10_year_treasury_rate
rf = 0.03 # Try to set the risk free rate of return to 1% (assumption)
# Calculate Sharpe ratio
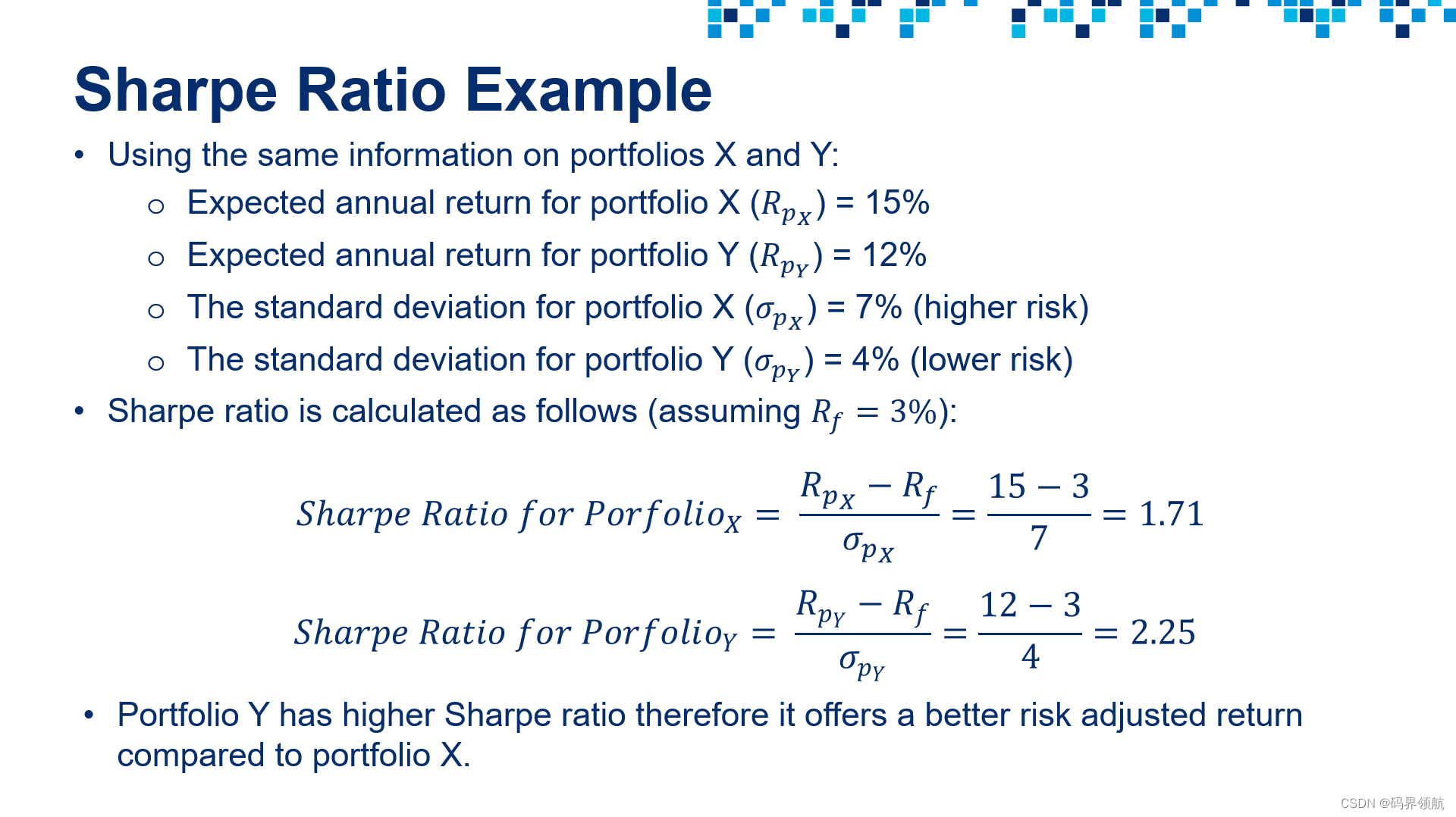
sharpe_ratio = (expected_portfolio_return - rf)/expected_volatility
return expected_portfolio_return, expected_volatility, sharpe_ratio, portfolio_df['Portfolio Value [$]'][-1:].values[0], return_on_investment.values[0]
# Let's test out the "simulation_engine" function and print out statistical metrics
# Define the initial investment amount
initial_investment = 1000000
portfolio_metrics = simulation_engine(weights, initial_investment)
print('Expected Portfolio Annual Return = {:.2f}%'.format(portfolio_metrics[0] * 100))
print('Portfolio Standard Deviation (Volatility) = {:.2f}%'.format(portfolio_metrics[1] * 100))
print('Sharpe Ratio = {:.2f}'.format(portfolio_metrics[2]))
print('Portfolio Final Value = ${:.2f}'.format(portfolio_metrics[3]))
print('Return on Investment = {:.2f}%'.format(portfolio_metrics[4]))
11. 运行蒙特卡罗模拟

# Set the number of simulation runs
sim_runs = 10000
initial_investment = 1000000
# Placeholder to store all weights
weights_runs = np.zeros((sim_runs, n))
# Placeholder to store all Sharpe ratios
sharpe_ratio_runs = np.zeros(sim_runs)
# Placeholder to store all expected returns
expected_portfolio_returns_runs = np.zeros(sim_runs)
# Placeholder to store all volatility values
volatility_runs = np.zeros(sim_runs)
# Placeholder to store all returns on investment
return_on_investment_runs = np.zeros(sim_runs)
# Placeholder to store all final portfolio values
final_value_runs = np.zeros(sim_runs)
for i in range(sim_runs):
# Generate random weights
weights = generate_portfolio_weights(n)
# Store the weights
weights_runs[i,:] = weights
# Call "simulation_engine" function and store Sharpe ratio, return and volatility
# Note that asset allocation is performed using the "asset_allocation" function
expected_portfolio_returns_runs[i], volatility_runs[i], sharpe_ratio_runs[i], final_value_runs[i], return_on_investment_runs[i] = simulation_engine(weights, initial_investment)
print("Simulation Run = {}".format(i))
print("Weights = {}, Final Value = ${:.2f}, Sharpe Ratio = {:.2f}".format(weights_runs[i].round(3), final_value_runs[i], sharpe_ratio_runs[i]))
print('\n')
12. 执行投资组合优化
# List all Sharpe ratios generated from the simulation
sharpe_ratio_runs
# Return the index of the maximum Sharpe ratio (Best simulation run)
sharpe_ratio_runs.argmax()
# Return the maximum Sharpe ratio value
sharpe_ratio_runs.max()
weights_runs
# Obtain the portfolio weights that correspond to the maximum Sharpe ratio (Golden set of weights!)
weights_runs[sharpe_ratio_runs.argmax(), :]
# Return Sharpe ratio, volatility corresponding to the best weights allocation (maximum Sharpe ratio)
optimal_portfolio_return, optimal_volatility, optimal_sharpe_ratio, highest_final_value, optimal_return_on_investment = simulation_engine(weights_runs[sharpe_ratio_runs.argmax(), :], initial_investment)
print('Best Portfolio Metrics Based on {} Monte Carlo Simulation Runs:'.format(sim_runs))
print(' - Portfolio Expected Annual Return = {:.02f}%'.format(optimal_portfolio_return * 100))
print(' - Portfolio Standard Deviation (Volatility) = {:.02f}%'.format(optimal_volatility * 100))
print(' - Sharpe Ratio = {:.02f}'.format(optimal_sharpe_ratio))
print(' - Final Value = ${:.02f}'.format(highest_final_value))
print(' - Return on Investment = {:.02f}%'.format(optimal_return_on_investment))
# Create a DataFrame that contains volatility, return, and Sharpe ratio for all simualation runs
sim_out_df = pd.DataFrame({'Volatility': volatility_runs.tolist(), 'Portfolio_Return': expected_portfolio_returns_runs.tolist(), 'Sharpe_Ratio': sharpe_ratio_runs.tolist() })
sim_out_df
# Plot volatility vs. return for all simulation runs
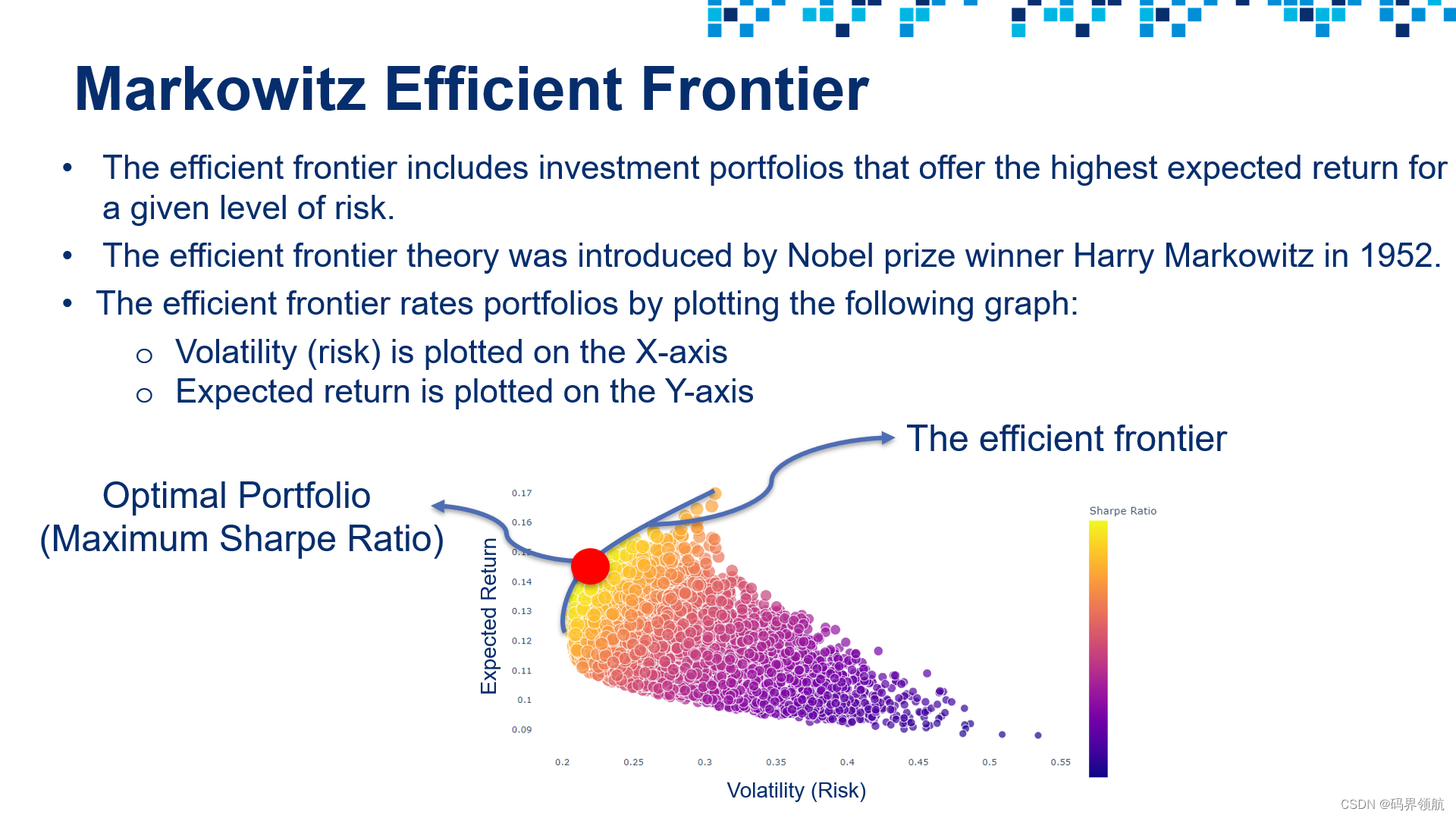
# Highlight the volatility and return that corresponds to the highest Sharpe ratio
import plotly.graph_objects as go
fig = px.scatter(sim_out_df, x = 'Volatility', y = 'Portfolio_Return', color = 'Sharpe_Ratio', size = 'Sharpe_Ratio', hover_data = ['Sharpe_Ratio'] )
fig.update_layout({'plot_bgcolor': "white"})
fig.show()
# Use this code if Sharpe ratio is negative
# fig = px.scatter(sim_out_df, x = 'Volatility', y = 'Portfolio_Return', color = 'Sharpe_Ratio', hover_data = ['Sharpe_Ratio'] )
# Let's highlight the point with the highest Sharpe ratio
fig = px.scatter(sim_out_df, x = 'Volatility', y = 'Portfolio_Return', color = 'Sharpe_Ratio', size = 'Sharpe_Ratio', hover_data = ['Sharpe_Ratio'] )
fig.add_trace(go.Scatter(x = [optimal_volatility], y = [optimal_portfolio_return], mode = 'markers', name = 'Optimal Point', marker = dict(size=[40], color = 'red')))
fig.update_layout(coloraxis_colorbar = dict(y = 0.7, dtick = 5))
fig.update_layout({'plot_bgcolor': "white"})
fig.show()