Apollo studio 官网:Apollo开发者社区 (baidu.com)
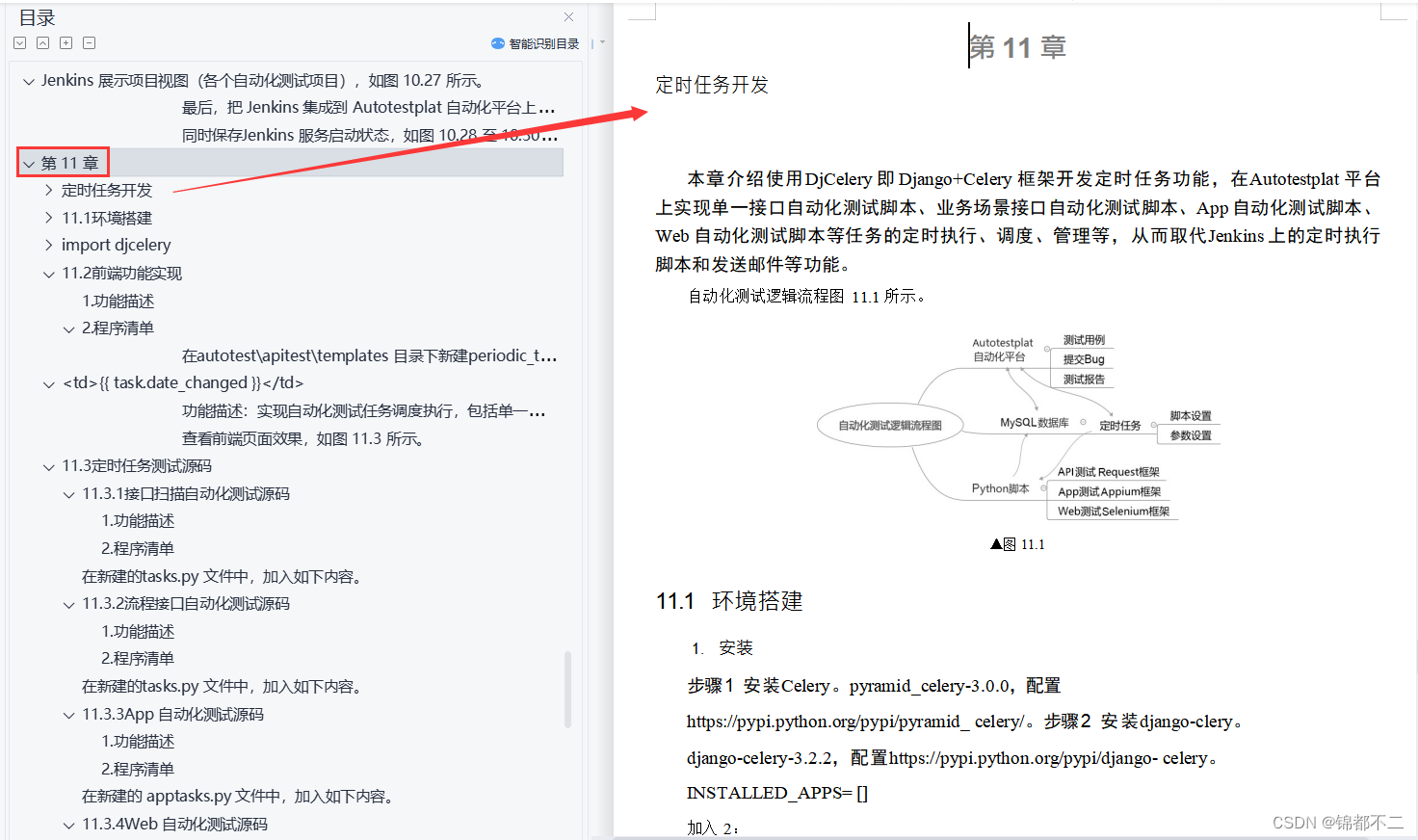
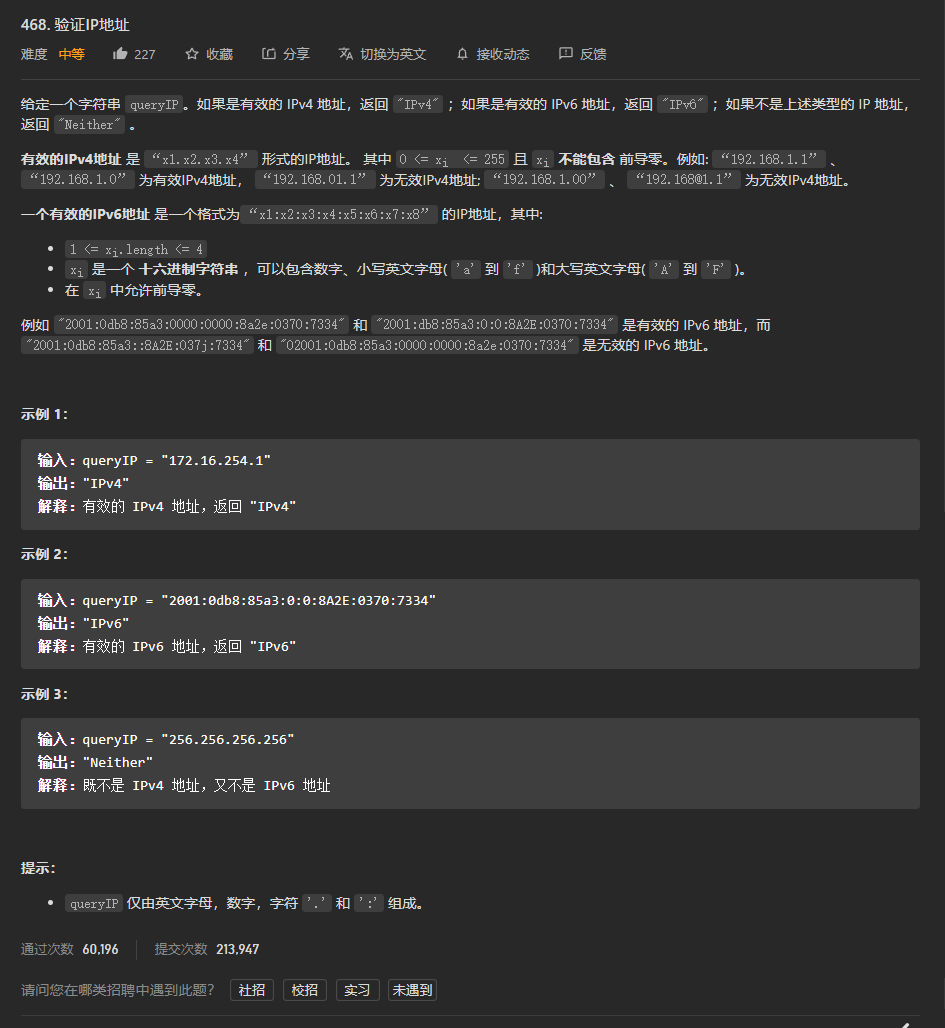
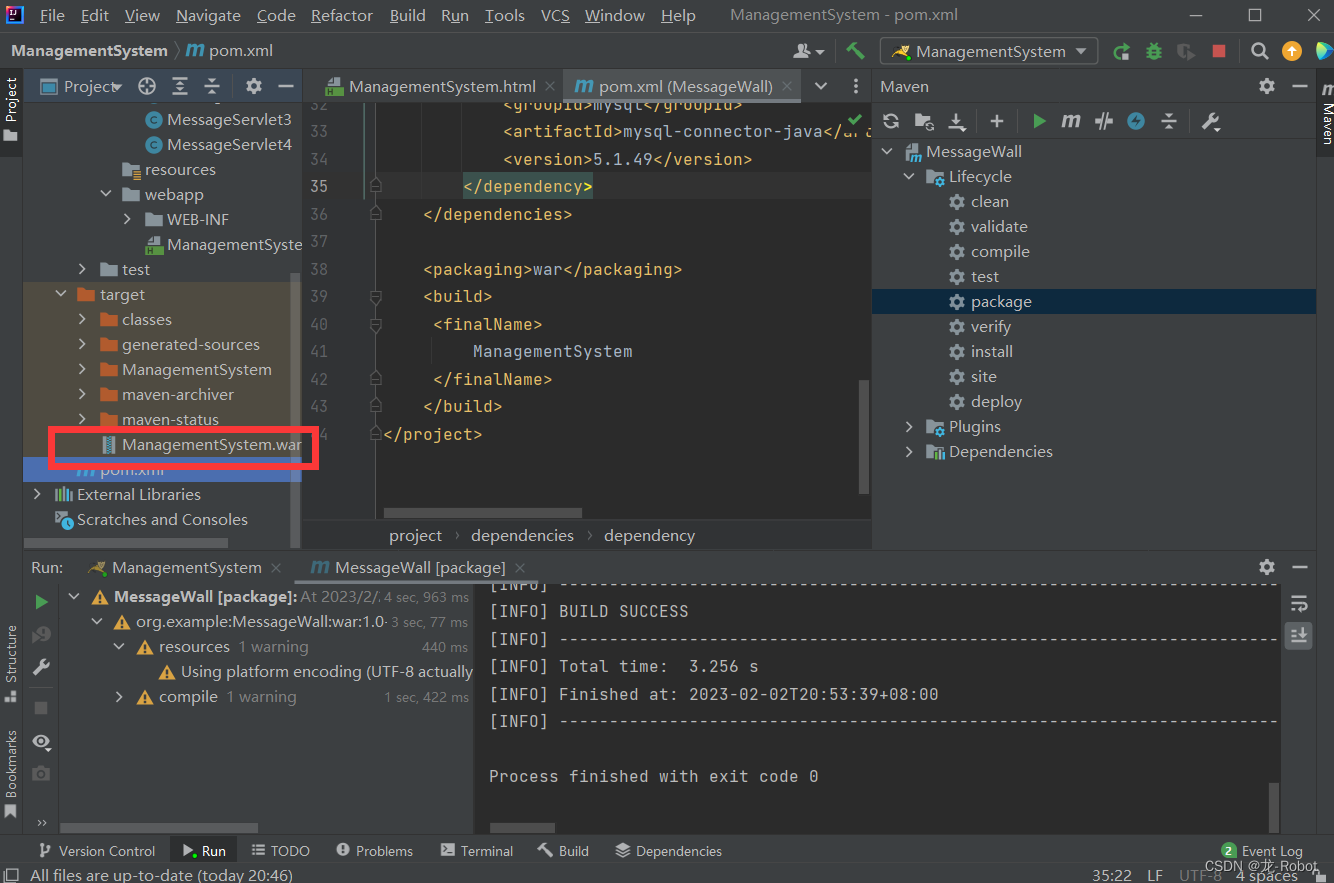
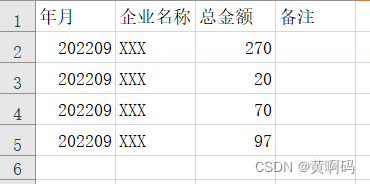
目录
1 参考线的作用
2 参考线的数据结构
2.1 ReferenceLine的数据结构
2.2 ReferencePoint的数据结构
3 参考线处理流程
4 参考线平滑算法
4.1 算法分类
4.2 参考线平滑算法流程
4.2.1 AnchorPoint
4.2.2 smooth
4.2.3 solve
5 具体算法
1 参考线的作用
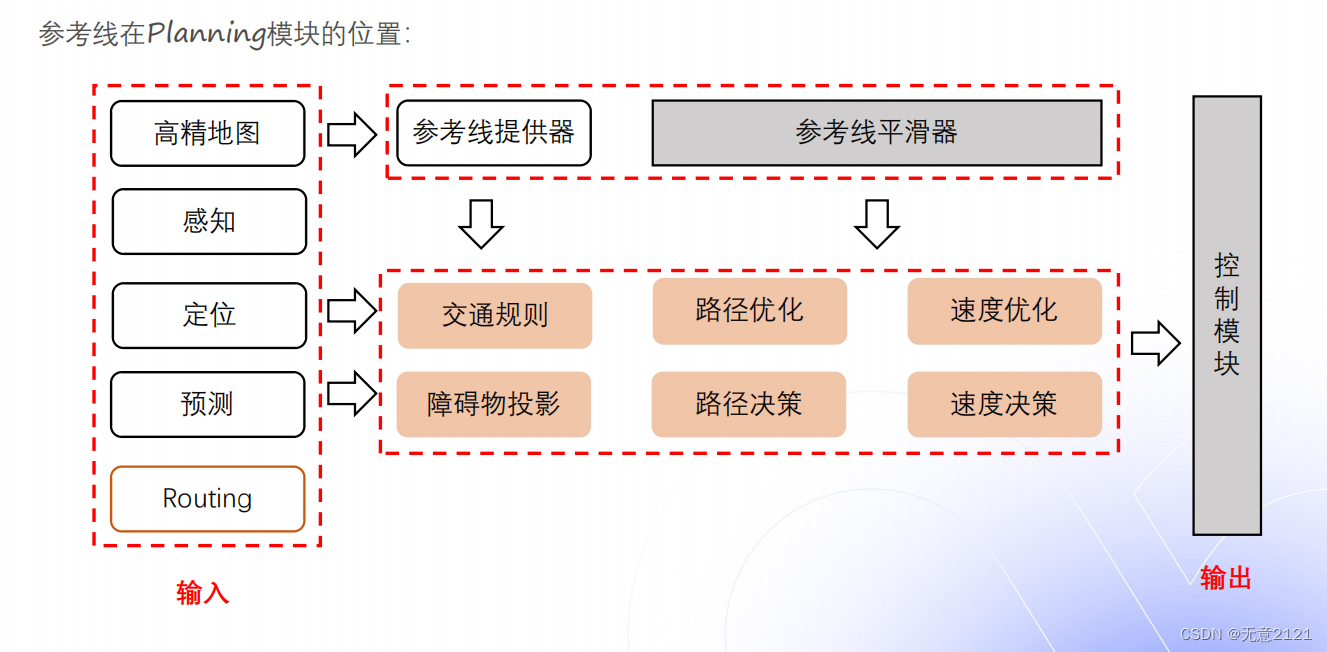
参考线在planning中的作用相当于一个地基,所有决策与优化都是在参考线的基础上进行

- Routing利用A*进行车道级别的规划
- 再对每一个车道赋予参考线,最后得到了车道级别的参考线
- 最后则是planning模块输出轨迹级别的规划结果

- HD map一般都是人为采集离散点,也就使得原始路径不平滑
- 同时全局导航的路径过长,障碍物的投影点也可能不唯一
- 所以我们需要生成一个局部的一定长度且光滑的参考线,也节省了算力
2 参考线的数据结构
2.1 ReferenceLine的数据结构
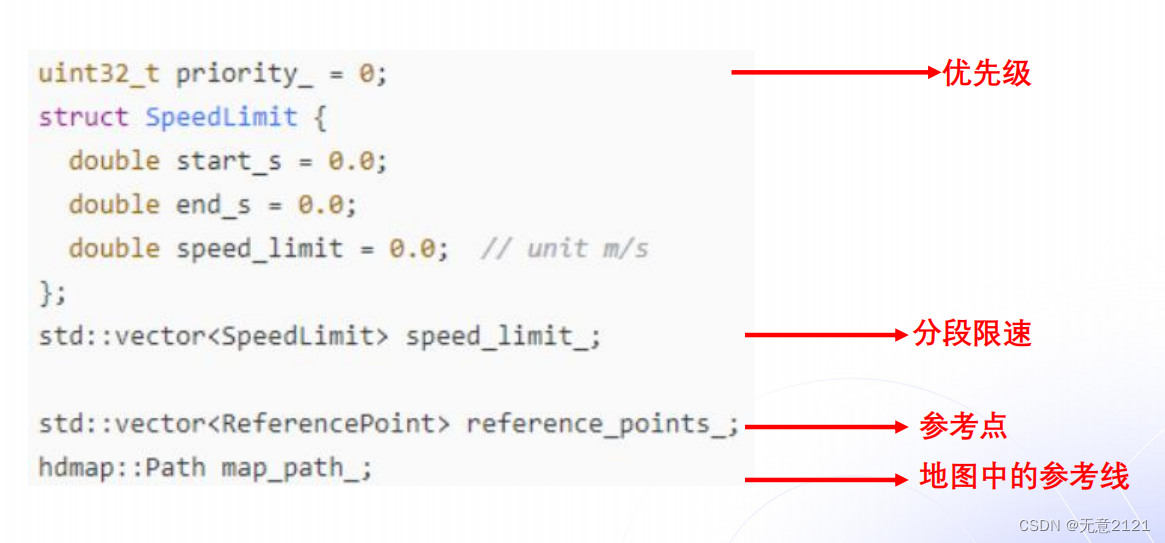
2.2 ReferencePoint的数据结构

3 参考线处理流程
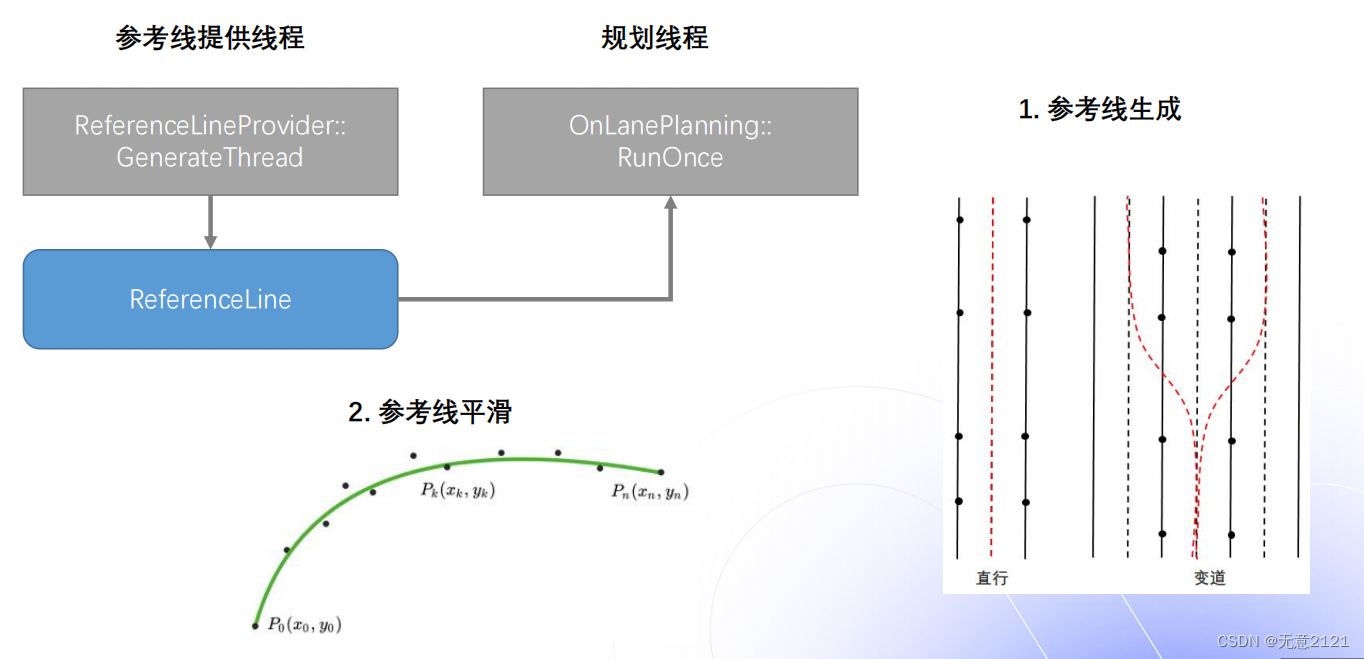
参考线处理分两步
- 生成参考线,这主要由Routing模块的输出决定
- 参考线平滑,接下来会详细讲解参考线的平滑的算法
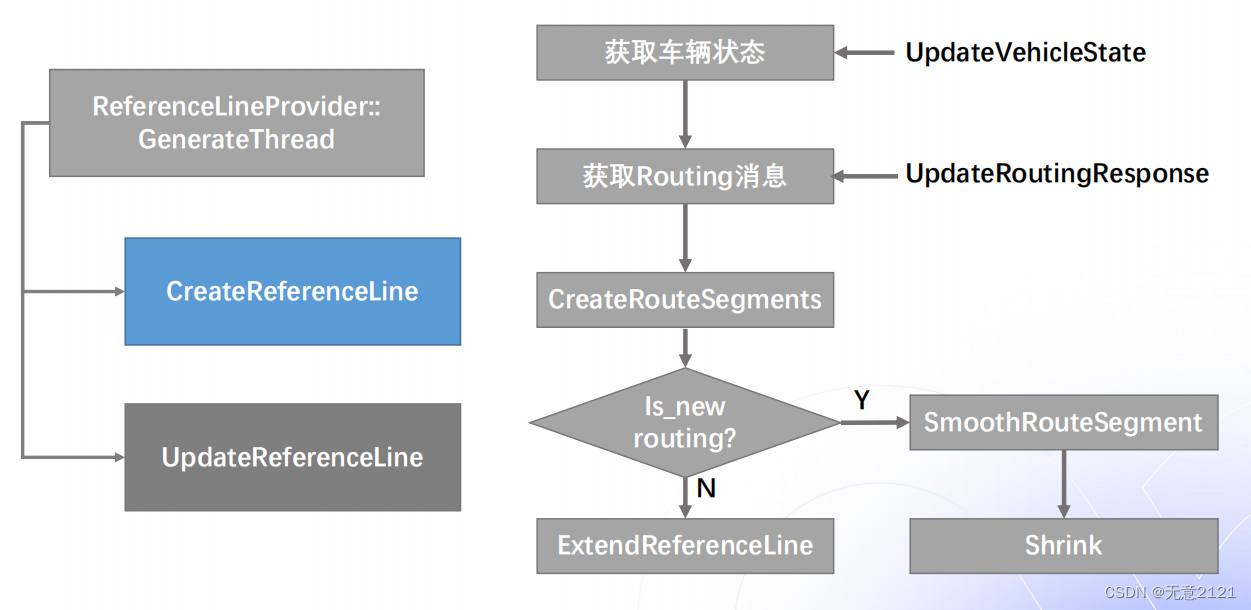 4 参考线平滑算法
4 参考线平滑算法
4.1 算法分类

参考线平滑算法主要有三种
- 离散点平滑
- 螺旋曲线平滑
- 多项式平滑
if (smoother_config_.has_qp_spline()) {
smoother_.reset(new QpSplineReferenceLineSmoother(smoother_config_));
} else if (smoother_config_.has_spiral()) {
smoother_.reset(new SpiralReferenceLineSmoother(smoother_config_));
} else if (smoother_config_.has_discrete_points()) {
smoother_.reset(new DiscretePointsReferenceLineSmoother(smoother_config_));
} else {
ACHECK(false) << "unknown smoother config "
<< smoother_config_.DebugString();
}
is_initialized_ = true;这里是对参考线平滑算法进行配置,Apollo系统中默认采用离散点平滑算法
4.2 参考线平滑算法流程
bool ReferenceLineProvider::SmoothReferenceLine(
const ReferenceLine &raw_reference_line, ReferenceLine *reference_line) {
if (!FLAGS_enable_smooth_reference_line) {
*reference_line = raw_reference_line;
return true;
}
// generate anchor points:
std::vector<AnchorPoint> anchor_points;
GetAnchorPoints(raw_reference_line, &anchor_points);
smoother_->SetAnchorPoints(anchor_points);
if (!smoother_->Smooth(raw_reference_line, reference_line)) {
AERROR << "Failed to smooth reference line with anchor points";
return false;
}
if (!IsReferenceLineSmoothValid(raw_reference_line, *reference_line)) {
AERROR << "The smoothed reference line error is too large";
return false;
}
return true;
}输入raw_reference_line,设置中间点(GetAnchorPoints),然后smooth,最后输出
4.2.1 AnchorPoint
struct AnchorPoint {
common::PathPoint path_point;
double lateral_bound = 0.0;
double longitudinal_bound = 0.0;
// enforce smoother to strictly follow this reference point
bool enforced = false;
};lateral_bound、longitudinal_bound代表裕度,enforced代表是否是强约束
max_constraint_interval : 0.25
longitudinal_boundary_bound : 2.0
max_lateral_boundary_bound : 0.5
min_lateral_boundary_bound : 0.1
curb_shift : 0.2
lateral_buffer : 0.2这是中间点的配置文件
4.2.2 smooth
bool status = false;
const auto& smoothing_method = config_.discrete_points().smoothing_method();
std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> smoothed_point2d;
switch (smoothing_method) {
case DiscretePointsSmootherConfig::COS_THETA_SMOOTHING:
status = CosThetaSmooth(raw_point2d, anchorpoints_lateralbound,
&smoothed_point2d);
break;
case DiscretePointsSmootherConfig::FEM_POS_DEVIATION_SMOOTHING:
status = FemPosSmooth(raw_point2d, anchorpoints_lateralbound,
&smoothed_point2d);
break;
default:
AERROR << "Smoother type not defined";
return false;
}
if (!status) {
AERROR << "discrete_points reference line smoother fails";
return false;bool DiscretePointsReferenceLineSmoother::FemPosSmooth(
const std::vector<std::pair<double, double>>& raw_point2d,
const std::vector<double>& bounds,
std::vector<std::pair<double, double>>* ptr_smoothed_point2d) {
const auto& fem_pos_config =
config_.discrete_points().fem_pos_deviation_smoothing();
FemPosDeviationSmoother smoother(fem_pos_config);
// box contraints on pos are used in fem pos smoother, thus shrink the
// bounds by 1.0 / sqrt(2.0)
// 裕度收缩
std::vector<double> box_bounds = bounds;
const double box_ratio = 1.0 / std::sqrt(2.0);
for (auto& bound : box_bounds) {
bound *= box_ratio;
}
std::vector<double> opt_x;
std::vector<double> opt_y;
// 问题求解
bool status = smoother.Solve(raw_point2d, box_bounds, &opt_x, &opt_y);
if (!status) {
AERROR << "Fem Pos reference line smoothing failed";
return false;
}
if (opt_x.size() < 2 || opt_y.size() < 2) {
AERROR << "Return by fem pos smoother is wrong. Size smaller than 2 ";
return false;
}4.2.3 solve
bool FemPosDeviationSmoother::Solve(
const std::vector<std::pair<double, double>>& raw_point2d,
const std::vector<double>& bounds, std::vector<double>* opt_x,
std::vector<double>* opt_y) {
// 考虑曲率约束
if (config_.apply_curvature_constraint()) {
if (config_.use_sqp()) {
// 线性求解
return SqpWithOsqp(raw_point2d, bounds, opt_x, opt_y);
} else {
// 非线性求解
return NlpWithIpopt(raw_point2d, bounds, opt_x, opt_y);
}
}
// 不考虑曲率约束
else
{
// 线性求解(默认)
return QpWithOsqp(raw_point2d, bounds, opt_x, opt_y);
}
return true;
}5 具体算法
r
离散点平滑算法也是基于评价函数来做的,分别衡量
- 曲线平滑度
- 曲线长度
- 点与参考点的误差
对于平滑度的衡量有两种方式
- FemPosSmooth相对不精准,但是只需用二次规划能快速求解
- CosThetaSmooth相对精准,但是需要非线性规划,计算量大

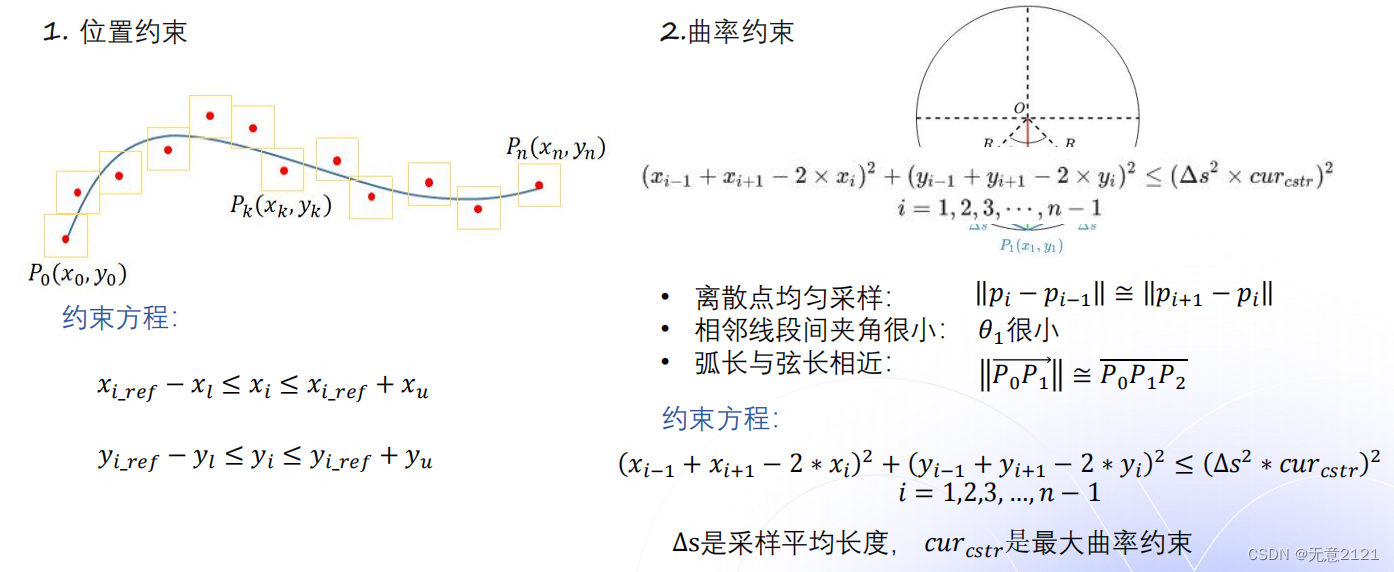 同时还需要满足约束条件
同时还需要满足约束条件
- 位置约束保证离散点相对于原来的不过于偏离
- 曲率约束使得参考线曲率尽量符合车辆运动学约束,易于跟踪