Context上下文
Context概述
Go 1.7 标准库引入 context,译作“上下文”,准确说它是 goroutine 的上下文,包含 goroutine 的运行状态、环境、现场等信息。
context 主要用来在 goroutine 之间传递上下文信息,包括:取消信号、超时时间、截止时间、k-v 等。
随着 context 包的引入,标准库中很多接口因此加上了 context 参数,例如 database/sql 包。context 几乎成为了并发控制和超时控制的标准做法。
在一组goroutine 之间传递共享的值、取消信号、deadline是Context的作用。
以典型的HTTPServer为例:
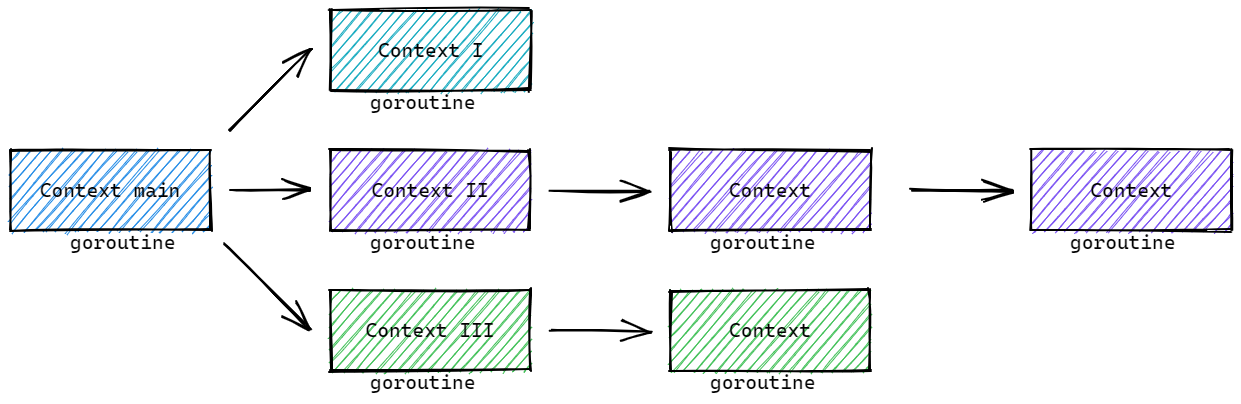
我们以 Context II为例,若没有上下文信号,当其中一个goroutine出现问题时,其他的goroutine不知道,还会继续工作。这样的无效的goroutine积攒起来,就会导致goroutine雪崩,进而导致服务宕机!
没有同步信号:
增加同步信号:

参考:Context传递取消信号 小结。
Context 核心结构
context.Context 是 Go 语言在 1.7 版本中引入标准库的接口,该接口定义了四个需要实现的方法:
type Context interface {
// 返回被取消的时间
Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool)
// 返回用于通知Context完结的channel
// 当这个 channel 被关闭时,说明 context 被取消了
// 在子协程里读这个 channel,除非被关闭,否则读不出来任何东西
Done() <-chan struct{}
// 返回Context取消的错误
Err() error
// 返回key对应的value
Value(key any) any
}
除了Context接口,还存在一个canceler接口,用于实现Context可以被取消:
type canceler interface {
cancel(removeFromParent bool, err error)
Done() <-chan struct{}
}
除了以上两个接口,还有4个预定义的Context类型:
// 空Context
type emptyCtx int
// 取消Context
type cancelCtx struct {
Context
mu sync.Mutex // protects following fields
done atomic.Value // of chan struct{}, created lazily, closed by first cancel call
children map[canceler]struct{} // set to nil by the first cancel call
err error // set to non-nil by the first cancel call
}
// 定时取消Context
type timerCtx struct {
cancelCtx
timer *time.Timer // Under cancelCtx.mu.
deadline time.Time
}
// KV值Context
type valueCtx struct {
Context
key, val any
}
默认(空)Context的使用
context 包中最常用的方法是 context.Background、context.TODO,这两个方法都会返回预先初始化好的私有变量 background 和 todo,它们会在同一个 Go 程序中被复用:
-
context.Background, 是上下文的默认值,所有其他的上下文都应该从它衍生出来,在多数情况下,如果当前函数没有上下文作为入参,我们都会使用
context.Background作为起始的上下文向下传递。 -
context.TODO,是一个备用,一个context占位,通常用在并不知道传递什么 context的情形。
使用示例,database/sql包中的执行:
func (db *DB) PingContext(ctx context.Context) error func (db *DB) ExecContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (Result, error) func (db *DB) QueryContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (*Rows, error) func (db *DB) QueryRowContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) *Row
方法,其中第一个参数就是context.Context。
例如:操作时:
db, _ := sql.Open("", "")
query := "DELETE FROM `table_name` WHERE `id` = ?"
db.ExecContext(context.Background(), query, 42)
当然,单独 database.sql包中,也支持不传递context.Context的方法。功能一致,但缺失了context.Context相关功能。
func (db *DB) Exec(query string, args ...any) (Result, error)
context.Background 和 context.TODO 返回的都是预定义好的 emptyCtx 类型数据,其结构如下:
// 创建方法
func Background() Context {
return background
}
func TODO() Context {
return todo
}
// 预定义变量
var (
background = new(emptyCtx)
todo = new(emptyCtx)
)
// emptyCtx 定义
type emptyCtx int
func (*emptyCtx) Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool) {
return
}
func (*emptyCtx) Done() <-chan struct{} {
return nil
}
func (*emptyCtx) Err() error {
return nil
}
func (*emptyCtx) Value(key any) any {
return nil
}
func (e *emptyCtx) String() string {
switch e {
case background:
return "context.Background"
case todo:
return "context.TODO"
}
return "unknown empty Context"
}
可见,emptyCtx 是不具备取消、KV值和Deadline的相关功能的,称为空Context,没有任何功能。
Context传递取消信号
context.WithCancel 函数能够从 context.Context 中衍生出一个新的子上下文并返回用于取消该上下文的函数。一旦我们执行返回的取消函数,当前上下文以及它的子上下文都会被取消,所有的 Goroutine 都会同步收到这一取消信号。取消操作通常分为主动取消,定时取消两类。
主动取消
需要的操作为:
-
创建带有cancel函数的Context,func WithCancel(parent Context) (ctx Context, cancel CancelFunc)
-
接收cancel的Channel,ctx.Done()
-
主动Cancel的函数,cancel CancelFunc

示例代码:
func ContextCancelCall() {
// 1. 创建cancelContext
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
wg := sync.WaitGroup{}
wg.Add(4)
// 2. 启动goroutine,携带cancelCtx
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
// 启动goroutine,携带ctx参数
go func(c context.Context, n int) {
defer wg.Done()
// 监听context的取消完成channel,来确定是否执行了主动cancel操作
for {
select {
// 等待接收c.Done()这个channel
case <-c.Done():
fmt.Println("Cancel")
return
default:
}
fmt.Println(strings.Repeat(" ", n), n)
time.Sleep(300 * time.Millisecond)
}
}(ctx, i)
}
// 3. 主动取消 cancel()
// 3s后取消
select {
case <-time.NewTimer(2 * time.Second).C:
cancel() // ctx.Done() <- struct{}
}
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
fmt.Println("main Cancel")
}
wg.Wait()
}
// ======
> go test -run TestContextCancelCall
3
1
0
2
1
3
2
0
0
1
3
2
2
1
3
0
0
1
3
2
2
1
0
3
3
0
1
2
main Cancel
Cancel
Cancel
Cancel
Cancel
PASS
ok goConcurrency 2.219s
当调用cancel()时,全部的goroutine会从 ctx.Done() 接收到内容,进而完成后续控制操作。
func WithCancel(parent Context) (ctx Context, cancel CancelFunc) 函数返回的Context是 context.cancelCtx 结构体对象,以及一个CancelFunc。
其中 context.cancelCtx 结构如下:
// A cancelCtx can be canceled. When canceled, it also cancels any children
// that implement canceler.
type cancelCtx struct {
Context
mu sync.Mutex // protects following fields
done atomic.Value // of chan struct{}, created lazily, closed by first cancel call
children map[canceler]struct{} // set to nil by the first cancel call
err error // set to non-nil by the first cancel call
}
其中:
-
Context,上级Context对象
-
mu, 互斥锁
-
done,用于处理cancel通知信号的channel。懒惰模式创建,调用cancel时关闭。
-
children,以该context为parent的可cancel的context们
-
err,error
Deadline和Timeout定时取消
与主动调用 CancelFunc 的差异在于,定时取消,增加了一个到时自动取消的机制:
-
Deadline,某个时间点后,使用
func WithDeadline(parent Context, d time.Time) (Context, CancelFunc)创建 -
Timeout,某个时间段后,使用
func WithTimeout(parent Context, timeout time.Duration) (Context, CancelFunc)创建
示例代码如下,与主动cancel的代码类似:
// 1s后cancel ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 1*time.Second) // 每天 20:30 cancel curr := time.Now() t := time.Date(curr.Year(), curr.Month(), curr.Day(), 20, 30, 0, 0, time.Local) ctx, cancel := context.WithDeadline(context.Background(), t)
其他代码一致,当时间到时,ctx.Done() 可以接收内容,进而控制goroutine停止。
不论WithDeadline和WithTimeout都会构建 *timerCtx 类型的Context,结构如下:
// A timerCtx carries a timer and a deadline. It embeds a cancelCtx to
// implement Done and Err. It implements cancel by stopping its timer then
// delegating to cancelCtx.cancel.
type timerCtx struct {
cancelCtx
timer *time.Timer // Under cancelCtx.mu.
deadline time.Time
}
其中:
-
cancelCtx,基于parent构建的cancelCtx
-
deadline,cancel时间
-
timer,定时器,用于自动cancel
Cancel操作的向下传递
当父上下文被取消时,子上下文也会被取消。Context 结构如下:
ctxOne | \ ctxTwo ctxThree | ctxFour
示例代码:
func ContextCancelDeep() {
ctxOne, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
ctxTwo, _ := context.WithCancel(ctxOne)
ctxThree, _ := context.WithCancel(ctxOne)
ctxFour, _ := context.WithCancel(ctxTwo)
// 带有timeout的cancel
//ctxOne, _ := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 1*time.Second)
//ctxTwo, cancel := context.WithTimeout(ctxOne, 1*time.Second)
//ctxThree, _ := context.WithTimeout(ctxOne, 1*time.Second)
//ctxFour, _ := context.WithTimeout(ctxTwo, 1*time.Second)
cancel()
wg := sync.WaitGroup{}
wg.Add(4)
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
select {
case <-ctxOne.Done():
fmt.Println("one cancel")
}
}()
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
select {
case <-ctxTwo.Done():
fmt.Println("two cancel")
}
}()
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
select {
case <-ctxThree.Done():
fmt.Println("three cancel")
}
}()
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
select {
case <-ctxFour.Done():
fmt.Println("four cancel")
}
}()
wg.Wait()
}
我们调用 ctxOne 的 cancel, 其后续的context都会接收到取消的信号。
如果调用了其他的cancel,例如ctxTwo,那么ctxOne和ctxThree是不会接收到信号的。
取消操作流程
创建cancelCtx的流程
使用 context.WithCancel, context.WithDeadlime, context.WithTimeout 创建cancelCtx或timerCtx的核心过程基本一致,以 context.WithCancel 为例:
func WithCancel(parent Context) (ctx Context, cancel CancelFunc) {
if parent == nil {
panic("cannot create context from nil parent")
}
// 构建cancelCtx对象
c := newCancelCtx(parent)
// 传播Cancel操作
propagateCancel(parent, &c)
// 返回值,注意第二个cancel函数的实现
return &c, func() { c.cancel(true, Canceled) }
}
func newCancelCtx(parent Context) cancelCtx {
return cancelCtx{Context: parent}
}
由此可见,核心过程有两个:
-
newCancelCtx, 使用 parent 构建 cancelCtx
-
propagateCancel, 传播Cancel操作,用来构建父子Context的关联,用于保证在父级Context取消时可以同步取消子级Context
核心的propagateCancel 的实现如下:
// propagateCancel arranges for child to be canceled when parent is.
func propagateCancel(parent Context, child canceler) {
// parent不会触发cancel操作
done := parent.Done()
if done == nil {
return // parent is never canceled
}
// parent已经触发了cancel操作
select {
case <-done:
// parent is already canceled
child.cancel(false, parent.Err())
return
default:
}
// parent还没有触发cancel操作
if p, ok := parentCancelCtx(parent); ok {
// 内置cancelCtx类型
p.mu.Lock()
if p.err != nil {
// parent has already been canceled
child.cancel(false, p.err)
} else {
if p.children == nil {
p.children = make(map[canceler]struct{})
}
// 将当前context放入parent.children中
p.children[child] = struct{}{}
}
p.mu.Unlock()
} else {
// 非内置cancelCtx类型
atomic.AddInt32(&goroutines, +1)
go func() {
select {
case <-parent.Done():
child.cancel(false, parent.Err())
case <-child.Done():
}
}()
}
}
以上代码在建立child和parent的cancelCtx联系时,处理了下面情况:
-
parent不会触发cancel操作,不做任何操作,直接返回
-
parent已经触发了cancel操作,执行child的cancel操作,返回
-
parent还没有触发cancel操作,
child会被加入parent的children列表中,等待parent释放取消信号 -
如果是自定义Context实现了可用的Done(),那么开启goroutine来监听parent.Done()和child.Done(),同样在parent.Done()时取消child。
如果是WithDeadline构建的timerCtx,构建的过程多了两步:
-
对截至时间的判定,判定是否已经截至
-
设置定时器
示例代码:
func WithDeadline(parent Context, d time.Time) (Context, CancelFunc) {
if parent == nil {
panic("cannot create context from nil parent")
}
if cur, ok := parent.Deadline(); ok && cur.Before(d) {
// The current deadline is already sooner than the new one.
return WithCancel(parent)
}
c := &timerCtx{
cancelCtx: newCancelCtx(parent),
deadline: d,
}
propagateCancel(parent, c)
dur := time.Until(d)
// 已过时
if dur <= 0 {
c.cancel(true, DeadlineExceeded) // deadline has already passed
return c, func() { c.cancel(false, Canceled) }
}
c.mu.Lock()
defer c.mu.Unlock()
// 设置定时器
if c.err == nil {
c.timer = time.AfterFunc(dur, func() {
c.cancel(true, DeadlineExceeded)
})
}
return c, func() { c.cancel(true, Canceled) }
}
ctx.Done() 初始信号channel流程
以 cancelCtx 为例:
func (c *cancelCtx) Done() <-chan struct{} {
// 加载已经存在的
d := c.done.Load()
if d != nil {
return d.(chan struct{})
}
c.mu.Lock()
defer c.mu.Unlock()
// 初始化新的
d = c.done.Load()
if d == nil {
d = make(chan struct{})
c.done.Store(d)
}
return d.(chan struct{})
}
其中两个步骤:
-
先尝试加载已经存在的
-
后初始化新的
核心要点是,当调用Done()时,初始化chan struct{}, 而不是在上限文cancelCtx创建时,就初始化完成了。称为懒惰初始化。
cancel()操作流程
取消流程,我们以 cancelCtx 的主动取消函数cancel的实现为例:
// cancel closes c.done, cancels each of c's children, and, if
// removeFromParent is true, removes c from its parent's children.
func (c *cancelCtx) cancel(removeFromParent bool, err error) {
if err == nil {
panic("context: internal error: missing cancel error")
}
c.mu.Lock()
if c.err != nil {
c.mu.Unlock()
return // already canceled
}
// 设置 err
c.err = err
// 关闭channel
d, _ := c.done.Load().(chan struct{})
if d == nil {
c.done.Store(closedchan)
} else {
close(d)
}
// 遍历全部可取消的子context
for child := range c.children {
// NOTE: acquiring the child's lock while holding parent's lock.
child.cancel(false, err)
}
c.children = nil
c.mu.Unlock()
// 从parent的children删除自己
if removeFromParent {
removeChild(c.Context, c)
}
}
以上流程的核心操作:
-
关闭channel,用来通知全部使用该ctx的goroutine
-
遍历全部可取消的子context,执行child的取消操作
-
从parent的children删除自己
Context传值

若希望在使用context时,携带额外的Key-Value数据,可以使用 context.WithValue 方法,构建带有值的context。并使用 Value(key any) any 方法获取值。带有值
对应方法的签名如下:
func WithValue(parent Context, key, val any) Context
type Context interface {
Value(key any) any
}
需要三个参数:
-
上级 Context
-
key 要求是comparable的(可比较的),实操时,推荐使用特定的Key类型,避免直接使用string或其他内置类型而带来package之间的冲突。
-
val any
示例代码
type MyContextKey string
func ContextValue() {
wg := sync.WaitGroup{}
ctx := context.WithValue(context.Background(), MyContextKey("title"), "Go")
wg.Add(1)
go func(c context.Context) {
defer wg.Done()
if v := c.Value(MyContextKey("title")); v != nil {
fmt.Println("found value:", v)
return
}
fmt.Println("key not found:", MyContextKey("title"))
}(ctx)
wg.Wait()
}
context.WithValue 方法返回 context.valueCtx 结构体类型。context.valueCtx 结构体包含了上级Context和key、value:
// A valueCtx carries a key-value pair. It implements Value for that key and
// delegates all other calls to the embedded Context.
type valueCtx struct {
Context
key, val any
}
func (c *valueCtx) Value(key any) any {
if c.key == key {
return c.val
}
return value(c.Context, key)
}
也就是除了 value 功能,其他Contenxt功能都由parent Context实现。
如果 context.valueCtx.Value 方法查询的 key 不存在于当前 valueCtx 中,就会从父上下文中查找该键对应的值直到某个父上下文中返回 nil 或者查找到对应的值。例如:
func ContextValueDeep() {
wgOne := sync.WaitGroup{}
ctxOne := context.WithValue(context.Background(), MyContextKey("title"), "One")
//ctxOne := context.WithValue(context.Background(), MyContextKey("key"), "Value")
//ctxTwo := context.WithValue(ctxOne, MyContextKey("title"), "Two")
ctxTwo := context.WithValue(ctxOne, MyContextKey("key"), "Value")
//ctxThree := context.WithValue(ctxTwo, MyContextKey("title"), "Three")
ctxThree := context.WithValue(ctxTwo, MyContextKey("key"), "Value")
wgOne.Add(1)
go func(c context.Context) {
defer wgOne.Done()
if v := c.Value(MyContextKey("title")); v != nil {
fmt.Println("found value:", v)
return
}
fmt.Println("key not found:", MyContextKey("title"))
}(ctxThree)
wgOne.Wait()
}
小结
特定的结构体类型:
-
emptyCtx,函数 context.Background, context.TODO
-
cancelCtx,函数 context.WithCancel
-
timerCtx, 函数 context.WithDeadline, context.WithTimeout
-
valueCtx, 函数 context.WithValue
官方博客对Context使用的建议:
-
直接将 Context 类型作为函数的第一参数,而且一般都命名为 ctx。
-
如果你实在不知道传什么,标准库给你准备好了一个 context.TODO。
-
context 存储的应该是一些goroutine共同的数据。
-
context 是并发安全的。