承接上一文 动态代理 ,这里探究spring 动态代理
会话1:spring动态代理 quick start
- 👧哥哥,哥哥,spring 怎么去搞动态代理的呢
- 👨 来来来,听我细细来说
quick start
通过Spring的 ProxyFactory去构建我们的代理对象,我对代理对象添加一个日志的动态扩展,打印日志LogAdvice
package com.example.demo;
import org.aopalliance.aop.Advice;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
import org.springframework.aop.Advisor;
import org.springframework.aop.TargetSource;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyConfig;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory;
import org.springframework.cglib.core.DebuggingClassWriter;
/**
* @author bigbird-0101
* @date 2024-07-03 22:20
*/
public class SpringProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "D:\\development\\idea workspace\\Study-Project\\com\\sun\\proxy");
MaiPiao proxy = (MaiPiao) getProxy(new TargetSource() {
@Override
public Class<?> getTargetClass() {
return ZhouJieLun.class;
}
@Override
public Object getTarget() {
return new ZhouJieLun();
}
}, SpringProxyTest.class.getClassLoader());
proxy.maiPiao();
}
public static class ZhouJieLun implements MaiPiao{
@Override
public void maiPiao() {
System.out.println("卖周杰伦的票咯");
}
}
public interface MaiPiao{
void maiPiao();
}
private static Object getProxy(TargetSource targetSource, ClassLoader classLoader) {
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(new ProxyConfig());
Advisor advisor = new Advisor() {
@Override
public Advice getAdvice() {
return new LogAdvice();
}
@Override
public boolean isPerInstance() {
return false;
}
};
Advisor[] advisors = new Advisor[]{advisor};
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(false);
return proxyFactory.getProxy(classLoader);
}
public static class LogAdvice implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("我开始执行");
Object proceed = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("我执行完了");
return proceed;
}
}
}
来来来 run一下,可以看到已经 成功打印了。
会话2:深入分析ProxyFactory
- 👧哇,哥哥好厉害,这个ProxyFactory是个什么啊?你可以帮我分析一下吗
- 👨 来来来,听我细细来说
首先我们看下ProxyFactory的类图
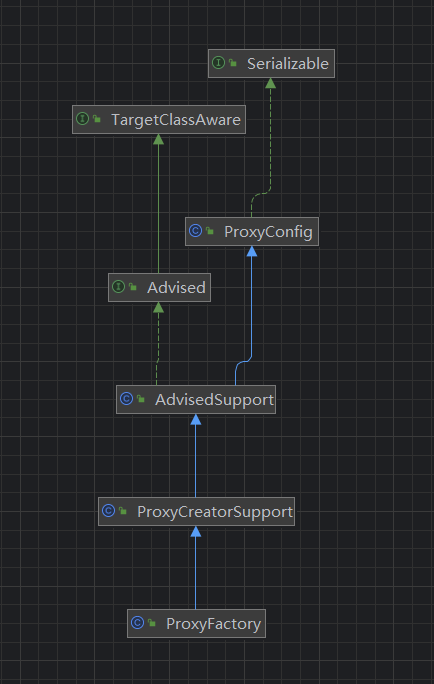
可以看到ProxyFactory实现了Advised接口,Advised是spring 代理非常核心的一个接口。
官方注释如下
Interface to be implemented by classes that hold the configuration of a factory of AOP proxies. This configuration includes the Interceptors and other advice, Advisors, and the proxied interfaces.
Any AOP proxy obtained from Spring can be cast to this interface to allow manipulation of its AOP advice.
他的意思是说 接口的实现类是一个aop 代理配置工厂,这个配置包含接口,advice,advisor和代理接口,任何的代理对象都能强转成这个接口,啥意思呢?意思是spring所有的代理类都实现了这个接口(这个我们稍后分析spring 代理工厂生成的代码是啥样的)。
总结概括:
1.spring所有的代理类都实现了这个接口
2.可以通过接口动态配置代理对象,包括动态添加切面和触发的事件,以及接口等。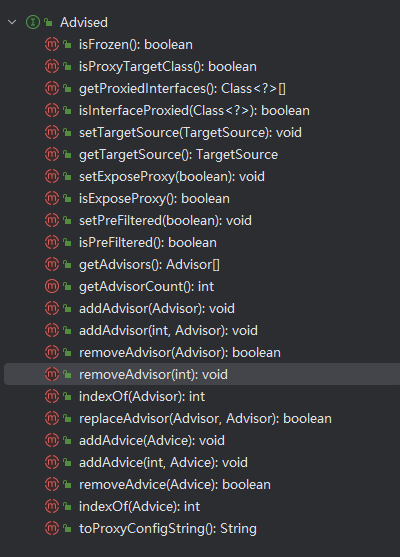
继续分析 ProxyCreatorSupport
可以看到真正的构建代理工厂是 AopProxyFactory这个类,我们看他的代码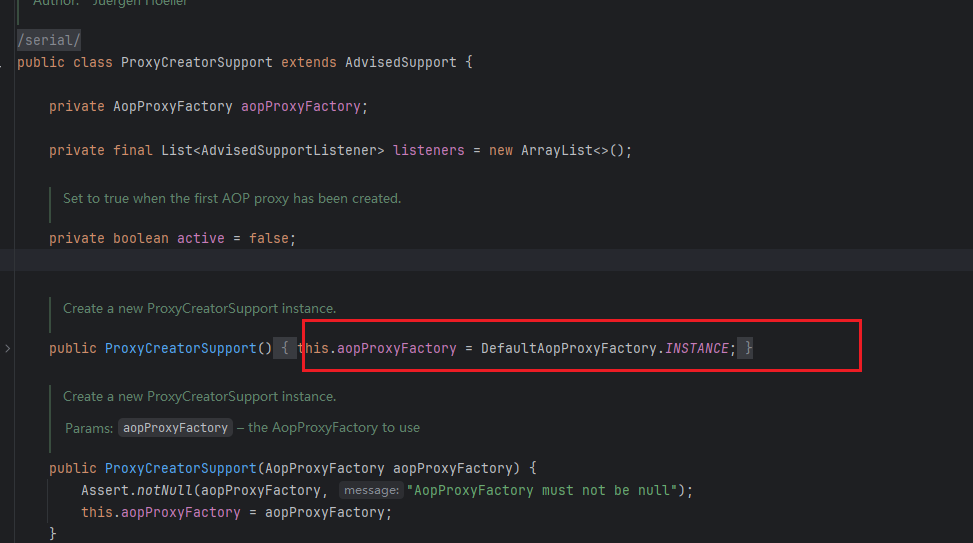
可以看到 通过代理配置 来决定使用 jdk生成代理 还是 cglib生成代理
可以看到** 满足Cglib的条件还是比较苛刻的**。spring还是希望尽量使用 jdk动态代理。除非你强制设置优化例如isOptimize 或者 ProxyTargetClass属性,可以看到就算你设置了 proxyTargetClass=true,但是你只要是接口都会使用jdk动态代理。
public class DefaultAopProxyFactory implements AopProxyFactory, Serializable {
/**
* Singleton instance of this class.
* @since 6.0.10
*/
public static final DefaultAopProxyFactory INSTANCE = new DefaultAopProxyFactory();
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7930414337282325166L;
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass) || ClassUtils.isLambdaClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
/**
* Determine whether the supplied {@link AdvisedSupport} has only the
* {@link org.springframework.aop.SpringProxy} interface specified
* (or no proxy interfaces specified at all).
*/
private boolean hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(AdvisedSupport config) {
Class<?>[] ifcs = config.getProxiedInterfaces();
return (ifcs.length == 0 || (ifcs.length == 1 && SpringProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(ifcs[0])));
}
}
我们继续分析 ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
看到下面这个方法
org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy#buildProxy
private Object buildProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader, boolean classOnly) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
//获取代理配置当中的需要被代理的对象的class
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
//如果被代理的对象已经是cglib代理
//则我们生成的代理 需要继承和实现 已是cglib类的父类和其实现的接口
if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
//拼接cglib代理
// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader smartClassLoader &&
smartClassLoader.isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
//设置继承的父类
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
//设置代理对象所有的接口
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setAttemptLoad(true);
//我们代码内部的生成策略 例如方法 字段 和参数等 我们详细分析
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
//获取回调函数 这个非常重要 这个是实现aop的关键 由他来驱动 Advice 的调用 第一个回调函数是DynamicAdvisedInterceptor
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above
ProxyCallbackFilter filter = new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset);
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(filter);
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
// ProxyCallbackFilter has method introspection capability with Advisor access.
try {
return (classOnly ? createProxyClass(enhancer) : createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks));
}
finally {
// Reduce ProxyCallbackFilter to key-only state for its class cache role
// in the CGLIB$CALLBACK_FILTER field, not leaking any Advisor state...
filter.advised.reduceToAdvisorKey();
}
}
catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +
": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}
第一个回调函数 DynamicAdvisedInterceptor 这个非常重要 这个是实现aop的关键 由他来驱动 Advice 的调用
来我们仔细分析一下 DynamicAdvisedInterceptor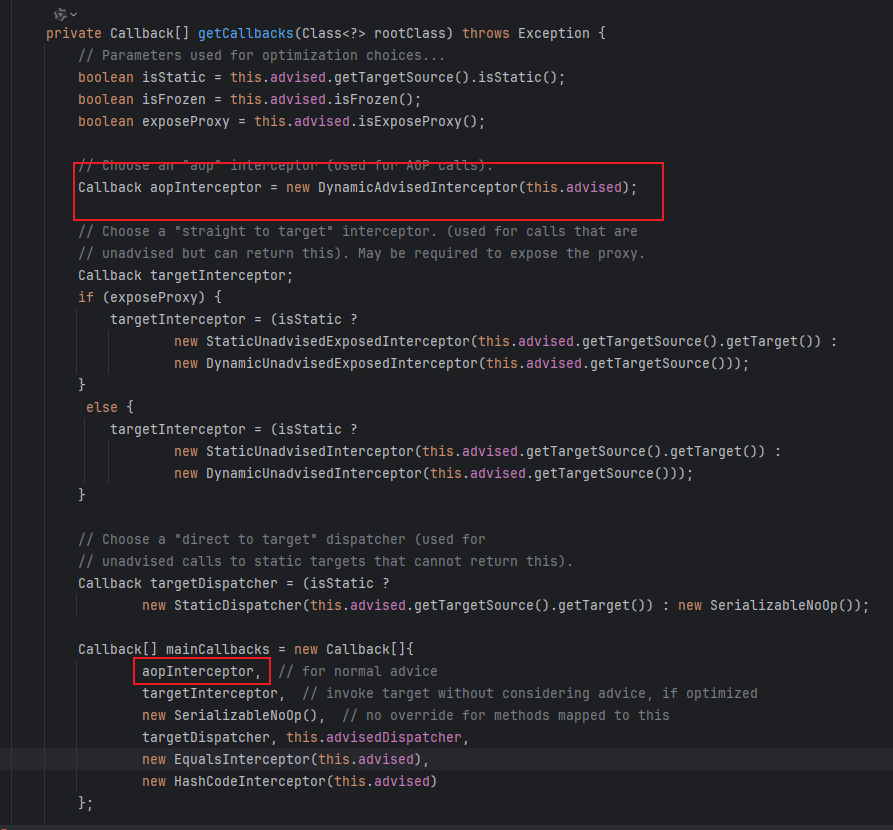
继续分析 DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept
第17行 通过代理配置类 advised 拿到所有的Advice 然后通过 CglibMethodInvocation 遍历调用 new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed()
@Override
@Nullable
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Object target = null;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource();
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
return processReturnType(proxy, target, method, args, retVal);
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
我们来看下 CglibMethodInvocation的类图。再看代码 发现他的核心逻辑在 其父类当中。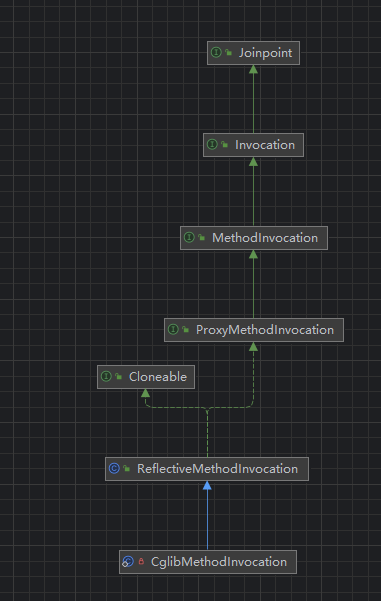
第27行 可以看到 开始调用了 Advice,那他是怎么实现循环的呢?当27行 执行时,会去 调用 quick start 当中的 LogAdvice的 invoke 方法 ,LogAdvice又会调用 MethodInvocation.proceed 所以又会回到这里 继续执行,然后发现 Advice已经遍历完了,然后就会去执行 第 6行 ,所以会去调用真实的 代理类的方法 。形成了一个循环调用。
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.matcher().matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor().invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
时序图如下 ** 第3步 和 第4步 如果有多个Advice会循环多次。**

继续分析 ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy
这个是其生成字节码的具体逻辑 可以看到这个generateClass 方法
@Override
public byte[] generate(ClassGenerator cg) throws Exception {
DebuggingClassWriter cw = getClassVisitor();
transform(cg).generateClass(cw);
return transform(cw.toByteArray());
}
他的实现是 org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer#generateClass 这个实现的 我们可以看到其代码
完整的展示了 这个class 是怎么生成的
public void generateClass(ClassVisitor v) throws Exception {
Class sc = (superclass == null) ? Object.class : superclass;
if (TypeUtils.isFinal(sc.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot subclass final class " + sc.getName());
}
List constructors = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(sc.getDeclaredConstructors()));
filterConstructors(sc, constructors);
// Order is very important: must add superclass, then
// its superclass chain, then each interface and
// its superinterfaces.
List actualMethods = new ArrayList();
List interfaceMethods = new ArrayList();
final Set forcePublic = new HashSet();
getMethods(sc, interfaces, actualMethods, interfaceMethods, forcePublic);
List methods = CollectionUtils.transform(actualMethods, value -> {
Method method = (Method) value;
int modifiers = Constants.ACC_FINAL
| (method.getModifiers()
& ~Constants.ACC_ABSTRACT
& ~Constants.ACC_NATIVE
& ~Constants.ACC_SYNCHRONIZED);
if (forcePublic.contains(MethodWrapper.create(method))) {
modifiers = (modifiers & ~Constants.ACC_PROTECTED) | Constants.ACC_PUBLIC;
}
return ReflectUtils.getMethodInfo(method, modifiers);
});
ClassEmitter e = new ClassEmitter(v);
if (currentData == null) {
e.begin_class(Constants.V1_8,
Constants.ACC_PUBLIC,
getClassName(),
Type.getType(sc),
(useFactory ?
TypeUtils.add(TypeUtils.getTypes(interfaces), FACTORY) :
TypeUtils.getTypes(interfaces)),
Constants.SOURCE_FILE);
}
else {
e.begin_class(Constants.V1_8,
Constants.ACC_PUBLIC,
getClassName(),
null,
new Type[]{FACTORY},
Constants.SOURCE_FILE);
}
List constructorInfo = CollectionUtils.transform(constructors, MethodInfoTransformer.getInstance());
e.declare_field(Constants.ACC_PRIVATE, BOUND_FIELD, Type.BOOLEAN_TYPE, null);
e.declare_field(Constants.ACC_PUBLIC | Constants.ACC_STATIC, FACTORY_DATA_FIELD, OBJECT_TYPE, null);
if (!interceptDuringConstruction) {
e.declare_field(Constants.ACC_PRIVATE, CONSTRUCTED_FIELD, Type.BOOLEAN_TYPE, null);
}
e.declare_field(Constants.PRIVATE_FINAL_STATIC, THREAD_CALLBACKS_FIELD, THREAD_LOCAL, null);
e.declare_field(Constants.PRIVATE_FINAL_STATIC, STATIC_CALLBACKS_FIELD, CALLBACK_ARRAY, null);
if (serialVersionUID != null) {
e.declare_field(Constants.PRIVATE_FINAL_STATIC, Constants.SUID_FIELD_NAME, Type.LONG_TYPE, serialVersionUID);
}
for (int i = 0; i < callbackTypes.length; i++) {
e.declare_field(Constants.ACC_PRIVATE, getCallbackField(i), callbackTypes[i], null);
}
// This is declared private to avoid "public field" pollution
e.declare_field(Constants.ACC_PRIVATE | Constants.ACC_STATIC, CALLBACK_FILTER_FIELD, OBJECT_TYPE, null);
if (currentData == null) {
emitMethods(e, methods, actualMethods);
emitConstructors(e, constructorInfo);
}
else {
emitDefaultConstructor(e);
}
emitSetThreadCallbacks(e);
emitSetStaticCallbacks(e);
emitBindCallbacks(e);
if (useFactory || currentData != null) {
int[] keys = getCallbackKeys();
emitNewInstanceCallbacks(e);
emitNewInstanceCallback(e);
emitNewInstanceMultiarg(e, constructorInfo);
emitGetCallback(e, keys);
emitSetCallback(e, keys);
emitGetCallbacks(e);
emitSetCallbacks(e);
}
e.end_class();
}
会话3:深入分析生成代理类
- 👧哇,哥哥真牛皮啊,哥哥,哥哥 我想看下 spring 到底生成了什么样的代理对象,他的代码到底是啥?
- 👨 好的 好的,看我一一给你介绍
以我们上面的quick start的为例,我们查看他生成的 代理类代码是啥样的。
我们设置下面这样的系统参数就可以看到spring生成的类了。
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "D:\\development\\idea workspace\\Study-Project\\com\\sun\\proxy");
这个就是spring 生成的代理类 哇,非常复杂非常多啊。他固定实现了 SpringProxy, Advised, Factory 这几个接口,所以每一个代理类都可以转成 Advised
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package com.example.demo;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.aopalliance.aop.Advice;
import org.springframework.aop.Advisor;
import org.springframework.aop.SpringProxy;
import org.springframework.aop.TargetClassAware;
import org.springframework.aop.TargetSource;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.Advised;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.AopConfigException;
import org.springframework.cglib.core.ReflectUtils;
import org.springframework.cglib.core.Signature;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Callback;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Dispatcher;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Factory;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.NoOp;
public class SpringProxyTest$ZhouJieLun$$SpringCGLIB$$0 extends SpringProxyTest.ZhouJieLun implements SpringProxy, Advised, Factory {
private boolean CGLIB$BOUND;
public static Object CGLIB$FACTORY_DATA;
private static final ThreadLocal CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS;
private static final Callback[] CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS;
private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_1;
private NoOp CGLIB$CALLBACK_2;
private NoOp CGLIB$CALLBACK_3;
private Dispatcher CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_5;
private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_6;
private static Object CGLIB$CALLBACK_FILTER;
private static final Method CGLIB$maiPiao$0$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$maiPiao$0$Proxy;
private static final Object[] CGLIB$emptyArgs;
private static final Method CGLIB$equals$1$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$toString$2$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$hashCode$3$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$clone$4$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy;
static void CGLIB$STATICHOOK1() {
CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS = new ThreadLocal();
CGLIB$emptyArgs = new Object[0];
Class var0 = Class.forName("com.example.demo.SpringProxyTest$ZhouJieLun$$SpringCGLIB$$0");
Class var1;
Method[] var10000 = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[]{"equals", "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z", "toString", "()Ljava/lang/String;", "hashCode", "()I", "clone", "()Ljava/lang/Object;"}, (var1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object")).getDeclaredMethods());
CGLIB$equals$1$Method = var10000[0];
CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z", "equals", "CGLIB$equals$1");
CGLIB$toString$2$Method = var10000[1];
CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "()Ljava/lang/String;", "toString", "CGLIB$toString$2");
CGLIB$hashCode$3$Method = var10000[2];
CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "()I", "hashCode", "CGLIB$hashCode$3");
CGLIB$clone$4$Method = var10000[3];
CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "()Ljava/lang/Object;", "clone", "CGLIB$clone$4");
CGLIB$maiPiao$0$Method = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[]{"maiPiao", "()V"}, (var1 = Class.forName("com.example.demo.SpringProxyTest$ZhouJieLun")).getDeclaredMethods())[0];
CGLIB$maiPiao$0$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "()V", "maiPiao", "CGLIB$maiPiao$0");
}
final void CGLIB$maiPiao$0() {
super.maiPiao();
}
public final void maiPiao() {
MethodInterceptor var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (var10000 != null) {
var10000.intercept(this, CGLIB$maiPiao$0$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$maiPiao$0$Proxy);
} else {
super.maiPiao();
}
}
final boolean CGLIB$equals$1(Object var1) {
return super.equals(var1);
}
public final boolean equals(Object var1) {
MethodInterceptor var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_5;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_5;
}
if (var10000 != null) {
Object var2 = var10000.intercept(this, CGLIB$equals$1$Method, new Object[]{var1}, CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy);
return var2 == null ? false : (Boolean)var2;
} else {
return super.equals(var1);
}
}
final String CGLIB$toString$2() {
return super.toString();
}
public final String toString() {
MethodInterceptor var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
return var10000 != null ? (String)var10000.intercept(this, CGLIB$toString$2$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy) : super.toString();
}
final int CGLIB$hashCode$3() {
return super.hashCode();
}
public final int hashCode() {
MethodInterceptor var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_6;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_6;
}
if (var10000 != null) {
Object var1 = var10000.intercept(this, CGLIB$hashCode$3$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy);
return var1 == null ? 0 : ((Number)var1).intValue();
} else {
return super.hashCode();
}
}
final Object CGLIB$clone$4() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
protected final Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
MethodInterceptor var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
return var10000 != null ? var10000.intercept(this, CGLIB$clone$4$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy) : super.clone();
}
public static MethodProxy CGLIB$findMethodProxy(Signature var0) {
String var10000 = var0.toString();
switch (var10000.hashCode()) {
case -508378822:
if (var10000.equals("clone()Ljava/lang/Object;")) {
return CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy;
}
break;
case 221771545:
if (var10000.equals("maiPiao()V")) {
return CGLIB$maiPiao$0$Proxy;
}
break;
case 1826985398:
if (var10000.equals("equals(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z")) {
return CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy;
}
break;
case 1913648695:
if (var10000.equals("toString()Ljava/lang/String;")) {
return CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy;
}
break;
case 1984935277:
if (var10000.equals("hashCode()I")) {
return CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy;
}
}
return null;
}
public final void setTargetSource(TargetSource var1) {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).setTargetSource(var1);
}
public final Class[] getProxiedInterfaces() {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).getProxiedInterfaces();
}
public final String toProxyConfigString() {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).toProxyConfigString();
}
public final void addAdvice(Advice var1) throws AopConfigException {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).addAdvice(var1);
}
public final void addAdvice(int var1, Advice var2) throws AopConfigException {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).addAdvice(var1, var2);
}
public final int getAdvisorCount() {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).getAdvisorCount();
}
public final void setExposeProxy(boolean var1) {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).setExposeProxy(var1);
}
public final boolean replaceAdvisor(Advisor var1, Advisor var2) throws AopConfigException {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).replaceAdvisor(var1, var2);
}
public final boolean removeAdvisor(Advisor var1) {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).removeAdvisor(var1);
}
public final void removeAdvisor(int var1) throws AopConfigException {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).removeAdvisor(var1);
}
public final boolean isPreFiltered() {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).isPreFiltered();
}
public final boolean isInterfaceProxied(Class var1) {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).isInterfaceProxied(var1);
}
public final boolean isExposeProxy() {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).isExposeProxy();
}
public final Advisor[] getAdvisors() {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).getAdvisors();
}
public final boolean removeAdvice(Advice var1) {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).removeAdvice(var1);
}
public final TargetSource getTargetSource() {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).getTargetSource();
}
public final boolean isProxyTargetClass() {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).isProxyTargetClass();
}
public final void setPreFiltered(boolean var1) {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).setPreFiltered(var1);
}
public final void addAdvisor(Advisor var1) throws AopConfigException {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).addAdvisor(var1);
}
public final void addAdvisor(int var1, Advisor var2) throws AopConfigException {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).addAdvisor(var1, var2);
}
public final int indexOf(Advice var1) {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).indexOf(var1);
}
public final int indexOf(Advisor var1) {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).indexOf(var1);
}
public final boolean isFrozen() {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised)var10000.loadObject()).isFrozen();
}
public final Class getTargetClass() {
Dispatcher var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((TargetClassAware)var10000.loadObject()).getTargetClass();
}
public SpringProxyTest$ZhouJieLun$$SpringCGLIB$$0() {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
}
public static void CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(Callback[] var0) {
CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS.set(var0);
}
public static void CGLIB$SET_STATIC_CALLBACKS(Callback[] var0) {
CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS = var0;
}
private static final void CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(Object var0) {
SpringProxyTest$ZhouJieLun$$SpringCGLIB$$0 var1 = (SpringProxyTest$ZhouJieLun$$SpringCGLIB$$0)var0;
if (!var1.CGLIB$BOUND) {
var1.CGLIB$BOUND = true;
Object var10000 = CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS.get();
if (var10000 == null) {
var10000 = CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS;
if (var10000 == null) {
return;
}
}
Callback[] var10001 = (Callback[])var10000;
var1.CGLIB$CALLBACK_6 = (MethodInterceptor)((Callback[])var10000)[6];
var1.CGLIB$CALLBACK_5 = (MethodInterceptor)var10001[5];
var1.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4 = (Dispatcher)var10001[4];
var1.CGLIB$CALLBACK_3 = (NoOp)var10001[3];
var1.CGLIB$CALLBACK_2 = (NoOp)var10001[2];
var1.CGLIB$CALLBACK_1 = (MethodInterceptor)var10001[1];
var1.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = (MethodInterceptor)var10001[0];
}
}
public Object newInstance(Callback[] var1) {
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(var1);
SpringProxyTest$ZhouJieLun$$SpringCGLIB$$0 var10000 = new SpringProxyTest$ZhouJieLun$$SpringCGLIB$$0();
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS((Callback[])null);
return var10000;
}
public Object newInstance(Callback var1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("More than one callback object required");
}
public Object newInstance(Class[] var1, Object[] var2, Callback[] var3) {
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(var3);
SpringProxyTest$ZhouJieLun$$SpringCGLIB$$0 var10000 = new SpringProxyTest$ZhouJieLun$$SpringCGLIB$$0;
switch (var1.length) {
case 0:
var10000.<init>();
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS((Callback[])null);
return var10000;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Constructor not found");
}
}
public Callback getCallback(int var1) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
Object var10000;
switch (var1) {
case 0:
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
break;
case 1:
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_1;
break;
case 2:
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_2;
break;
case 3:
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_3;
break;
case 4:
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
break;
case 5:
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_5;
break;
case 6:
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_6;
break;
default:
var10000 = null;
}
return (Callback)var10000;
}
public void setCallback(int var1, Callback var2) {
switch (var1) {
case 0:
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = (MethodInterceptor)var2;
break;
case 1:
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_1 = (MethodInterceptor)var2;
break;
case 2:
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_2 = (NoOp)var2;
break;
case 3:
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_3 = (NoOp)var2;
break;
case 4:
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4 = (Dispatcher)var2;
break;
case 5:
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_5 = (MethodInterceptor)var2;
break;
case 6:
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_6 = (MethodInterceptor)var2;
}
}
public Callback[] getCallbacks() {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
return new Callback[]{this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0, this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_1, this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_2, this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_3, this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4, this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_5, this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_6};
}
public void setCallbacks(Callback[] var1) {
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = (MethodInterceptor)var1[0];
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_1 = (MethodInterceptor)var1[1];
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_2 = (NoOp)var1[2];
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_3 = (NoOp)var1[3];
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4 = (Dispatcher)var1[4];
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_5 = (MethodInterceptor)var1[5];
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_6 = (MethodInterceptor)var1[6];
}
static {
CGLIB$STATICHOOK1();
}
}
可以看到 这个 MethodInterceptor var10000 就是我们上面的 DynamicAdvisedInterceptor
public final void maiPiao() {
MethodInterceptor var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (var10000 != null) {
var10000.intercept(this, CGLIB$maiPiao$0$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$maiPiao$0$Proxy);
} else {
super.maiPiao();
}
}
会话4: spring是如何使用这个 ProxyFactory的呢?
- 👧哇,哥哥讲的非常透彻啊,我还想知道spring怎么使用这个的呢?
- 👨 哈哈哈哈哈哈,好哇听我细细将来。
spring主要是通过 InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator来构建基础设施类的代理,当然还有其他类例如 AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator(主要是Aspectj),这里我们不细说Aspectj,我们继续说InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator,他是通过BeanFactoryPostProcess来注入这个基础设施bean ,我们可以通过AopAutoConfiguration来看到这样一段代码。通过下面这行代码进行将这个bean 声明的。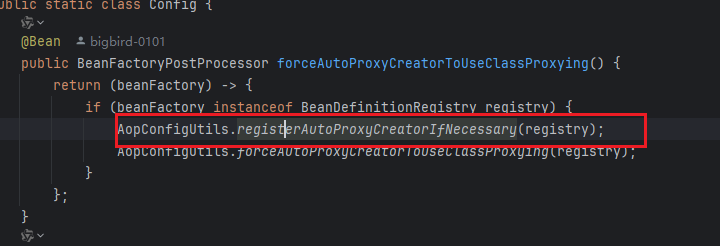
继续我们来看 InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 这个类,这个类主要是来自动创建类的代理,我们可以看下他的类图,看看它到底是啥?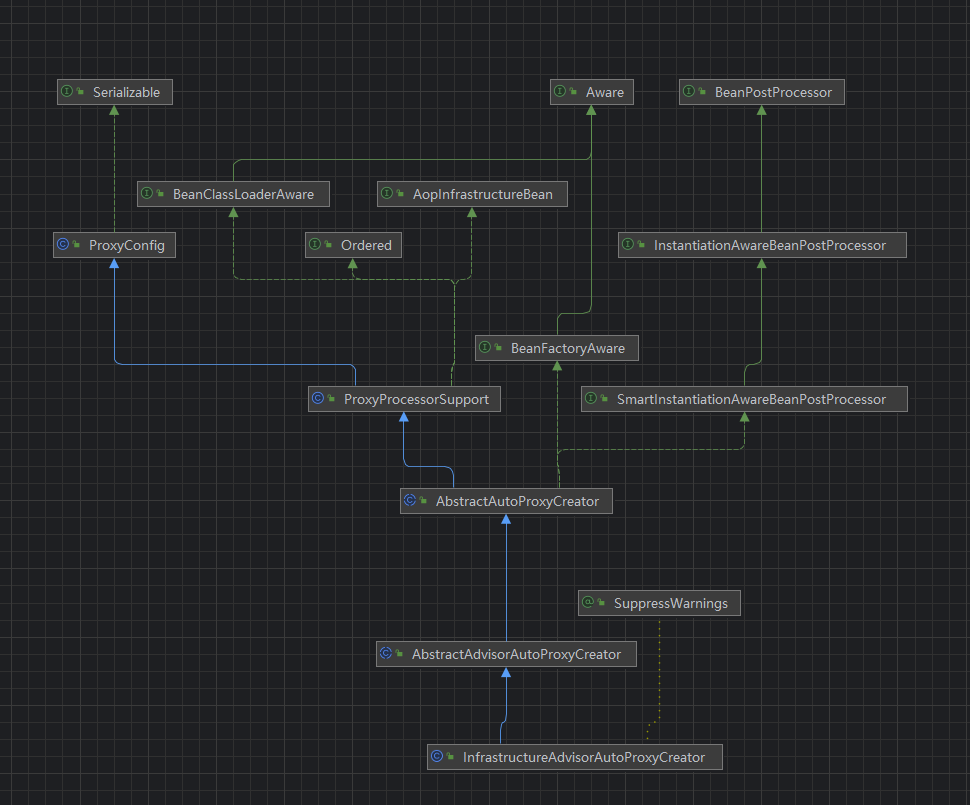
果然源码之下没有任何秘密,他是BeanPostProcessor的实现类,当创建bean时 会经过这个类的处理,我们来细看一下他的具体实现org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessBeforeInstantiation, 可以看到第24行 开始构建代理对象。
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName);
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) {
return null;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return null;
}
}
// Create proxy here if we have a custom TargetSource.
// Suppresses unnecessary default instantiation of the target bean:
// The TargetSource will handle target instances in a custom fashion.
TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);
if (targetSource != null) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName)) {
this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);
}
//获取这个bean上面符合的切面。
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource);
Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
return null;
}
他是怎么获取 符合的切面对象呢?
通过一些过滤手段来过滤 切面,例如在切面当中的Pointcut切点,来判断这个代理对象是否需要这个切面。
我们细看这两个方法,在这个AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类中
@Override
@Nullable
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
/**
* Find all eligible Advisors for auto-proxying this class.
* @param beanClass the clazz to find advisors for
* @param beanName the name of the currently proxied bean
* @return the empty List, not {@code null},
* if there are no pointcuts or interceptors
* @see #findCandidateAdvisors
* @see #sortAdvisors
* @see #extendAdvisors
*/
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
//找到候选的切面对象
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
//通过一些过滤手段来过滤 切面,例如在切面当中的切点,来判断这个代理对象是否需要这个切面。
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
try {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Advisor sorting failed with unexpected bean creation, probably due " +
"to custom use of the Ordered interface. Consider using the @Order annotation instead.", ex);
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
这个看到这个代码的调用时序图如下,在AopUtils当中真正调用了Pointcut,来来来我们继续追,为我们再细看AopUtils的 findAdvisorsThatCanApply方法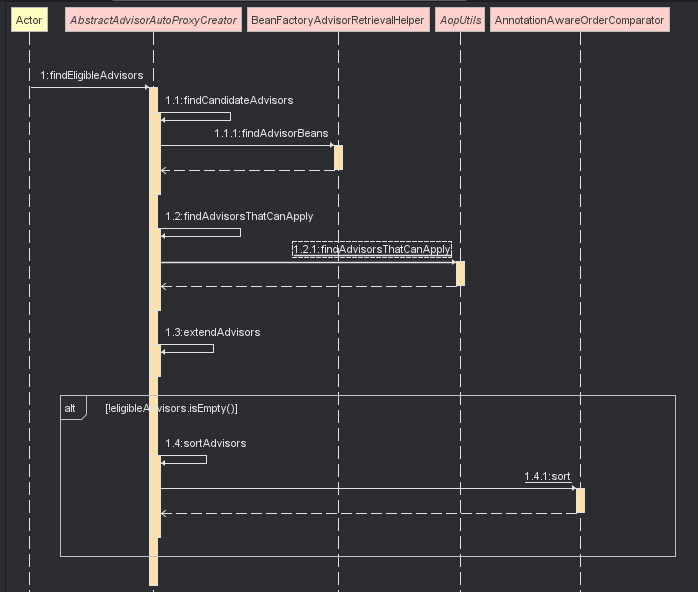
canApply就是拿到了Pointcut 的 ClassFilter 来过滤,当前这个bean的class是否符合 这个切面,到这里我们已经成功的分析了几乎所有链路,打完收工
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
return candidateAdvisors;
}
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// already processed
continue;
}
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);
}
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
// It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies.
return true;
}
}
注意点:
InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 当中 有一个这样的判断 判断切面是否需要被过滤。这个切面的角色需要时基础设施层的切面。
protected boolean isEligibleAdvisorBean(String beanName) {
return (this.beanFactory != null && this.beanFactory.containsBeanDefinition(beanName) &&
this.beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName).getRole() == BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
}
会话5: spring aop用例
- 👧哇,哥哥哥哥你咋这么厉害。我还想看 你举个完整的例子,自定义日志切面,来实现日志打印的需求
- 👨 哈哈哈哈哈哈,好好好。
看我表演嘿嘿
package com.example.demo;
import org.aopalliance.aop.Advice;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
import org.springframework.aop.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.aop.config.AopConfigUtils;
import org.springframework.aop.support.AbstractPointcutAdvisor;
import org.springframework.aop.support.annotation.AnnotationMatchingPointcut;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Role;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author bigbird-0101
* @date 2024-06-27 22:55
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class,
LogAdvisor.class,A.class,B.class);
MaiPiao bean = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(MaiPiao.class);
bean.maiPiao();
annotationConfigApplicationContext.close();
}
@Configuration
public static class Config {
@Bean
public BeanFactoryPostProcessor forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying() {
return (beanFactory) -> {
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
AopConfigUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
}
};
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public Test.LogAdvisor logAdvisor(){
return new Test.LogAdvisor();
}
}
@Component
public static class LogAdvisor extends AbstractPointcutAdvisor {
public LogAdvisor() {
System.out.println("LogAdvisor");
}
@Override
public Pointcut getPointcut() {
return new AnnotationMatchingPointcut(null,Log.class,false);
}
@Override
public Advice getAdvice() {
return new LogMethodInterceptor();
}
private static class LogMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("before");
Object result = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("after");
return result;
}
}
}
public interface MaiPiao {
void maiPiao();
}
/**
* @author bigbird-0101
* @date 2024-06-27 23:07
*/
@Documented
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Log {
String value() default "";
}
@Service
public static class B {
@Log("123")
public void maiPiao()
{
System.out.println("B mai piao");
}
}
@Service
public static class A implements MaiPiao{
@Autowired
private B b;
@Override
public void maiPiao() {
b.maiPiao();
}
}
}
请注意我们的切面一定要声明这个 @Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE) 不然会跳过 前面已经讲过为啥会跳过
运行一下 可以看到已经成功运行,但是我们发现 这个日志切面对象LogAdvisor被构建了两次 这个咋回事呢?为啥?不是单例吗?我们debug一下,找下根本的问题。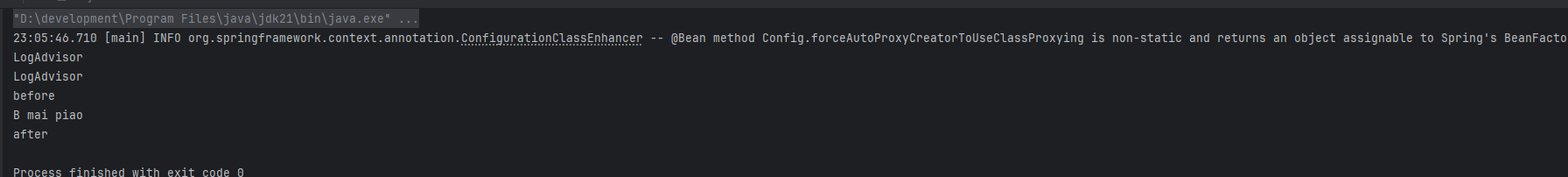
这个是第一次被调用的时候的截图。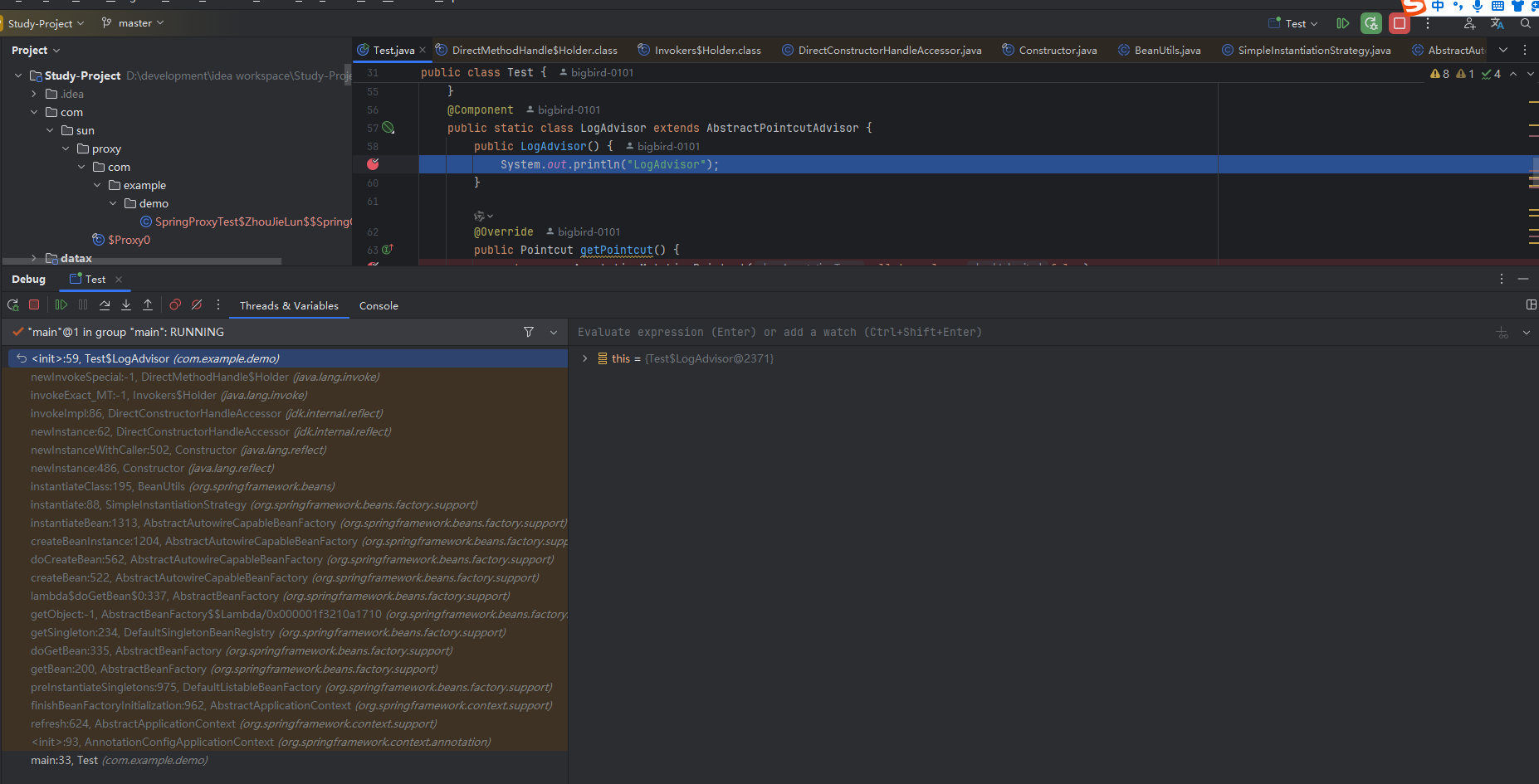
这个是第二次被调用时候的截图,卧槽我发现了 原来我的 LogAdvisor 被 Component注解修饰了,然后我又去声明导致创建了两次,去除Component这个注解重新运行一下。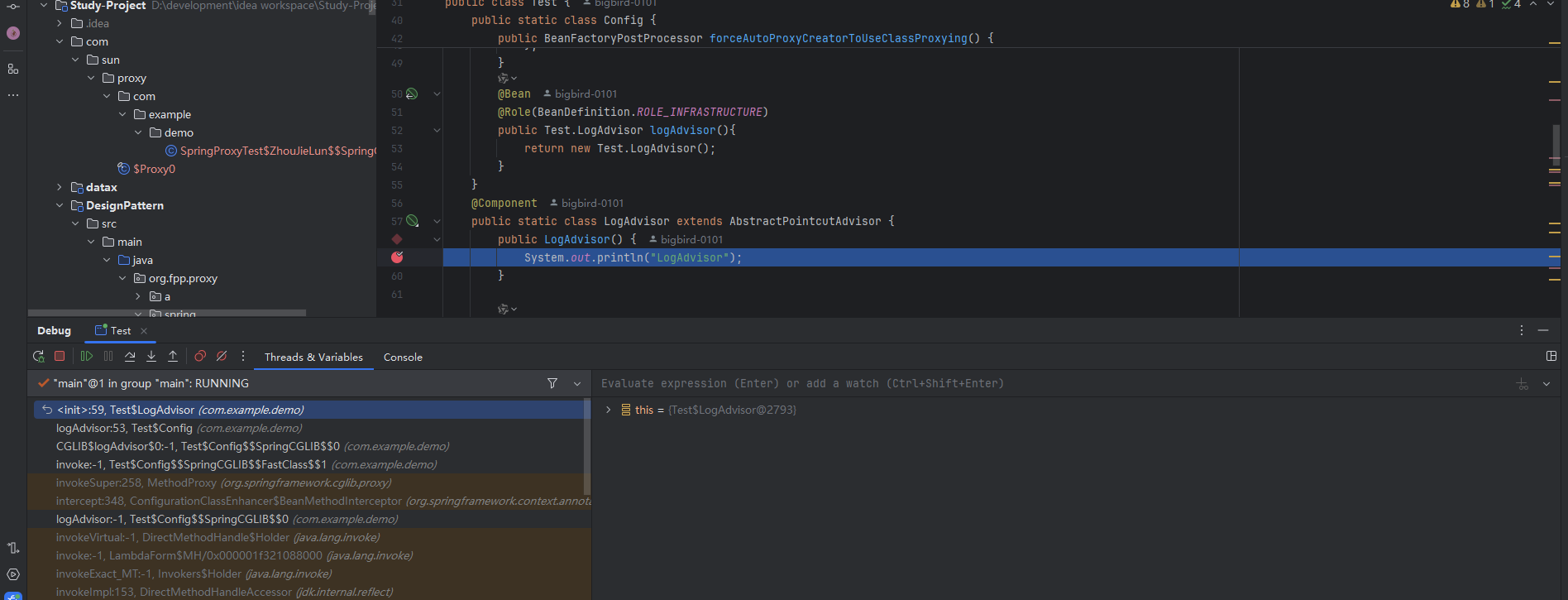
这个是结果 卧槽 咋还是两次 哪里还有声明,我仔细检查一看 卧槽前面 还声明了一次 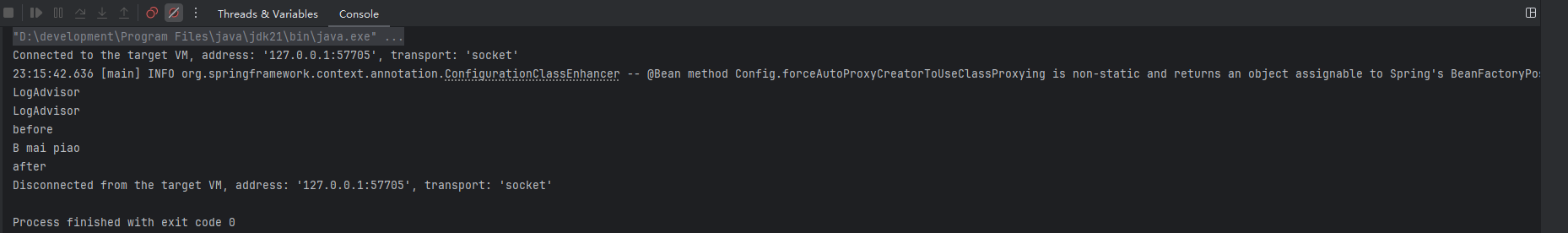
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class,
LogAdvisor.class,A.class,B.class);
去除其中的LogAdvisor,再试一下。
可以可以终于正常了,不容易啊。之前debug 没注意 写上去了。打完收工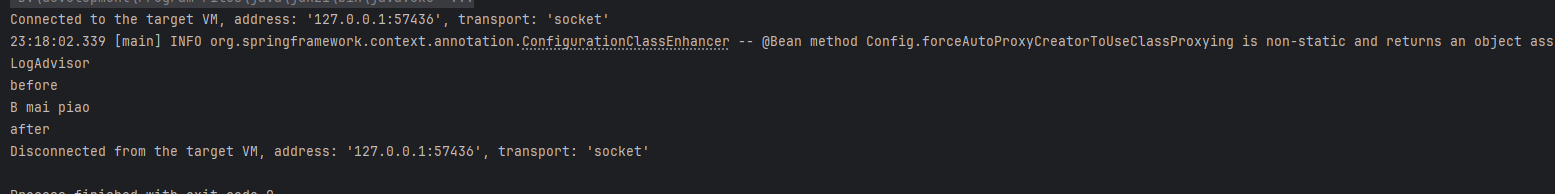
会话6:结束
- 👧哇,哥哥好厉害好厉害。
- 👨 哈哈哈哈哈哈,马马虎虎了。