- 一、操作数据库前的准备
- 二、封装操作数据库数据的相关操作
- 三、设计前后端交互的 API
- 四、实现在线编译运行功能
一、操作数据库前的准备
设计数据库表
我们需要对数据库中存储的题目进行操作.
创建一个 “题目表” oj_table
题目的序号 id. 作为题目表的自增主键。
标题 title.
难度 level. 题目分为 “简单”,“中等”,“困难” 三种难度。
描述 description. 题目的基本描述,示例,提示等信息。
代码模板 templateCode. 给用户展示的初始代码,用户要在此代码模板上开发。
测试用例 testCode. 一组测试的代码,判断用户的代码是否正确。
create database if not exists oj_database;
use oj_database;
drop table if exists oj_table;
create table oj_table(
id int primary key auto_increment,
title varchar(50),
level varchar(50),
description varchar(4096),
templateCode varchar(4096),
testCode varchar(4096)
);
封装数据库操作 DBUtil
public class DBUtil {
private static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/oj_database?characterEncoding=utf8%useSSL=false";
// 自己电脑上的 MySQL 账户密码
private static final String USERNAME = "root";
private static final String PASSWORD = "root";
//懒汉式
private static volatile DataSource dataSource = null;
private static DataSource getDataSource() {
if (dataSource == null) {
synchronized (DBUtil.class) {
if (dataSource == null) {
MysqlDataSource mysqlDataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
mysqlDataSource.setURL(URL);
mysqlDataSource.setUser(USERNAME);
mysqlDataSource.setPassword(PASSWORD);
dataSource = mysqlDataSource;
}
}
}
return dataSource;
}
// 提供方法获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return getDataSource().getConnection();
}
// 关闭释放连接的操作
public static void close(Connection connection, PreparedStatement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
存储题目实体类的Problem
public class Problem {
private int id;
private String title;
private String level;
private String description;
private String templateCode;
private String testCode;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getLevel() {
return level;
}
public void setLevel(String level) {
this.level = level;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public String getTemplateCode() {
return templateCode;
}
public void setTemplateCode(String templateCode) {
this.templateCode = templateCode;
}
public String getTestCode() {
return testCode;
}
public void setTestCode(String testCode) {
this.testCode = testCode;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Problem{" +
"id=" + id +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
", level='" + level + '\'' +
", description='" + description + '\'' +
", templateCode='" + templateCode + '\'' +
", testCode='" + testCode + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
二、封装操作数据库数据的相关操作
ProblemDAO
// 通过这个类来实现题目的增删改查
// 1. 新增题目
// 2. 删除题目
// 3. 查询题目列表
// 4. 查询题目详情
public class ProblemDAO {
// 1. 新增题目
public void insert(Problem problem) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
// 1. 获取数据库连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
// 2. 构造 SQL
String sql = "insert into oj_table values(null, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
// 3. 动态替换
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1, problem.getTitle());
statement.setString(2, problem.getLevel());
statement.setString(3, problem.getDescription());
statement.setString(4, problem.getTemplateCode());
statement.setString(5, problem.getTestCode());
// 4. 执行 SQL
int ret = statement.executeUpdate();
if (ret != 1) {
System.out.println("新增题目失败");
} else {
System.out.println("新增题目成功");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, null);
}
}
// 2. 删除题目
public void delete(int id) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "delete from oj_table where id = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1, id);
int ret = statement.executeUpdate();
if (ret != 1) {
System.out.println("删除题目失败!");
} else {
System.out.println("删除题目成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, null);
}
}
// 3. 查询题目
public List<Problem> selectAll() {
List<Problem> problems = new ArrayList<>();
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select id, title, level from oj_table";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()) {
Problem problem = new Problem();
problem.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
problem.setTitle(resultSet.getString("title"));
problem.setLevel(resultSet.getString("level"));
problems.add(problem);
}
return problems;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
return null;
}
// 4. 查询题目详情
public Problem selectOne(int id) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from oj_table where id = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1, id);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()) {
Problem problem = new Problem();
problem.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
problem.setTitle(resultSet.getString("title"));
problem.setLevel(resultSet.getString("level"));
problem.setDescription(resultSet.getString("description"));
problem.setTemplateCode(resultSet.getString("templateCode"));
problem.setTestCode(resultSet.getString("testCode"));
return problem;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
return null;
}
}
单元测试
测试功能是否有问题.
// 单元测试
private static void testInsert() {
ProblemDAO problemDAO = new ProblemDAO();
Problem problem = new Problem();
problem.setTitle("两数之和");
problem.setLevel("简单");
problem.setDescription("给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。\n" +
"\n" +
"你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。\n" +
"\n" +
"你可以按任意顺序返回答案。\n" +
"\n" +
" \n" +
"\n" +
"示例 1:\n" +
"\n" +
"输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9\n" +
"输出:[0,1]\n" +
"解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。\n" +
"示例 2:\n" +
"\n" +
"输入:nums = [3,2,4], target = 6\n" +
"输出:[1,2]\n" +
"示例 3:\n" +
"\n" +
"输入:nums = [3,3], target = 6\n" +
"输出:[0,1]\n" +
" \n" +
"\n" +
"提示:\n" +
"\n" +
"2 <= nums.length <= 104\n" +
"-109 <= nums[i] <= 109\n" +
"-109 <= target <= 109\n" +
"只会存在一个有效答案\n" +
" \n" +
"\n" +
"进阶:你可以想出一个时间复杂度小于 O(n2) 的算法吗?\n" +
"\n" +
"来源:力扣(LeetCode)\n" +
"链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/two-sum\n" +
"著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。");
problem.setTemplateCode("class Solution {\n" +
" public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {\n" +
"\n" +
" }\n" +
"}");
problem.setTestCode(" // 这个 main 方法就相当于测试用例的代码.\n" +
" public static void main(String[] args) {\n" +
" Solution solution = new Solution();\n" +
" // testcase1\n" +
" int[] nums = {2,7,11,15};\n" +
" int target = 9;\n" +
" int[] result = solution.twoSum(nums, target);\n" +
" if (result.length == 2 && result[0] == 0 && result[1] == 1) {\n" +
" System.out.println(\"testcase1 OK\");\n" +
" } else {\n" +
" System.out.println(\"testcase1 failed!\");\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" // testcase2\n" +
" int[] nums2 = {3,2,4};\n" +
" int target2 = 6;\n" +
" int[] result2 = solution.twoSum(nums2, target2);\n" +
" if (result2.length == 2 && result[0] == 1 && result[1] == 2) {\n" +
" System.out.println(\"testcase2 OK\");\n" +
" } else {\n" +
" System.out.println(\"testcase2 failed!\");\n" +
" }\n" +
" }");
problemDAO.insert(problem);
}
private static void testSelectAll() {
ProblemDAO problemDAO = new ProblemDAO();
List<Problem> problems = problemDAO.selectAll();
System.out.println(problems);
}
private static void testSelectOne() {
ProblemDAO problemDAO = new ProblemDAO();
Problem problem = problemDAO.selectOne(2);
System.out.println(problem);
}
private static void testDelete() {
ProblemDAO problemDAO = new ProblemDAO();
problemDAO.delete(2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// testInsert();
// testSelectAll();
// testSelectOne();
testDelete();
}
}
三、设计前后端交互的 API
已经把数据库的相关操作封装好了。
接下来可以设计服务器提供的 API,一些 HTTP 风格的接口,通过这些接口和网页前端进行交互。
需要设计哪些网页?
a)题目列表页。功能是展示当前题目的列表。方法:向服务器发送请求,题目的列表。
b)题目详情页。
功能一:展示题目的详细要求。方法:向服务器请求,获取指定题目的详细信息。
功能二:能够有一个代码编辑框,让用户来编写代码。此过程不需要和服务器交互,前端实现。
功能三:有提交按钮,点击提交按钮,就能把用户编辑的代码发送到服务器上,进行编译和运行,最后返回结果。方法:向服务器发送用户当前编写的代码,并获取到结果。
约定 API
目前比较流行的前后端交互的方式,主要是通过 JSON 格式来组织的。我们可以引入第三方库来帮忙解析 JSON 格式,会方便很多。
Jackson 依赖导入
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.fasterxml.jackson.core/jackson-databind -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.13.0</version>
</dependency>
具体设计以下几个前后端交互的 API
向服务器请求,题目的列表.
请求:GET /problem
响应:[{id:1, title:“两数之和”, level:“简单”,}, {id:2, title:“两数相加”, level:“简单”,}]
向服务器请求,获取指定题目的详细信息.
请求:GET /problem?id=1
响应:{id:1, title:“两数之和”, level:“简单”, description:“题目的详细要求…”, templateCode:“代码模板”, testCode:" ",}
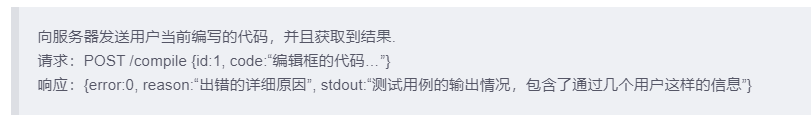
向服务器发送用户当前编写的代码,并且获取到结果.
请求:POST /compile {id:1, code:“编辑框的代码…”}
响应:{error:0, reason:“出错的详细原因”, stdout:“测试用例的输出情况,包含了通过几个用户这样的信息”}
编写获取题目列表和题目详细信息的功能
@WebServlet("/problem")
public class ProblemServlet extends HttpServlet {
// json 的核心类
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 设置状态码和格式
resp.setStatus(200);
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf8");
ProblemDAO problemDAO = new ProblemDAO();
// 尝试获取 id 参数,如果能获取到,说明是获取题目详情;如果不能获取到,说明是获取题目列表
String idString = req.getParameter("id");
if (idString == null || "".equals(idString)) {
// 没有获取到 id 字段,查询题目列表
List<Problem> problems = problemDAO.selectAll();
// 将 problems 进行转换成 json 结构的字符串
String respString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(problems);
// 将得到的字符串响应回去-设置 HTTP 响应的 body 部分
resp.getWriter().write(respString);
} else {
// 获取到了题目的 id,查询题目详情
Problem problem = problemDAO.selectOne(Integer.parseInt(idString));
String respString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(problem);
resp.getWriter().write(respString);
}
}
}
然后配置并启动 Tomcat,我们来测试是否能接收到请求。
能够通过网页请求到数据。
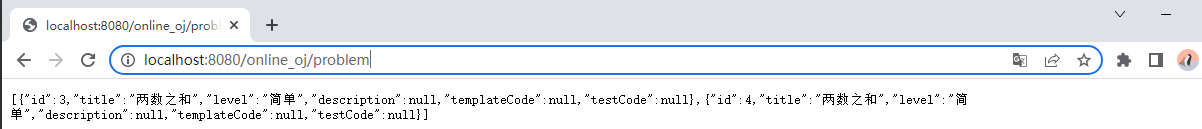
通过 Postman 也能够显示数据。
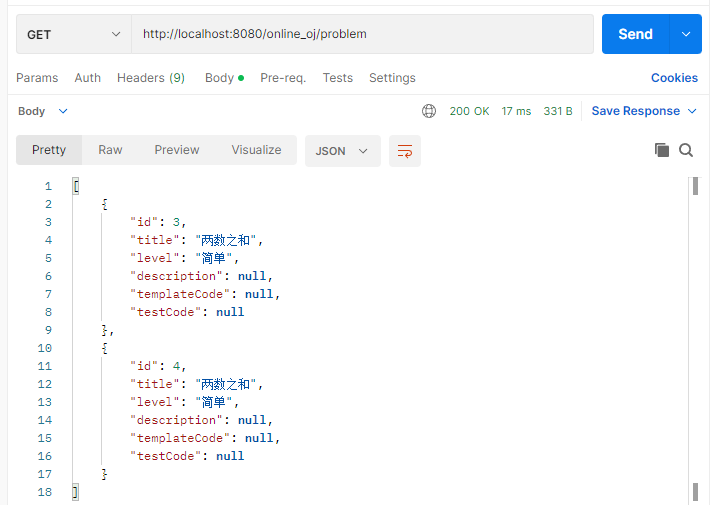
由于代码中通过 if 区分两种 API,所以我们可以尝试获取前端请求的 id 来测试是否能够获取到数据。
查找 id 为 1 的题目,显示 null。
通过 Postman 查询 id 为 4 的题目,能够显示。
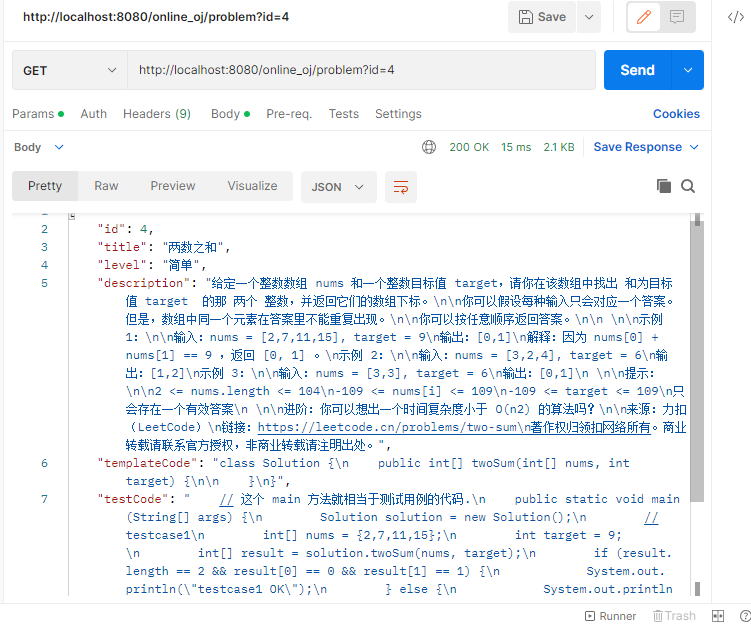
很显然可以获取到数据,接下来我们实现在线编译运行功能。
四、实现在线编译运行功能
用户提交的代码,只是一个 Solution 这样的类,里面包含了一个核心方法。而要想编译运行,还需要一个 main 方法。main 方法在测试用例代码中,测试用例代码就在数据库中。
当前编译运行,请求和响应都是 JSON 格式的数据。为了方便解析和构造,就可以创建两个类,来对应这两个 JSON 结构。
static class CompileRequest {
public int id;
public String code;
}
static class CompileResponse {
// 0 表示没问题,1 表示编译出错,2 表示运行异常,3 表示其它错误
public int error;
public String reason;
public String stdout;
}
这两个类可以写在 CompileServlet 类中.
@WebServlet("/compile")
public class CompileServlet extends HttpServlet {
static class CompileRequest {
public int id;
public String code;
}
static class CompileResponse {
// 0 表示没问题,1 表示编译出错,2 表示运行异常,3 表示其它错误
public int error;
public String stdout;
public String reason;
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
// 1. 读取请求的正文
String body = readBody(req);
// 2. 根据 id 从数据库中查找到题目的详情 - 得到测试用例代码
// 3. 把用户提交的代码和测试用例代码,拼接成一个完整的代码
// 4. 创建一个 Task 实例,调用里面的 compileAndRun 来解析编译运行
// 5. 根据 Task 运行的结果,包装成一个 HTTP 响应
}
我们要实现编译运行功能,需要经过以下几个步骤:
- 读取请求的正文
- 根据 id 从数据库中查找到题目的详情 - 得到测试用例代码
- 把用户提交的代码和测试用例代码,拼接成一个完整的代码
- 创建一个 Task 实例,调用里面的 compileAndRun 来解析编译运行
- 根据 Task 运行的结果,包装成一个 HTTP 响应
先看第一步,读取到请求的正文
我们使用个方法 readBody,封装一下获取请求正文的操作。
//获取请求头中的内容,转换成字符串类型
private static String readBody(HttpServletRequest req) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
// 1. 根据请求头里面的 ContentLength 获取到 body 的长度
int contentLength = req.getContentLength();
// 2. 按照这个长度准备好一个 byte[]
byte[] buffer = new byte[contentLength];
// 3. 通过 req 里面的方法,获取到 body 的流对象
try(InputStream inputStream = req.getInputStream()) {
// 4. 基于这个流对象,读取内容,然后把内容放到 byte[] 数字中即可
inputStream.read(buffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 5. 把这个 byte[] 的内容构造成一个 String,同时设置转换字符集格式
return new String(buffer, "utf8");
}
return new String(buffer, "utf8");
这段代码,相当于把一个二进制数据,转换成一个文本数据。
把 byte[] (以字节为单位),转换成 String (以字符为单位)。
而后续的 "utf8" 是为了在转换的过程中指定字符集,告诉编码方式。
从请求中读取的 byte[] 不清楚是哪种格式,需要在构造 String 的时候告诉 String,当前的 byte[] 是按照啥样的格式来编码。
补充完 readBody 方法,我们继续
package api;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import compile.Answer;
import compile.Question;
import compile.Task;
import dao.Problem;
import dao.ProblemDAO;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletInputStream;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
/**
* Created by cc
* Description:
* User: CZH
* Date: 2023-01-29
* Time: 14:43
*/
@WebServlet("/compile")
public class CompileServlet extends HttpServlet {
static class CompileRequest {
public int id;
public String code;
}
static class CompileResponse {
// 0 表示没问题,1 表示编译出错,2 表示运行异常,3 表示其它错误
public int error;
public String stdout;
public String reason;
}
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 1. 读取请求的正文,别按照 JSON 格式解析
String body = readBody(req);
// 类对象,获取类的信息
CompileRequest compileRequest = objectMapper.readValue(body, CompileRequest.class);
// 2. 根据 id 从数据库中查找到题目的详情 - 得到测试用例代码
// 3. 把用户提交的代码和测试用例代码,拼接成一个完整的代码
// 4. 创建一个 Task 实例,调用里面的 compileAndRun 来解析编译运行
// 5. 根据 Task 运行的结果,包装成一个 HTTP 响应
}
// 通过请求头获取数据,转换成String 返回
private static String readBody(HttpServletRequest req) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
int contentLength = req.getContentLength();
byte[] bytes = new byte[contentLength];
try(InputStream inputStream = req.getInputStream()) {
inputStream.read(bytes);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new String(bytes, "utf8");
}
}

这段代码,就是根据类对象 CompileRequest.class,获取到 CompileRequest 这个类都有哪些属性,叫什么名字,依次遍历这些属性。
例如拿到 id 这个属性,就去 json 字符串中找 key 为 id 的键值对。发现 value 是 2,于是就把 2 赋值到 new 出来的 CompileRequest 的 id 字段中。
完成步骤二的代码.
根据 id 从数据库中查找到题目的详情,从而得到测试用例代码。
// 2. 根据 id 从数据库中查找到题目的详情 - 得到测试用例代码
ProblemDAO problemDAO = new ProblemDAO();
Problem problem = problemDAO.selectOne(compileRequest.id);
// testCode 是测试用例的代码
String testCode = problem.getTestCode();
// requestCode 是用户提交的代码
String requestCode = compileRequest.code;
完成步骤三的代码.
把用户提交的代码和测试用例代码,拼接成一个完整的代码。
拼接的思路呢,其实就是把 testCode 的这个 main 方法,嵌入到 requestCode 里面,做法就是把 testCode 放到 Solution 的最后一个 } 的前面即可~
// 3. 把用户提交的代码和测试用例代码,拼接成一个完整的代码
String finalCode = mergeCode(requestCode, testCode);
// 拼接代码
private static String mergeCode(String requestCode, String testCode) {
// 1. 查找 requestCode 最后一个 }
int pos = requestCode.lastIndexOf("}");
if (pos == -1) {
return null;
}
// 2. 截取字符串
String substring = requestCode.substring(0, pos);
// 3. 拼接字符串并返回
return substring + testCode + "\n}";
}
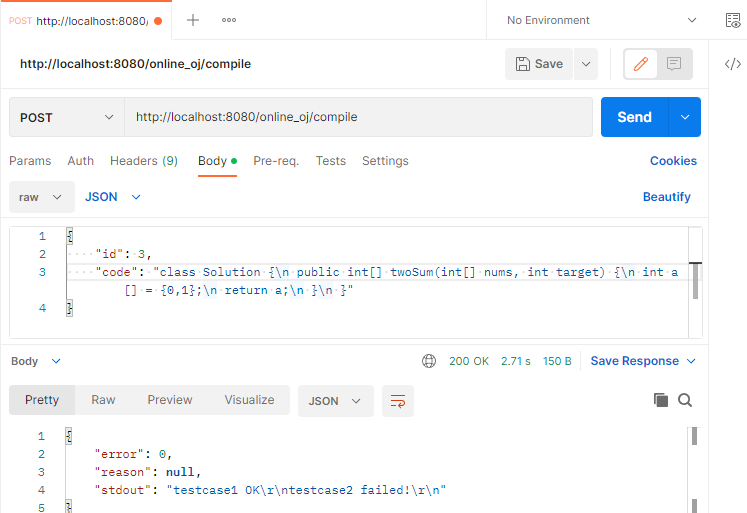
到这里我们测试一波~
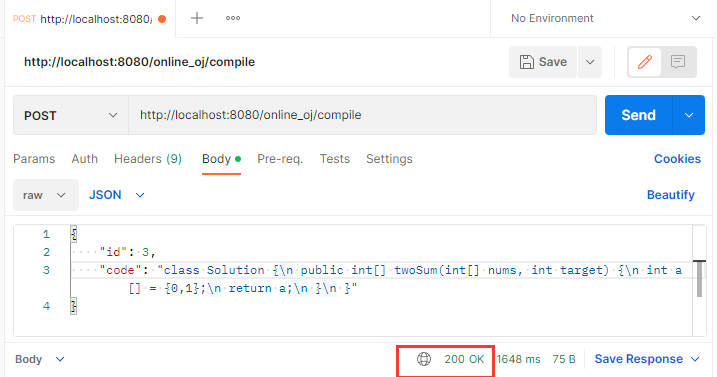
目前看没什么问题,继续…
完成步骤四代码.
创建一个 Task 实例,调用里面的 compileAndRun 来解析编译运行.
// 4. 创建一个 Task 实例,调用里面的 compileAndRun 来解析编译运行
Task task = new Task();
Question question = new Question();
question.setCode(finalCode);
Answer answer = task.compileAndRun(question);
完成步骤五代码.
根据 Task 运行的结果,包装成一个 HTTP 响应.
// 5. 根据 Task 运行的结果,包装成一个 HTTP 响应
CompileResponse compileResponse = new CompileResponse();
compileResponse.error = answer.getError();
compileResponse.reason = answer.getReason();
compileResponse.stdout = answer.getStdout();
String respString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(compileResponse);
resp.getWriter().write(respString);
进行测试~
能够得到数据,没问题~