一、链表的概念及结构
概念:链表是⼀种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。
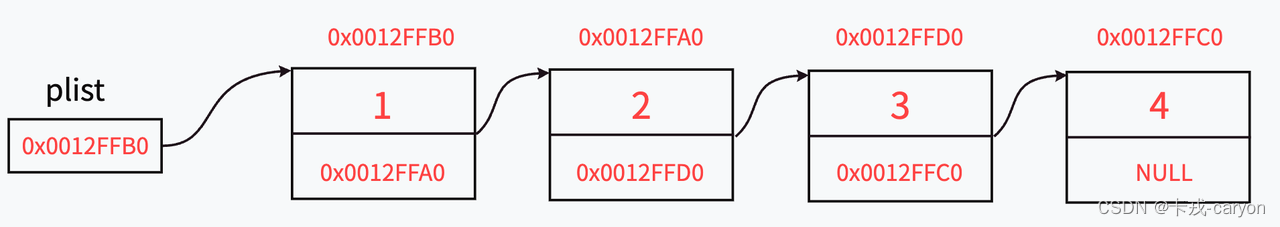
节点的组成主要有两个部分:当前节点要保存的数据和保存下⼀个节点的地址(指针变量)。
补充说明:
1.链式机构在逻辑上是连续的,在物理结构上不⼀定连续
2、节点⼀般是从堆上申请的
3、从堆上申请来的空间,是按照⼀定策略分配出来的,每次申请的空间可能连续,可能不连续
二、单链表的实现
2.1节点的定义
typedef int SLDataType;
//定义链表结构体
typedef struct SList
{
SLDataType data;//数据域
struct SList* next;//指针域
}SL;
2.2单链表的打印
void SLPrint(SL** pphead)
{
SL* cur = *pphead;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
2.3单链表的增删查改
这里由于申请结点使用较多,我们将其封装为一个函数。
//获得新节点
SL* SListBuynode(SLDataType x)
{
SL* newnode = (SL*)malloc(sizeof(SL));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("SListBuyNode is failed");
return 1;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
//尾插
void SLPushBack(SL** pphead, SLDataType x)
{
assert(pphead);
SL* newnode = SListBuynode(x);
//链表没有元素时
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newnode;
return;
}
//链表有元素时
SL* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
//尾删
void SLPopBack(SL** pphead)
{
assert(*pphead);
assert(pphead);
//删除的时头结点
if ((*pphead)->next==NULL)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
return;
}
//删除的不是头结点
SL* cur_tail = *pphead;
SL* cur = NULL;
while (cur_tail->next)
{
cur = cur_tail;
cur_tail = cur_tail->next;
}
cur->next = NULL;
free(cur_tail);
cur_tail = NULL;
}
//头插
void SLPushFront(SL** pphead, SLDataType x)
{
assert(pphead);
SL* newnode = SListBuynode(x);
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
//头删
void SLPopFront(SL** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
SL* cur_head = (*pphead)->next;
free(*pphead);
*pphead = cur_head;
}
//查找
SL* SLFind(SL** pphead, SLDataType x)
{
assert(pphead);
SL* cur = *pphead;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//任意位置之前插入
void SLInsert(SL** pphead, SL* pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
assert(pos);
SL* newnode = SListBuynode(x);
//pos是头结点
if (*pphead == pos)
{
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
return;
}
//pos不是头结点
SL* cur = *pphead;
while (cur->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
newnode->next =pos;
cur->next = newnode;
}
//指定位置之后插入
void SLInsertAfter(SL* pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
SL* newnode = SListBuynode(x);
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
}
//任意位置删除
void SLErase(SL** pphead, SL* pos)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
assert(pos);
//pos是头结点
if (*pphead == pos)
{
SL* newhead = (*pphead)->next;
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
*pphead = newhead;
return;
}
//pos不是头结点
SL* cur = *pphead;
while (cur->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}
//删除指定位置之后的元素
void SLEraseAfter(SL* pos)
{
assert(pos);
assert(pos->next);
SL* cur = pos->next;
pos->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
2.4单链表的销毁
//销毁链表
void SLDestroy(SL** pphead)
{
SL* cur = *pphead;
while (cur)
{
SL* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
*pphead = NULL;
}
2.5 单链表的源代码
//SingleList.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SList
{
SLDataType data;
struct SList* next;
}SL;
void SLPrint(SL** pphead);//打印
void SLPushBack(SL** pphead, SLDataType x);//尾插
void SLPopBack(SL** pphead);//尾删
void SLPushFront(SL** pphead, SLDataType x);//头插
void SLPopFront(SL** pphead);//头删
void SLInsert(SL** pphead, SL* pos, SLDataType x);//指定位置之前插入
void SLInsertAfter( SL* pos, SLDataType x);//指定位置之后插入
SL* SLFind(SL** pphead, SLDataType x);//查找
void SLErase(SL** pphead, SL* pos);//指定位置元素删除
void SLEraseAfter(SL* pos);//删除指定位置之后的元素
void SLDestroy(SL** pphead);//销毁链表
//SingleList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"SL.h"
void SLPrint(SL** pphead)
{
SL* cur = *pphead;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
SL* SListBuynode(SLDataType x)//获得新节点
{
SL* newnode = (SL*)malloc(sizeof(SL));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("SListBuyNode is failed");
return 1;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
void SLPushBack(SL** pphead, SLDataType x)//尾插
{
assert(pphead);
SL* newnode = SListBuynode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newnode;
return;
}
SL* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
void SLPopBack(SL** pphead)//尾删
{
assert(*pphead);
assert(pphead);
if ((*pphead)->next==NULL)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
return;
}
SL* cur_tail = *pphead;
SL* cur = NULL;
while (cur_tail->next)
{
cur = cur_tail;
cur_tail = cur_tail->next;
}
cur->next = NULL;
free(cur_tail);
cur_tail = NULL;
}
void SLPushFront(SL** pphead, SLDataType x)//头插
{
assert(pphead);
SL* newnode = SListBuynode(x);
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
void SLPopFront(SL** pphead)//头删
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
SL* cur_head = (*pphead)->next;
free(*pphead);
*pphead = cur_head;
}
SL* SLFind(SL** pphead, SLDataType x)//查找
{
assert(pphead);
SL* cur = *pphead;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
void SLInsert(SL** pphead, SL* pos, SLDataType x)//任意位置插入
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
assert(pos);
SL* newnode = SListBuynode(x);
if (*pphead == pos)//pos是头结点
{
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
return;
}
//pos不是头结点
SL* cur = *pphead;
while (cur->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
newnode->next =pos;
cur->next = newnode;
}
void SLInsertAfter(SL* pos, SLDataType x)//指定位置之后插入
{
assert(pos);
SL* newnode = SListBuynode(x);
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
}
void SLErase(SL** pphead, SL* pos)//任意位置删除
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
assert(pos);
//pos是头结点
if (*pphead == pos)
{
SL* newhead = (*pphead)->next;
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
*pphead = newhead;
return;
}
//pos不是头结点
SL* cur = *pphead;
while (cur->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}
void SLEraseAfter(SL* pos)//删除指定位置之后的元素
{
assert(pos);
assert(pos->next);
SL* cur = pos->next;
pos->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
void SLDestroy(SL** pphead)//销毁链表
{
SL* cur = *pphead;
while (cur)
{
SL* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
cur = next;
}
*pphead = NULL;
}
三、链表的分类
链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有8种(2x2x2)链表结构:
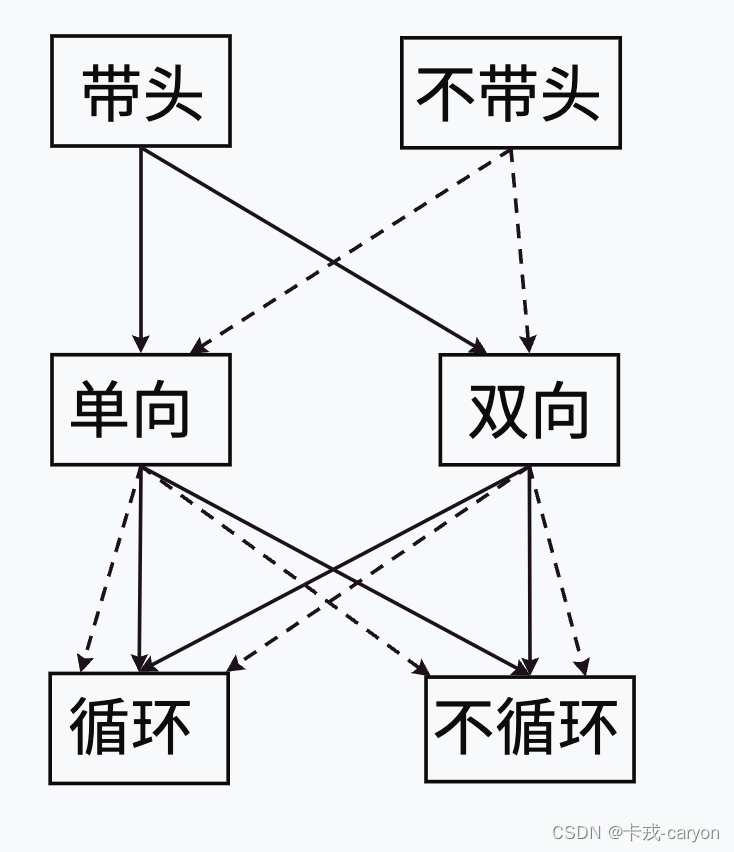
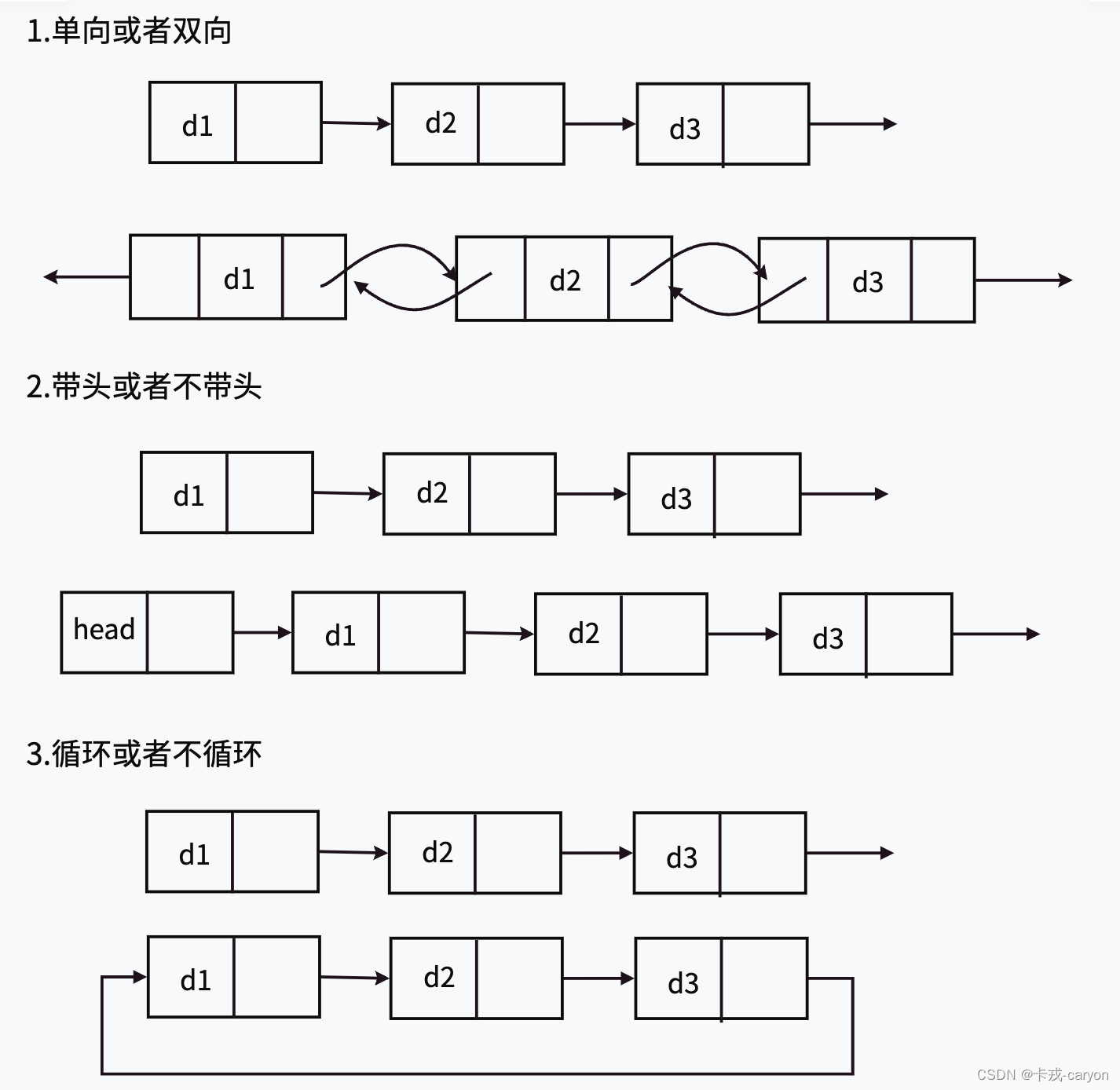
虽然有这么多的链表的结构,但是我们实际中最常用还是两种结构:单链表和双向带头循环链表
- 无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,⼀般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。
- 带头双向循环链表:结构最复杂,⼀般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。另外这个结构虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现结构会带来很多优势,实现反而简单了,后面我们代码实现了就知道了。