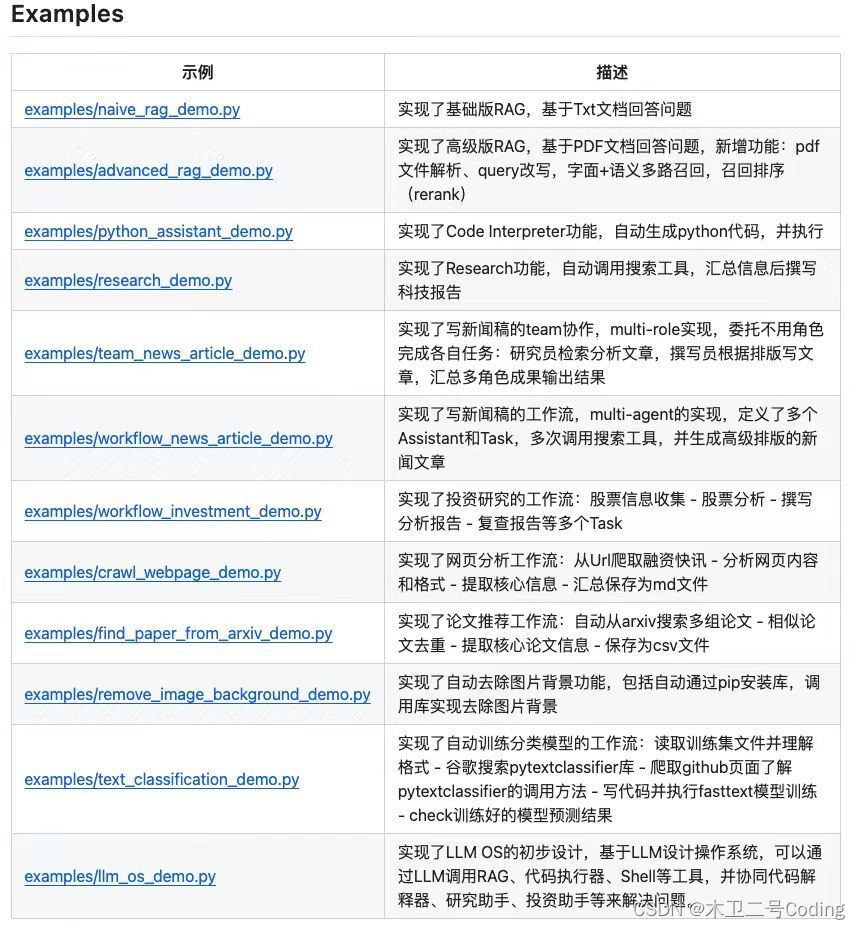
文章目录
- 快速失败机制(fail-fast)
- for-each删除元素为什么报错
- 原因分析
- 逻辑分析
- 如何正确的删除元素
- remove 后 break
- for 循环
- 使用 Iterator
- 总结
快速失败机制(fail-fast)
In systems design, a fail-fast system is one which immediately reports at its interface any condition that is likely to indicate a failure. Fail-fast systems are usually designed to stop normal operation rather than attempt to continue a possibly flawed process. Such designs often check the system’s state at several points in an operation, so any failures can be detected early. The responsibility of a fail-fast module is detecting errors, then letting the next-highest level of the system handle them.
这是快速失败机制的英文解释。翻译过来就是:系统设计中,“fail-fast”指的是一种策略,系统或模块被设计成在出现错误或失败时立即检测并报告。这种方法旨在通过停止正常操作而不是继续可能存在缺陷的过程来最小化失败的影响。fail-fast系统通常在操作的多个点检查系统状态,以便及早发现任何失败。fail-fast模块的责任是检测错误,然后让系统的更高级别处理它们。
这段话的大致意思就是,fail-fast 是一种通用的系统设计思想,一旦检测到可能会发生错误,就立马抛出异常,程序将不再往下执行
很多时候,我们会把 fail-fast 归类为 Java 集合框架的一种错误检测机制,但其实 fail-fast 并不是 Java 集合框架特有的机制
for-each删除元素为什么报错
下面这段代码:
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
list.add("3");
for (String str : list) {
if ("1".equals(str)) {
list.remove(str);
}
}
System.out.println(list);
在执行完之后就会报错
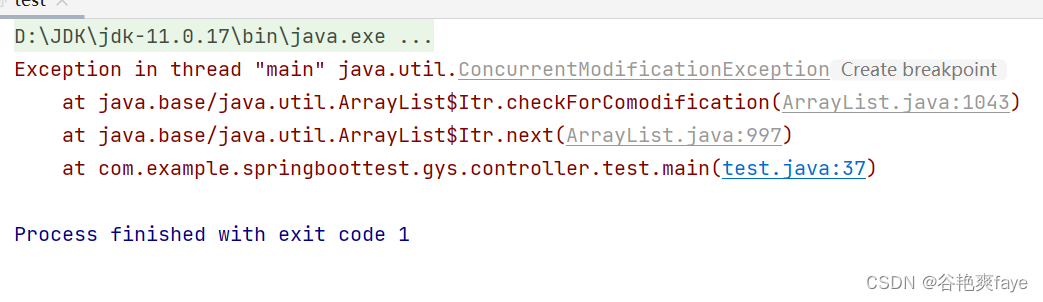
看一下报错的原因是在checkForComodification这里报的错。下面是具体的代码
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
也就是说,remove 的时候触发执行了 checkForComodification 方法,该方法对 modCount 和 expectedModCount 进行了比较,发现两者不等,就抛出了 ConcurrentModificationException 异常。
原因分析
为什么会执行checkForComodification 方法呢?是因为for-each的底层是迭代器Iterator配合while来实现的
List<String> list = new ArrayList();
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
list.add("3");
Iterator var2 = list.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
String str = (String)var2.next();
if ("1".equals(str)) {
list.remove(str);
}
}
System.out.println(list);
看一下list的迭代器,点进iterator这个方法,发现它实现了Iterator接口
再去看一下 Itr 这个类。
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
// prevent creating a synthetic constructor
Itr() {}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
@Override
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i < size) {
final Object[] es = elementData;
if (i >= es.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
for (; i < size && modCount == expectedModCount; i++)
action.accept(elementAt(es, i));
// update once at end to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
也就是说 new Itr() 的时候 expectedModCount 被赋值为 modCount,而 modCount 是 ArrayList 中的一个计数器,用于记录 ArrayList 对象被修改的次数。ArrayList 的修改操作包括添加、删除、设置元素值等。每次对 ArrayList 进行修改操作时,modCount 的值会自增 1。
在迭代 ArrayList 时,如果迭代过程中发现 modCount 的值与迭代器的 expectedModCount 不一致,则说明 ArrayList 已被修改过,此时会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 异常。这种机制可以保证迭代器在遍历 ArrayList 时,不会遗漏或重复元素,同时也可以在多线程环境下检测到并发修改问题。
逻辑分析
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
list.add("3");
for (String str : list) {
if ("1".equals(str)) {
list.remove(str);
}
}
System.out.println(list);
由于 list 此前执行了 3 次 add 方法。
- add 方法调用 ensureCapacityInternal 方法
- ensureCapacityInternal 方法调用ensureExplicitCapacity 方法
- ensureExplicitCapacity 方法中会执行 modCount++
所以 modCount 的值在经过三次 add 后为 3,于是 new Itr() 后 expectedModCount 的值也为 3(回到前面去看一下 Itr 的源码)。
接着来执行 for-each 的循环遍历。
执行第一次循环时,发现“沉默王二”等于 str,于是执行 list.remove(str)。
- remove 方法调用 fastRemove 方法
- fastRemove 方法中会执行 modCount++
modCount 的值变成了 4。
第二次遍历时,会执行 Itr 的 next 方法(String str = (String) var3.next();),next 方法就会调用 checkForComodification 方法。
此时 expectedModCount 为 3,modCount 为 4,就只好抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 异常了。
如何正确的删除元素
remove 后 break
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
list.add("3");
for (String str : list) {
if (1".equals(str)) {
list.remove(str);
break;
}
}
break 后循环就不再遍历了,意味着 Iterator 的 next 方法不再执行了,也就意味着 checkForComodification 方法不再执行了,所以异常也就不会抛出了。
但是呢,当 List 中有重复元素要删除的时候,break 就不合适了。
for 循环
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
list.add("3");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String str = list.get(i);
if ("1".equals(str)) {
list.remove(str);
}
}
for 循环虽然可以避开 fail-fast 保护机制,也就说 remove 元素后不再抛出异常;但是呢,这段程序在原则上是有问题的。为什么呢?
第一次循环的时候,i 为 0,list.size() 为 3,当执行完 remove 方法后,i 为 1,list.size() 却变成了 2,因为 list 的大小在 remove 后发生了变化,也就意味着“2”这个元素被跳过了。能明白吗?
remove 之前 list.get(1) 为“2”;但 remove 之后 list.get(1) 变成了“3”,而 list.get(0) 变成了“2”
使用 Iterator
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
list.add("3");
Iterator<String> itr = list.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
String str = itr.next();
if ("1".equals(str)) {
itr.remove();
}
}
为什么使用 Iterator 的 remove 方法就可以避开 fail-fast 保护机制呢?看一下 remove 的源码就明白了。
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0) // 如果没有上一个返回元素的索引,则抛出异常
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification(); // 检查 ArrayList 是否被修改过
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet); // 删除上一个返回元素
cursor = lastRet; // 更新下一个元素的索引
lastRet = -1; // 清空上一个返回元素的索引
expectedModCount = modCount; // 更新 ArrayList 的修改次数
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); // 抛出异常
}
}
删除完会执行 expectedModCount = modCount,保证了 expectedModCount 与 modCount 的同步
总结
在使用 foreach 循环(或称 for-each 循环)遍历集合时,通常不能直接删除集合中的元素,原因如下:
Concurrent Modification Exception:
当使用 foreach 循环遍历集合时,集合的结构不能被修改(例如添加或删除元素),否则会导致 ConcurrentModificationException 异常。这是因为 foreach 循环在背后使用迭代器来遍历集合,而迭代器在遍历时会维护一个 expected modCount(修改计数器),如果在遍历过程中修改了集合的结构,迭代器会检测到并抛出异常。
Invalidation of Iterator:
删除元素后,集合的结构发生变化,这可能会使当前的迭代器失效。如果集合的结构发生了变化,迭代器可能无法正确遍历集合的剩余部分或者导致未定义行为。
Potential Logical Errors:
直接在 foreach 循环内删除元素可能会导致逻辑错误。例如,如果不正确地更新迭代器或集合的大小,可能会导致遍历的元素不完整或错误。
为了安全地从集合中删除元素,应该使用迭代器的 remove() 方法。迭代器的 remove() 方法允许在遍历时安全地删除当前元素,同时更新集合的结构和迭代器的状态,避免了上述问题。







![[软件安装]linux下安装steam](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/089759e656584af0acde53542e679911.png)