本文主要探讨C++类的相关知识。
构造和析构函数
构造函数(可多个):对象产生时调用初始化class属性、分配class内部需要的动态内存
析构函数(一个):对对象消亡时调用回收分配动态内存
C++提供默认构造和析构,构造函数可重载,析构函数不需重载
构造和析构函数不需要返回值类型,构造函数可带参或不带参,析构函数不带参
无其他构造函数时默认构造函数可省略,有构造函数时默认构造函数不能省
class声明时可给构造函数形参赋默认值,调用时不传参则使用默认值,调用不能有重载歧义
所有参数都带默认值构造函数,可以表示所有构造函数
拷贝构造函数:用对象来初始化对象,函数不需重载
浅拷贝:普通成员变量初始化的拷贝构造函数(默认提供),有动态内存分配时出错
深拷贝:浅拷贝无法拷贝对象的成员指针已分配的内存空间,深拷贝可以
拷贝显式提供copy constructor为深拷贝,拷贝构造函数用原来的析构函数
权限
public类内、类外可访问,子类可访问父类公共成员
protected类内可访问,类外不可,子类可访问父类保护成员
private类内可访问,类外不可,子类不可访问父类私有成员
默认是private继承,struct是public继承
继承中父类所有权限继承给子类
public继承:父类成员在子类中保持原有访问权限
private继承:父类成员在子类中变为private权限
protected继承:父类public变protected,protected为protected,private为private
using:private/protected继承父类public中成员后权限变小,可通过using回归到public权限
struct和class
C不支持成员函数,C++支持
C不支持static成员,C++中支持
C默认public,C++默认public,c++可指定public/private/protected权限
C不支持继承(通过包含结构体指针实现),C++支持且struct和class可互相继承
C++中struct和class:struct默认public,class默认private,struct和class交叉继承权限取决子类
派生类和基类
派生类不继承基类构造和析构函数,只继承成员变量和成员方法,派生类有自己构造和析构
派生类构造函数执行前,先调用基类构造函数,再调用自己构造函数
派生类先执行自己析构函数,再执行基类析构函数
派生类覆盖基类同名成员(重定义),父类的同名成员存在且被隐藏,可通过全域路径调用被隐藏的方法,可添加派生类独有成员
派生类是基类的超集,基类对象放大成派生类可能出错,派生类赋值给基类可正常使用(类似char和int的兼容性)
多继承二义性和多态
C多继承A和B,A和B有同名成员、菱形继承(B1:A, B2:A, C:B1,B2)造成二义性
全域路径调用方法,重定义子类方法,重写虚函数解决二义性
基类方法声明为virtual,派生类重写同名方以实现多态
重载函数名相同参数列表不同,重定义子类实现父类同名方法后把父类方法隐藏
重写子类去实现父类同名virtual方法实现多态特性
虚函数
抽象类:有纯虚函数的类,抽象类只能为基类派生新类,不可实例化对象
派生类必须实现基类纯虚函数才能用于实例化对象,否则派生类仍为基类
接口:类中所有成员函数是public且是纯虚函数
无虚构造函数,包含虚函数的类只能作为基类派生新类,无法实例化对象,构造函数是在实例化的时候被调用的,故无虚构造函数
抽象基类(接口)指针指向派生类(new派生类对象:person *p = new man; delete p;),抽象基类(接口)析构函数需要为虚,才可删除指针时能正确调用派生类析构函数,否则不会调用派生类析构函数
抽象基类(接口)指针指向派生类(定义好的派生类man m;person *p = &m;),抽象基类(接口)析构函数是否为虚,都能正常调用派生类析构函数,一般抽象基类(接口)的析构函数都定义为虚
运算符重载
运算符重载是重定义对象运算符对应函数
赋值运算符=默认提供,重载有指针成员时涉及浅拷贝和深拷贝
++a对应Type& operator++(void);
a++,对应Type& operator++(int x);
不可重载运算符: .,.*, ->*,sizeof,?,:,#
静态成员
静态成员属于class本身,不属于对象
静态成员变量在类的多个对象中均可访问,且是同一个
静态成员变量和方法可以用对象调用,也可不产生对象的本身调用
静态数据成员不在类中初始化,类只定义模版
静态数据成员不在类构造函数中初始化,构造函数用于构建对象时初始化对象成员
静态数据成员值默认0,遵循public,private,protected访问准则
静态方法只访问静态成员变量和方法,不能直接访问非静态,需要通过函数传参访问非静态
静态成员变量可用于统计对象数
静态类:内部全是静态成员,不能被实例化,不包括构造函数,不能实现接口(不能被继承),不能有实例成员
静态类成员不能有protected或protected internal访问保护修饰符
友元函数
友元函数不是本类成员函数,是外部函数
友元函数在private或protected或public都可
可以通过类来访问友元函数,不能直接通过友元函数访问类(常用传参访问)
友元函数破坏了封装机制,实现类之间数据共享时减少系统开销,提高效率
运算符重载可用友元函数除=,->,[],()
类间的数据共享可用友元函数
demo1:
类成员权限,构造和析构函数,深拷贝和浅拷贝
目录:
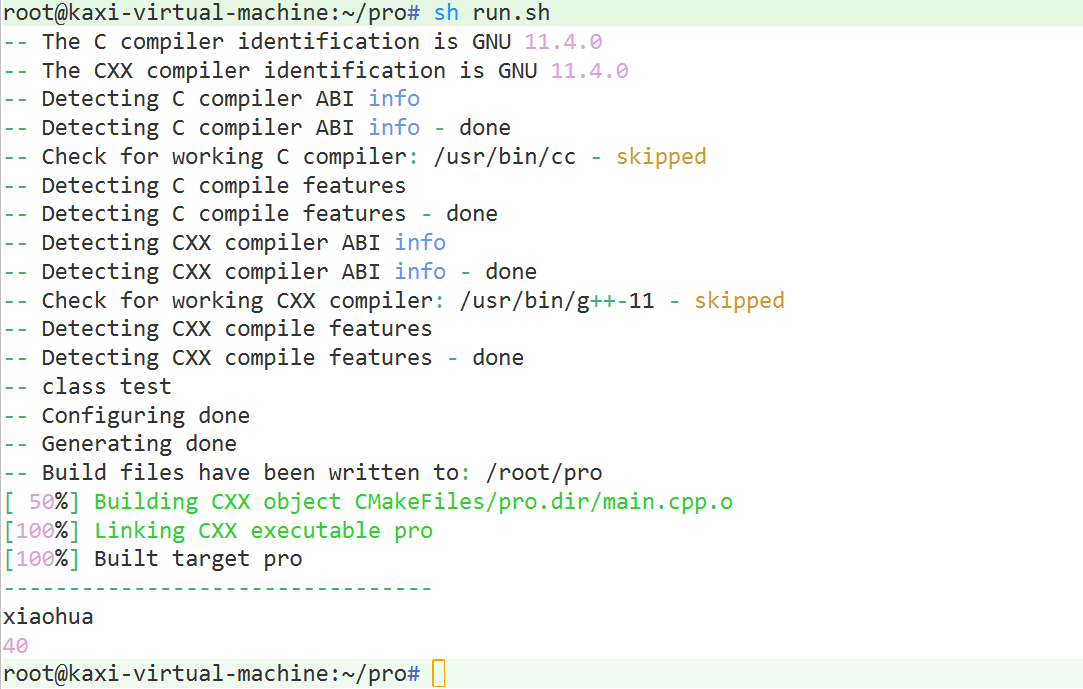
run.sh
#!/bin/bash
if [ -f ./Makefile ]
then
make clean
fi
cmake .
make
echo "---------------------------------"
./proCMakeLists.txt
CMAKE_MINIMUM_REQUIRED(VERSION 2.20) #最低版本要求
SET(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER "g++") #设置g++编译器
PROJECT(CLASS) #设置工程名
MESSAGE(STATUS "class test") #打印消息
ADD_EXECUTABLE(pro main.cpp person.cpp) #生成可执行文件person.hpp
#ifndef __PERSON_HPP__
#define __PERSON_HPP__
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace People
{
class Person
{
public:
string name;
int age;
string sex;
string description;
int *luck_num;
Person();
Person(string name = "xxx",int age = 0,string sex = "none",string description = "none");
Person(const Person &p);
~Person();
void set_info(string name,int age,string sex,string description);
void print_info();
void set_income(int income);
int get_income();
void set_savings_account(int savings_account);
int get_savings_account();
private:
int income;
int savings_account;
};
}
#endifperson.cpp
#include "person.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void People::Person::set_info(string name,int age,string sex,string description)
{
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
this->sex = sex;
this->description = description;
}
void People::Person::print_info()
{
cout << "name :" << this->name << endl;
cout << "age :" << this->age << endl;
cout << "sex :" << this->sex << endl;
cout << "description :" << this->description << endl;
cout << "income " << get_income() << endl;
cout << "savings_account " << get_savings_account() << endl;
cout << "luck_num : " << this->luck_num[0] << " " << this->luck_num[1] << endl;
}
void People::Person::set_income(int income)
{
this->income = income;
}
int People::Person::get_income()
{
return this->income;
}
void People::Person::set_savings_account(int savings_account)
{
this->savings_account = savings_account;
}
int People::Person::get_savings_account()
{
return this->savings_account;
}
People::Person::Person()
{
cout << "default constructor function" << endl;
}
People::Person::Person(string name,int age,string sex,string description):name(name),age(age),sex(sex),description(description)
{
this->luck_num = new int[2];
cout << "user define constructor function" << endl;
}
People::Person::~Person()
{
delete [] this->luck_num;
cout << "user define destructor function" << endl;
}
People::Person::Person(const Person &p):name(p.name),age(p.age),sex(p.sex),description(p.description)
{
luck_num = new int(*p.luck_num);
cout << "user define deep copy constructor function" << endl;
}main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "person.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace People;
int main()
{
Person p1("xiaoming",23,"male","high");
p1.set_income(50);
p1.set_savings_account(100);
p1.luck_num[0] = 2;
p1.luck_num[1] = 7;
p1.print_info();
Person p2(p1);
p2.set_income(20);
p2.set_savings_account(10);
p2.luck_num[0] = 36;
p2.luck_num[1] = 72;
p2.print_info();
Person p3 = p2;
p3.set_income(10);
p3.set_savings_account(40);
p3.luck_num[0] = 5;
p3.luck_num[1] = 8;
p3.print_info();
return 0;
}结果示例:
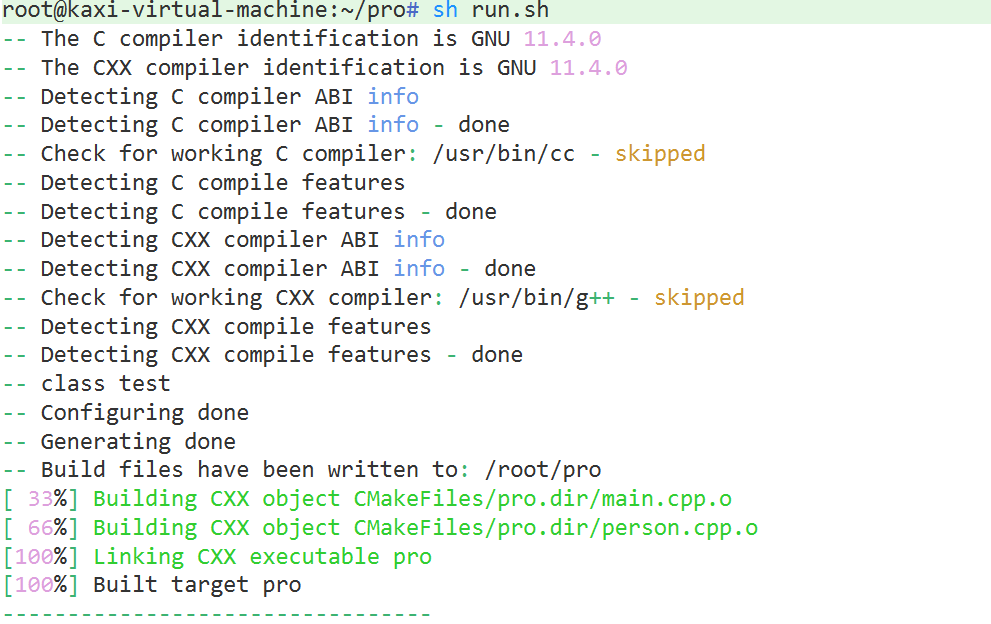
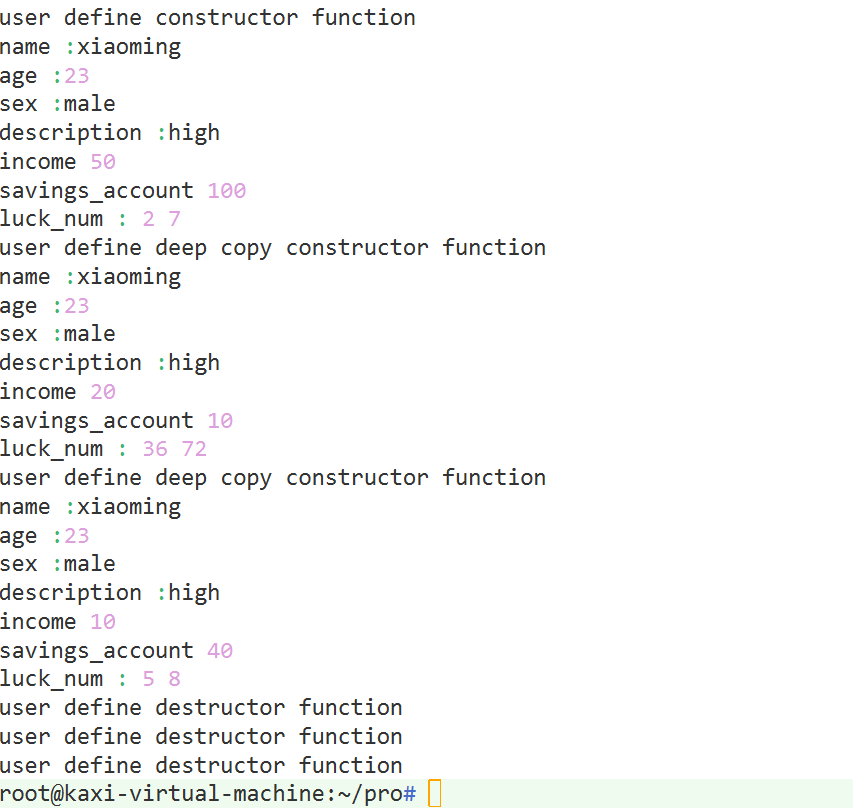
demo2:
继承和多态,虚函数,抽象类,接口
目录:
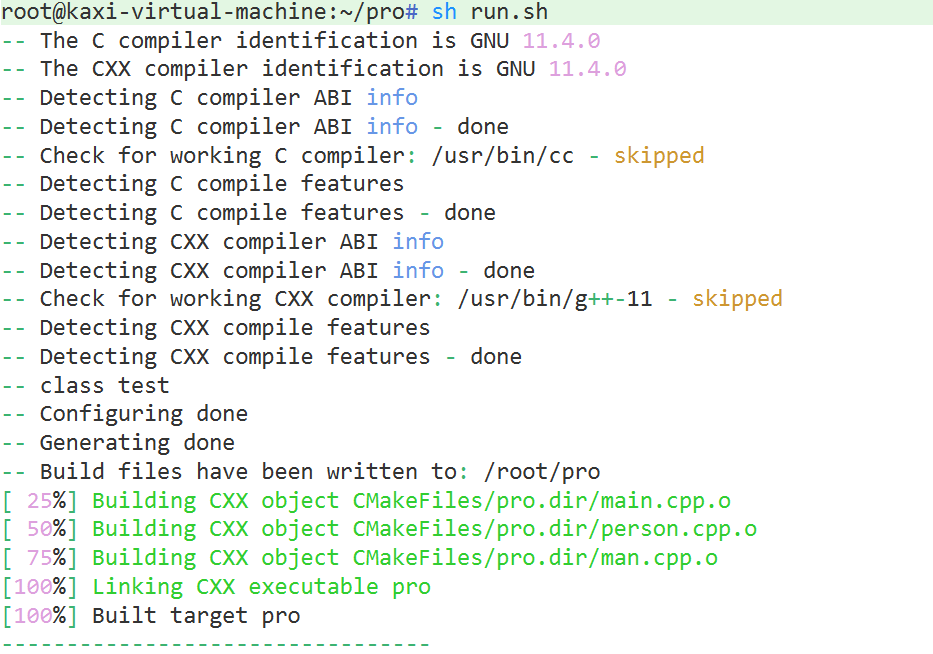
run.sh
#!/bin/bash
if [ -f ./Makefile ]
then
make clean
fi
cmake .
make
echo "---------------------------------"
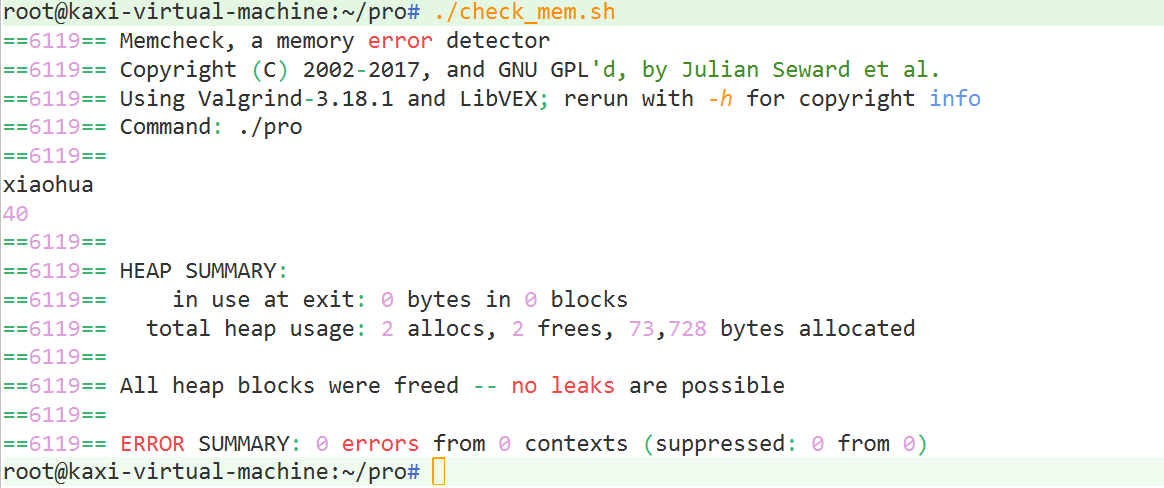
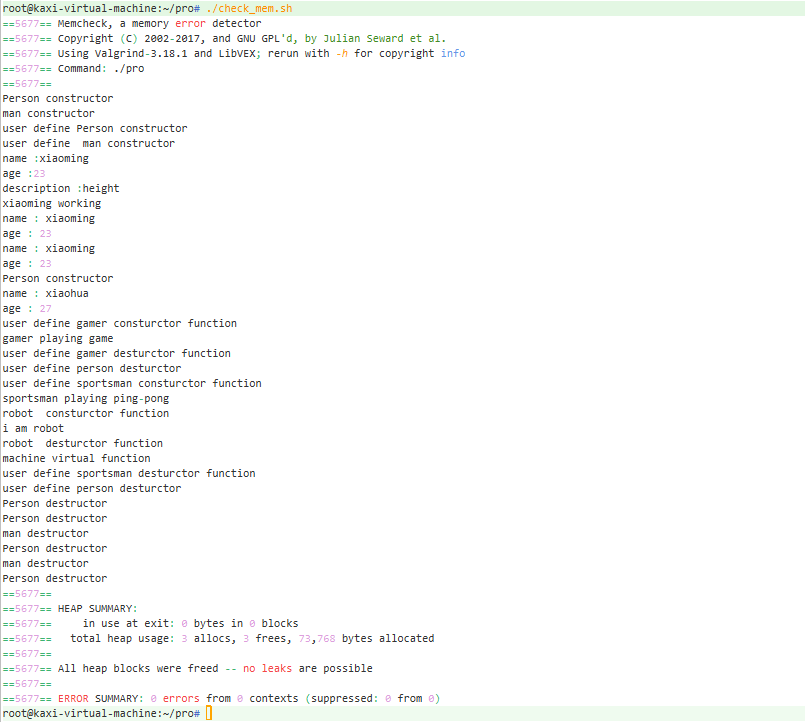
./procheck_mem.sh
valgrind --tool=memcheck --leak-check=full --show-reachable=yes --trace-children=yes -s ./proCMakeLists.txt
CMAKE_MINIMUM_REQUIRED(VERSION 2.20) #最低版本要求
SET(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER "g++-11") #设置g++编译器
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -g") #添加编译选项
PROJECT(CLASS) #设置工程名
MESSAGE(STATUS "class test") #打印消息
ADD_EXECUTABLE(pro main.cpp person.cpp man.cpp) #生成可执行文件person.hpp
#ifndef __PERSON_HPP__
#define __PERSON_HPP__
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace People
{
class Person
{
public:
string name;
int age;
void print_info();
Person();
Person(string name,int age);
~Person();
private:
int income;
protected:
};
class person
{
public:
string name;
virtual void play() = 0;
virtual ~person();
};
class machine
{
public:
virtual void introduce() = 0;
virtual ~machine();
};
}
#endifperson.cpp
#include "person.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void People::Person::print_info()
{
cout << "name : " << this->name << endl;
cout << "age : " << this->age << endl;
}
People::Person::Person()
{
cout << "Person constructor" << endl;
}
People::Person::Person(string name,int age):name(name),age(age)
{
cout << "user define Person constructor" << endl;
}
People::Person::~Person()
{
cout << "Person destructor" << endl;
}
People::person::~person()
{
cout << "user define person desturctor" << endl;
}
People::machine::~machine()
{
cout << "machine virtual function" << endl;
}man.hpp
#ifndef __MAN_HPP__
#define __MAN_HPP__
#include "person.hpp"
class Man:public People::Person
{
public:
string description;
void do_job();
void print_info();
Man();
Man(string name,int age,string description);
~Man();
private:
protected:
};
class man:private People::Person
{
public:
using Person::name;
using Person::age;
using Person::print_info;
};
class gamer:public People::person
{
public:
void play();
gamer();
~gamer();
};
class sportsman:public People::person
{
public:
void play();
sportsman();
~sportsman();
};
class robot:public People::machine
{
public:
void introduce();
robot();
~robot();
};
#endifman.cpp
#include "man.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void Man::do_job()
{
cout << this->name << " working" << endl;
}
void Man::print_info()
{
cout << "name :" << this->name << endl;
cout << "age :" << this->age << endl;
cout << "description :" << this->description << endl;
}
void gamer::play()
{
cout << this->name << " playing game" << endl;
}
gamer::gamer()
{
cout << "user define gamer consturctor function" << endl;
}
gamer::~gamer()
{
cout << "user define gamer desturctor function" << endl;
}
sportsman::sportsman()
{
cout << "user define sportsman consturctor function" << endl;
}
sportsman::~sportsman()
{
cout << "user define sportsman desturctor function" << endl;
}
void sportsman::play()
{
cout << this->name << " playing ping-pong" << endl;
}
void robot::introduce()
{
cout << "i am robot" << endl;
}
robot::robot()
{
cout << "robot consturctor function" << endl;
}
robot::~robot()
{
cout << "robot desturctor function" << endl;
}
Man::Man()
{
cout << "man constructor" << endl;
}
Man::Man(string name = "xxx",int age = 0,string description = "xxx"):Person(name,age),description(description)
{
cout << "user define man constructor" << endl;
}
Man::~Man()
{
cout << "man destructor" << endl;
}main.cpp
#include "person.hpp"
#include "man.hpp"
using namespace People;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
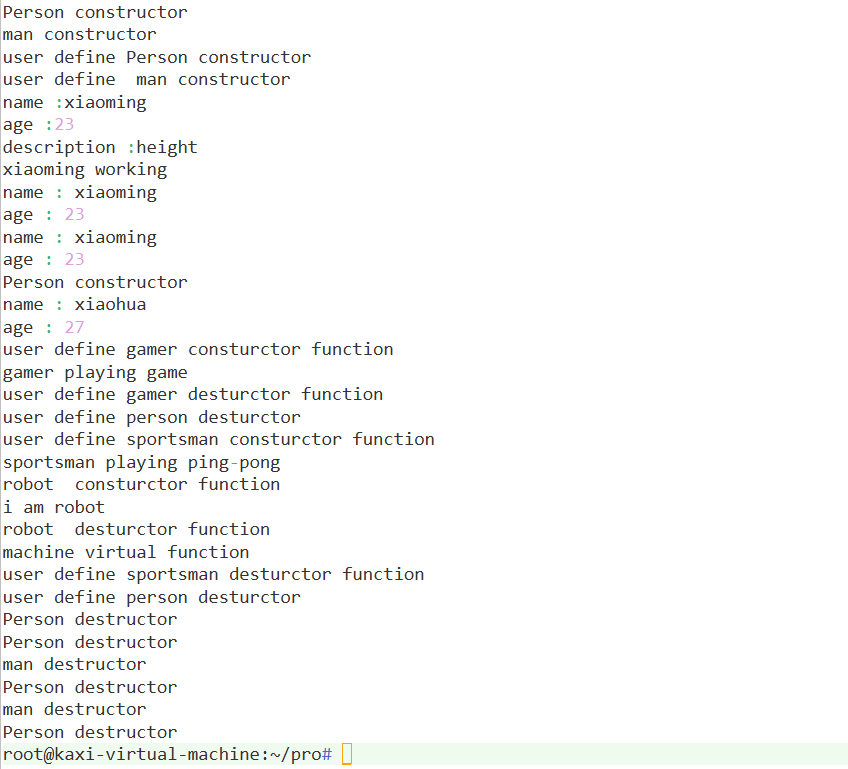
Man m1; //父类构造->子类构造->子类析构->父类析构
Man m2("xiaoming",23,"height");
m2.print_info();
m2.do_job();
m2.Person::print_info(); //全域路径访问隐藏父类方法
Person p1 = m2; //子类初始化父类
p1.print_info();
man m3;
m3.name = "xiaohua";
m3.age = 27;
m3.print_info(); //using放开保护继承(class A :private/protected B)
//需要保证抽象基类的析构函数为虚才能正常调用派生类析构函数
person *p = new gamer;
p->name = "gamer";
p->play();
delete p;
//抽象基类的析构函数是否为虚都能调用派生类析构函数
sportsman s;
s.name = "sportsman";
person *t = &s;
t->play();
//接口和抽象基类的析构函数一般定义为虚
robot r;
r.introduce();
return 0;
}结果示例:
 demo4:
demo4:
运算符重载
目录:
run.sh
#!/bin/bash
if [ -f ./Makefile ]
then
make clean
fi
cmake .
make
echo "---------------------------------"
./procheck_mem.sh
valgrind --tool=memcheck --leak-check=full --show-reachable=yes --trace-children=yes -s ./proclean.sh
#!/bin/bash
rm -rf CMakeFiles pro Makefile CMakeCache.txt cmake_install.cmakeCMakeLists.txt
CMAKE_MINIMUM_REQUIRED(VERSION 2.20) #最低版本要求
SET(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER "g++-11") #设置g++编译器
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -g") #添加编译选项
PROJECT(CLASS) #设置工程名
MESSAGE(STATUS "class test") #打印消息
ADD_EXECUTABLE(pro main.cpp) #生成可执行文件main.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class coordinate
{
public:
int *px;
int *py;
coordinate();
coordinate(const coordinate &cd);
coordinate(int x,int y);
~coordinate();
void print_coordinate();
coordinate operator+(const coordinate & other);
coordinate operator=(const coordinate & other);
coordinate operator++(int x); //i++
coordinate operator++(void); //++i
bool operator==(const coordinate & other);
friend void operator+=(coordinate & a,const coordinate & b); //友元函数只能传参方式调用类成员
};
coordinate::coordinate()
{
this->px = new int(0);
this->py = new int(0);
}
coordinate::coordinate(int x,int y)
{
this->px = new int(x);
this->py = new int(y);
}
coordinate::coordinate(const coordinate &cd)
{
cout << "copy" << endl;
this->px = new int(*(cd.px));
this->py = new int(*(cd.py));
}
coordinate::~coordinate()
{
delete this->px;
delete this->py;
}
void coordinate::print_coordinate()
{
cout << "(" << *(this->px) << "," << *(this->py) << ")" << endl;
return;
}
coordinate coordinate::operator+(const coordinate & other)
{
cout << "+" << endl;
coordinate tmp;
*(tmp.px) = *(this->px) + *(other.px);
*(tmp.py) = *(this->py) + *(other.py);
return tmp;
}
coordinate coordinate::operator=(const coordinate & other)
{
cout << "=" << endl;
if(this != &other)
{
*(this->px) = *(other.px);
*(this->py) = *(other.py);
}
return *this;
}
coordinate coordinate::operator++(void)
{
*(this->px) += 1;
*(this->py) += 1;
return *this;
}
coordinate coordinate::operator++(int x)
{
coordinate tmp;
*(tmp.px) = *(this->px);
*(tmp.py) = *(this->py);
*(this->px) += 1;
*(this->py) += 1;
return tmp;
}
void operator+=(coordinate & a,const coordinate & b)
{
*(a.px) += *(b.px);
*(a.py) += *(b.py);
return;
}
bool coordinate::operator==(const coordinate & other)
{
if(*(this->px) == *(other.px) && *(this->py) == *(other.py))
return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
coordinate c1(1,1);
coordinate c2(2,2);
cout << "------------3" << endl;
coordinate c3;
c3 = c1 + c2; //先定义再赋值时,先调用加法,在调用自定义=,在调用自定义拷贝(深浅拷贝均相同,浅拷贝时若为定义=和拷贝,则调用默认)
c3.print_coordinate();
cout << "------------4" << endl;
coordinate c4 = c1 + c2; //只调用+(深浅拷贝均相同)
c4.print_coordinate();
cout << "------------5" << endl;
coordinate c5 = c1; //调用自定义拷贝(浅拷贝调用默认)
c5.print_coordinate();
cout << "------------6" << endl;
coordinate c6(c1); //调用自定义拷贝(浅拷贝调用默认)
c6.print_coordinate();
cout << "tmp------------7" << endl;
coordinate tmp;
coordinate c7;
tmp = c7++;
tmp.print_coordinate();
cout << "tmp------------8" << endl;
coordinate c8;
tmp = ++c8;
tmp.print_coordinate();
cout << "------------9" << endl;
coordinate c9(1,1);
operator+=(c9,c9);
c9.print_coordinate();
cout << "------------10" << endl;
coordinate c10(1,1);
bool res = (c10 == c1);
cout << boolalpha << res << endl;
return 0;
}结果示例:
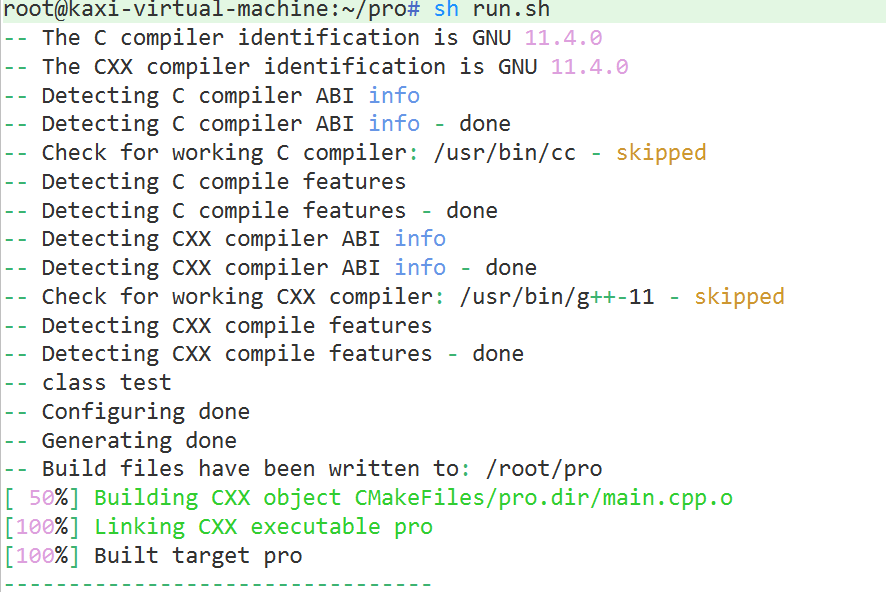
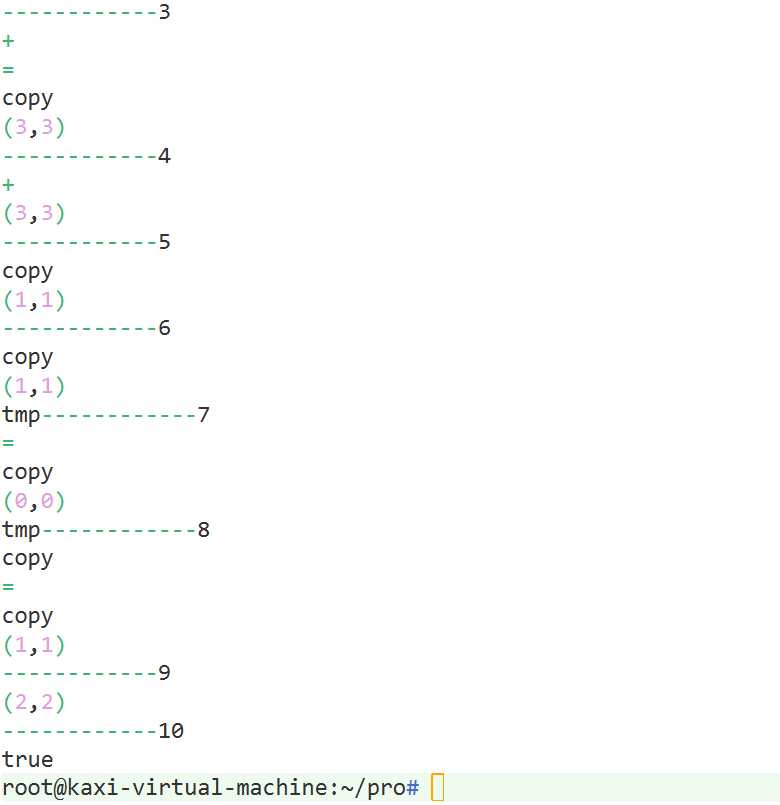

demo5:
类静态成员
目录:
run.sh
#!/bin/bash
if [ -f ./Makefile ]
then
make clean
fi
cmake .
make
echo "---------------------------------"
./proclean.sh
#!/bin/bash
rm -rf CMakeFiles pro Makefile CMakeCache.txt cmake_install.cmakecheck_mem.sh
valgrind --tool=memcheck --leak-check=full --show-reachable=yes --trace-children=yes -s ./proCMakeLists.txt
CMAKE_MINIMUM_REQUIRED(VERSION 2.20) #最低版本要求
SET(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER "g++-11") #设置g++编译器
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -g") #添加编译选项
PROJECT(CLASS) #设置工程名
MESSAGE(STATUS "class test") #打印消息
ADD_EXECUTABLE(pro main.cpp) #生成可执行文件main.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
string name;
Person();
Person(string name);
static int objetcion_num;
static void print_obj_num();
static void print_name(string name); //静态方法传参访问非静态成员
};
//静态类
class constant
{
public:
static int week_day_num; //一周的天数
static int earth_radius; //地球半径
static void print_info();
};
int constant::week_day_num = 7;
int constant::earth_radius = 6371;
void constant::print_info()
{
cout << "days of the week :" << constant::week_day_num << endl;
cout << "radius of the earth :" << constant::earth_radius << endl;
}
int Person::objetcion_num = 0; //<==>int objetcion_num;
//类中静态成员的访问方式
Person::Person()
{
objetcion_num++;
}
Person::Person(string name)
{
this->name = name;
this->objetcion_num++;
}
void Person::print_obj_num()
{
cout << "obj_num :" << Person::objetcion_num << endl;
}
void Person::print_name(string name)
{
cout << "person name :" << name << endl;
}
int main()
{
//类外静态成员的访问方式
Person p1;
cout << "obj_num :" << p1.objetcion_num << endl;
Person p2("xaioming");
cout << "obj_num :" << Person::objetcion_num << endl;
Person p3("xaiohua");
p3.print_obj_num();
constant::print_info();
return 0;
}结果示例:
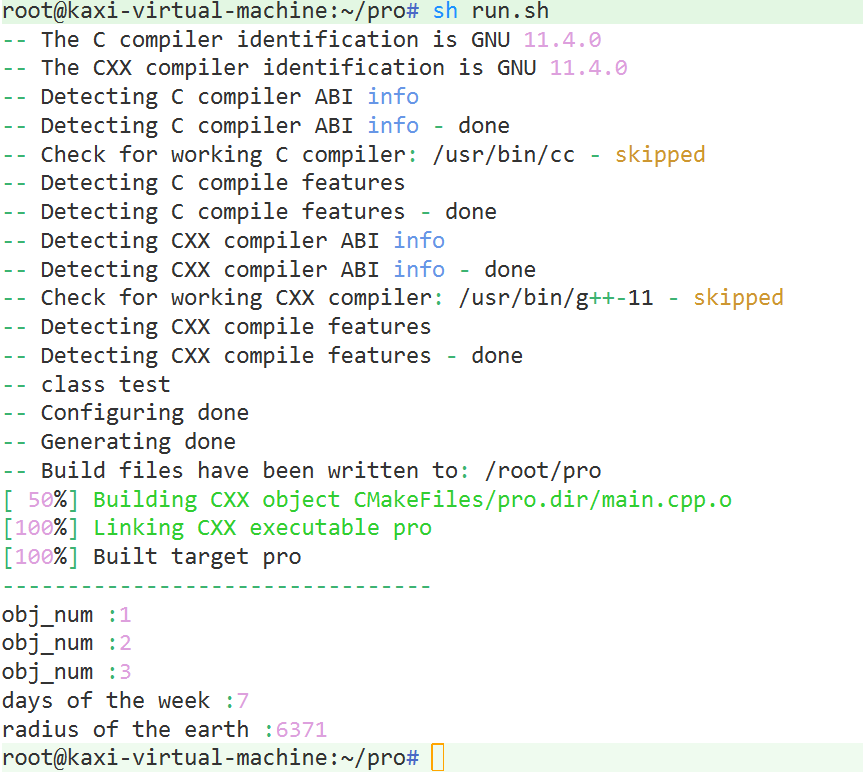
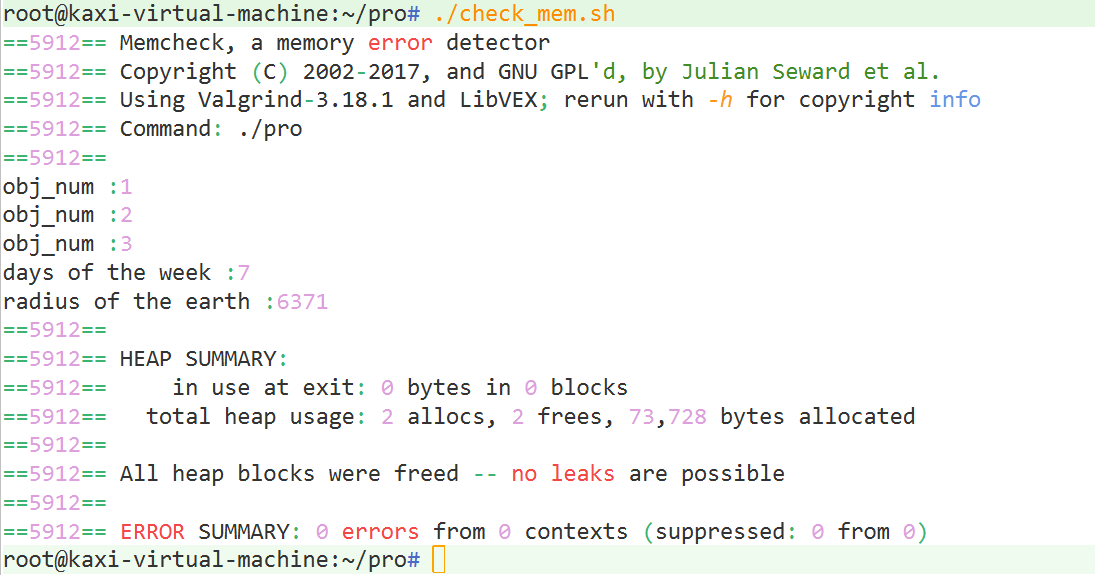
demo6:
友元函数,友元类
目录:
run.sh
#!/bin/bash
if [ -f ./Makefile ]
then
make clean
fi
cmake .
make
echo "---------------------------------"
./procheck_mem.sh
valgrind --tool=memcheck --leak-check=full --show-reachable=yes --trace-children=yes -s ./proclean.sh
#!/bin/bash
rm -rf CMakeFiles pro Makefile CMakeCache.txt cmake_install.cmakeCMakeLists.txt
CMAKE_MINIMUM_REQUIRED(VERSION 2.20) #最低版本要求
SET(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER "g++-11") #设置g++编译器
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -g") #添加编译选项
PROJECT(CLASS) #设置工程名
MESSAGE(STATUS "class test") #打印消息
ADD_EXECUTABLE(pro main.cpp) #生成可执行文件main.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//前置申明解决友元类未定义
class Father;
class Son;
class Father
{
public:
string name;
int age;
Father();
Father(string name,int age);
void print_name(string name);
friend class Son;
};
class Son
{
public:
string name;
int age;
Son();
Son(string name,int age);
void print_age(int age);
friend class Father;
};
Father::Father(string name,int age)
{
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
}
void Father::print_name(string name)
{
cout << name << endl;
}
Son::Son(string name,int age)
{
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
}
void Son::print_age(int age)
{
cout << age << endl;
}
int main()
{
Father f("xiaoming",40);
Son s("xiaohua",20);
f.print_name(s.name);
s.print_age(f.age);
return 0;
}结果示例: